Superpowers
5.0(2)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:12 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
What is a superpower?
A nation with the means to project power and influence anywhere in the world and to be a dominant global force
2
New cards
Some examples of superpowers in the past are…
- the British empire
- the USSR (its fall lead to a unipolar world, lead by the USA)
- USA (current)
- the USSR (its fall lead to a unipolar world, lead by the USA)
- USA (current)
3
New cards
What is a unipolar world?
When there is only one superpower exerting hegemonic influence over the world
4
New cards
What is a bipolar world?
When there is two superpowers exerting hegemonic influence over the world (eg USA+ USSR in 1960s)
5
New cards
What is a multipolar world?
When multiple superpowers exert EQUAL hegemonic influence over the world
6
New cards
What are some indicators of being a superpower?
- large military power (eg USA spends more than the next 10 countries combined on military and has the most air craft carriers in the world- initiation)
- large amount of resources / land (control of other countries without)
- large population
- culture (and its influence in the world, eg USA in media)
- strong economy. (Can use money to project power)
- large amount of resources / land (control of other countries without)
- large population
- culture (and its influence in the world, eg USA in media)
- strong economy. (Can use money to project power)
7
New cards
What is a hyper power?
A superpower that has become more powerful to the point it cannot be knocked out of its place. Some say the USA is a hyper power.
8
New cards
What is an emerging power?
A country with the potential to become a superpower. (Eg China)
9
New cards
What is a regional power?
A country with with hegemonic influence at a local / regional scale
10
New cards
What is a hegemon?
A country with the ability to dominate others
11
New cards
What are the types of power can a superpower can use to keep control?
Hard and soft power
Eg
Hard= military, economic sanctions
Soft= culture and ideology
Eg
Hard= military, economic sanctions
Soft= culture and ideology
12
New cards
What is the geo-strategic location theory?
A theory by developed in 1904 (a British geographer) which states that whoever is in control of Eurasia/ the heartland (largest landmass) could control the world.
This could be done by controlling Russia, and due to its location could control Eurasia.
Therefore the further away a country is from Russian the less control Russia has over it.
This could be done by controlling Russia, and due to its location could control Eurasia.
Therefore the further away a country is from Russian the less control Russia has over it.
13
New cards
What evidence supports the geo- strategic theory?
- Russia was a superpower 1945-1991
- Russia's ability to attack Ukrainian in 2022
- Russia's intervention in Syria
- This theory had influence on many foreign policies (many in the Cold War) and so remains highly relevant today.
- Russia's ability to attack Ukrainian in 2022
- Russia's intervention in Syria
- This theory had influence on many foreign policies (many in the Cold War) and so remains highly relevant today.
14
New cards
What evidence is against the geo- strategic theory?
- Russia is no longer a superpower
- USA, china and India all have more power than Russia
- geopolitical landscape has changed since 1904
- land area is not necessarily a good indicator for power
- low population in the ‘heartland area’
- USA, china and India all have more power than Russia
- geopolitical landscape has changed since 1904
- land area is not necessarily a good indicator for power
- low population in the ‘heartland area’
15
New cards
CASE STUDY
BELT + ROAD INITIATIVE (over 7 years)
- write up separately
- china invest in other countries (60+) infrastructure to make it easier for china to sell trade
Eg big port in Pakistan, channel in Nicaragua (planning underway) , roads across Africa (Kenya and Uganda
Eg possibly spratley islands- protecting shipping route
- some think this is their way to ‘take control of the world’
- write up separately
- china invest in other countries (60+) infrastructure to make it easier for china to sell trade
Eg big port in Pakistan, channel in Nicaragua (planning underway) , roads across Africa (Kenya and Uganda
Eg possibly spratley islands- protecting shipping route
- some think this is their way to ‘take control of the world’
16
New cards
What is a proxy war?
An indirect conflict between countries
17
New cards
CASE STUDY 2
THE BRITISH EMPIRE (a3 sheet)
18
New cards
CASE STUDY 3
THE COLDWAR (a3 sheet)
19
New cards
What is colonialism?
Direct control of another country
Done by creating a social divide between the colonised and the colonisers.
Eg the British empire in India ( caste system)
Eg apartheid in South Africa
Done by creating a social divide between the colonised and the colonisers.
Eg the British empire in India ( caste system)
Eg apartheid in South Africa
20
New cards
What is neo colonialism?
The INdirect control of another country.
Done by economic control and influence
Eg USA putting sanctions and tariffs on other countries
Eg IMF and World Bank ‘structural adjustment policies’
Done by economic control and influence
Eg USA putting sanctions and tariffs on other countries
Eg IMF and World Bank ‘structural adjustment policies’
21
New cards
CASE STUDY
USA AS A SUPERPOWER (rose after ww1 as Europe ran out of money), ww2 made it great, current)
22
New cards
CASE STUDY
DAVOS IN SWITZERLAND ?
23
New cards
What is a free market?
It’s when the government is not involved greatly in the economy - ‘small government’
And so businesses run independently and efficiently due to the incentive of profit. Eg UK
And so businesses run independently and efficiently due to the incentive of profit. Eg UK
24
New cards
What is a planned economy?
Where the government is highly involved in the economy whereby they ensure all profits reach a certain value and then is shared equally between everyone.
So overall only the government profits. Eg Vietnam
So overall only the government profits. Eg Vietnam
25
New cards
Examples of planned economies that converted to free market capitalism are…
China and Russia
26
New cards
What are soft methods that superpowers use to exert power through TNCs?
- cultural globalisation
- promoting ideology
- promoting a country as being a role model
- promoting ideology
- promoting a country as being a role model
27
New cards
What are hard methods that superpowers use to exert power through TNCs?
- using them to produce military technology and resources such as weapons and GPS
28
New cards
What are the two types of TNC?
- publicly traded- they are owned by numerous stakeholders
- state owned- are owned by the government, Eg Saudi Aramco
- state owned- are owned by the government, Eg Saudi Aramco
29
New cards
Which type of TNC is more common in emerging superpowers?
State owned TNCs
30
New cards
Why are TNCs so good for exerting a countries power?
- as developing countries want their investment, they have the power to influence government policies
- their large scale (can outcompete smaller companies) (and they are well know)
- their large bank balances
- they have benefitted from free market capitalism
- their large scale (can outcompete smaller companies) (and they are well know)
- their large bank balances
- they have benefitted from free market capitalism
31
New cards
What are the 3 main theories surrounding the changing patterns of power?
- modernisation theory
- dependency theory
- world systems theory
- dependency theory
- world systems theory
32
New cards
What is the modernisation theory?
A theory developed by Rostow, that states that the only way to develop is via capitalism like the UK and USA. This theory is used and supported by said capitalist rich countries however it doesn’t work for all countries as a development gap still exists.
33
New cards
What is the dependency theory?
A theory developed by Frank, that states that the worlds economic system is reinforcing inequality between countries as it allows richer countries to take advantage of poorer countries due to DEPENDENCY.
Disproves modernisation theory
Disproves modernisation theory
34
New cards
What is the world system theory?
A theory developed by Wallerstein, It can also been knows as the core periphery model. Core= Rich countries. Per= poor countries
- the per provides core with materials
- and the core provides per with money (with strings attached) or goods
(Shows development gap)
It can explain why not all countries can follow the modernisation theory.
- the per provides core with materials
- and the core provides per with money (with strings attached) or goods
(Shows development gap)
It can explain why not all countries can follow the modernisation theory.
35
New cards
What is the UN Security Council?
It is an inter governmental organisation which is the primary mechanism for maintaining international peace.
36
New cards
What methods does the UN Security Council use to keep peace?
- applying military or diplomatic sanctions
- requiring authorisation of military force against another country
- authorising a UN peace keeping force
- requiring authorisation of military force against another country
- authorising a UN peace keeping force
37
New cards
what is the international court of justice?
Is the judicial branch of the United Nations that settles disputes between members.
38
New cards
What is a peace keeping mission?
Sending in troops/ soldiers on behalf of the united nations to stop fighting in other countries. Eg- Congo civil war
39
New cards
CASE STUDY
USA military interference
40
New cards
What is geopolitics?
International relations influenced by geographical factors
41
New cards
What is an international player?
Any key organisation or countries that influence geopolitics
42
New cards
What are some military, economic, environmental and political examples of international players?
Military- NATO
Economic- EU
Environmental- IPCC (international panel on climate change)
Political- the UN
Economic- EU
Environmental- IPCC (international panel on climate change)
Political- the UN
43
New cards
What impacts do superpowers have on the environment?
- large emissions (USA and China have largest emissions)
- this is due to employment distributions eg many factories ( secondary employment) in china = high emissions
- or due to level of development- whether or not renewable energy can be afforded. Eg India which disagreed with initiatives at cop26
- also due to population / level of consumption eg USA and China
- finally, developing or corrupt countries have less laws and regulations to allow for more economic benefit
- oil spills
- land degradation for urbanisation, agriculture and timber
- air pollution
- this is due to employment distributions eg many factories ( secondary employment) in china = high emissions
- or due to level of development- whether or not renewable energy can be afforded. Eg India which disagreed with initiatives at cop26
- also due to population / level of consumption eg USA and China
- finally, developing or corrupt countries have less laws and regulations to allow for more economic benefit
- oil spills
- land degradation for urbanisation, agriculture and timber
- air pollution
44
New cards
What is the trend of the environmental Kuznets curve?
Developments initially worsens emissions, but as GDP increases and therefore there is excess money to develop, renewable energy can be implemented and emissions/ land degradation goes down.
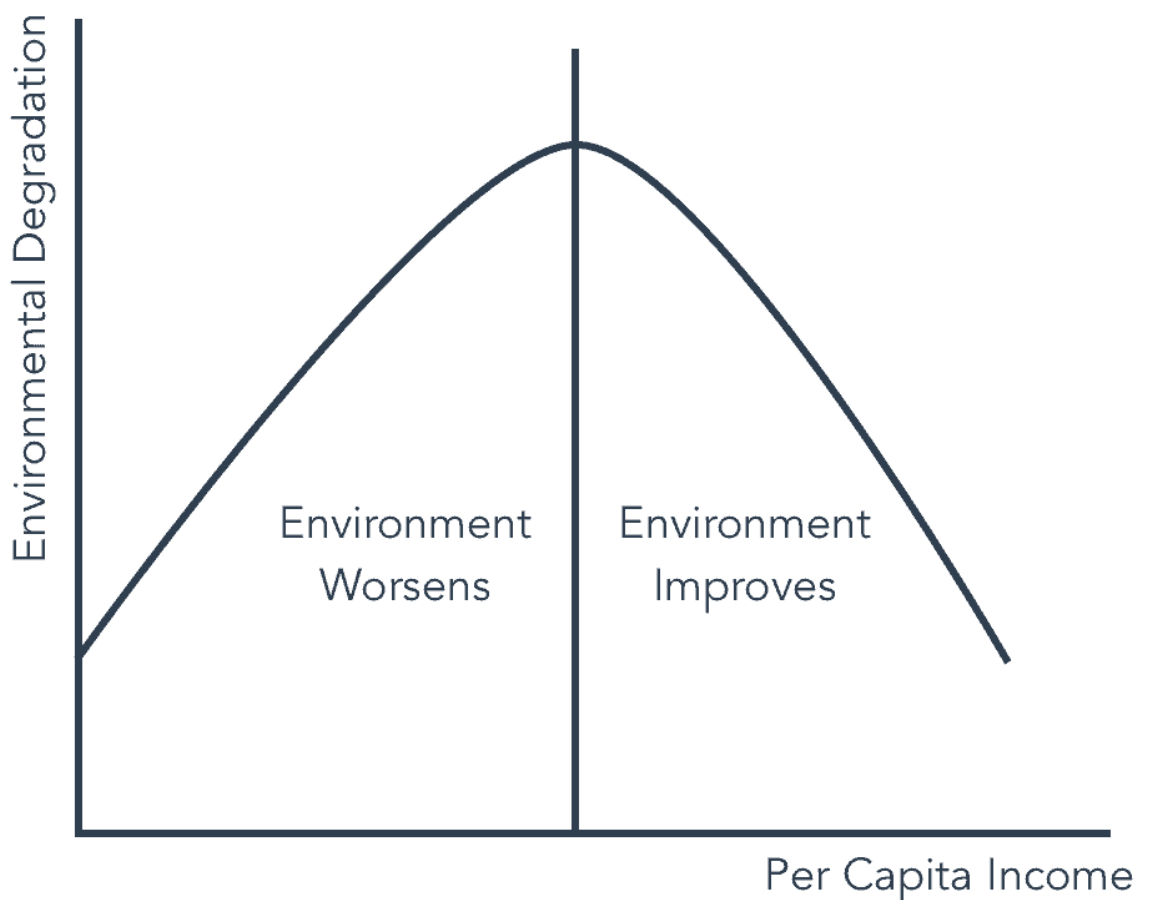
45
New cards
What is the middle class sweet spot/ growth sweet spot?
When there are a high number of middle class people with money to buy products, this consumptions drives economic growth
46
New cards
Chinas economy phases (CASE STUDY?)
1- manufacturing for export
2- constriction eg railways and bridges ect
3- consumption- growth sweet spot (make middle class richer)
2- constriction eg railways and bridges ect
3- consumption- growth sweet spot (make middle class richer)
47
New cards
What are the impacts having a large middle class?
- more emissions
- less malnutrition
- deforestation to keep up with housing and goods demands (eg meat consumption)
-
- less malnutrition
- deforestation to keep up with housing and goods demands (eg meat consumption)
-
48
New cards
CASE STUDY
Counterfeit goods in china
49
New cards
What is a sphere of influence?
The area of which a country has influence over. Either by hard or soft power
50
New cards
CASE STUDY
BRITISH EMPIRE (links to course again later on) all 4 case studies \/ are sphere of influence examples + apply to other parts of the course
51
New cards
CASE STUDY
Of neo-colonialism (later in course- Africa and china)
52
New cards
CASE STUDY
ARCTIC OCEAN (north west and north east passage)
53
New cards
CASE STUDY
South China Sea
54
New cards
CASE STUDY
China and India
55
New cards
CASE STUD(IES)
Middle East case studies (multiple)
56
New cards
7\.9 c notes