10. colour by design
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:13 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Arenes or aromatic compounds
contain a benzene ring
2
New cards
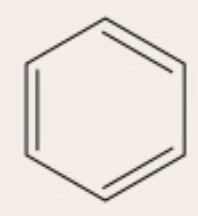
kekulé structure
benzene ring with alternating single and double bonds which continuously flip
3
New cards
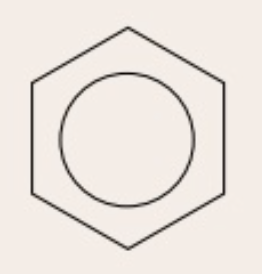
delocalised structure
benzene ring with ring of electrons
4
New cards
kelulé problem
C-C should be longer than C=C bond but is is not proved by x ray diffraction studies.
5
New cards
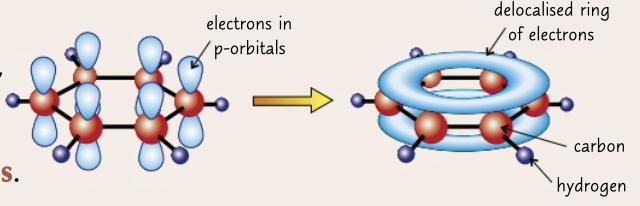
delocalised model
electrons from p orbital form a delocalised ring
6
New cards
electrophilic substitution of bromine
bromine combines with an alkene but acting as an electrophile attaching to the C=C
7
New cards
subsitution of bromine with benzene
delocalised ring is more stable due to the electrons been more spread out so a catalyst is required for them to react. a hydrogen is swapped with bromine so benzene doesn't have to lose an electron
8
New cards
enthalpy changes prove delocalisation
hydrogenation of cyclohexane with one C=C is -120kJ mol-1 so benzene should be -360kJ mol-1 but instead its -208kJ mol-1
9
New cards
enthalpy change of benzene
\-208kJ mol-1 suggests lots of energy needed to break bond and the structure is more stable
10
New cards
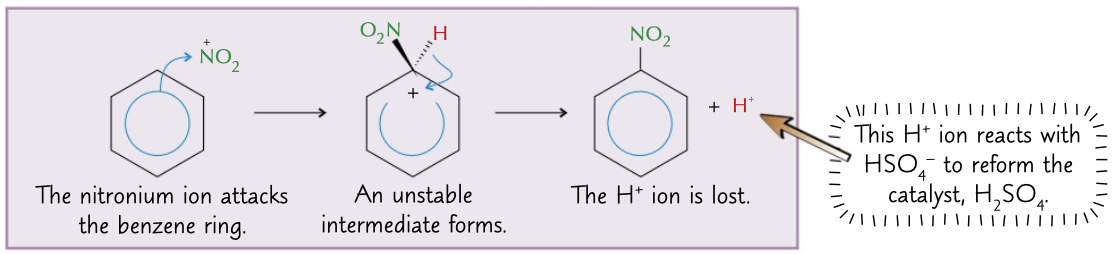
benzene warmed with concentrated nitric and sulphuric acids
process to get nitrobenzene with an acid catalyst and a NO2+ electrophile
11
New cards
monotriration
where one NO2 added to benzene when its kept below 55 degrees
12
New cards
quick way to make benzenesulfonic acid
warm benzene to 40 degrees with fuming sulfuric acid for 30 mins. as the fuming acid contains lots of dissolved SO3
13
New cards
slow way to make benzenesulfonic acid
boil benzene under reflux with concentrated sulfuric acid for several hours. as the acid contains H2SO3 which breaks down to SO3
14
New cards
benzenesulfonic acid mechanism
SO3 attacks benzenes delocalised ring due to S been +ve. O -ve then takes h from the benzene where it has bonded and electrons return to the delocalised ring. form of electrophilic substitution
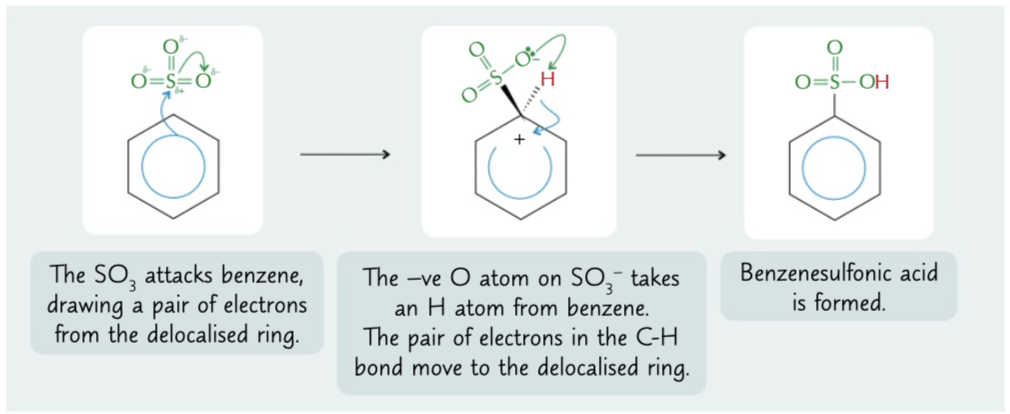
15
New cards
halogen carrier
A catalyst that makes a compound more positive allowing it to bond with benzene
16
New cards
halogen carrier process
catalyst accepts lone pair of electrons from halogen containing polar molecule. polarising a electrophile. sometimes produces a carbocation
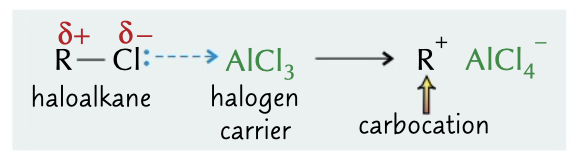
17
New cards
carbocation
organic ion with a positive carbon
18
New cards
alkyl group
groups with one H atom less than alkane molecules eg CH3. which bond to other things
19
New cards
reactants to make methylbenzene
reflux chloroalkane and benzene with a halogen carrier (Al3)
20
New cards
how methylbenzene made
* carbocation (CH3+) formed from chloroalkane and AlCl3.
* carbocation reacts with benzene via electrophilic substitution
* AlCl4- reacts with H+ formed regenerating the catalyst and HCl
* carbocation reacts with benzene via electrophilic substitution
* AlCl4- reacts with H+ formed regenerating the catalyst and HCl
21
New cards
Friedel-Crafts alkylation
method to attach alkyl group to benzene
22
New cards
acyl group
groups containing C=O
23
New cards
process to join acyl to benzene
Frieda crafts technique but refluxing benzene with acyl chlorine. the electrophile acylium ion CH3CO+ is used and produced.
24
New cards
azo dye
man made dye containing ago group -N=N- which typically joins 2 aromatic groups. these become part pf the delocalised structure and are very stable.
25
New cards
light absorption
causes colour due do defect results from different aromatic groups and amide combinations
26
New cards
couple reaction
type of reaction to make azo dye
27
New cards
process to make azo dye
first diazonium salt made (contains -N+///N-) which is then joined to a aromatic compound
28
New cards
process to make diazonium salt
* nitrous acid is unstable so made in situ from sodium nitrate and hydrochloric acid
* nitrous acid then reacts with phenylamine and hydrochloric acid forming benzendiazomium chloride. below 5℃ or phenol forms
* nitrous acid then reacts with phenylamine and hydrochloric acid forming benzendiazomium chloride. below 5℃ or phenol forms

29
New cards
process to make azo dye from diazonium salt and phenol
* phenol dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution to make sodium phenoxide
* added to ice and chilled benzenediazonium chloride/diazonium salt added
* azo dye precipitates once its coupled
* added to ice and chilled benzenediazonium chloride/diazonium salt added
* azo dye precipitates once its coupled
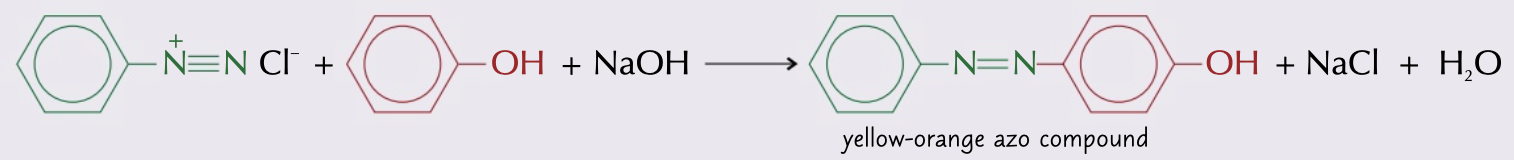
30
New cards
colourfast
a dye that won’t wash out or fade in light. depends on bonding between dyes and fibres
31
New cards
dye bonding types
* hydrogen bonding -weak
* instantaneous dipole induced dipole
* ionic bonding between charged groups
* fibre reactive dyes- strongest
* instantaneous dipole induced dipole
* ionic bonding between charged groups
* fibre reactive dyes- strongest
32
New cards
hydrogen bonding
bonding between amine (NH2) and alcohol (OH) groups and alcohol (OH) groups on fibres like cotton and cellulose with interactions relating to lone pairs of electrons. Usually liner close fitting molecules for maximum strength
33
New cards
ionic bonding
dyes become acidic when dissolved in water due to SO3- groups, and fibres with NH2 groups become NH3+ groups in acidic conditions, allowing bonding between the two. eg nylon, wool, silk
34
New cards
mordanting
metal ion used to join dye to fabric where both from dative bonds with metal informing chelate complex ions eg Al3+ and Cr3+
35
New cards
chromophores
structures which give a molecule there colour
36
New cards
how chromophores give colour
certain wavelengths absorbed and others reflected, the ones reflected as visible light gives the colour.
37
New cards
chromophore characteristics
contain double or triple bonds, lone electron pairs or benzene rings, these normally form fart of a delocalised system across large part of the molecule.
38
New cards
modifying chromophores
functional groups containing O or N with lone pairs can be added which alters the delocalised system and the colour of the dye
39
New cards
make dyes more water soluble
stabilising functional groups incorporated to dyes like ionic groups eg sulphate ion. these can become polar
40
New cards
covalent bond
where atomic orbitals link up to become molecular orbitals
41
New cards
exited state
when I electron moves up a orbital by absorbing uv or visible light
42
New cards
complementary colours
relationship between the colours absorbed and reflected
43
New cards
single covalent bonds
2 atomic orbitals with 1 electron form 2 molecular orbitals where. only one is filled (2e). the energy gap between orbitals is large so requires high frequency UV to excite electrons
44
New cards
double bond
2 atomic orbitals with 1 electron form 4 molecular orbitals. The energy gap between orbitals is small as there’s 4 so requires low frequency UV to excite electrons
45
New cards
delocalised systems
many molecular orbitals formed which are close in energy levels so electrons only need to absorb very low frequency UV and visible light to be excited. eg benzene
46
New cards
primary alcohol
heating alcohol with a oxidant agent (acidified potassium dichromate VI) makes an aldehyde, the scan further oxidise to form a carboxyl acid. to get a aldehyde you have to distil it immediately
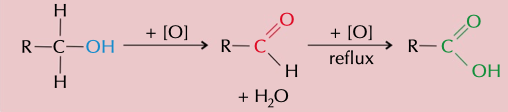
47
New cards
secondary alcohol
reflux a alcohol to with an oxidising agent to make a ketone
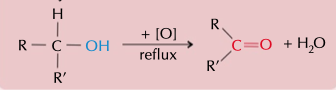
48
New cards
Fehlings solution
solution used to test for aldehydes and ketones, which is a complex of copper ii ions dissolved in sodium hydroxide
49
New cards
blue solution
colour or fehlings solution
50
New cards
fehlings solution method
heat (water bath) the solution (2cm3)with the aldehyde or ketone (5 drops), if aldehydes the copper is reduced to become brick red precipitate coper oxide Cu2O
51
New cards
tollens reagent/silver mirror test
reagent to test for aldehydes and ketones
52
New cards
tollens reagent method
* 2cm3 of 0.1 mild-3 silver nitrate
* few drops of dilute sodium nitrate solution forming a light brown ppt
* add few drops of ammonia till down ppt dissolves completely- now made the reagent
* put test tube in hot water bath and add 10 drops of aldehyde or ketone
* few drops of dilute sodium nitrate solution forming a light brown ppt
* add few drops of ammonia till down ppt dissolves completely- now made the reagent
* put test tube in hot water bath and add 10 drops of aldehyde or ketone
53
New cards
tollens reagent results
if aldehyde then silver mirror made, if ketone then nothing happens
54
New cards
hydrogen cyanide HCH
a weak acid that partially dissociates in water to from H+ and CN-
55
New cards
hydrogen cyanide reacts with carbonyls by nucleophilic addition
* CN- attacks partially possible C and donates 2e to the O
* H+ from HCH or water bonds to the other O forming OH
* this creates cyanohydrin
* H+ from HCH or water bonds to the other O forming OH
* this creates cyanohydrin
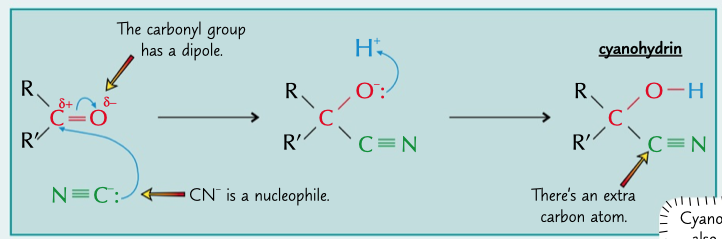
56
New cards
naming functional groups
* main functional group is the suffix- end
* others added as prefix- start
* alphabetical order
* others added as prefix- start
* alphabetical order
57
New cards
polyfunctional molecule
molecule with many functional groups
58
New cards
testing for polyfunctional molecules
* use multiple solutions to test
* further test melting/boiling point to tell if there is one or multiple compounds
* further test melting/boiling point to tell if there is one or multiple compounds
59
New cards
addition reaction
reaction where 2 molecules join together by breaking a double bond, eg alkenes, COOH and C=O
60
New cards
elimination reaction
removal of a functional group releasing it as part of a small molecule, often forming double bond, eg -halogen (H-halogen, eliminated) or -OH (H2O eliminated)
61
New cards
substation reaction
functional groups are swapped eg -halogen, -OH, -benzne
62
New cards
condensation reaction
2 molecules join releasing water, eg -COOH, -COCl, -CONH2
63
New cards
hydrolysis reaction
water used to slip a molecule into 2, eg -COO-, CO-O-CO-
64
New cards
oxidation reaction
loss of electrons, where a molecule typically gains oxygen or loses hydrogen, eg as shown in picture
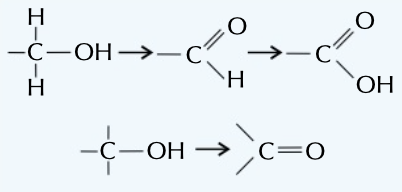
65
New cards
reduction reaction
gain of electrons typically gaining. hydrogen or losing oxygen eg as shown in picture
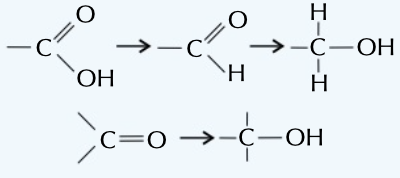
66
New cards
bromine water test
test for alkenes/double bonds, where a positive result goes colourless to orange. 2:2cm3 of each and shake
67
New cards
acidified potassium dichromate
10 drops of alcohol to 2cm3 of test solution, warm and watch for colour change
* primary- orange to green aldehyde (if further heating oxidised to carboxylic acid)
* secondary- orange turns to green Ketone
* tertiary- nothing
* primary- orange to green aldehyde (if further heating oxidised to carboxylic acid)
* secondary- orange turns to green Ketone
* tertiary- nothing
68
New cards
test for primary vs secondary alcohol
collect some of the product from adding acidified potassium dichromate by using distillation
test for which alcohol with tollens reagent or fehlings solution.
test for which alcohol with tollens reagent or fehlings solution.
69
New cards
included in description of how to make something
* special procedures
* conditions needed
* safety precautions
* conditions needed
* safety precautions
70
New cards
retrosynthesis
method of backward planning a practical
* identify functional groups
* identify any bonds made between groups
* further split up any molecules further
* identify functional groups
* identify any bonds made between groups
* further split up any molecules further
71
New cards
fatty acids
carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains on end, saturated with no double bonds or unsaturated with double bonds. test for with bromine water
72
New cards
triglycerides
* animal and vegetable fats and oils.
* contain ester -COO- 3 times.
* made with glycerol and 3 fatty acids
* 2 OH on glycerol link with 3 OH on fatty acids in condensation reaction
* contain ester -COO- 3 times.
* made with glycerol and 3 fatty acids
* 2 OH on glycerol link with 3 OH on fatty acids in condensation reaction
73
New cards
mobile phase
phase in GLC where its a solid or viscous liquid with a high boiling point coating a porous support inside a coiled tube in a oven
74
New cards
mobile phase
phase in GLC which is an inert carrier gas
75
New cards
GLC process
* sample injected into gas stream
* compounds cycle through dissolving in stationary and evaporating into mobile phase
* time dissolving depends on there solubility and effects how ling it takes to reach detector
* compounds cycle through dissolving in stationary and evaporating into mobile phase
* time dissolving depends on there solubility and effects how ling it takes to reach detector
76
New cards
retention time
Time taken to reach detector in GLC a
77
New cards
relative amount of a substance
area under a peak
78
New cards
gas liquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
sample separated by GLC then fed into a mass spectrometer to identify each component
79
New cards
fibre reactive dyes
reactive group on dye forms a bridge with fibre groups like -OH and -NH-
80
New cards
instantaneous dipole induced dipole bonds
dyes with few polar groups are suspended in water and form weak bonds with the fibre, no OH or NH groups