MICR5831 L6: DNA Cloning I 7/29/25
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Describe the two approaches to cloning genes (slide 8)
1) Random Cloning:
-Cloning random restricted DNA fragments
-Use restriction enzymes
-Do not need to know sequence of target gene
-Not specific for gene of interest (need phenotype)
-Wrong RE can cut inside gene of interest
2) PCR Cloning:
-Cloning specific PCR fragments
-Very specific amplification of gene
-Must know sequence of target gene for design of primers
What are the methods needed for cloning (slide 9)
1) Method for isolating genomic DNA from donor
2) Method for fragmenting donor and recipient vector DNA
3) Method of ligating the two pieces of DNA together
4) Method for transferring the recombinant molecule → E. coli host
5) Method for identifying which bacterial transformants carrying the recombinant plasmid of interest
6) Methods for purifying and analyzing recombinant plasmid
What are the properties of restriction enzymes (slide 10)
Type I:
-Cleave the phosphodiester bond at specific sites in the DNA duplex (restriction site)
-Requires Magnesium for activity
-Restriction site is 4-10 bp palindrome
Type II: (Important)
-Cuts fixed position, sticky or cohesive ends, blunt ends
-Used in cloning experiments
Type I and Type III: More irrelevant
-Cuts random site outside recognition sequence
-Not used in cloning experiments
What is a palindrome in DNA and what is the role of this in restriction digestion? (slide 10 and 13)
-Sequence of one strand reads in reverse order to that of the complementary strand
-Restriction site is a palindrome
-Role: Provide recognition sites to restriction enzymes
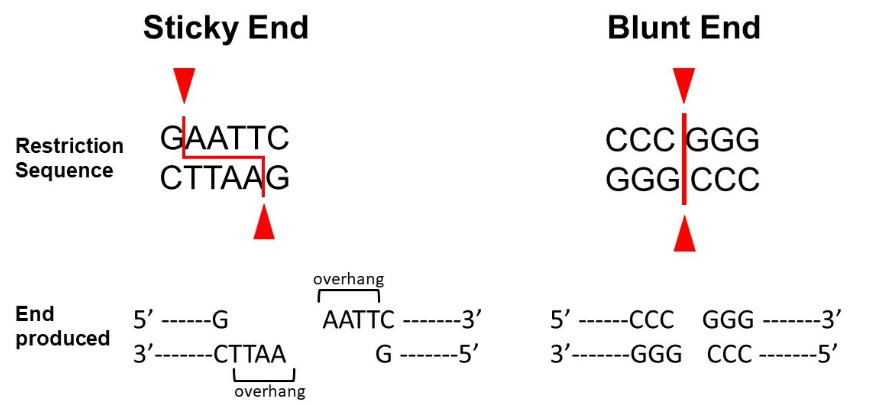
Using a figure describe "sticky" and "blunt" ended DNA (slide 11 and 12)
Sticky Ends:
-EcoRI (5' overhang)
-PstI (3' overhang)
Blunt Ends:
-SmaI
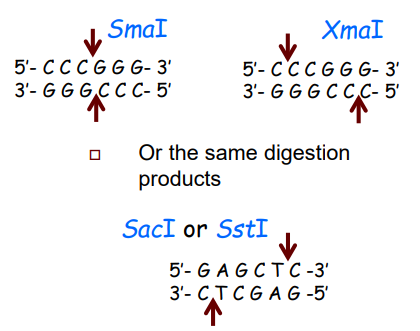
What is an Isoschizomers? (slide 12)
-REs that recognize the same palindrome
-Produce either same or different digestion products
How is the frequency of cutting by restriction endonucleases determined (slide 14)
-Related to length of recognition sequence
-Probability that each bp is found consecutively
-1 site per 256 bp (1/4^4) for a 4 base cutter recognizing one sequence
-Must take into account specificity of RE (HincII cuts 1/1024 bp)
What are the properties of agarose gels (slide 14)
-Polymer of repeating di-galactan unit
-Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE)/Tris- borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer pH8
-Heating agarose -> soluble -> cast gel
-Cooled -> porous gel
-Concentration determines porosity
-Large fragment migrates slower than small
How does an agarose gel separate DNA fragments? (slide 15)
-DNA molecules separated according to length during migration through porous gel
-DNA negatively charged at pH 8
-DNA migrates towards positive electrode when subjected to an electric current
-Visualization: Ethidium bromide stain (cancer), UV fluorescence
What are the features and properties of cloning vectors (slide 18)
-Small plasmids
-Selectable marker (antibiotic resistance)
-Multiple restriction enzyme sites for cloning
-Origin of replication (oriV, low copy 1-2 high copy >50)
-Mechanism for detecting recombinant vectors: blue white screening, antibiotic resistance gene as marker
What are the components in a DNA ligation reaction? (slide 19)
-DNA with compatible ends
-Molar ratio of vector to insert is 1:3
-T4 DNA ligase from T4 bacteriophage
-100x more enzyme for blunt ends
-ATP
-Mg++
-Optimal Buffer pH
-Incubation at 16C
How can the re-ligation of vector be prevented? (slide 20)
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP):
-Removes 5' phosphates from the termini of cut DNA
-Must be removed/ destroyed before ligation
Sources of AP:
-Bacterial
-Calf intestinal
-Shrimp
How can cleaved DNA be treated to create compatible ends? (slide 21)
1) Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I:
-Fill in 5' overhangs by 5'→3' DNA polymerase activity
-3' → 5' exonuclease activity removes 3' overhangs (sticky ends)
2) T4 DNA polymerase
-Same activities as Klenow
-Exonuclease activity 200x that of Klenow
Describe the chemical method for bacterial transformation (slide 24)
-Log phase of E. coli culture
-Centrifuge
-Resuspend bacterial pellet in CaCl2 solution
-Chill on ice
-Aliquot competent cells, store at 80C and amplify plasmid DNA then chill on ice
-Heat shock in 42C water bath
-Plate on LB and ampicillin
-10E6-10E8 colonies/ug DNA
What is this?
-Plasmids
-Circular (single or multiple copies)
-Supercoiled dsDNA (2-200 kb)
-Replicate independently of the host chromosome
True or False: Genes carried on plasmids are essential to the host's survival
False, plasmid genes may be useful in certain environments but will move in/out of bacteria
True or False: Since Plasmids don't belong to the genome, they can be spit out if unhelpful
True
What are some genes that might be carried on a plasmid?
-F-plasmid
-Resistances e.g. antibiotics, pesticides
-Virulence genes
-Metabolism
What is an example of a bacteria with a plasmid that confers huge genetic islands of resistance?
Staphylococcus aureus
What is this?
-Restriction Endonucleases (RE)
-Enzymes that can cleave the phosphodiester bond at restriction sites
-Restriction site is a 4 -10 base pair palindrome
-Mg2+ needed for activity
What is needed for RE activity?
Magnesium (Mg2+)
What is EcoRI named after?
Escherichia coli strain R
What is this?
-Restriction site
-Specific sites in the DNA duplex
-Cleaves the phosphodiester bonds here
-4-10 base pair palindrome
-Sequence of one strand reads in reverse order to that of the complementary strand
What Type of RE is this?
-Cuts at fixed position within restriction site
-Sticky or cohesive ends
-Blunt ends
-Used in cloning experiments
Type II Restriction Endonuclease
What Type of RE is this?
-Cut at random sites outside recognition sequence
-Binds to restriction sequence and cuts bp up or downstream
-Not used in cloning experiments
Type I and Type III Restriction Endonucleases
What ends do these RE produce?
-AluI
-HaeIII
Hint: Alucard is in Hell for using blunt force trauma.
Blunt ends
What ends do these RE produce?
-BamHI
-EcoRI
-HindIII
Sticky ends
What is this?
-Isoschizomers
-Recognise the same palindrome and produce either different or the same digestion products
-Can be uses to directionally clone
What is this?
-Sticky Ends
-Cuts at beginning or end of recognition sequence
-Phosphate/hydroxyl at end of cuts, used to stick DNA back together
-5' or 3' overhang
What is this?
-Blunt ends
-Cuts right in middle
-Always even number of nucleotides
-Nondirectional cloning
True or False: Some Type II REs recognise more than one palindrome
True
Why are some Type II REs able to recognize more than one palindrome?
-Allow substitutions in one or more positions of the recognition sequence
What is an example of a Type II RE that can recognize more than one palindrome?
-HincII
-Has substitutions in the two central positions of the recognition sequence
-But not at the top or bottom
How are purines (A, G) designated?
Memory: Pure silver
R
How are pyrimidines (C or T) designated?
Memory: See the pyramids, sip some Tea
Y
What ends do these have?
-EcoRI
-HindIII
-XmaI
Sticky (5') ends
What ends do these have?
-EcoRV
-HincII
-SmaI
Blunt ends
What ends do these have?
-KpnI
Sticky (3') ends
What determines the frequency of the RE cuts?
Length of the recognition sequence
If a 4 base cutter recognizes 1 sequence, how many bases per site will the fragments be?
4-mer = (1/4)^4 = 1/256
1 site per 256 bases
How many bp does HincII cut?
1/1024 bp
If a 6 base cutter recognizes 1 sequence, how many bases per site will the fragments be?
(1/4)^6 = 1/4096
1 site per 4096 bp
What is this?
-Agarose
-Polymer of repeating di-galactan unit
-Separates DNA molecules according to length during migration through gel
-Porosity determines concentration
Which DNA fragment will move slower through agarose gel, a large or smaller one?
Larger
Which separates DNA fragments better, higher concentrated gel or lower concentration gel?
Higher concentration
How do you produce cast gel out of agarose?
-Heat it up
-Gel becomes soluble
How do you produce soluble gel out of agarose?
Cool it down
What repeating unit does agarose gel have?
Di-galactan
What buffers does agarose gel have?
-Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE)
-Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE)
-pH of 8
What happens when DNA is at pH 8 and subjected to an electric current?
Negatively-charged DNA migrates towards positive electrode
What can you use to visualize DNA during agarose gel electrophoresis?
-Ethidium bromide (carcinogen)
-UV fluorescence
-Nontoxic dye: Cytogreen
What is this?
-DNA Cloning
-Isolates genes from the rest of the genome
-Amplifies DNA, makes multiple copies
-Good for DNA mapping, sequencing, unknown gene identification
How does DNA cloning allow for DNA manipulation?
-Study mutation gene function and regulation
-Express and purify proteins to study structure
How do you create a recombinant vector?
-Use restriction enzyme to cut vector plasmid up and digest it
-Take cut vector, insert new genes
-Ligate genes to cut vector
What is this?
-Hemolysin
-Enzyme that lyses/disrupts RBCS membrane
-Gene (cleR) -> Protein (CleR)
-Carried by Streptococcus
How can you detect the presence of hemolysin?
-Use blood agar
-Zone of hemolysis around bacteria colonies
What are some possible strategies to move cleR gene from source DNA into a recipient vector?
-Random cloning of fragmented genomic DNA via common restriction site
-Specific cloning of PCR-amplified DNA
Name an example of a destination for cleR
Cloning vectors/plasmids
Name an example of a destination host for cleR
-E. coli K12 usually
-Yeast host also possible, but other hosts rare
If the DNA sequence of cleR is unknown and there is no prior work, how would you isolate the gene of interest?
-Search for gene with same phenotype only
-Identification via sequence similarity to other known hemolysins
What are the pros of cloning randomly restricted fragments via restriction enzymes?
Do not need to know the sequence of the target gene
What are the cons of cloning randomly restricted fragments via restriction enzymes?
-Not specific for gene of interest
-RE may cut inside gene of interest, so need to try different RE
What are the pros of PCR cloning?
Very specific amplification of gene
What are the cons of PCR cloning?
Must know sequence of target gene for design of primers
Name this method for isolating genomic DNA from donor Streptococcus:
-High quality, high Molecular Weight DNA
Random cloning
Name this method for isolating genomic DNA from donor Streptococcus:
-Low quality DNA (boil prep) sufficient for PCR
-Just emulsify in water
PCR
Name this enzyme used for fragmenting/cutting donor DNA and recipient vector DNA
-Restriction Endonucleases/Enzyme
-Need to know restriction sites
Name this enzyme used for ligating the two pieces of DNA together
T4 DNA ligase
Name this method used for transferring the recombinant molecule into E. coli so it can replicate
Bacterial transformation
What is this?
-Small plasmids
-Selectable marker for antibiotic resistance
Cloning vectors
True or False: Cloning vectors only have one restriction enzyme site
False, cloning vectors can have multiple cloning sites
What is this?
-Cloning vector site where plasmid starts replication
-Determines if low copy or high copy
-Low copy: Stringent 1-2 copies
-High copy: Relaxed >50 copies
Origin of replication (oriV)
How do you detect recombinant vectors?
-Insertional inactivation
-Blue-white screening
-Antibiotic resistance gene as marker
What is this?
-Phosphodiester bond between the 3' hydroxyl of one nucleotide and the 5' phosphate of another
Ligation
Ligation is a phosphodiester bond between a 3' (Blank 1) and 5' (Blank 2)
1) Hydroxyl (3')
2) Phosphate (5')
What are the requirements for a successful DNA ligation?
1) DNA with compatible ends
2) T4 DNA ligase from T4 bacteriophage
3) ATP
4) Mg2+
5) pH optimal buffer
6) Incubation at 16C
What is the molar ratio of Vector to Insert in DNA ligation?
1:3
How can you stop your vector from self-ligating, causing complementary sticky ends to get stuck together?
Alkaline Phosphatase (AP)
What is this?
-Alkaline Phosphatase
-Removes 5' phosphates from cut DNA terminus
-Must be removed/destroyed before ligation
What are some sources of Alkaline Phosphatase, the enzyme that removes 5' phosphates from cut DNA termini?
-Bacteria
-Calf intestine
-Shrimp
When should you remove/destroy Alkaline Phosphatase?
Before ligation occurs
What are compatible ends?
-All blunt ends
-Cohesive ends that are identical
What can you use to make all cohesive ends into blunt ends so they will become compatible ends?
1) Klenow fragment of DNApol I
2) T4 DNA Polymerase
What is this?
-Helps create blunt ends that are compatible
-Fill in 5' overhangs
-5'→3' DNA polymerase activity
-3' → 5' exonuclease activity removes 3' overhangs
Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I
What is this?
-Helps create blunt ends that are compatible
-Fill in 5' overhangs
-5'→3' DNA polymerase activity
-Exonuclease activity is 200x stronger
T4 DNA Polymerase
If the Klenow fragment of DNAPol I and T4 DNAPol are responsible for filling in 5' overhangs:
-What thermostable DNAPol is responsible for producing 3' overhangs?
Taq (Thermus aquaticus)
What is this?
-Cloning process where Taq adds 3' overhangs to PCR product
TA Cloning
Before cloning into blunt restriction site via Taq (Thermus aquaticus), what should PCR fragments be treated with?
Klenow/T4 DNAPol
What are some thermostable enzymes used in PCR that also produce blunt-ended DNA fragments via 3'->5' exonuclease proofreading?
-Pfu (Pyrococcus furiosus)
-Kod (Thermococcus kodakaraensis)
What is a disadvantage of TA cloning (using Taq to add 3' overhangs to PCR fragments)?
-Nondirectional cloning, can go either way
-Low efficiency using blunt ends instead of sticky
-Limited to Taq fragments
What are some benefits of incorporating Restriction sites into PCR primers at the 5' end?
-Sticky end ligation is efficient
-Directional cloning when 2 different restriction sites are incorporated
Name the steps for expressing a cloned gene in a new host
1) DNA ligation of cleR into new vector
2) Transformation into E. coli and plasmid replication
3) Bacteria plated on Medium + Antibiotic
4) Vector containing insert survives, forms clones
5) Clones incubated overnight
6) Blood Agar plate inoculation
7) Hemolysis observed, confirms gene expression
What type of Transformation is used here to express a clone gene in a new bacterial host?
1) Log phase of E. coli culture, centrifuge
2) Resuspend bacterial pellet in CaCl2 solution
3) Chill on ice
4) Aliquot competent cells, store at 80C while plasmid DNA gets slowly amplified
5) Heat shock cells
6) Plate on LB Medium + Ampicillin
7) 10E6-10E8 colonies/ug DNA that are ampicillin resistant
Chemical Method: Cloning small fragments, <20 kB
What type of Transformation is used here to express a clone gene in a new bacterial host?
1) Log phase of E. coli culture, centrifuge
2) Resuspend bacterial pellet in sterile H₂O
3) Chill on ice, centrifuge and resuspend bacterial pellet in sterile H2O
4) Amplify plasmid DNA and use competent cells immediately
5) Electroshock
6) Add to microtube with saline buffer
7) Place on LB Medium + Ampicillin
8) 10E8-10E10 colonies/ug DNA that are ampicillin resistant
Electroporation: Cloning fragments >20kB