Math 21 (Memorization)
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for memorizing (perfect cutie!)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
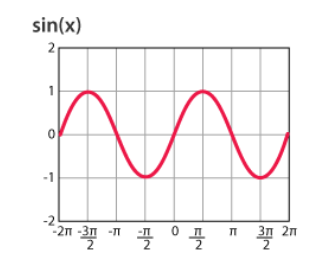
Graph of Sine (sin)
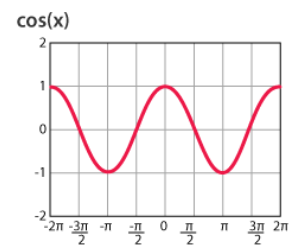
Graph of Cosine (cos)
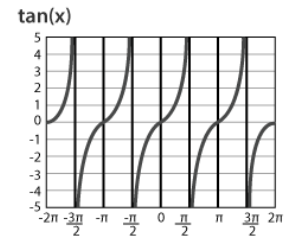
Graph of Tangent (tan)
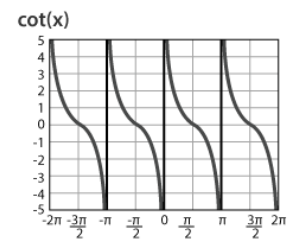
Graph of Cotangent (cot)
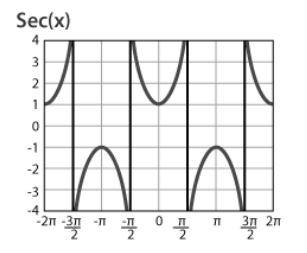
Graph of Secant (sec)
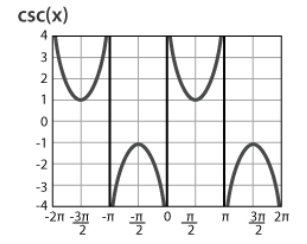
Graph of Cosecant (csc)
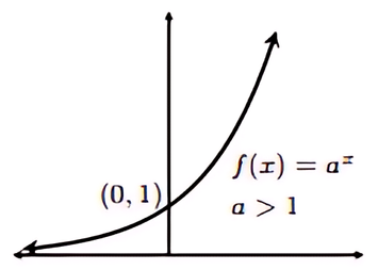
Exponential Function (a > 1)
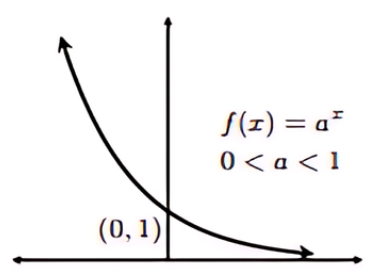
Exponential Function (0< a <1)
Logarithmic Function (a > 1)
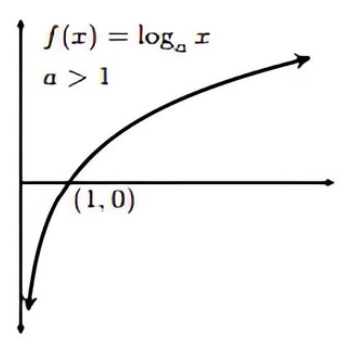
Logarithmic Function (0< a <1)
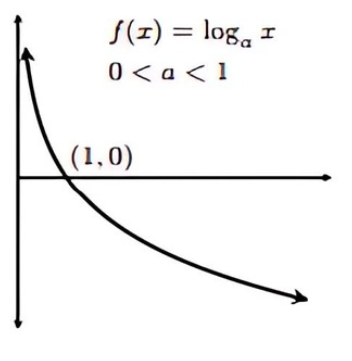
Graph of Sine Inverse (sin⁻¹)
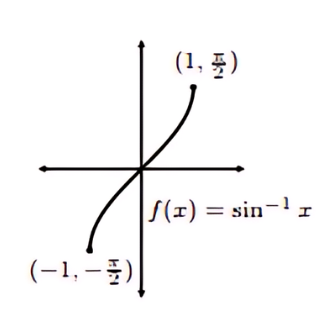
Graph of Cosine Inverse (cos⁻¹)
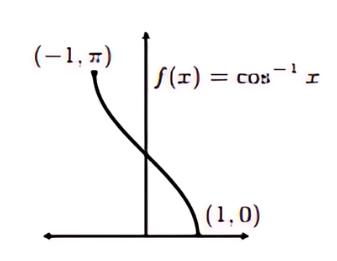
Graph of Tangent Inverse (tan⁻¹)
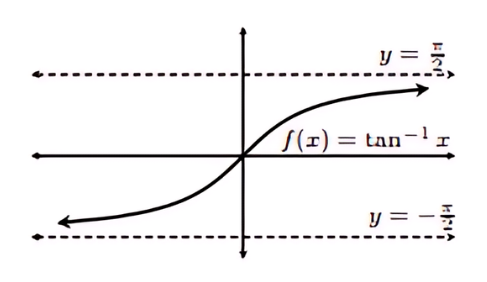
Graph of Cotangent Inverse (cot⁻¹)
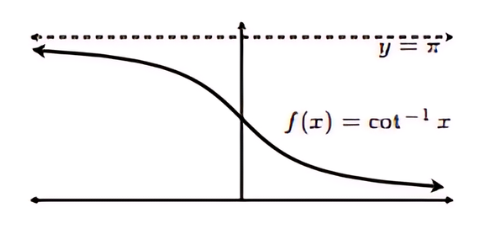
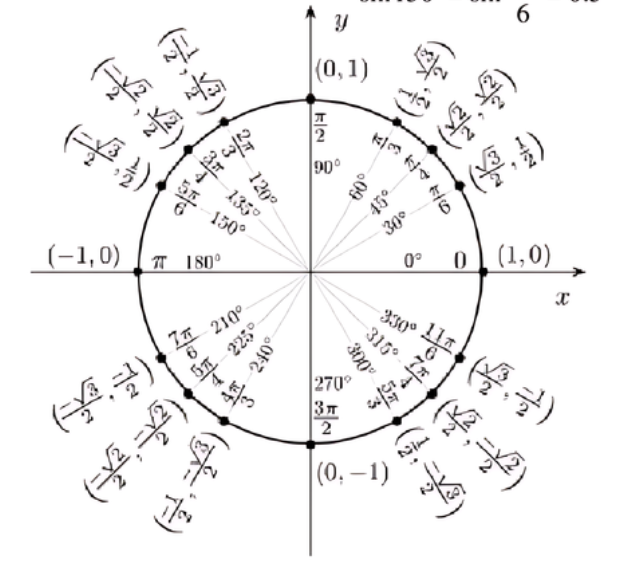
Unit Circle
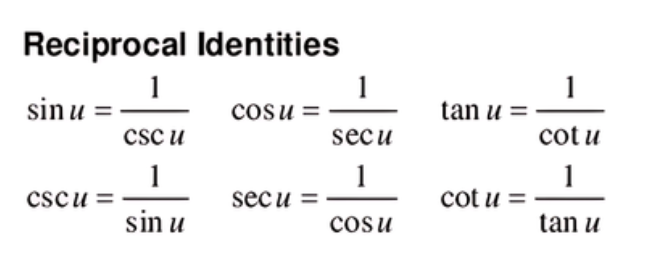
Reciprocal Identities
Tangent and Cotangent Identities
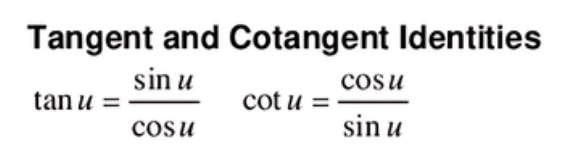
Pythagorean Identities

Squeeze Theorem Identites
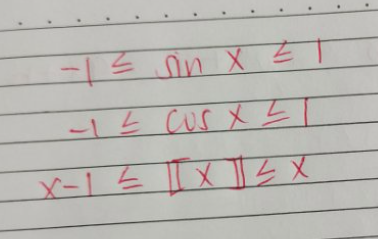
Special Limits of Rational Sine and Cosine (lim f(x) = 0)
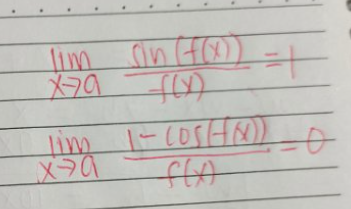
IVT Statement
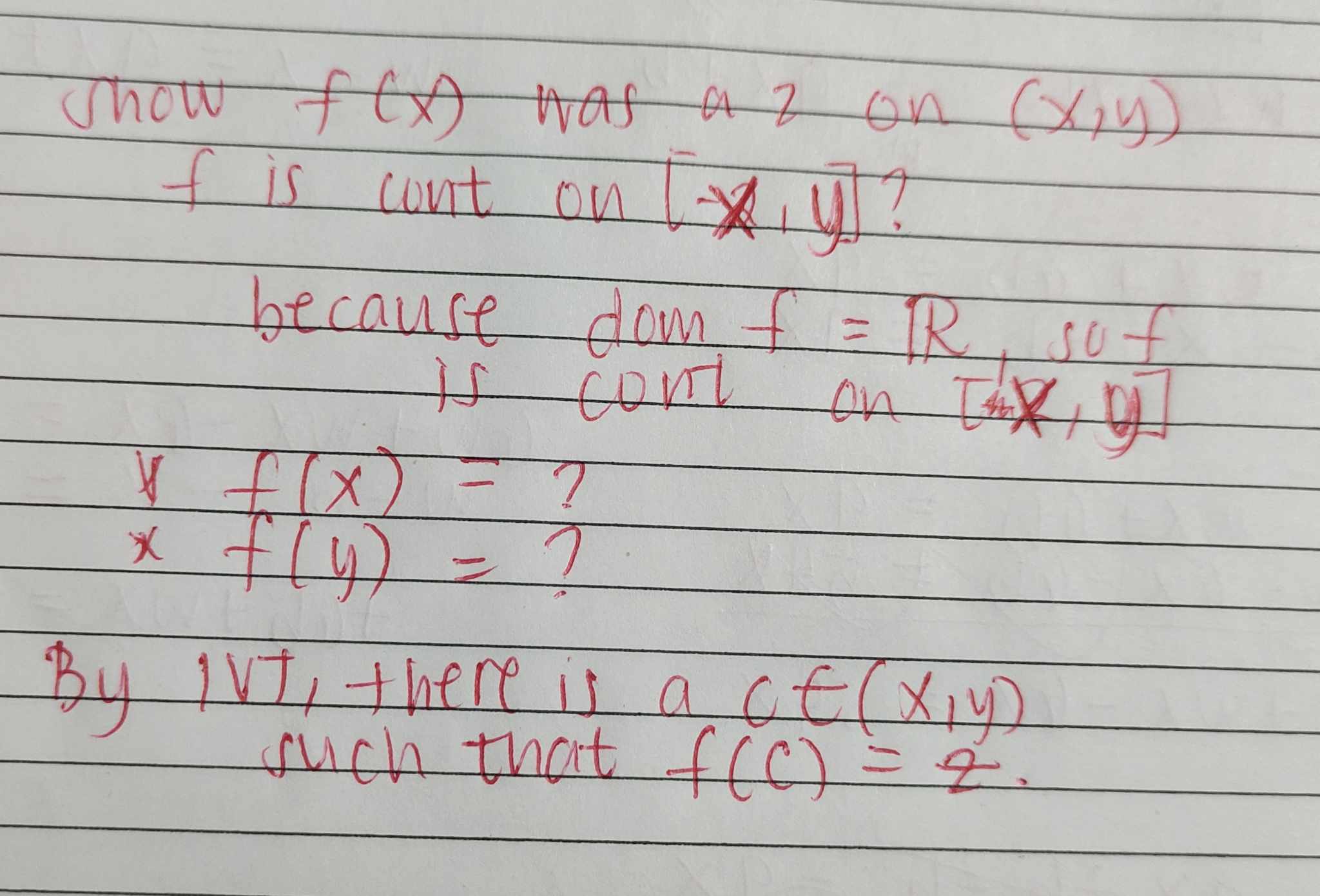
ln│e│
1
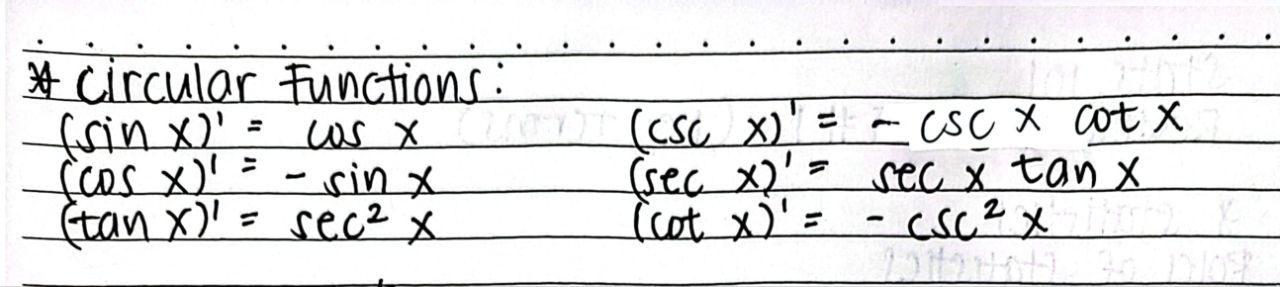
Derivatives of Circular Trigonometric Functions
Derivatives of Exponential and Log Functions

Derivatives of INVERSE Circular Trigonometric Functions

Derivatives of Hyperbolic Trigonometric Functions

Log Differentiation

Properties of Normal Logarithm

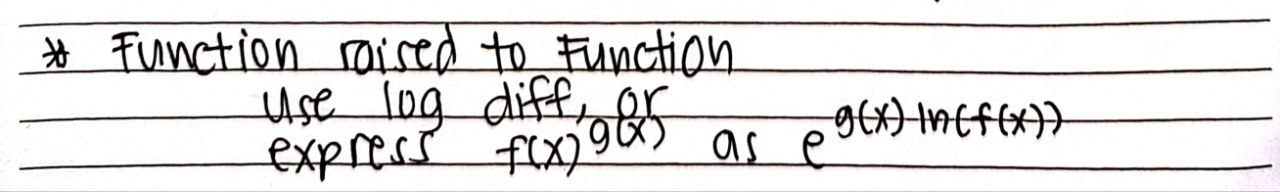
Function raised to Function Equivalent
Sinh Equation
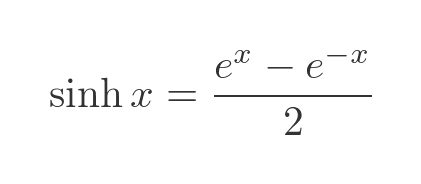
Cosh Equation
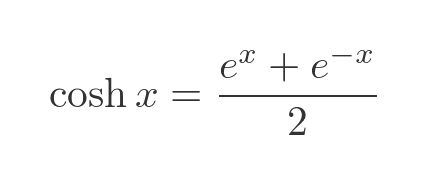
Equation and Slope of Tangent Line
First Derivative, then Substitute and Solve for f’(x)
Slope of Normal Line
Negative Reciprocal of Tangent Slope
Tanh 0
0
Concavity is Dependent on?
Second Derivative
Properties of Concave Up
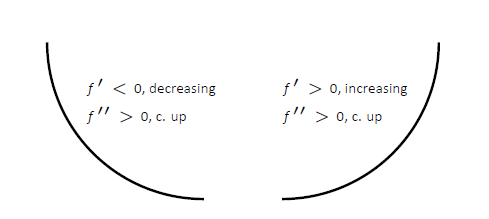
Properties of Concave Down
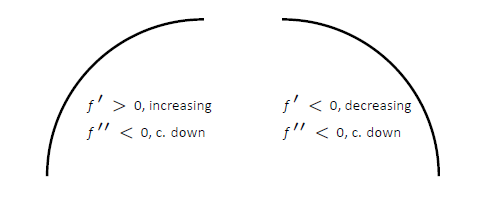
Horizontal Asymptote

ln (1)
0
FDT
“Table of Signs”

SDT

Open Interval in Rel. Ext.
If more than 1 CN or paired with close interval, solve for it’s limit. (Ex. (a, b), use a from the right and b from the left.
FDT vs SDT
Use FDT if rational function and if SDT is hard to compute, use SDT otherwise.
Piecewise Function (Abs. Ext.)
Check if cont. If Yes, diff., if point of possible disc. not diff, it’s a CN as well. Then, evaluate which is abs min and abs max.
If SDT is 0.
It is inconclusive, use FDT intead.
Steps in Problem Solving
Illustrate the problem.
Assign variables to illustration. Provide given and construct working equations. Find x and y intercepts if graph involved.
Find working eqn. in terms of one variable. Then, maximize or minimize.
Determine constraint (domain).
Determine if function is cont. at constraint. If yes, differentiate and find CN.
Express abs. min and/or abs max. And state conclusion. Don’t forget the unit.
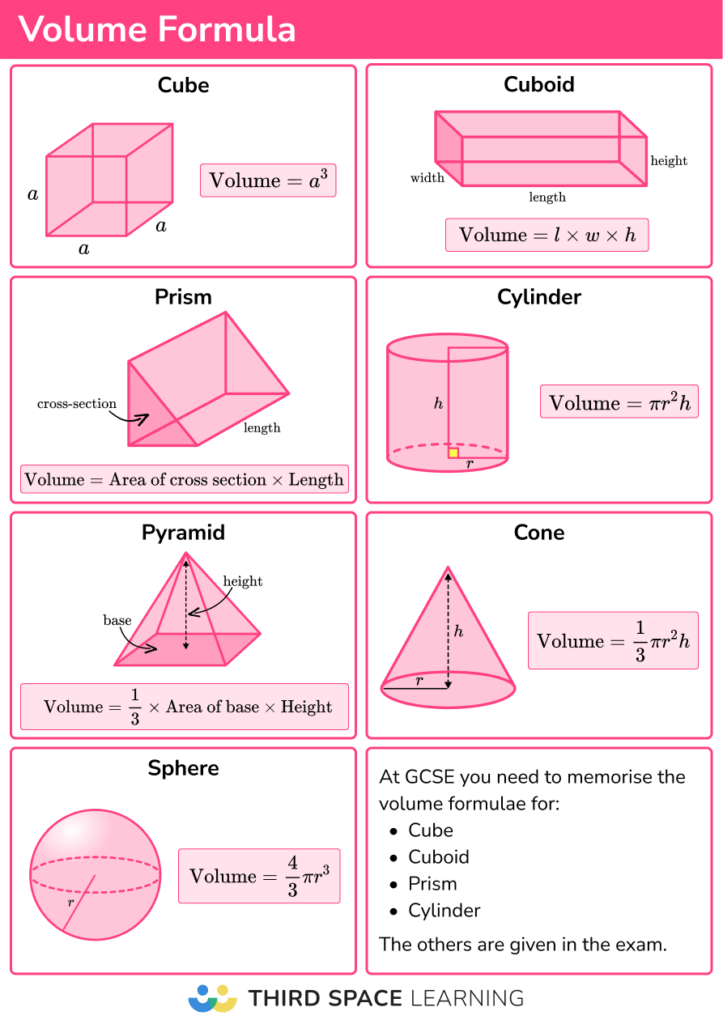
Volumes
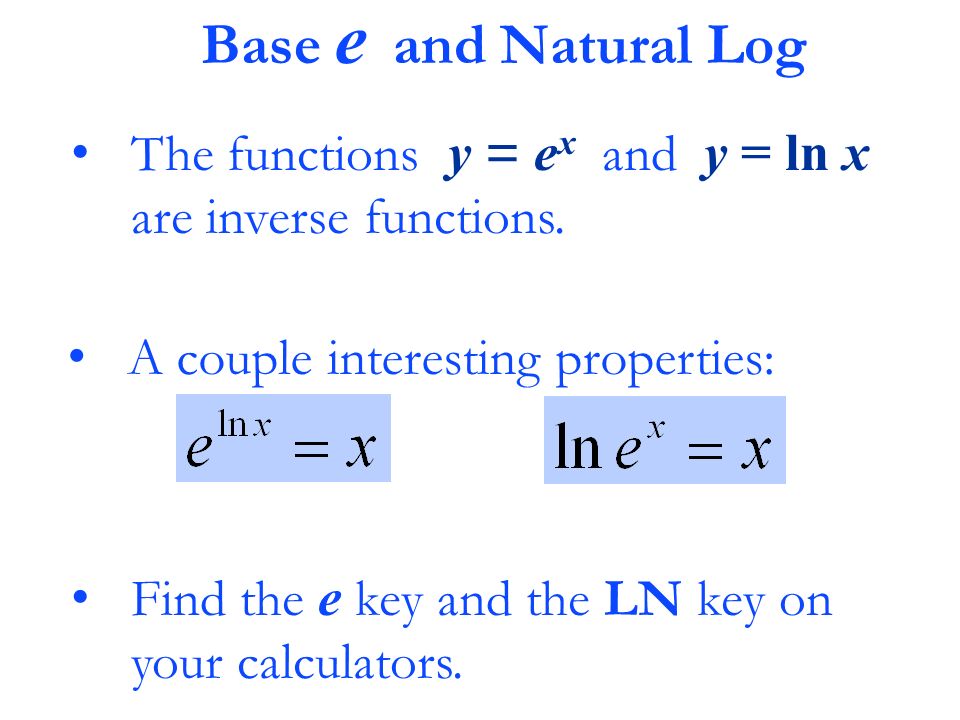
Base e and Natural Log
Rectilinear Motion Practice Table
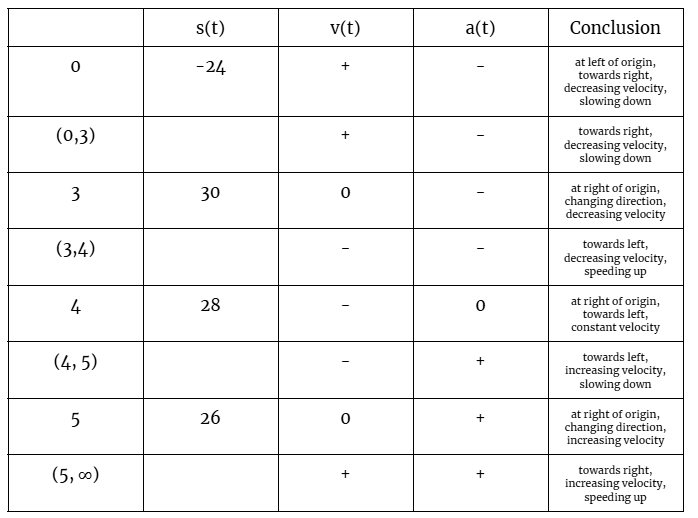
Local Linear Approximation Formula
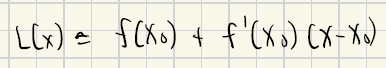
LLA of Measurement of Error
The error (w/c is always nonnegative). Abs. val. dx.
Related Rates Cone
Approach with similar triangles, conver the cone to a triangle figure.
L’Hopital’s Rule
Only applies w/ 0/0 or infinity/infinity. Don’t do quotient rule.
Exponential Indeterminate (Hopital’s Rule)
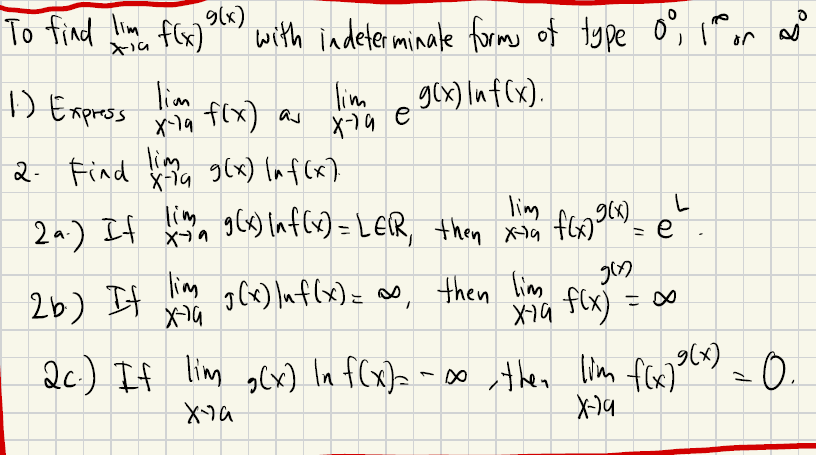
Special Right Triangles
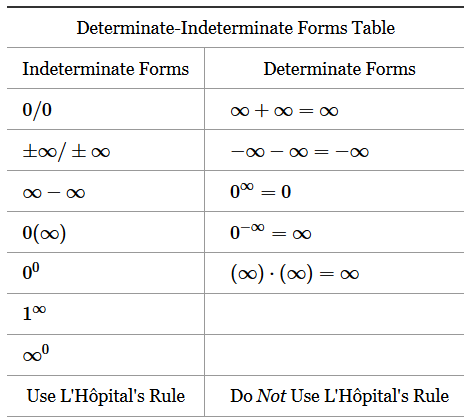
Indeterminate Forms
ln (e^x) or e^(ln x)
= x