IB ESS Topic 5: Soil Systems and Terrestrial Food Production Systems and Societies
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Pedosphere
The outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil.
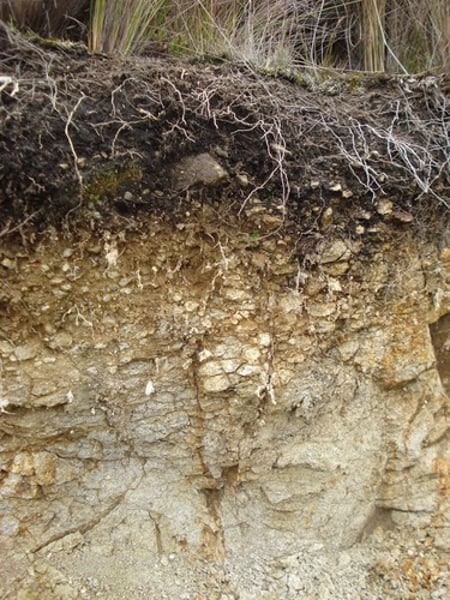

Soil
A complex ecosystem made up of minerals, organic material, gases and liquids which forms the habitat for many species of plant and animal. A non-renewable resource as it cannot be replenished quickly.
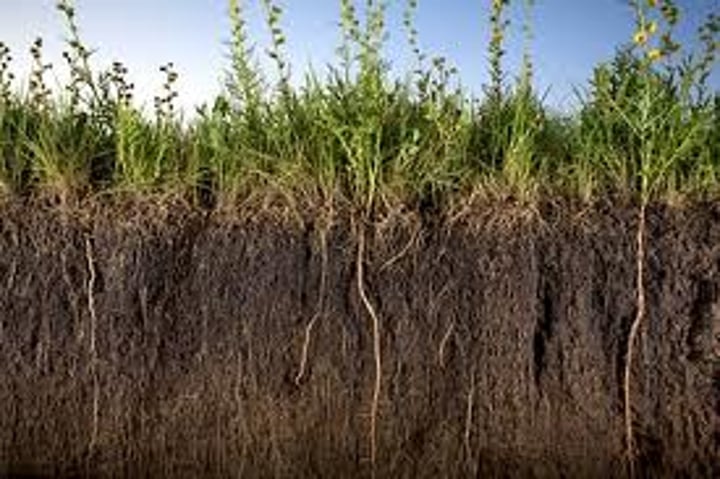

Soil Storages
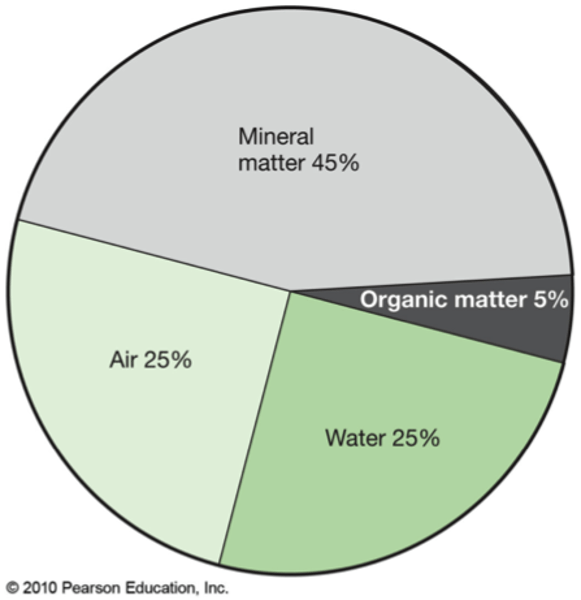
Organic matter, organisms, nutrients, minerals, air and water.
Soil Transfers
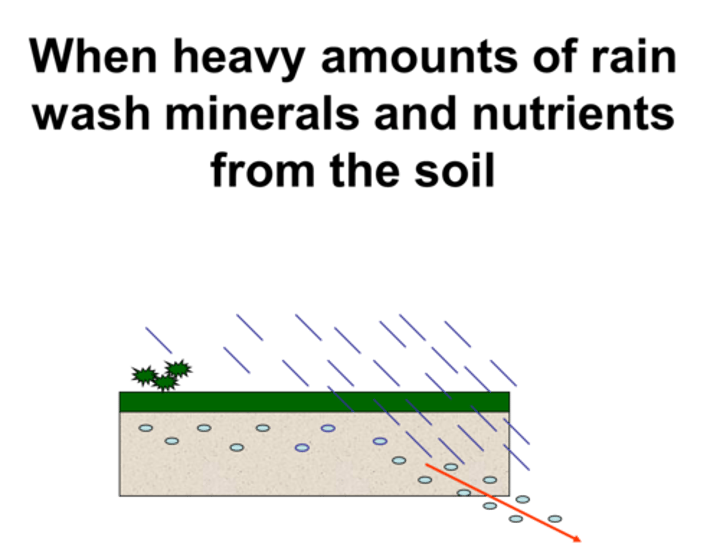
including biological mixing and leaching (minerals dissolved in water moving through soil)
Leaching
Minerals dissolved in water moving through the soil
Soil Inputs
Organic matter from leaf litter and dead or decaying organisms - inorganic matter from parent material (rock), precipitation and energy

Soil Outputs
Absorption by plants (minerals and water), soil erosion.

Soil Transformations
Decomposition, weathering and nutrient cycling.

Minerals
Inorganic nutrients (ie, ions) that occur naturally in rocks and soil.

Humus
Plant and animal material in the process of decomposition - generally found in the top layer of soil

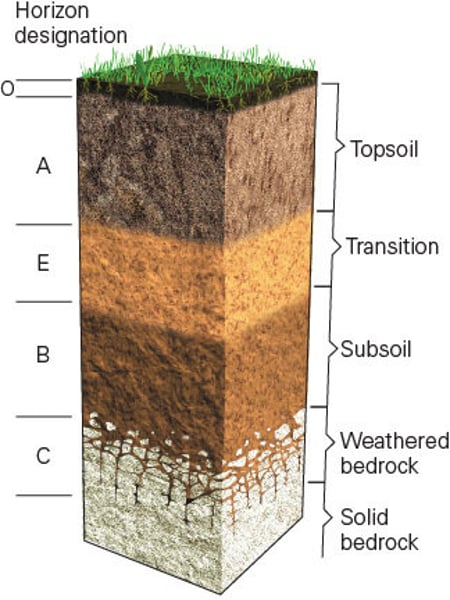
Soil Horizons / Soil Profile
The layers of soil in a cross-section which is modified over time as organic material leaches downwards and mineral material moves upwards. Note that not all soils contain all the horizons and sometimes the horizons are not clearly distinguishable.
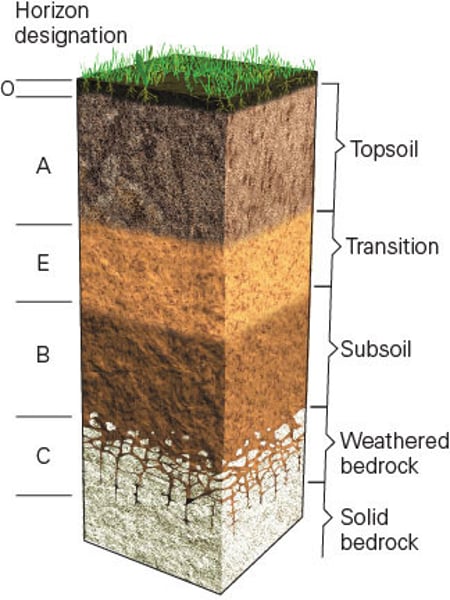
O (soil horizon)
Leaf litter - newly added organic material and formation of humus.
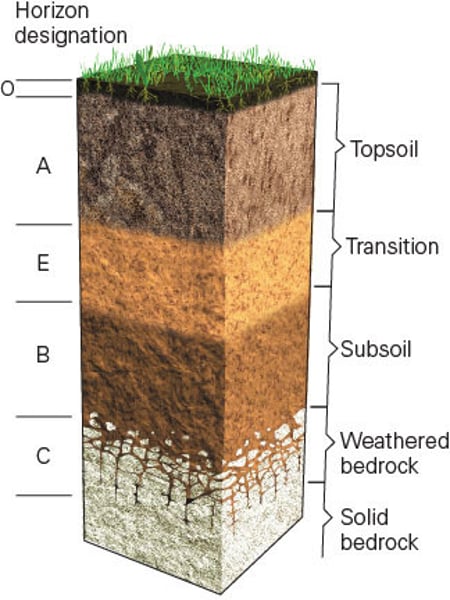
A (soil horizon)
Mineral horizon at the surface showing organic matter enrichment - where humus accumulates.
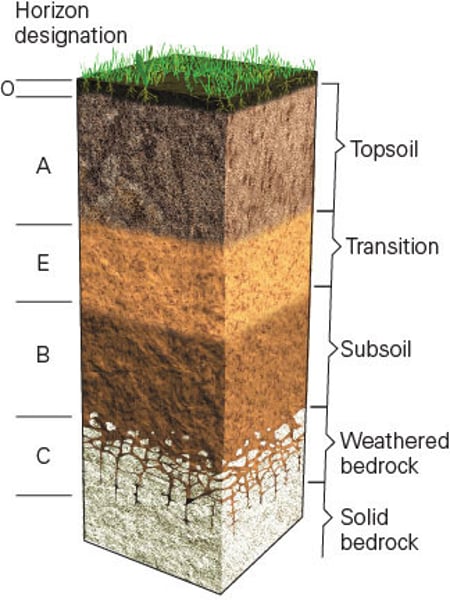
E (soil horizon)
Subsurface horizon showing depletion of organic matter, clay, iron and aluminium compounds
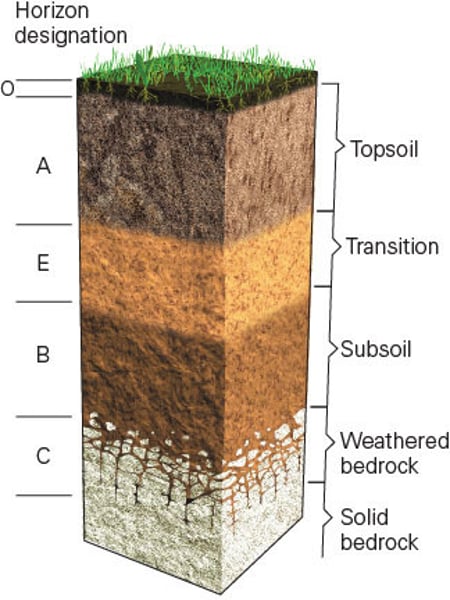
B (soil horizon)
Subsoil horizon showing enrichment of clay material, iron aluminum, or organic compounds - where soluble minerals and organic matter tends to be deposited from the layer above
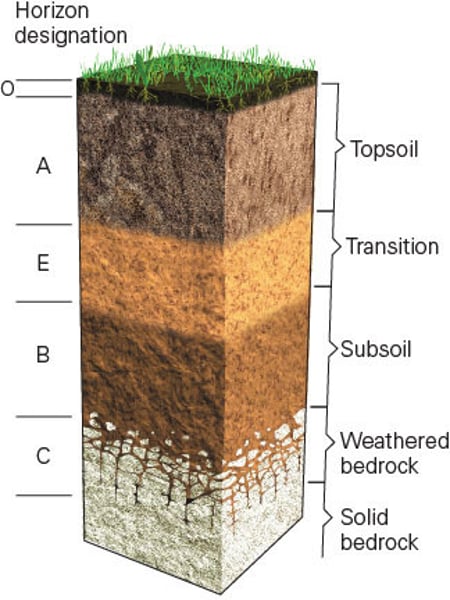
C (soil horizon)
Horizons of loosened or unconsolidated material - mainly weathered rock from which soil forms
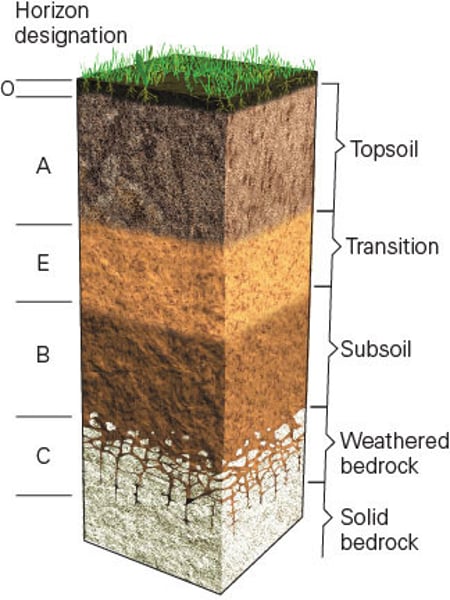
R (soil horizon)
Hard bedrock - unweathered parent material
Soil Structure
The proportions of clay (<0.002mm particles), silt (0.002 - 0.05mm particles), and sand (0.05 - 2mm particles)
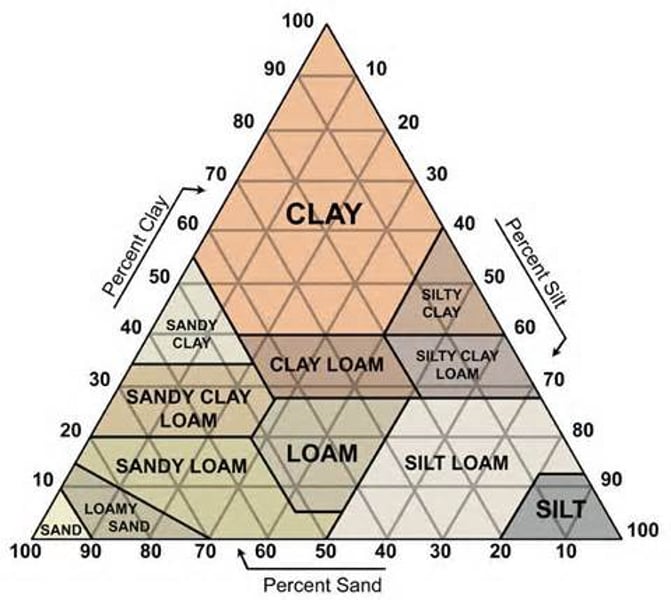
Sand
One component of soil. A granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles. Soils high in this are gritty and fall apart easily. Soils high in this have good drainage and air supply to the roots, however, leaching is rapid.

Clay
One component of soil. A type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals. Develops plasticity when we, but becomes hard and brittle upon drying. Soils high in this have good nutrient retention, but poor water drainage.

Loam soils
Roughly 40% sand, 40% silt and 20% clay. Ideal for agriculture due to sand's drainage and porosity, clay's nutrient retention and silt keeping the other two together.

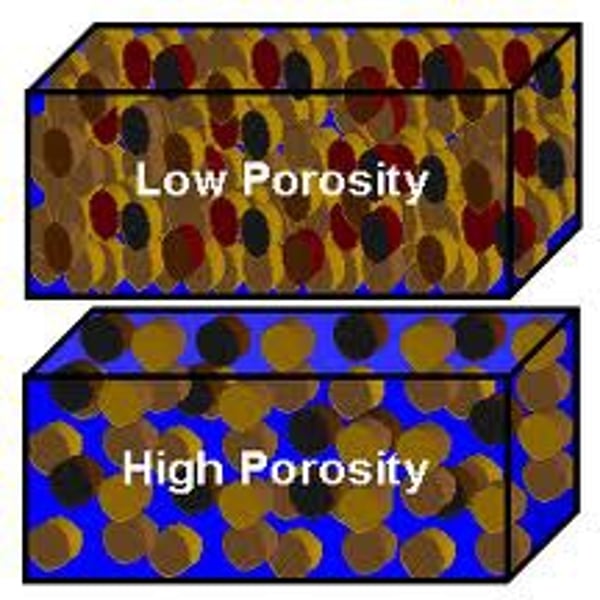
Soil Porosity
A measurement of space between particles in soil.
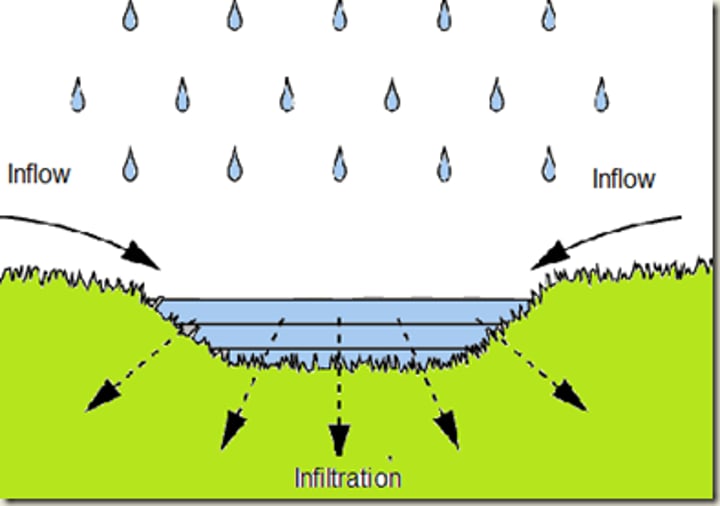
Soil Permeability
Describes how easy it is for fluids to flow between particles in soil.

Infiltration
The penetration of water into the soil.
NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium)
The most important soil nutrients for plant growth - often leach out or may be removed when plants are harvested.

Terrestrial
Relating to the land (ie, not aquatic).

Agribusiness
Business of agriculture production including farming, seed supply, breeding, chemicals for agriculture, machinery, food harvesting, distribution, processing and storage.

Commercial agriculture/farming
Large scale production of crops and livestock for sale

Subsistence agriculture/farming
Farming for self-sufficiency to grow enough for a family

Cash Crop
A crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower. Ie, wheat, corn, soy.

Extensive Farming
Farming using more land with a lower density of stocking or planting and lower inputs = lower outputs

Intensive Farming
Farming using land more intensively with high levels of input and output per area

Pastoral Farming
raising animals, usually on grass and on land that is not suitable for crops

Arable Farming
Growing crops on good land to be eaten directly, or to be fed to animals.

Mixed Farming
Farming of both crops and animals - animal waste may be used as fertiliser and to improve soil quality, and some crops are used to feed animals

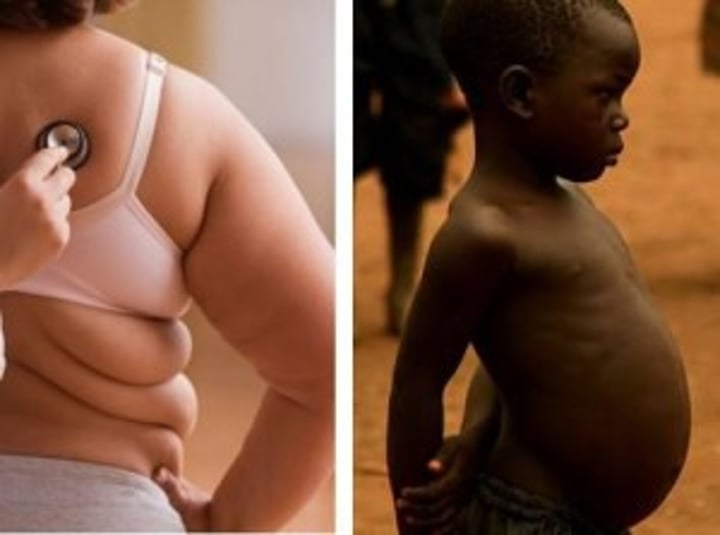
Malnutrition
"bad nutrition" - a diet which is unbalanced (may be too much or not enough of nutrients).
Wheat
A staple grain source for over a third of the world's population.

Irrigation
The supply of water for crops other than natural process such as rain or water tables

Animal Domestication
The taming of or enslavement of animals for human use. Ie, dogs, cows, chickens.

Livestock
A term used to describe animals being bred, bought and sold as property of farmers.

Monoculture Farming
A single species of plant grown on a field, usually in high density.

Harvesting
the removal of biomass from the field, soil and ecosystem - results in a loss of quality of the soil as nutrient which would have been recycled back into the soil are removed (and must be replaced).

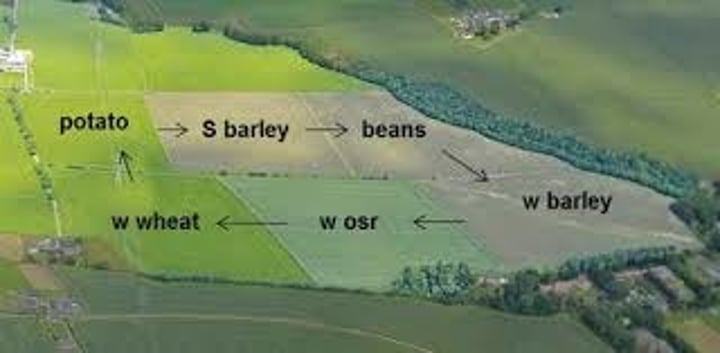
Crop Rotation
A way to reduce the loss of soil fertility. A different crop is grown on a piece of land each year or land is sometimes left fallow (unseeded). The rotation allows for different nutrients to be extracted or replenished in the soil. Fallowing gives time for soil to recover or for pathogen lifecycles to be broken.
Palm Oil
An oil from palm trees that is used widely in food and cosmetic products around the world. Has led to significant deforestation of rainforests in Southeast Asia.
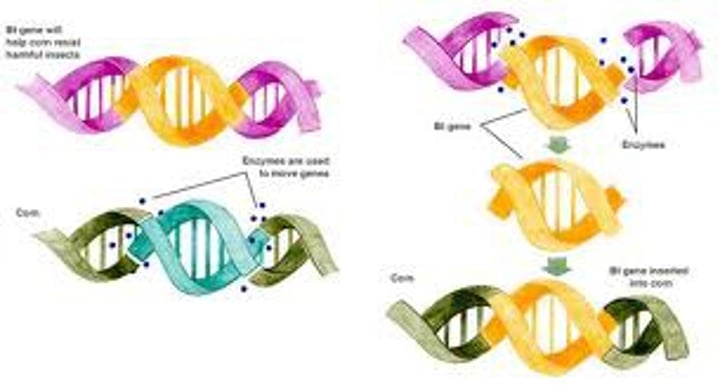
Genetically Modified (GM) Crops
Organisms with modified genes chosen to provide a benefit.
Soil Degradation
The loss of some or all of a soil's ability to support plant growth. Can be due to deforestation or unsustainable farming practices like overcropping and overgrazing.

Soil Erosion
The process of soil being taken away by wind or water.

Overgrazing
Too many animals graze (eat grass/plants) in the same area - results in bare patches of soil where roots no longer hold the soil together leaving it open to soil erosion from wind and rain.

Overcropping
Deplete soil fertility by growing crops continuously on it and not replacing the nutrients that are removed.
Deforestation
The removal of trees which often results in soil being left exposed, leading to soil erosion

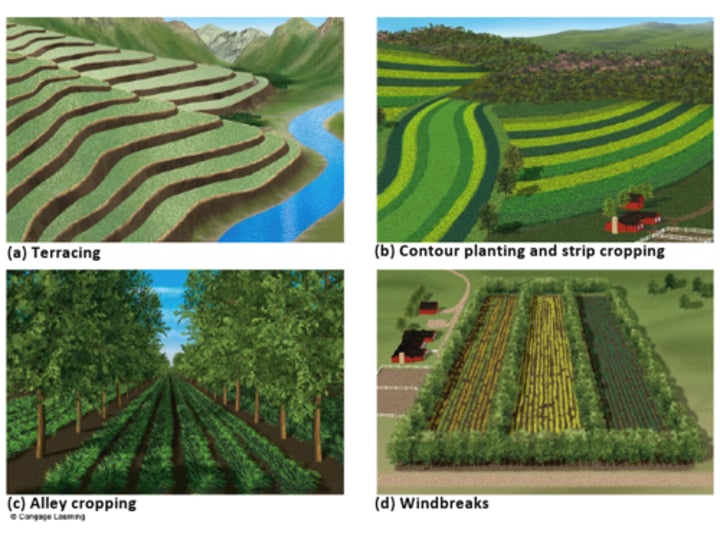
Soil Conservation
Maintaining or improving soil fertility.
Soil Conditioners
A soil conservation strategy used to increase soil pH and counteract acidification (from acid deposition and soil processes). e.g. adding lime and organic material to soil

Wind Reduction
A soil conservation strategy involving planting trees or bushes between fields (shelter belts) or by alternating low and high crops in adjacent fields. The goal is to reduce erosion from the wind.

Cover Crops
A soil conservation strategy that involves the use of fast growing crops between harvesting of main crops to ensure bare soil is not exposed for too long.

Terracing
A soil conservation strategy in which slope is converted into a series of horizontal terraces separated by walls. This prevents erosion from run-off and is common in Asian wet rice fields.
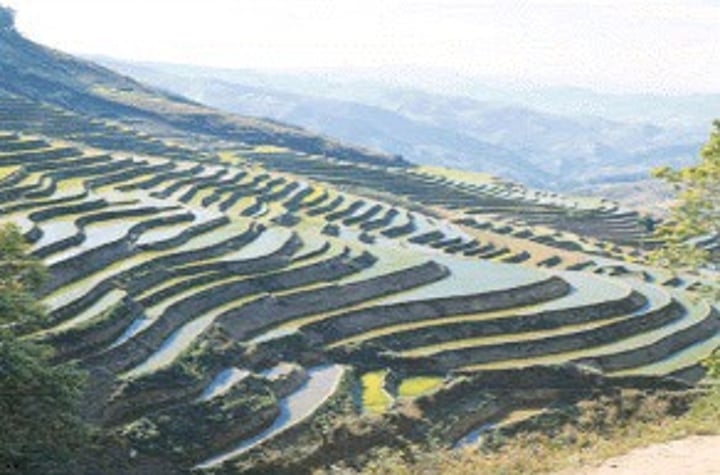

Reduced Plowing / Tilling
Soil conservation strategies in which fields are not tilled (ploughed) or seeds are directly sown without ploughing.

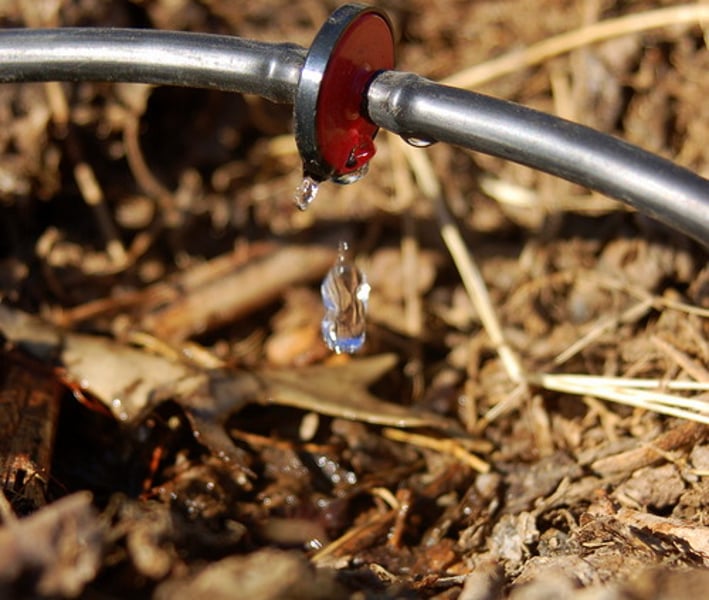
Improved Irrigation
A soil conservation technique in which careful planning and construction of irrigation systems can reduce evaporation and therefore reduce salinization.
e.g. drip irrigation (trickle irrigation) - uses a series of pipes throughout a field to add water slowly = less evaporation

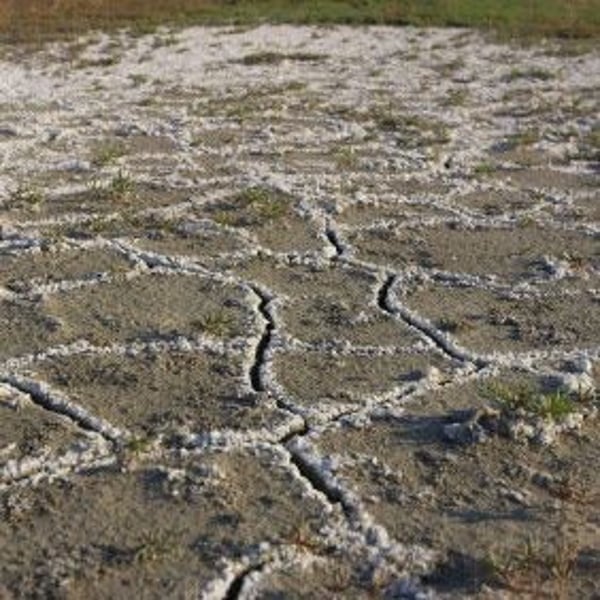
Salinization
The increase in salt levels of soil due to water evaporation leaving salts and chemicals behind.

Sustainability of Terrestrial Food Production Systems
Influenced by factors such as industrialization; mechanization; fossil fuel use; seed, crop and livestock choices; water use; fertilizers; pest control; pollinators; antibiotics; legislation; and levels of commercial versus subsistence food production.

Strategies to Increase Sustainability of Terrestrial Food Production Systems
- altering human activity to reduce meat consumption and increase consumption of organically grown and locally produced terrestrial food products
- improving the accuracy of food labels to assist consumers in making informed food choices
- monitoring and control of the standards and practices of multinational and national food corporations by governmental and intergovernmental bodies
- planting of buffer zones around land suitable for food production to absorb nutrient runoff.
Soil Fertility
A measure of how well soil supports plant growth. It is decreased through deforestation, intensive grazing, urbanization and certain agricultural practices (such as irrigation and monoculture). Commercial, industrialized food production systems generally tend to reduce this more than small-scale subsistence farming methods. It is increased during succession as soil deepens to accommodate a diverse community.

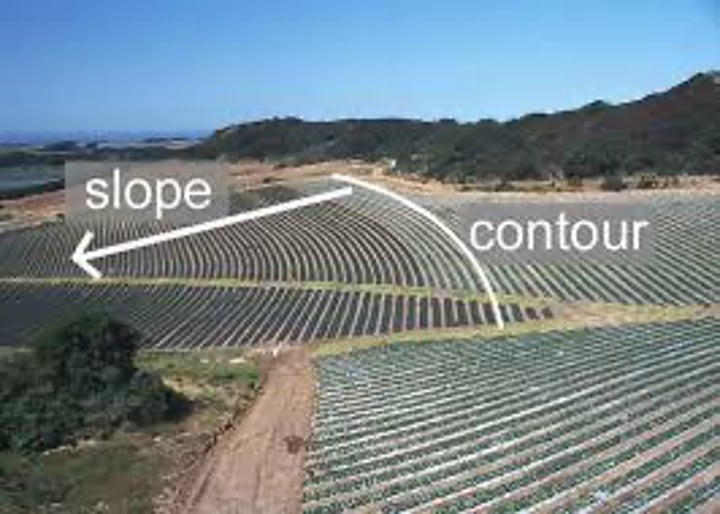
Soil Conservation Strategies
- soil conditioners (such as organic materials and lime)
- wind reduction techniques (wind breaks, shelter belts)
- cultivation techniques (terracing, contour ploughing, strip cultivation)
- avoiding the use of marginal lands.

Silt
One component of soil. Granular soil material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Usually has a floury feel when dry, and lacks plasticity when wet.

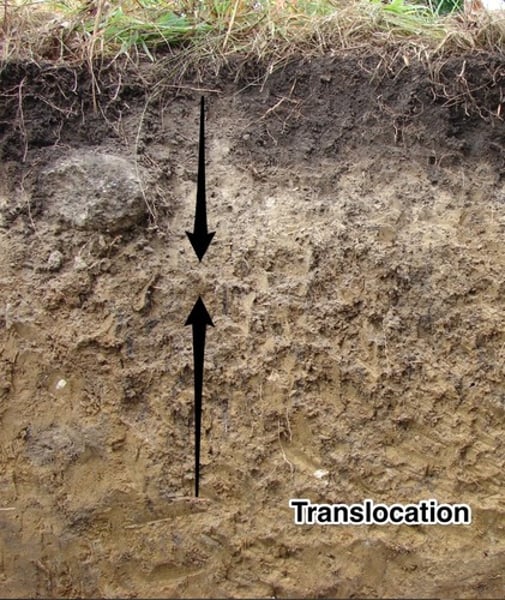
Translocation
The movement of soil particles within and between horizons by water. Water goes upward when precipitation (P) < evaporation (E). Water goes downward when P > E.

Soil Acidification
The lowering of pH of soils from acid rain caused by industrial pollution. Acidic soils release higher concentrations of aluminum and iron ions, which can damage plants.

Factors that Influence Food Choice
1. Climate
2. Culture / Religion
3. Politics (ie, taxes, subsidies)
4. Socio-Economic (prices)

Bush Meat
Any wild animal killed for food (sometimes "game")
a controversial term as it often brings to mind in many parts of the world where the bush meat may be under threat of endangerment e.g. harvesting of apes leading to orphaned young.

Factors that Decrease Agricultural Land
1. Soil erosion
2. Salinization
3. Desertification
4. Urbanization
Unsustainable Agricultural Techniques
1. Total removal of crops at harvest leaves soil open to erosion.
2. Plowing in direction of the slope creates channels for water runoff to erode topsoil.
3. Excessive use of pesticides can lead to toxification of soil.
4. Irrigation in which much of the water evaporates before it reaches the plants (leads to salinization).
5. Monocultures can lead to the same nutrient being depleted from the soil, decreasing fertility.
Weathering
Decomposition and disintegration of rocks. Chemical weathering occurs when chemical reactions (ie, from acid rain or organisms) decompose rock. Examples of mechanical weathering include roots exerting pressure to break rocks, waves crashing against rocks, etc.

Import Tariffs / Taxes
Taxes on imported goods to make them more expensive. When MEDCs use import tariffs, it can reduce demand for goods from LEDCs.

Export Subsidies
Government payments to domestic producers to enable them to reduce the price of a good or service to foreign buyers. In MEDCs these can lower the price to such an extent that farmers in LEDCs cannot make a living producing the product.

Shifting Cultivation / Slash and Burn
New land is cleared by cutting down small areas of forest trees and setting fire to them. The ash fertilizes the soil for a while and the clearing produced enables crops to be grown. Once the land in one area has been exhausted (e.g. minerals in the soil depleted), the farmer moves on to clear a new area.

Edaphology
One of the two main divisions in soil science. The science that deals with the influence of soils on living things, particularly plants, including human use of land for plant growth.

Pedology
One of the two main divisions in soil science. It is the study of natural soil systems to describe soil formation, classification and properties.

Edaphic Factors
The soil properties that affect the diversity of organisms living in the soil environment. These include soil structure, temperature, pH, and salinity. Some of them are influenced by man, but most are independent of human activity.