AP Environmental Science - Review
Unit 1 - The Living World: Ecosystems
Introduction to ecosystems
Biotic (once / currently living) / Abiotic (never lived)
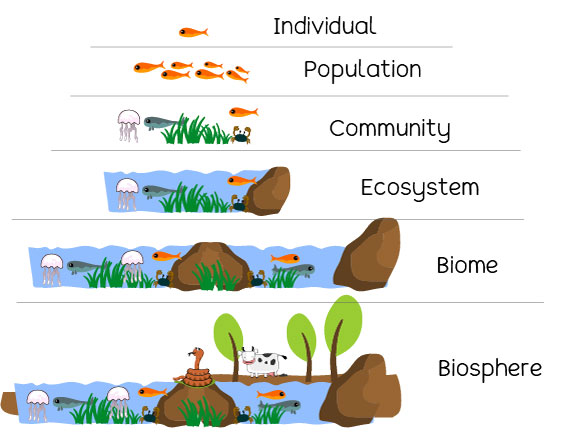
Organism (living being) → Population (a group of the same organisms) → Community (a group of different populations) → Ecosystem (a community and its abiotic factors)
Biome (a unique environment with distinct characteristics) → Biosphere (all of the biomes on Earth)
Terrestrial and aquatic biomes
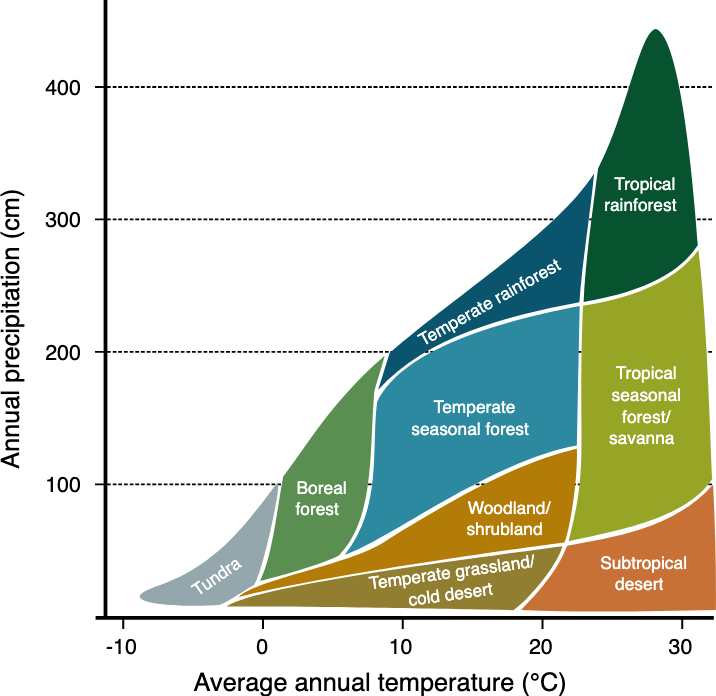
Terrestrial Biomes are primarily affected by precipitation and temperature
Common Terrestrial Biomes
Tundra, Taiga, Prairie, Shrubland, Desert, Temperate Deciduous Forest, Rainforest
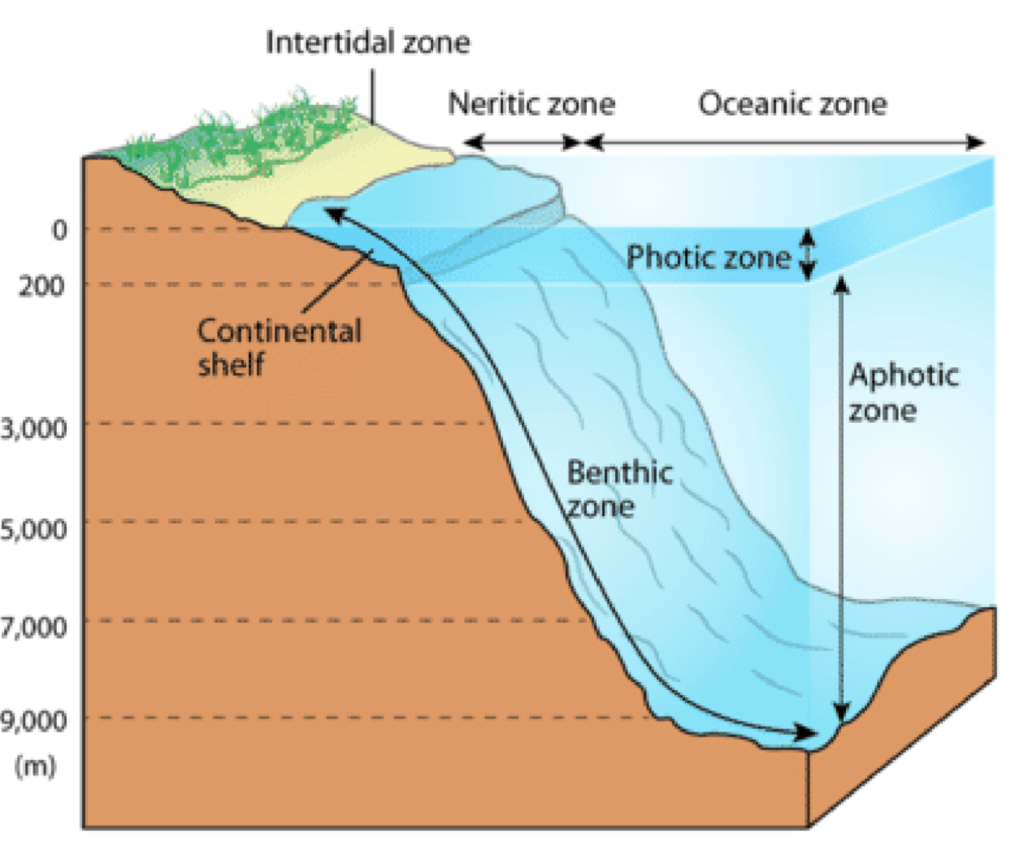
Common Aquatic Biomes
River / Stream, Pond, Lake, Wetland (Bog, Marsh, Swamp), Coral Reef, Ocean, etc.
Climatograms
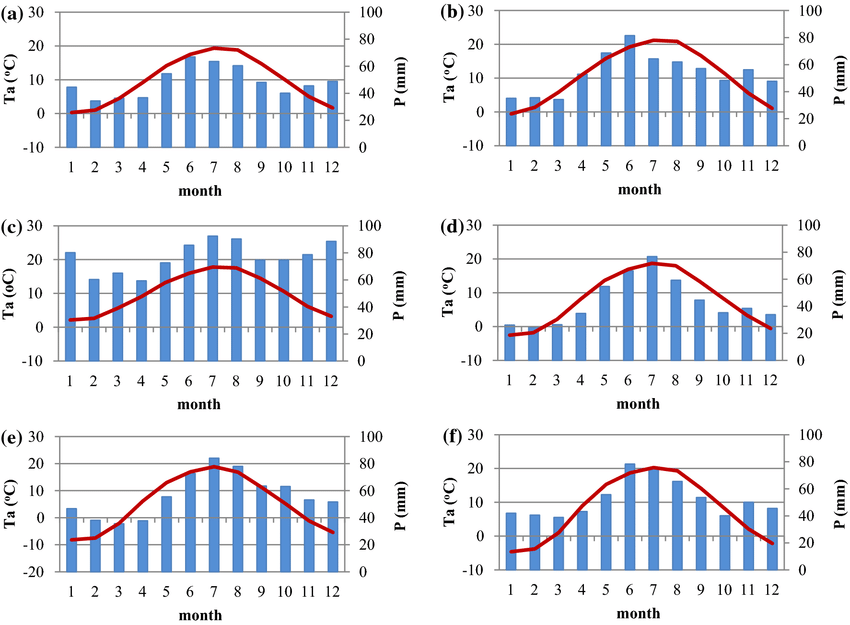
Help determine type of biome
Primary productivity
Photosynthesis basic formula: CO₂ + H₂O (+ sunlight) → sugar + O₂
NPP (Net Primary Productivity) = GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) - R (Respiration)
Net Primary Productivity is the energy available from plants accounting for their respiration
Eutrophication - a process in which runoff from humans pollutes water with excess nutrients, causing an overflow of plants
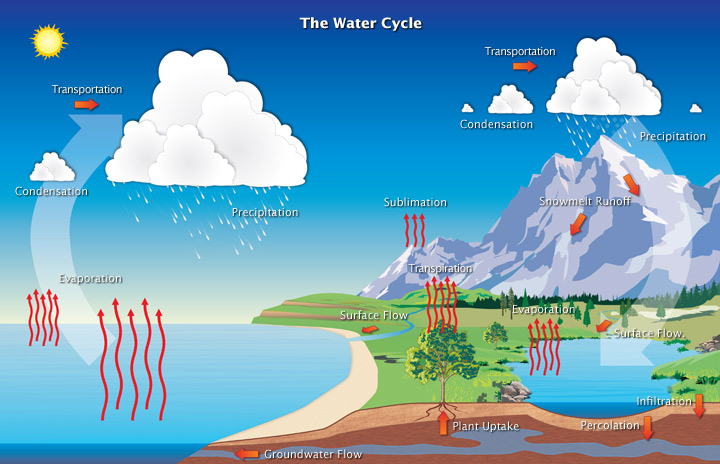
Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and water cycles
Carbon Cycle
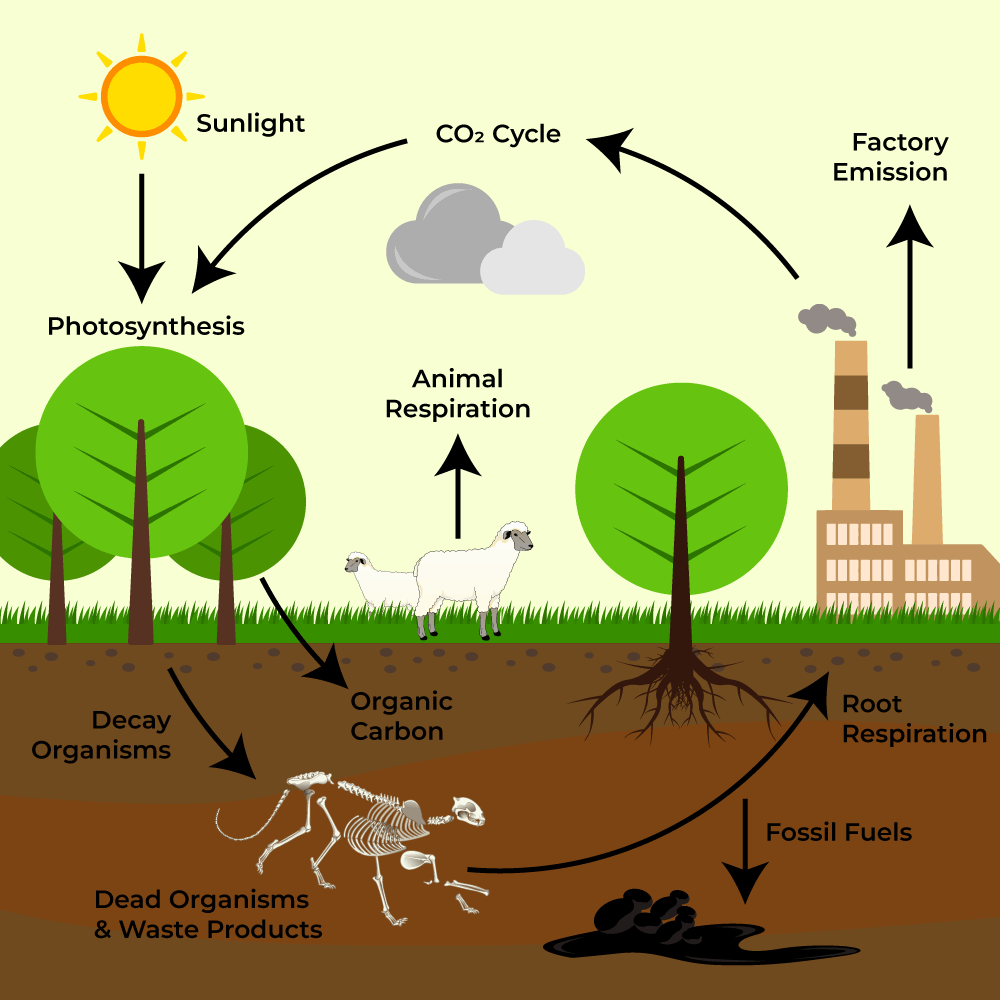
Nitrogen Cycle
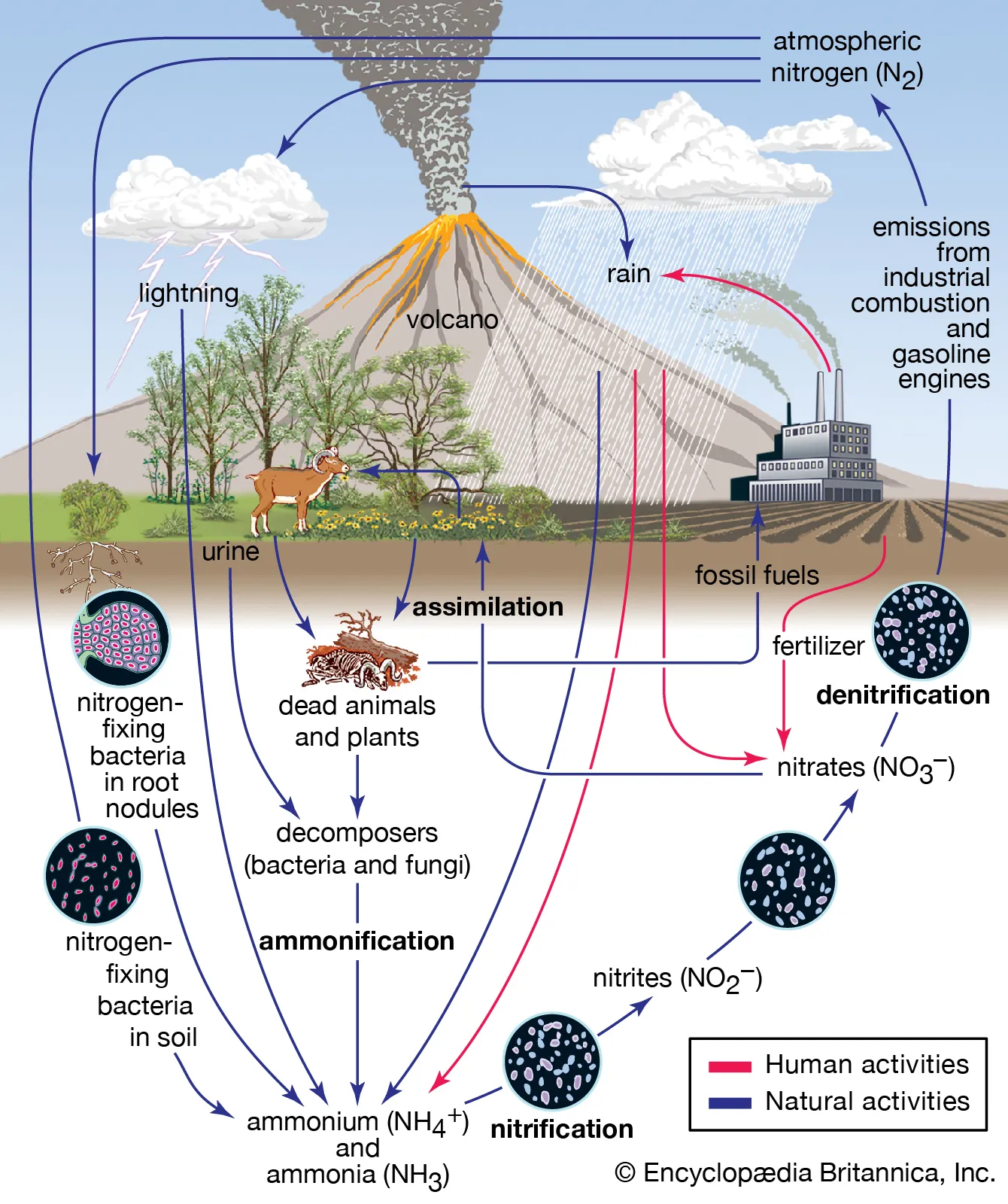
Phosphorus Cycle
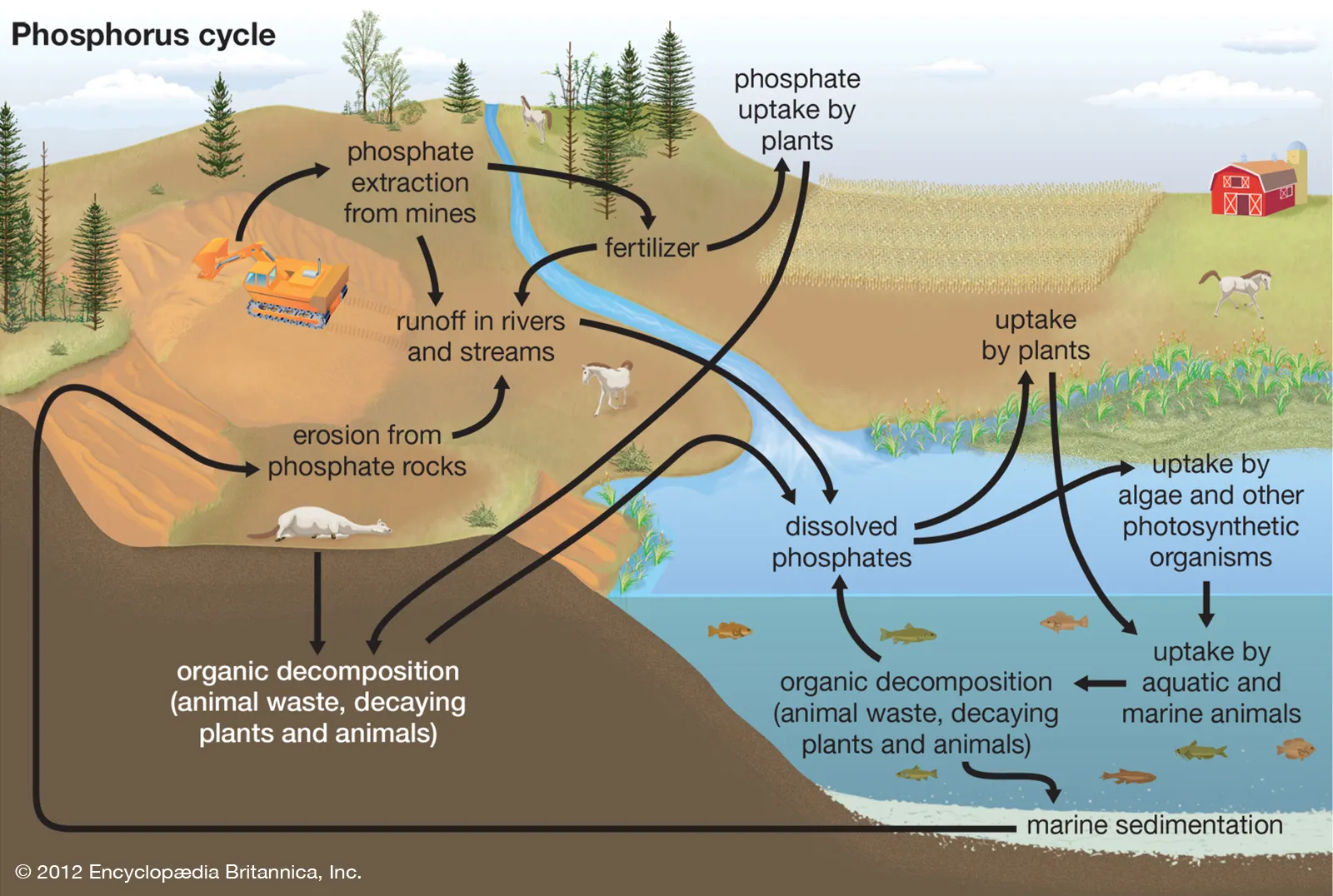
Water Cycle
Trophic levels
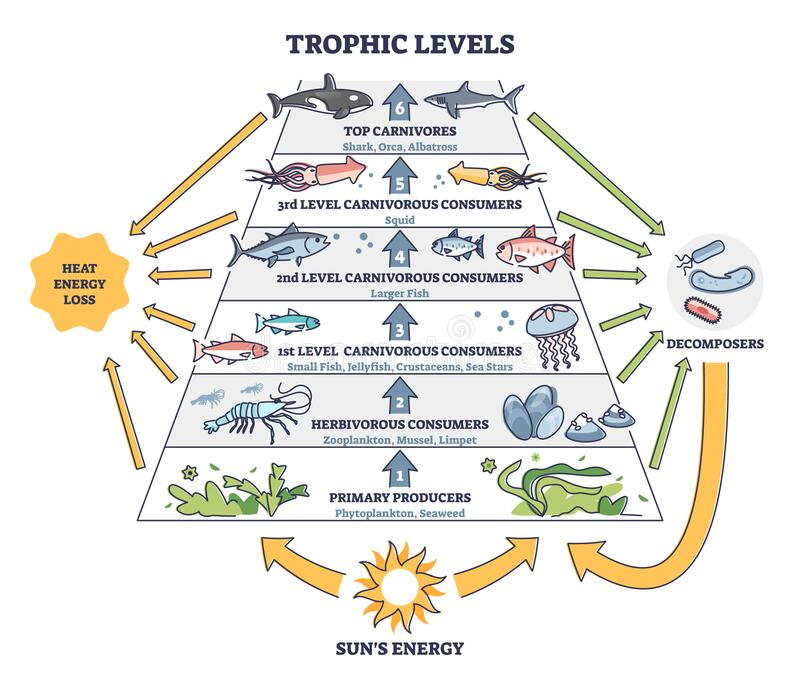
Each trophic level of an ecosystem is the next highest layer of consumption
The flow of energy in an ecosystem and the 10% rule
In a food diagram, arrows go from where the energy starts to where it ends
Each level of a food chain consumes about 10% of the energy of the lower level
Energy begins with primary producers (getting energy from the sun) to primary consumers to secondary consumers and so on, and at each stage decomposers return some energy to producers
Herbivores eat only plants, omnivores eat both plants and animals, and carnivores eat only animals
Autotrophs can produce their own food, heterotrophs require consumption to get energy
Trophic Cascades are events that affect the presence of one organism that highlight the complex relationships of ecosystems
Bottom-up Ecosystems - producers limit the consumer populations
Top-down Ecosystems - consumers control producer populations
Types of Relationships
Competition (limited resources): intraspecies (within one) and interspecies (across multiple)
specialists - consume a specific type of resource
generalists - consumer a variety of types of resources
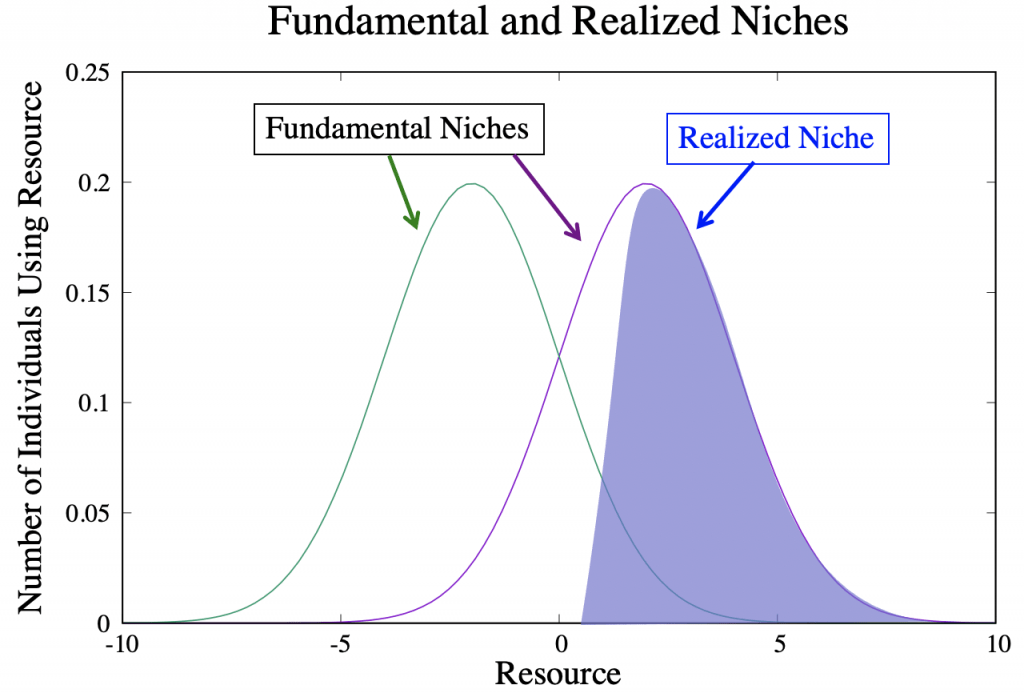
when species overlap in consumption, one is successful (the original niches of both organisms are the fundamental niches, while the after-competition niches of both organisms are the realized niches)
resource partitioning is when organisms consume a specific resource (ex: birds eating different parts of trees)
Symbiosis - living together in harmony
Mutualism (both organisms benefit), Commensalism (one organism benefits and the other is unaffected), Parasitism (one organism benefits and the other is harmed)
Food chains and food webs
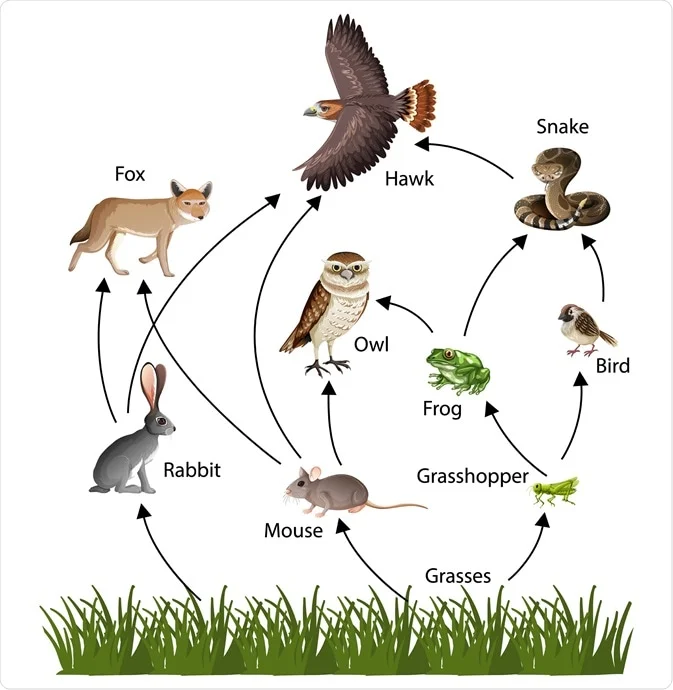
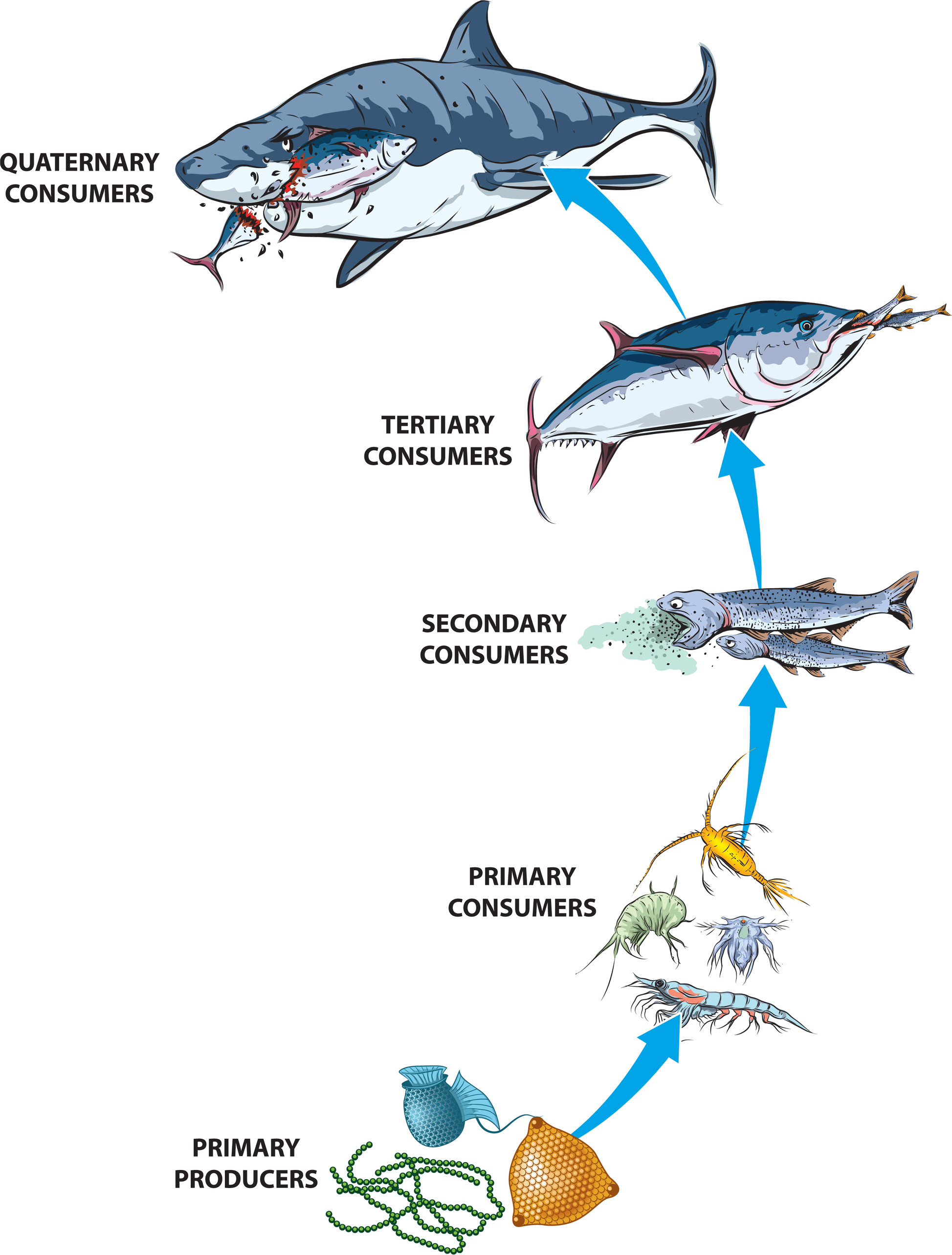
Unit 2 - The Living World: Biodiversity
Introduction to biodiversity
Biodiversity and Evolution - genetic mutations lead to varying traits within a species, and the spread of these genes help drive evolution based on whether the trait is harmful, uneffective, or beneficial
Types of Biodiversity - Genetic (variation of alleles within a species), Species (variation of species within an ecosystem), Ecological (variation of ecosystems within a region/biosphere)
- species richness is how many species are present and species evenness is the proportion of each species
Darwin’s Postulates (of Evolution)
Traits must be varied in a species
The focused trait must be heritable
Selective Pressure - not all organisms survive
The trait helps reproduction/survival
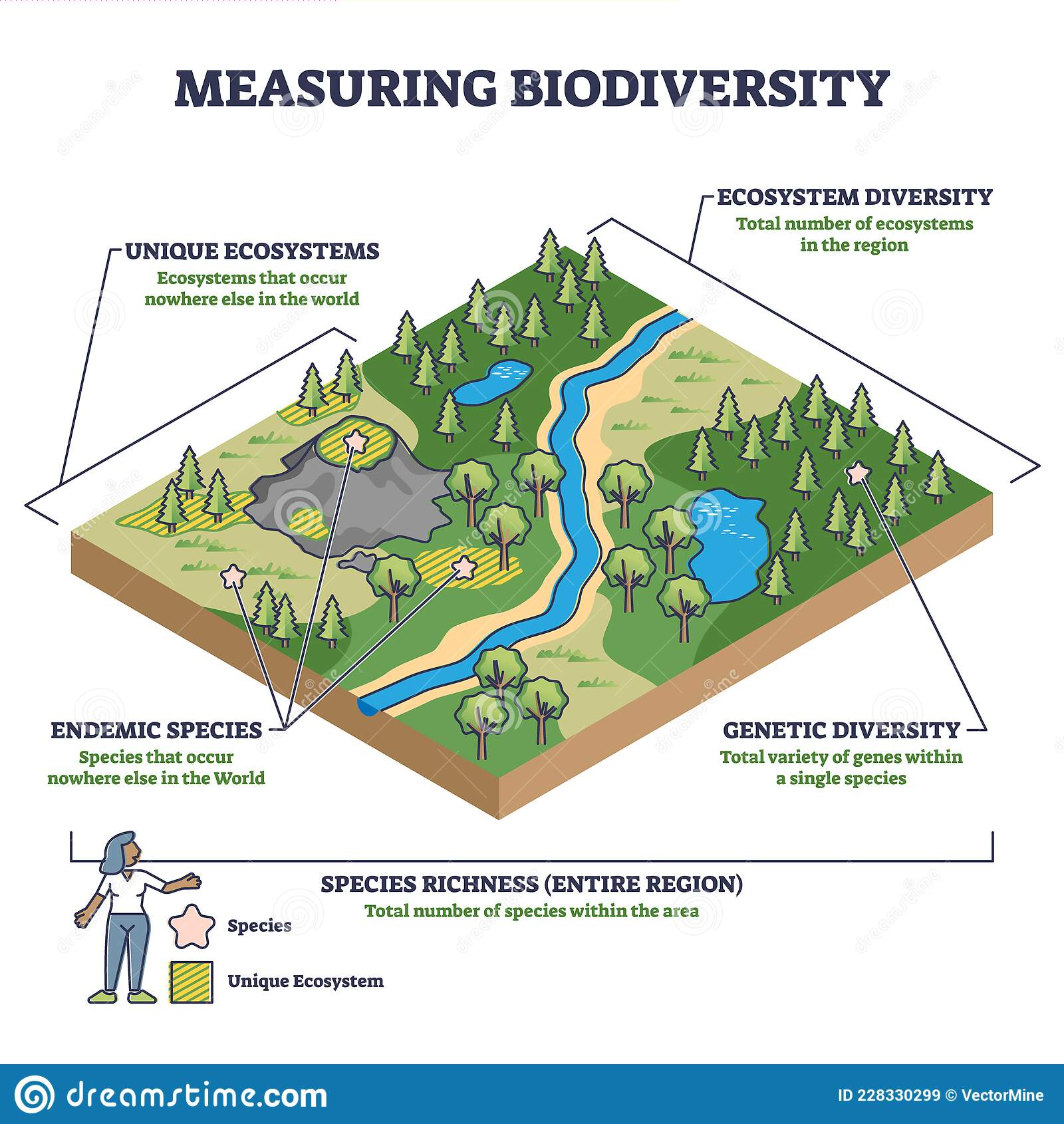
Ecosystem services
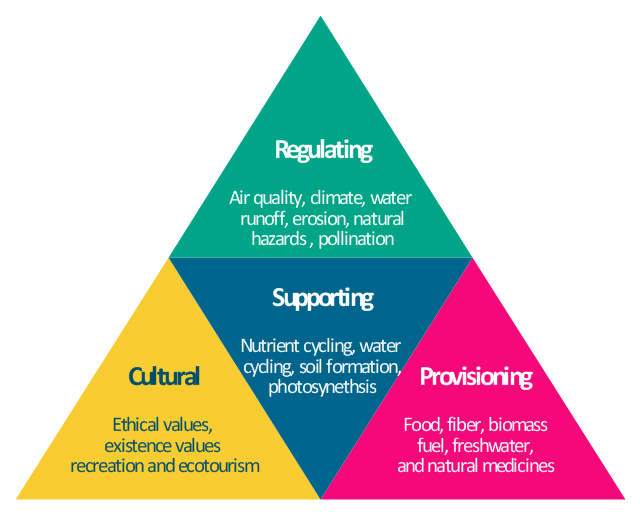
Regulating - benefits to environment from ecosystems
- ex: air quality, runoff/erosion control, natural hazard resistance, pollination
Supporting - helps ecosystem health to provide other benefits
- nutrient cycling, soil formation, photosynthesis
Provisioning - material production
- ex: food, biomass, fuel, medicine, etc.
Cultural - cultural benefits of ecosystems (recreational, health, etc.)
- ex: religious practices, tourism, etc.
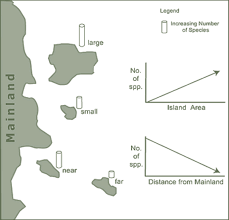
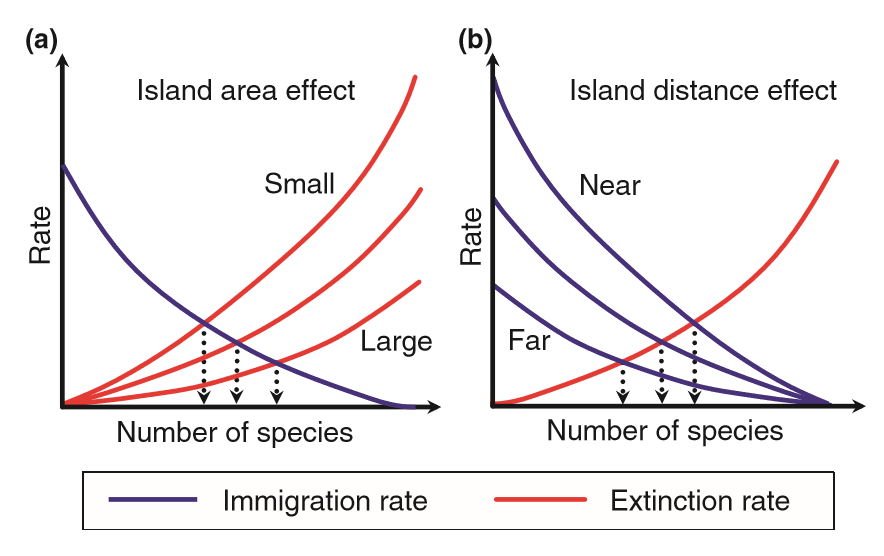
Island Biogeography
Ecological tolerance
Ecosystem Resilience - how well an ecosystem is able to recover from an ecosystems disruption
Ecosystem Resistance - how well an ecosystem responds to an ecosystems disruption
Tolerance - the ability to live in a variety of environmental conditions
Keystone Species - species required for ecosystem stability
Indicator Species - have a very low tolerance and indicate environmental conditions
Invasive Species - non-native and harmful species
Natural disruptions to ecosystems
Bottleneck Effect - a decrease in the number of alleles in a species, leads to either recovery or extinction
Ecosystem Disruptions - an event or process that harms ecosystem health (usually decreasing biodiversity)
- ex: extreme changes in temperature or precipitation, sea level rise, natural disasters (tornadoes, tsunamis, floods, forest fires, etc.), migration, invasive species, human activity (habitat destruction, pollution, etc.)
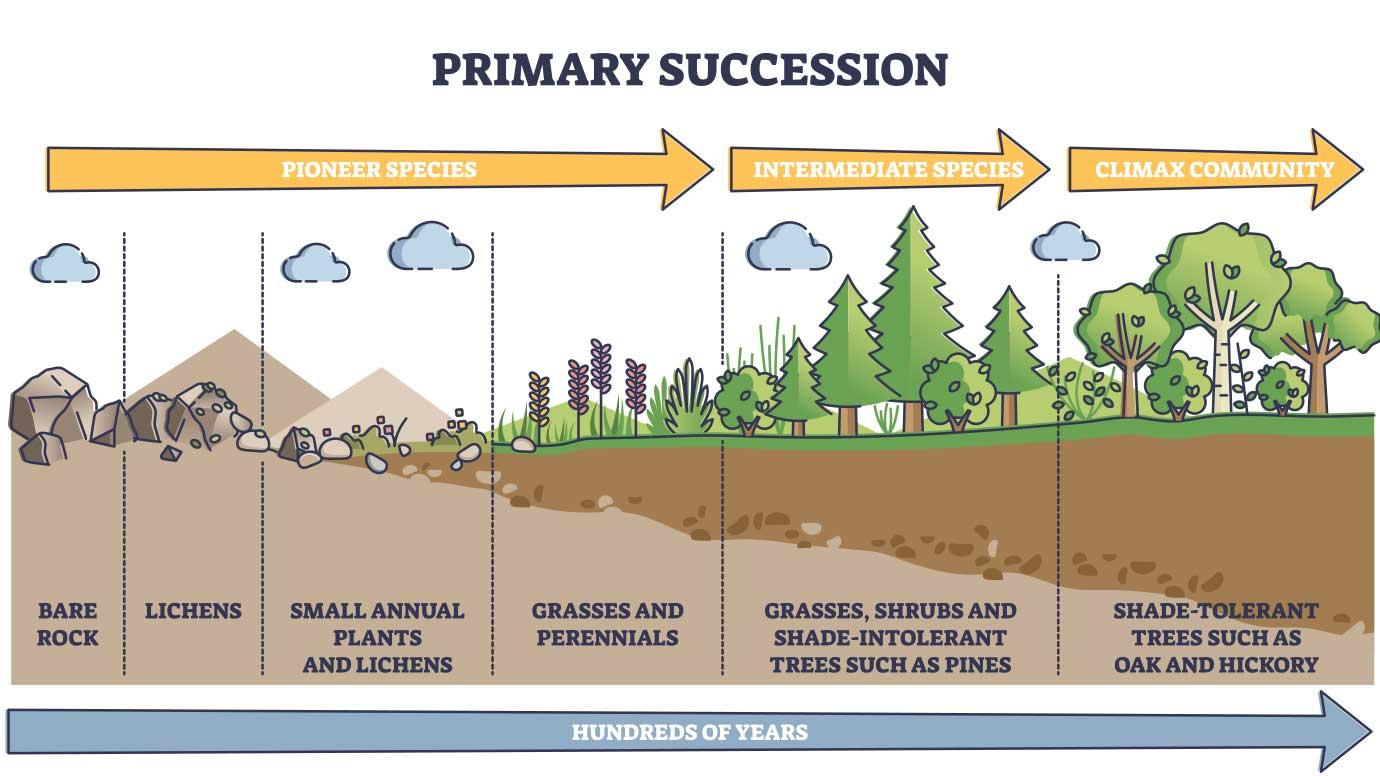
Ecological succession
Primary Succession - the development of an ecosystem from scratch (takes thousands of years)
soil isn’t developed
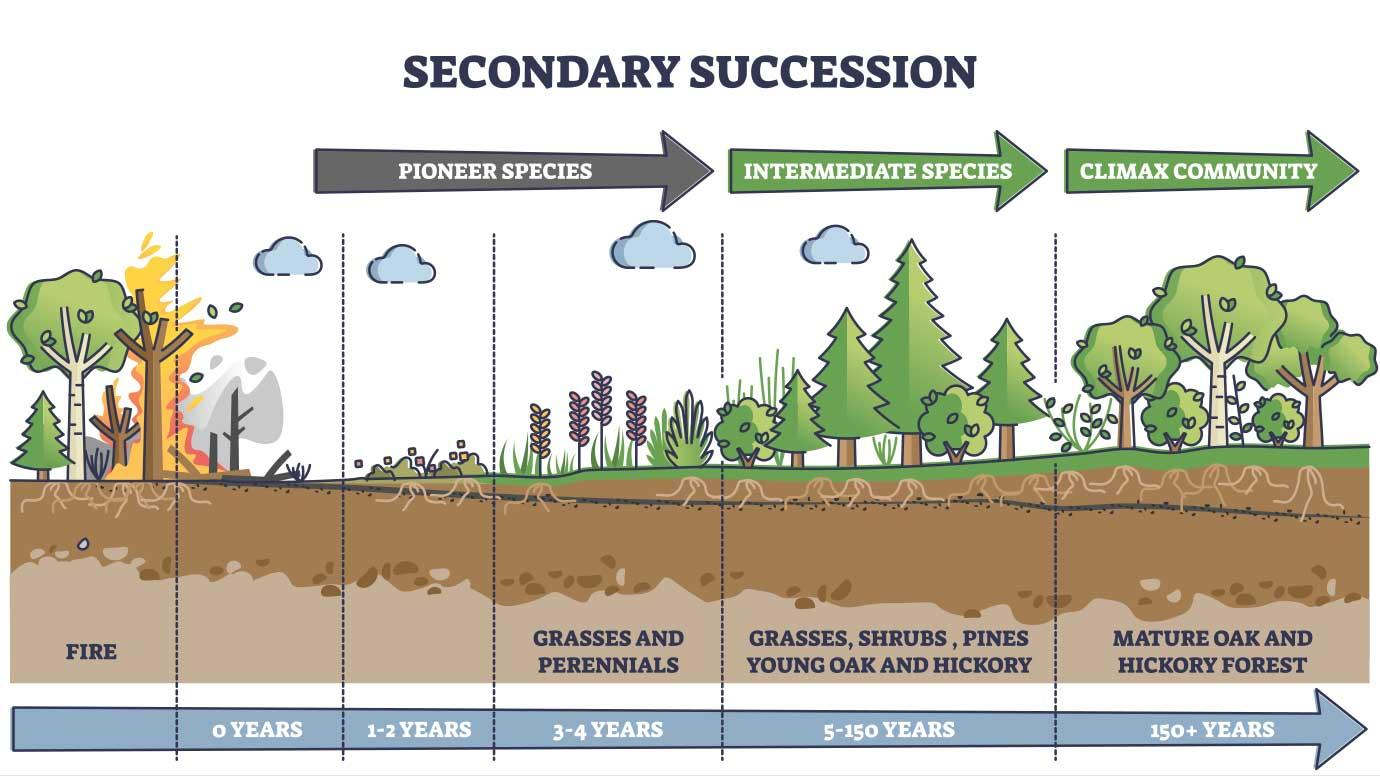
Secondary Succession - the development of an ecosystem after an ecosystem disruption (takes at least 50 years)
soil is already developed
Unit 3 - Populations
Generalist and specialist species
Generalists use a variety of resources and are adaptable, while specialist species use specific resources and are susceptible to change
Survivorship curves
Type I - few and rare offspring (ex: tortoises)
Type II - in between (ex: birds)
Type III - lots of and frequent offspring (ex: bacteria)
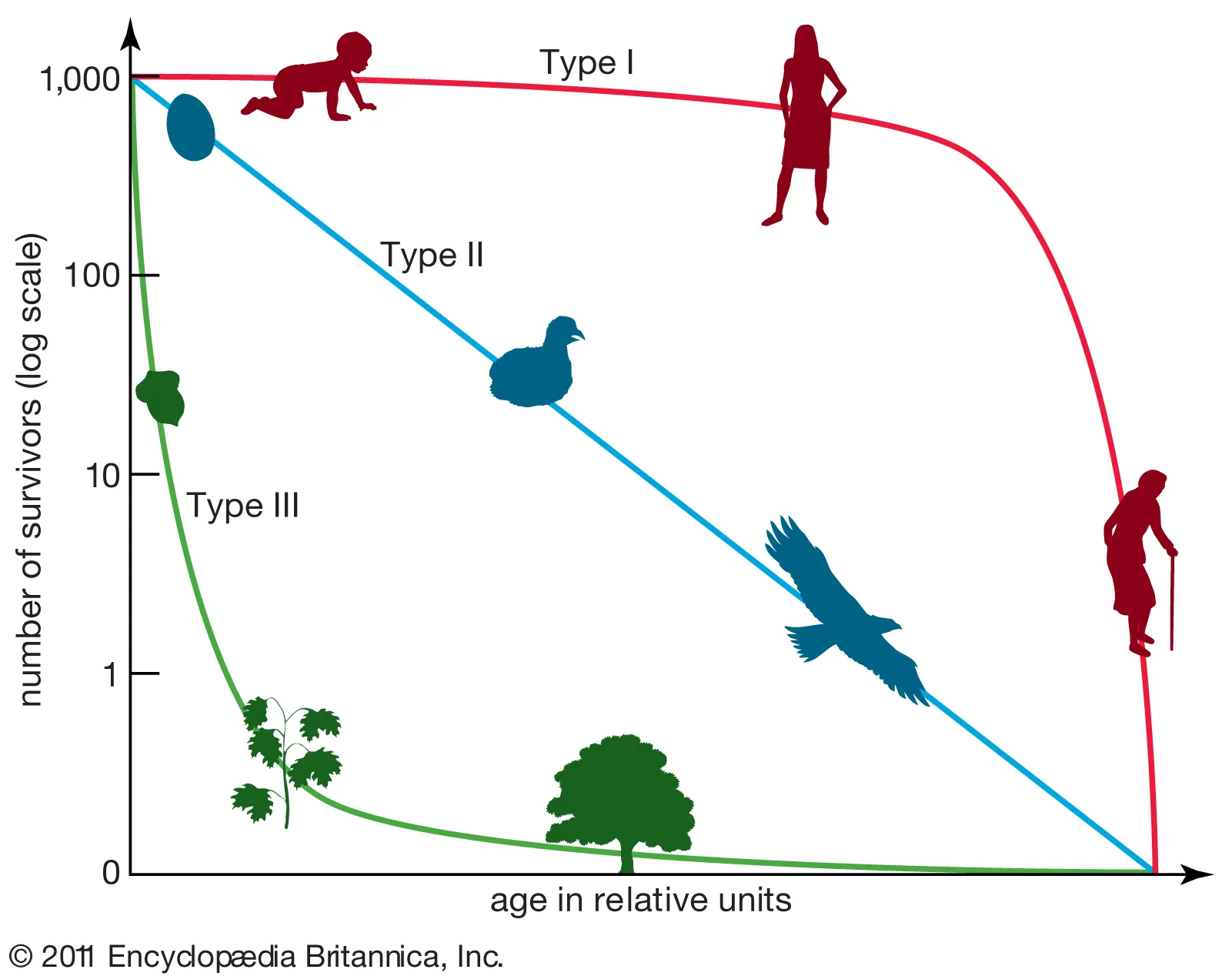
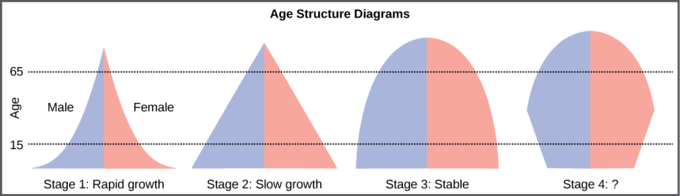
r-selected species - unstable environment, high fecundity, short generations, small size, type III
K-selected species - stable environment, high parental care, fewer offspring, large size, type I
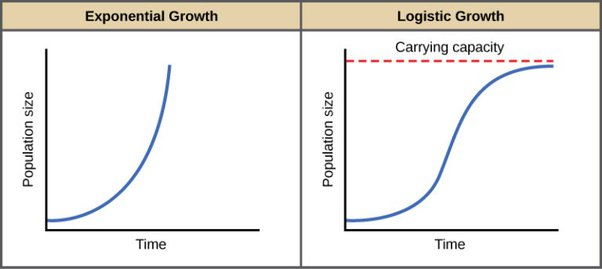
Population growth and resource availability
Carrying Capacity - the maximum number of individuals that can be supported
The most important resources are food and space
(Births(+) - Deaths(-)) + (Immigration(+) - Emigration(-)) = Natural Increase + Net Migration = Growth Rate
Population Limiting Factors -
- Density-dependent - competition, disease, parasitism, predation
- Density-independent - pollution, natural disasters
Doubling time = growth rate / 70
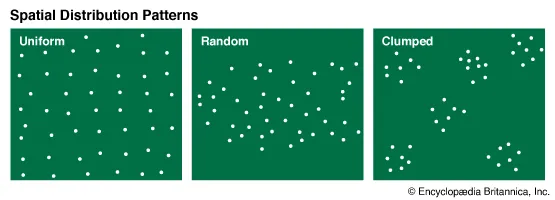
Population Distributions
Types of Growth
Age structure diagrams
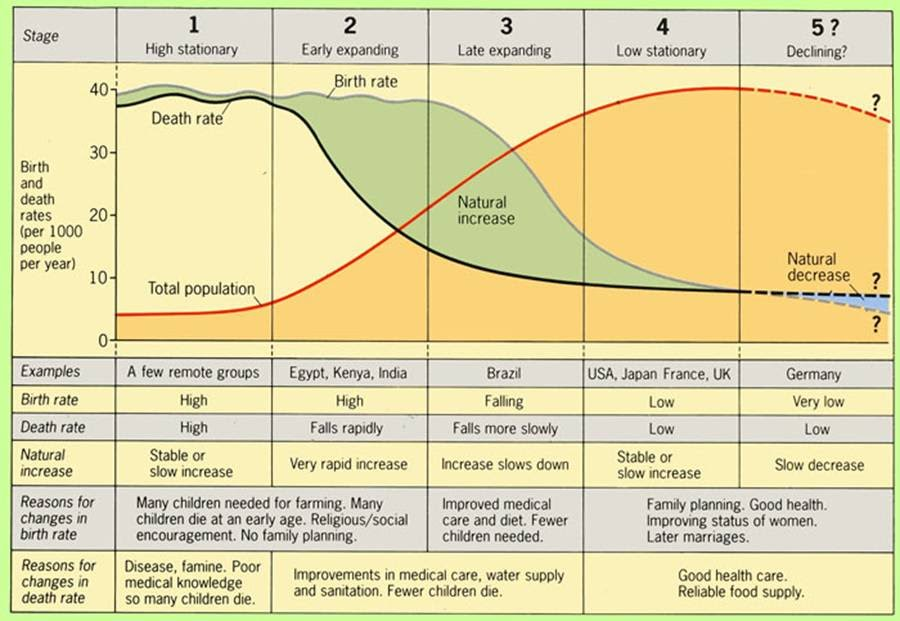
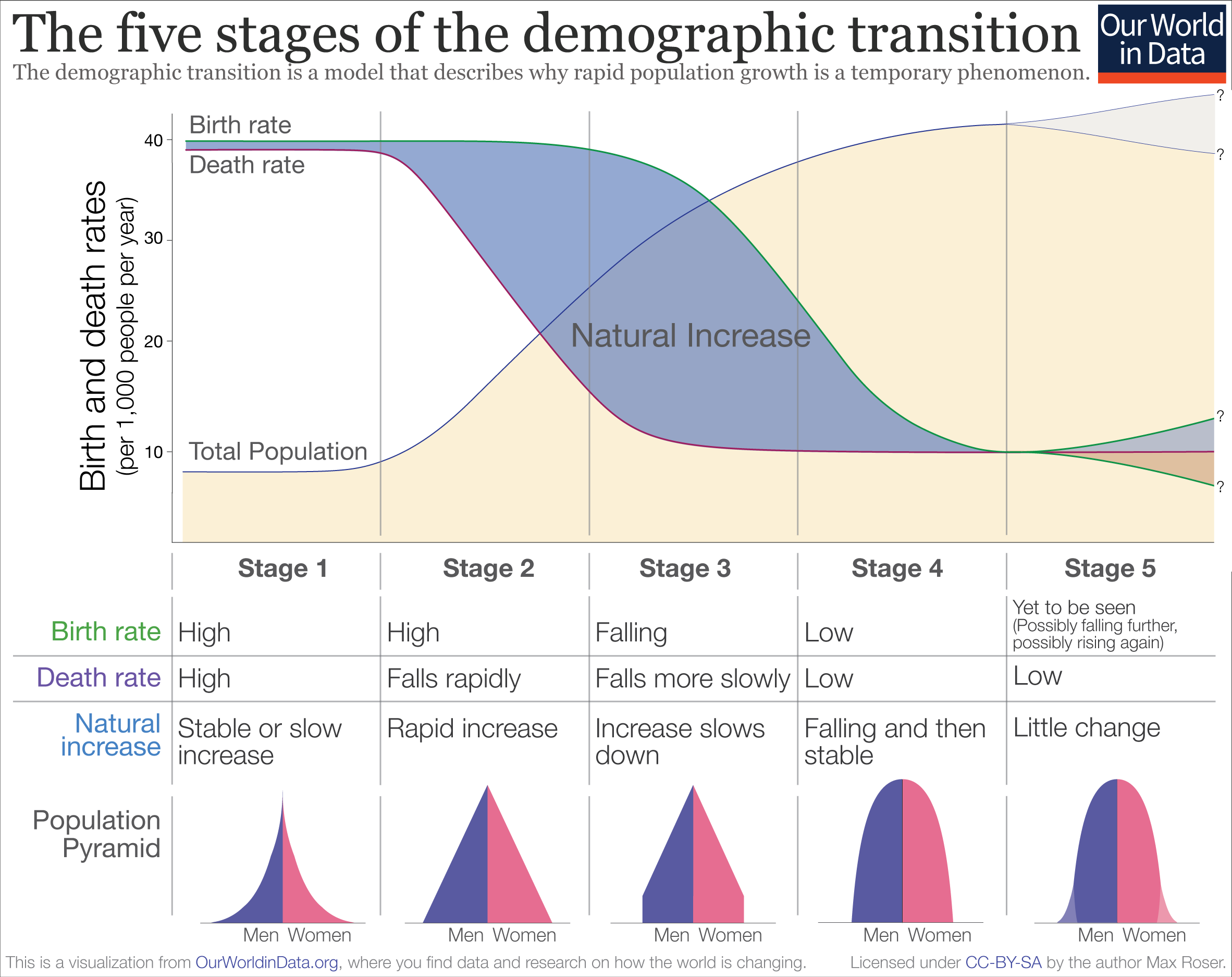
Human population dynamics
Total Fertility Rate = (Children / Women)
Unit 4 - Earth Systems and Resources
Tectonic plates
Types: oceanic or continental, and convergent, divergent, or transform
Convergent - two plates push together, causing one to slide up and one to submerge
- causes volcanoes, islands, mountains, etc.
Divergent - two plates slide away from one another
- causes mountains, volcanoes, rifts
- Mid-atlantic Ridge
Transform - two plates slide against one another
- causes earthquakes
Faults, hotspots, and islands form at boundaries
Pacific Ring of Fire
Soil formation and erosion
Parent Material - original rock substance that gets broken down
Weathering - the process of breaking down rocks (wind, rain, etc.)
- factors: type of parent material, climate, topography, biological factors, time
Soil Profile - the layers of soil
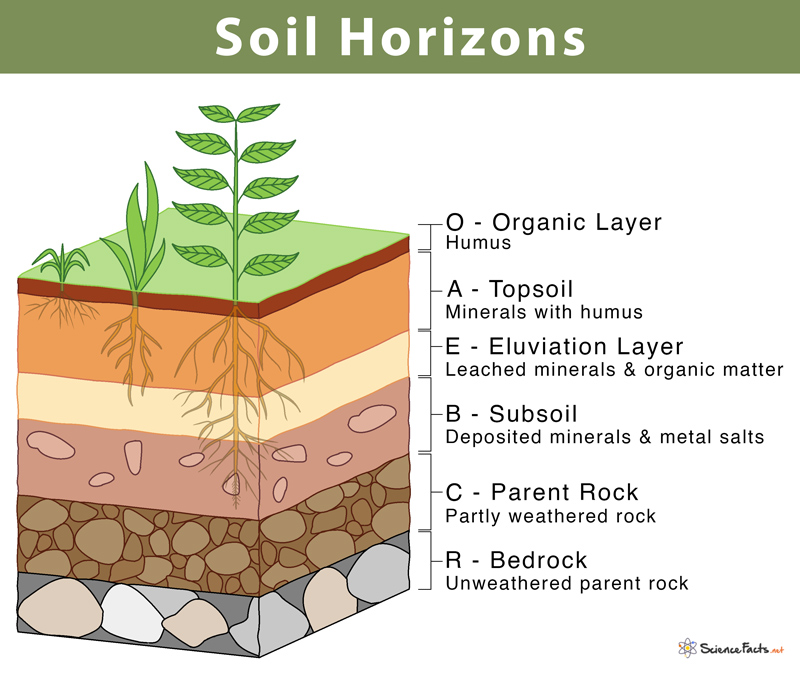
Soil Erosion - movement of soil caused by water, wind, gravity, topography, and human impacts (deforestation, overgrazing, pesticides/fertilizers, tillage, etc.)
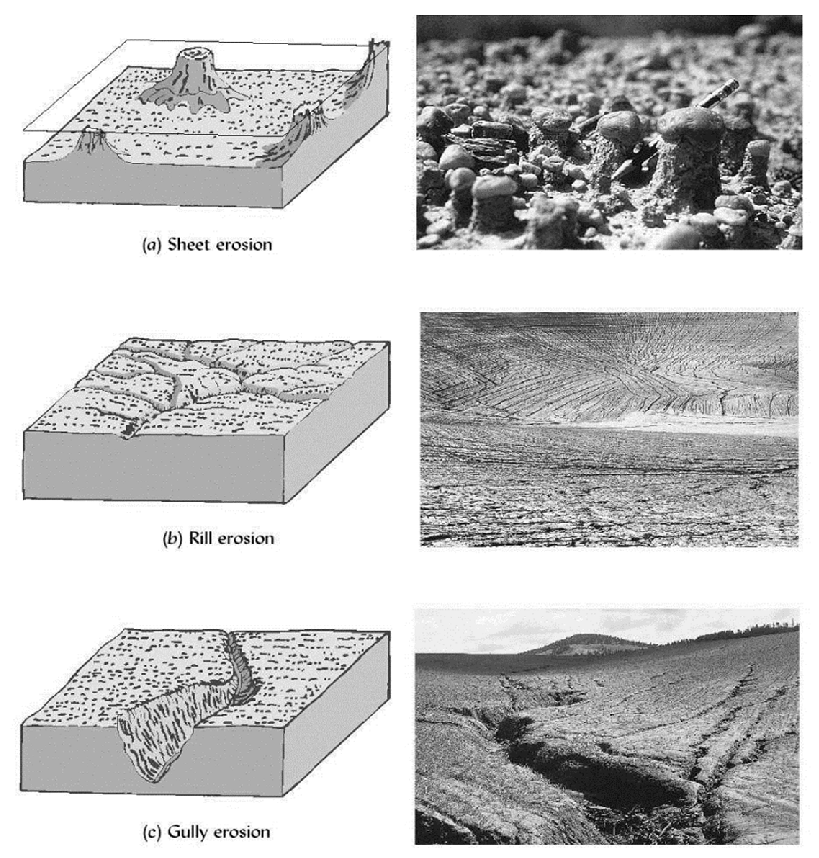
Solutions to Erosion:
- Sheet - plant cover
- Rill - strip cropping
- Gully - diverting water, contour farming
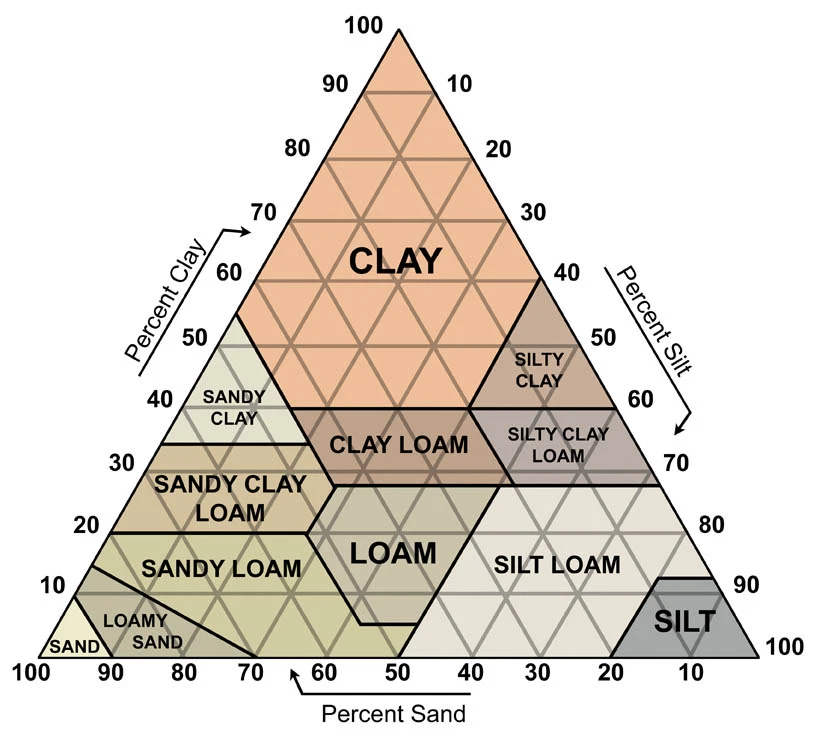
Soil Texture - mix of sand (largest, most permeable), silt (medium), and clay (smallest, least permeable)
Soil Tests: chemical (nitrogen, phosphorus, pH), physical (soil composition, water retention), biological (earthworms, bacteria, etc.)
Percolation - water moving into the ground
Infiltration - chemicals moving into the ground with water
Earth's atmosphere
Troposphere (tropopause) - causes weather
Stratosphere - ozone layer
Mesosphere - asteroids
Thermosphere - Aurora Borealis
Exosphere - outside
Global wind patterns
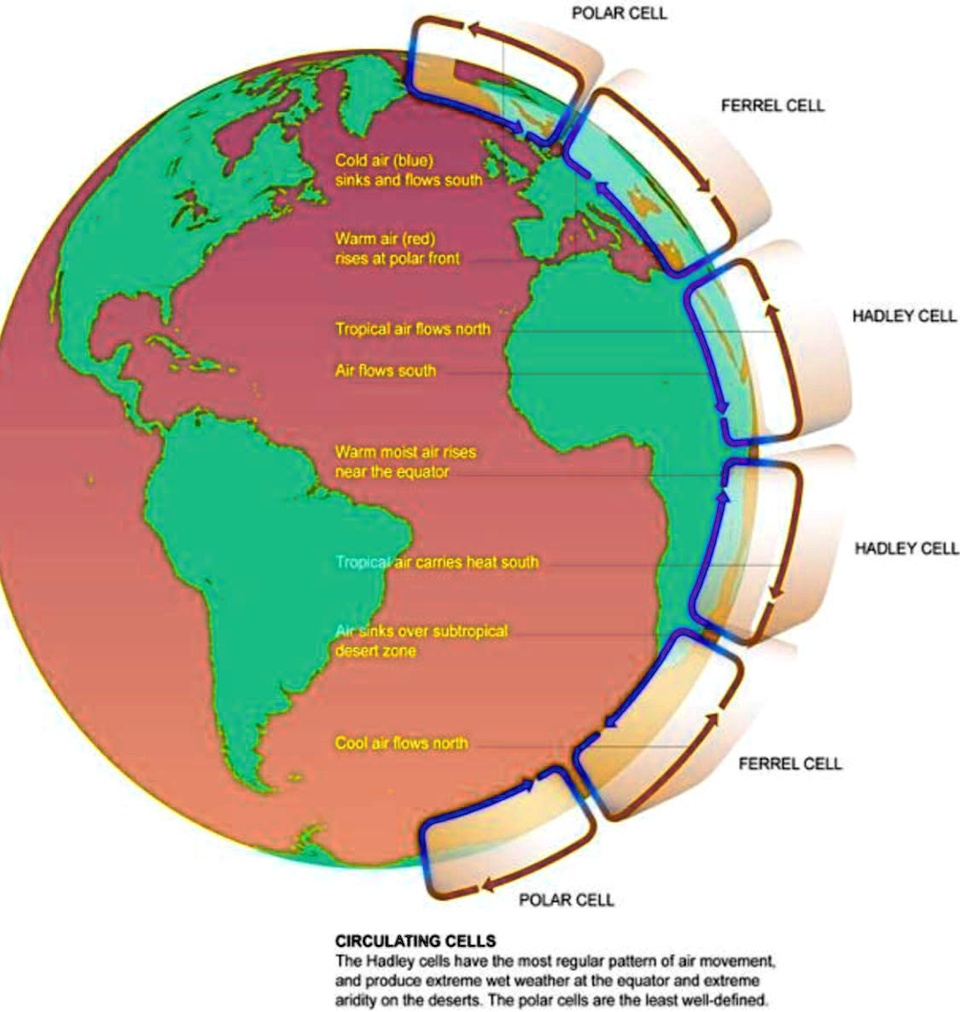
Wind cells drive currents called jet streams
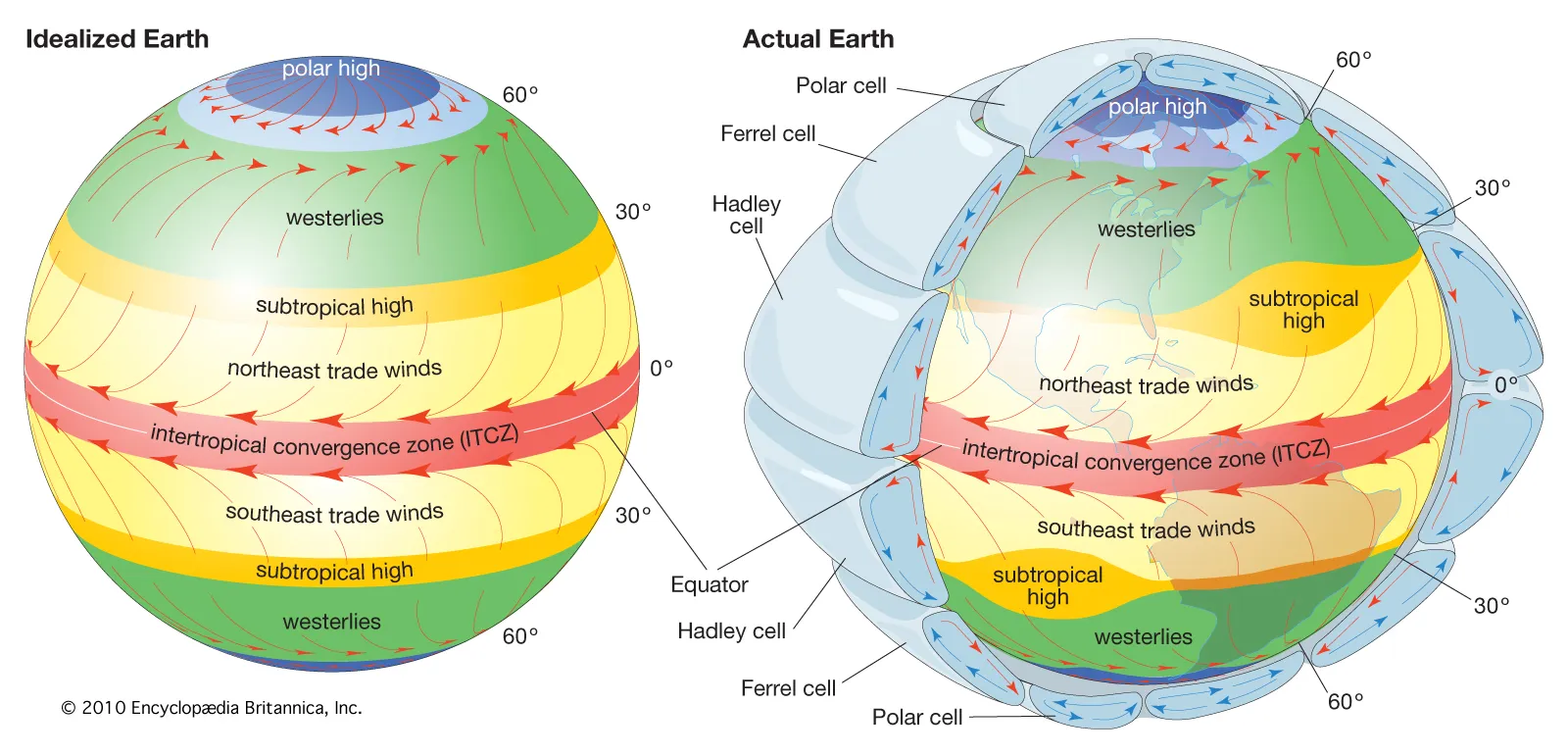
Trade winds are predictable winds that occur at different latitudes
- impacted by the spinning of Earth as well (Coriolis Effect)
Earth's geography and climate
Climate is long-term while weather is short-term
Earth’s 23.5 degree tilt is what primarily causes seasons
Albedo - ability to absorb light (white is high, black is low)
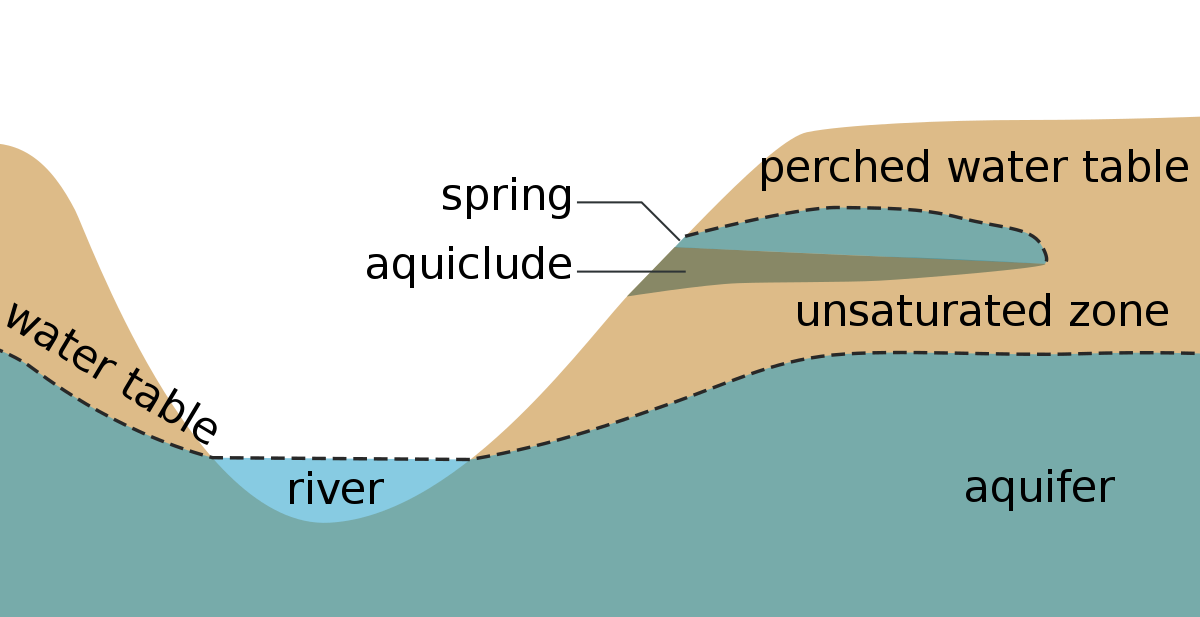
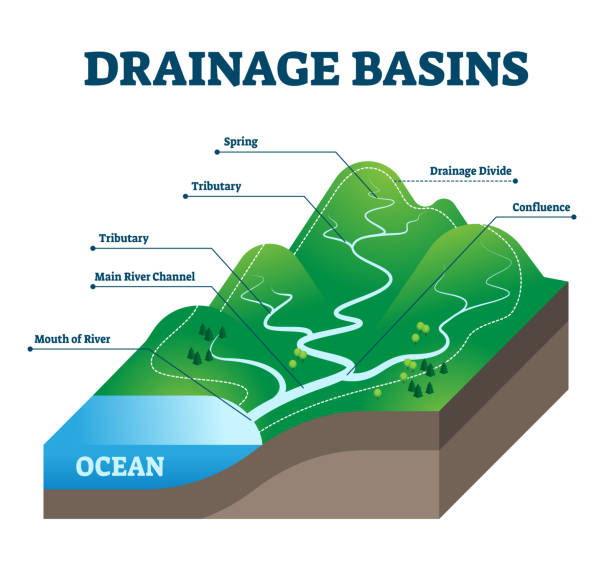
Watershed
El Niño and La Niña
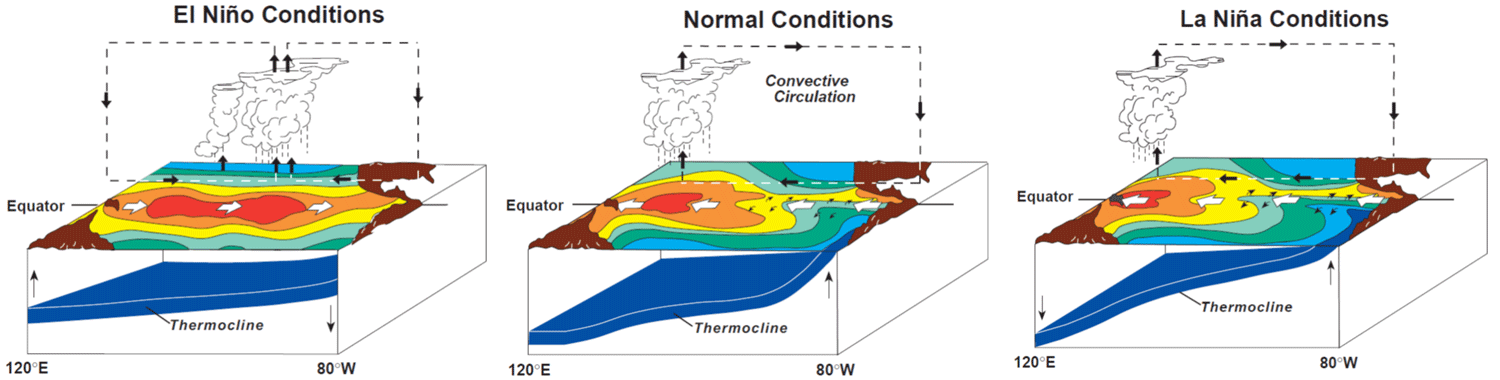
Caused by changes in trade winds
Effects: affects agriculture and climate, and causes upwelling
Unit 5 - Land and Water Use
The tragedy of the commons
If a resource goes unused, it will just get used by other organizations.
The Green Revolution
Agricultural technologies improved heavily, allowing greater support for a greater population.
- Increased greenhouse gases (25% of total emissions)
GMOs (Genetically-modified Organisms)
- Benefits: more nutritious, less land, better soil quality, resistant to diseases/pests/environmental conditions
- Drawbacks: genes can mutate (can activate sleeper genes), cause more powerful pests/diseases, affects biosphere genetic diversity
Synthetic Fertilizers (help provide nutrients for organisms)
- Haber-Bosch Process helps make nitrogen consumable
- Benefits: cheap, easy to produce/use, animal independent
- Drawbacks: excess runoff, decreased soil quality, uses fossil fuels
Types and effects of irrigation
| Irrigation Practice | Description | Benefits / Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Flooding |  | ==- Ruins typical river flow (harms river ecosystem)- Causes erosion==- Causes salinization- Easy |
| Furrowing |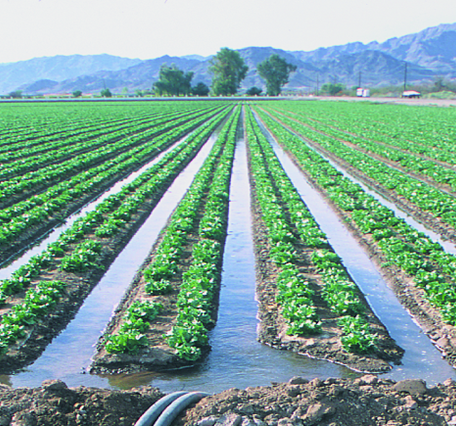  | ==- Ruins typical river flow (harms river ecosystem)- Causes erosion==- Causes salinization- Easy |
| Spraying |  | ==- Expensive==- Lots of evaporation |
| Dripping |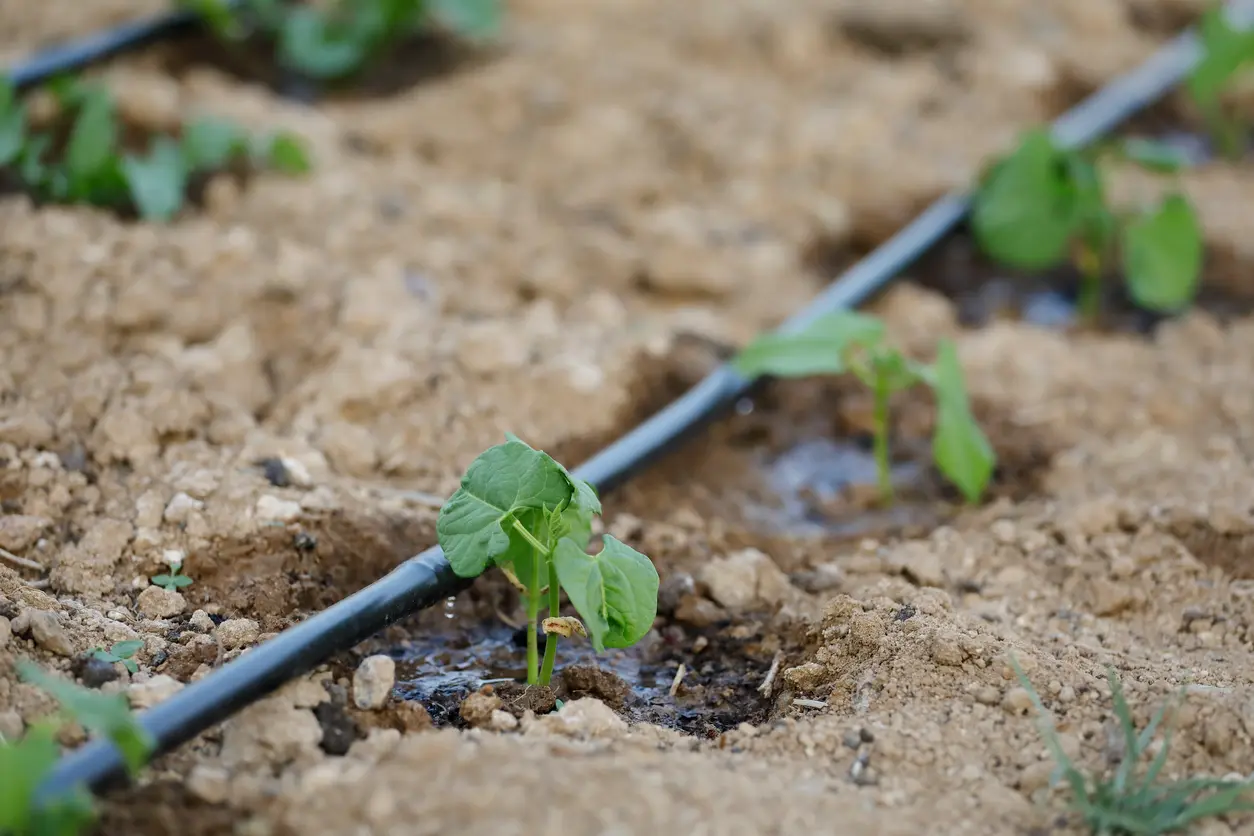  | %%- Efficient water use%%==- Expensive== |
Pest-control methods
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): controls pests (expensive but sustainable and long-term cheap)
| IPM Practice | Description | Benefits / Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Biological (gophers, chickens, etc.) |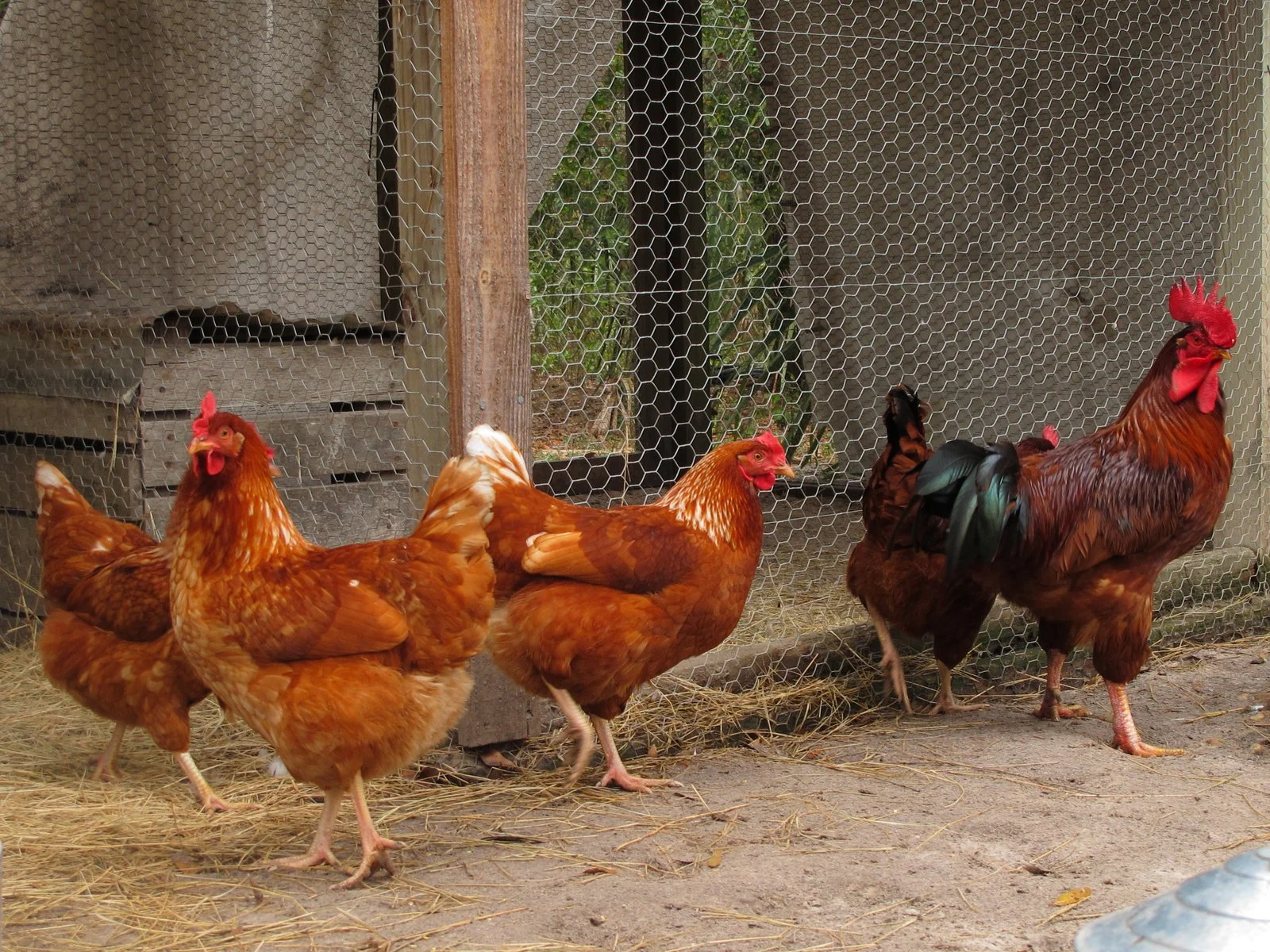  | %%- Cheap%%- Effective- Helps maintain ecosystem- Little effort |
| Physical (scarecrows, prescribed burns) |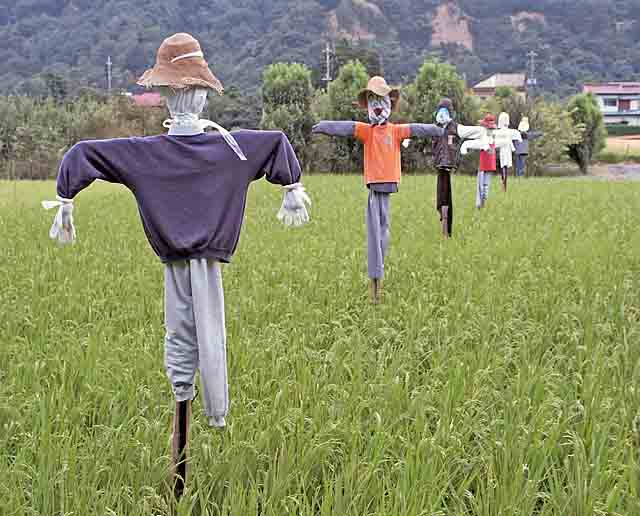  | %%- Cheap%%==- Ineffective== |
| Chemical (pesticides) |  | ==- Expensive==%%- Effective%%==- Ruins soil and ecosystem== |
Meat production methods and overfishing
| Meat Practice | Description | Benefits / Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| General |  | - High resource cost (land for grazing and growing food)- Pollution through emissions- Excess waste- High demand |
| Clear-cutting |  | |
| Overcrowding |  | - Breeds and spreads infectious diseases- Cheaper |
| Rotating Fields |  | - Maintains soil and plants- Requires more land |
| GMOs |  |
The impacts of mining
Urbanization and ecological footprints
Urbanization
Negative Impacts: less permeability and high pollution, less plant cover, overconsumption (and far away from resources), saltwater intrusion for coasts, urban heat island
- Positive Impacts and Solutions: building up not out, less travel distances and more efficient transportation usage, more efficient resource usage (ex: heating/cooling), ecosystems destruction, urban heat island
Introduction to sustainable practices including crop rotation and aquaculture
Sustainability is when inputs are equal to outputs
Bad Agricultural Practices: clear-cutting removes forests and therefore biodiversity, monoculture drains the soil of specific nutrients, GMOs can harm biodiversity and can cause pest resistance, synthetic fertilizers affect soil quality, tilling destroys top layers of soil, slash and burn ruins ecosystems, pesticides pollute soil/water and can cause cancer
- Solutions: crop rotation allows for soil restoration, green manure is a natural fertilizer, GMOs can reduce land use, contour farming and terracing helps with runoff, windbreaks prevent erosion, strip-cropping and cover crops and intercropping helps with runoff, no-till agriculture helps allow the soil ecosystems perpetuate, perennial crops help keep soil intact, spraying and drip irrigation efficiently use water and reduce salinization
Bad Aquatic Practices: commercial fishing technology (general), long-line fishing, drift/gill nets leads to lots of bycatch, pursing leads to lots of bycatch, trawling destroys seafloors, sonar is efficient but kills fish, aquaculture helps with demand but can lead to excess waste
Unit 6 - Energy Resources and Consumption
Energy sources and fuel types, including fossil fuels, ethanol, and nuclear power
NONRENEWABLE
Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) are the primary sources of energy today, with nuclear energy behind it
- both nonrenewable energy sources
Coal to Energy conversion: coal is burned, which heats water, which turns into steam, which spins a turbine, which spins a magnet and coils, which uses a generator to convert to electricity
- Cogeneration: when electricity is used but the resulting products have additional benefits (ex: heated water goes to houses after spinning turbines)
Coal Formation: Peat/Humus are condensed using heat and pressure into lignite, which then condenses to bituminous (most common), which finally turns into anthracite (cleanest)
- oil and gas have similar processes, just in marine ecosystems
Natural gas is composed of hydrocarbons
Fracking (hydraulic fracturing) is done by drilling a hole and blowing it up to release gas (causes earthquakes and harmful gases to release)
Fractional Distillation is the separation of crude oil into usable oils based on heating point (highest - liquid petroleum gas, petrol, paraffin, diesel, fuel oil - lowest)
Nuclear Energy is efficient and clean, but has long-lasting nuclear waste, can explode, causes ionizing radiation, and can cause meltdowns (excess heat)
- Nuclear Energy is formed by sending a neutron to a uranium atom which releases energy through fission and creates a chain reaction of more neutron releases
The electric grid uses transformers and checkpoints to alter voltage
Global energy consumption and distribution of natural resources
Mining Types: surface, subsurface, strip, and mountain top
- ore underground is overburden and above ground is spoils
- ore is separated into target material and waste
Uranium (nuclear) - Australia, Kazakhstan, Canada
Crude Oil - Middle East, North Asia, North America
Natural Gas - North America, Asia (primarily Russia)
Coal - everywhere except Western Europe and Africa
Natural sources of energy, including solar power, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power
RENEWABLE
Wind Turbines - forms by wind spinning turbines which powers a generator
Solar Panels - forms by
Hydrogen
Energy conservation methods
Unit 7 - Atmospheric Pollution
Introduction to air pollution
Legislation - Clean Air Act of 1956 (London)
Natural Sources of Pollution - pollen, spores, bacteria, dust, soil
There is a positive geometric correlation between temperature and ground level ozone
Clean Air Act of 1970 (U.S.A.)
response to haze in cities
limited the following pollutants: sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter (PM#), lead (Pb), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO)
- Particulate Matter - small particles based on micron size (forms from partially combusted “soot”)
VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
composed of C, O, H, Cl & S, come from extraction/transportation of fossil fuels, refining/manufacturing of petrochemicals, consumer use (of products), lack of waste management, etc.
occur naturally, mainly anthropogenically produced
- carcinogens that can affect organ systems
when these react with the sun, they form PANs (Peroxyacyl Nitrates)
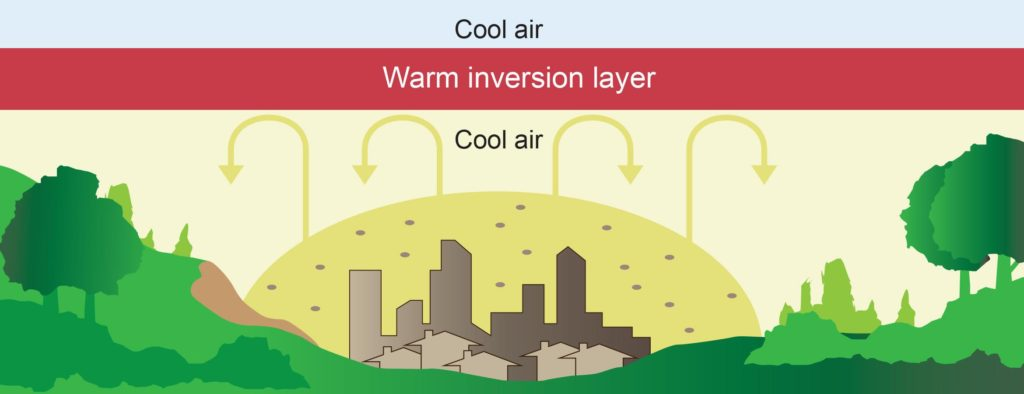
Thermal Inversion
When a high pressure layer of hot air forms, cold air is trapped above and below, increasing pollution in the lower layer
Photochemical smog
Smog - smoke + fog; thick gray haze that forms when coal is burned and mixes with moisture
- photochemical (sunlight-caused) and industrial (moisture-caused)
- primarily from fossil fuel combustion (factories or vehicles)
Primary Pollutants (CHONS) →(sunlight)→ Secondary Pollutants
- primary: CO, CO2, SO2, NOx, N2O, NH3, hydrocarbons, VOCs, PM10, PM2.5
- NOx → O3
- NO + VOC → NO2, + UV → NO + O, + O2 → O3
- NO + VOC → O3 + PANs
Indoor air pollution
Methods to reduce air pollutants
Maintain vehicles (last longer), sustainable vehicles, catalytic converters, electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers, etc.