ORGCHEM FINALS
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
called when a carbonyl group is attached to at least one H atom (RCHO)
aldehyde
called when a carbonyl group is attached to two carbon groups (RCOR)
ketone
(IUPAC) In naming aldehydes, Name the longest carbon chain by replacing the e in the alkane name with _____
Then we name and number substituents by counting the carbonyl group as carbon ___.
-al, 1
(Common names) In naming aldehydes, for the first four aldehydes, they use the prefixes:
__________ (1C)
___________(2C)
___________(3C)
___________(4C)
followed by __________
Form-
Acet-
Propion-
Butyr-
-aldehyde
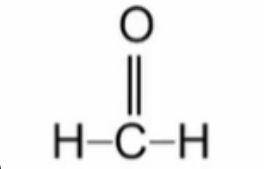
Name this aldehyde
Methanal (formaldehyde)
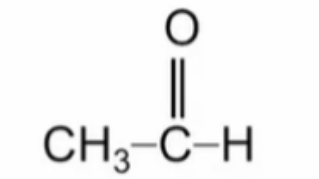
Name this aldehyde
Ethanal (acetaldehyde)
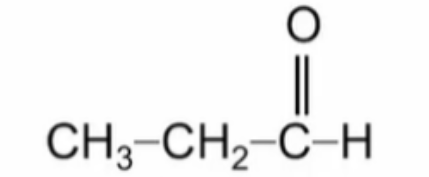
Name this aldehyde
Propanal (propionaldehyde)
What are the aldehydes for these flavorings:
almonds: ______________
cinnamon: _______________
vanilla: _____________
benzaldehyde
cinnamaldehyde
vanillin
(IUPAC) In naming ketones, Name the longest carbon chain by replacing the e in the alkane name with _________;, the carbonyl group is indicated by _______-
-one, number
(COMMON NAME) In naming ketones, name by indicating the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl group in __________ order, folllowed by ________.
alphabetical, ketone
Name this ketone
What are the common use of the ketone:
butanedione
as butter flavoring
Polar carbonyl
Polar carbonyl groups (does/does not) have H on the oxygen atom
does not
Polar carbonyl groups (can/cannot) form hydrogen bonds
cannot
Aldehydes and ketones have (polar/nonpolar) carbonyl groups
polar
Aldehydes and ketones have (attractions/repulsions) between polar groups
attractions
Aldehydes and ketones have (higher/lower) boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass
higher
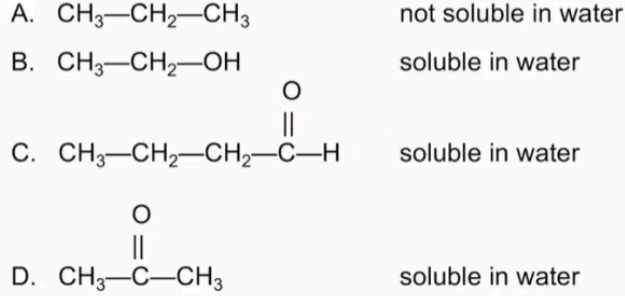
Aldehydes and ketones are (soluble/insoluble) in water
soluble
Aldehydes and ketones have electronegative _____ atoms in their carbonyl groups that form ______ bonds with water
Oxygen, hydrogen
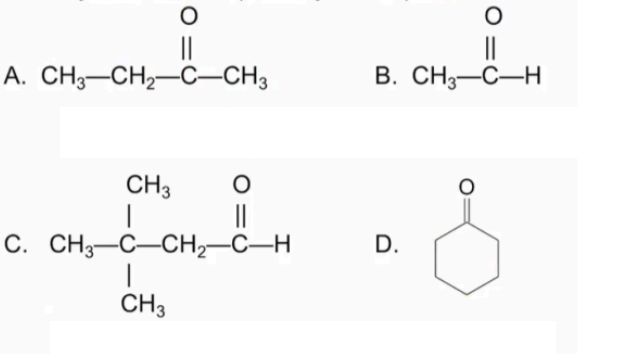
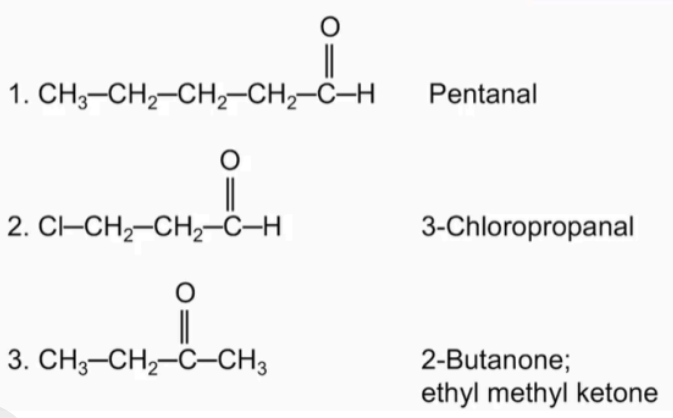
Classify each as an 1) aldehyde or 2) ketone
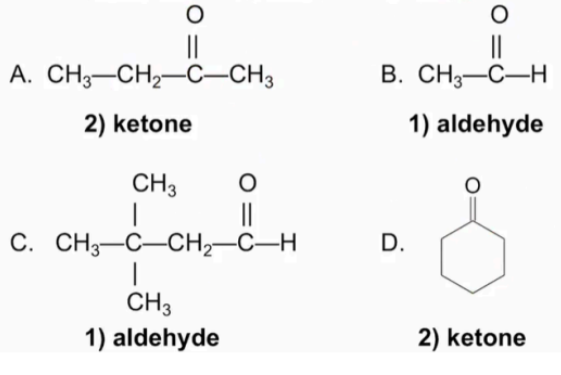
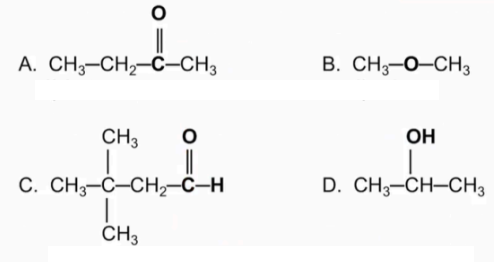
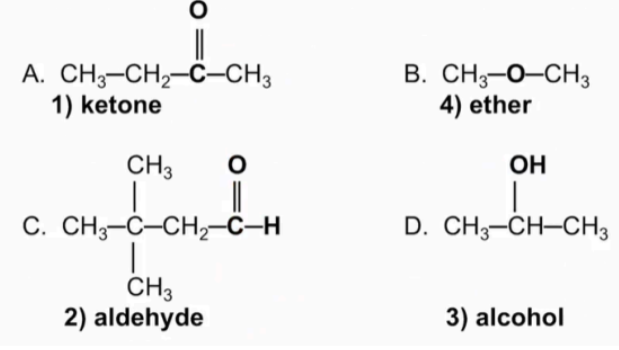
Classify each as an 1) aldehyde or 2) ketone
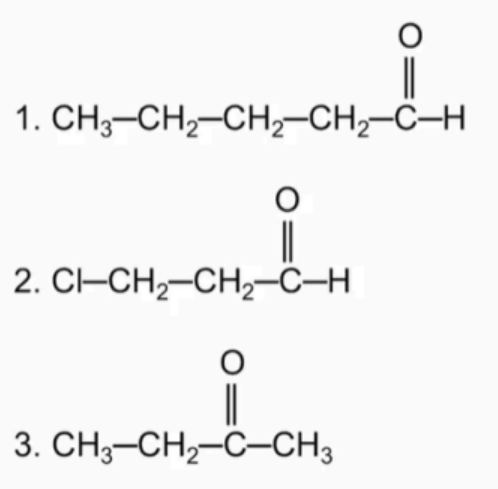
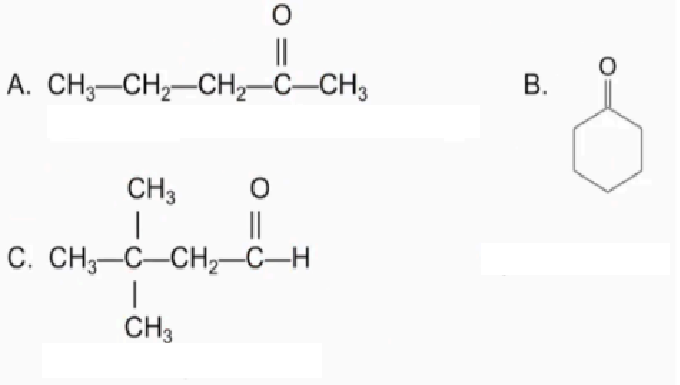
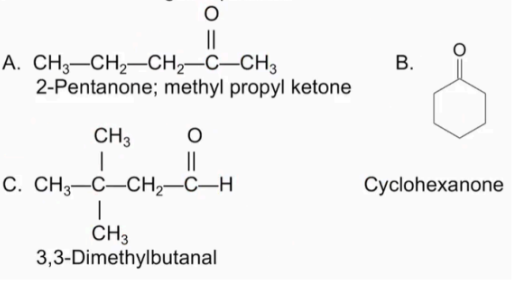
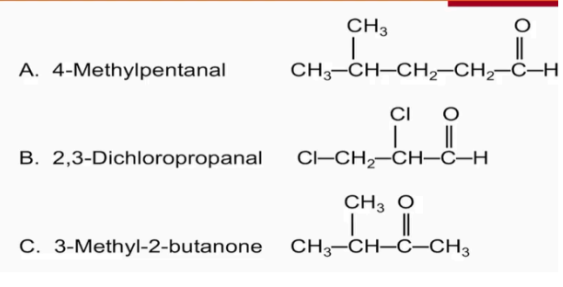
Name the following compounds
Name the following compounds

Draw the condensed forms of these compounds
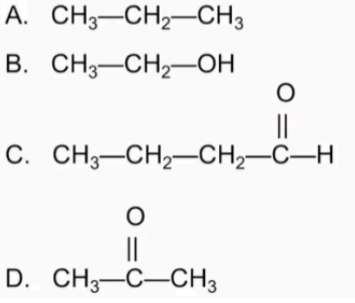
Indicate if each of the following is or is not soluble in water:
functional group that contains a carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group (C═O) attached to a hydroxyl group (—OH)
carboxylic acid
carboxylic acid has the carboxyl group on carbon _____
1
In naming carboxylic acids,
for nonaromatics, identify the carbon chain containing the carboxyl group and replace the -e in the alkane name by __________
-oic acid
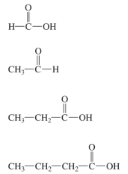
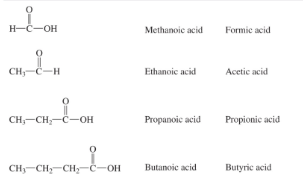
Give IUPAC name and Common name for each of the condensed structures:
Methanoic acid - Formic Acid
Ethanoic acid - Acetic acid
Propionic acid - Propionic acid
Butanoic acid - Butyric acid
The common names of simple carboxylic acids are:
________ (1C)
_________ (2C)
_________ (3C)
_________ (4C)
formic acid
acetic acid
propionic acid
butyric acid
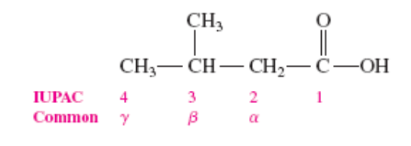
The common names of carboxylic acids use letters ___, __, or __ to indicate locations of substituents
α, β, or γ
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) occur naturally in ____, ____, and ______
fruit, milk, and sugarcane
______________ are used in skin care products
Alpha Hydroxy Acids
is the aromatic carboxylic acid
Benzoic acid
Benzoic acid locates substituents by assigning number ____ to the carbon attached to the carboxyl group
1
Benzoic acid has common names that assign the prefixes:
________ - 1,2 location
________ - 1,3 location
_________ - 1,4 location
ortho, meta, para
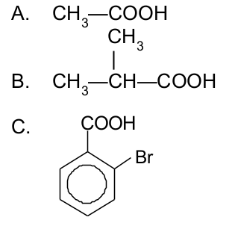
Give the IUPAC and common names for each of the following:
a. ethanoic acid (acetic acid)
b. 2-methylpropanoic acid (α-methylpropionic acid)
c. 2-bromobenzoic acid (o-bromobenzoic acid)
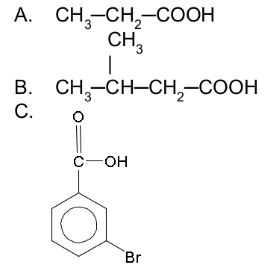
Give the IUPAC and common names for the following:
a. Propanoic acid (propionic acid)
b. 3-Methylbutanoic acid (β-methylbutyric acid)
c. 3-Bromobenzoic acid (m-bromobenzoic acid)
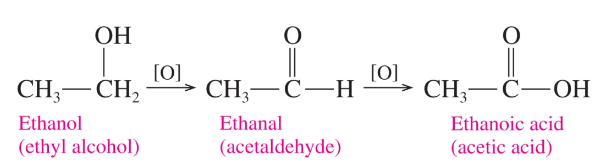
Carboxylic acids are prepared
> by oxidizing _______ or ___________
>from the oxidation of ______, which prodyces ethanoic acid (acetic acid)
primary alcohols or aldehydes
ethanol
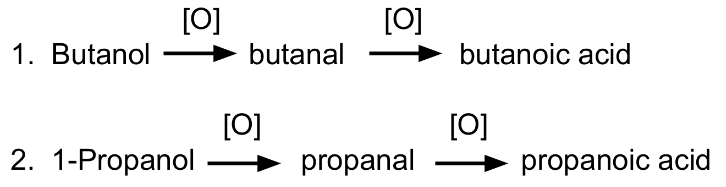
What alcohol would be used to prepare the following:
Butanoic acid
Propanoic acid
Butanol
1-propanol
Carboxylic acids are (weakly/strongly) polar
strongly
Carboxylic acids have two (polar/nonpolar) groups:
hydroxyl (−OH) and carbonyl (C═O)
polar
The boiling points (bp) of carboxylic acids are (higher/lower) than those of alcohols, ketones, and aldehydes of similar mass
higher
The boiling points (bp) of carboxylic acids are high because they form _____ in which hydrogen bonds form between two polar carboxyl groups
dimers
Carboxylic acids form ________ bonds with many water molecules
hydrogen
Carboxylic acids with __________ carbon atoms are very soluble in water
1-4
Carboxylic acids are (strong/weak) acids
They ionize in water to produce ___________ ions and __________ ions
weak
carboxylate, hydronium
Carboxylic acids have (large/small) Ka values
small
Carboxylic acids exist mostly as ____________ and a few ions in aqueous solutions
molecules
Carboxylic acid salts are a product of a carboxylic acid with a ______ base
strong
Carboxylic acid salts are used as ________ and _________ enhancers
preservatives, flavor
Write the equation for the reaction of propanoic acid with:
a. water
b. KOH
a. water
CH3—CH2—COOH + H2O <====> CH3—CH2—COO– + H3O+
b. KOH
CH3—CH2—COOH + KOH <==> CH3—CH2—COO– K+ + H2O
In an ester, the H in the carboxyl group is replaced with an _______ group
alkyl
is the reaction of a carboxylic acid and alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an ester
Esterification
Write the equation for the reaction of propanoic acid and methanol in the presence of an acid catalyst.
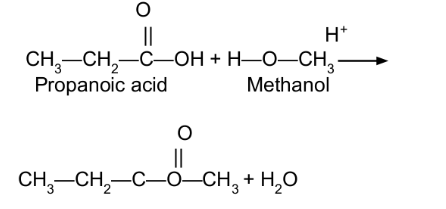
is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation (w/chemical name)
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)
Aspirin is an ester of ________ and ___________
salicylic acid and acetic acid
is used to soothe sore muscles (w/chemical name)
Oil of wintergreen (Methyl salicylate)
Oil of wintergreen is an ester of ________ and _________
salicylic acid and methanol
What is flavor/odor does propyl ethanoate (propyl acetate) pertain to?
Pears

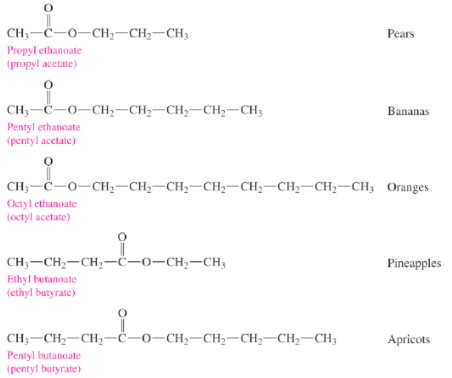
What are the respective flavors/odors for these esters
Pears
Bananas
Oranges
Pineapples
Apricots
In naming esters,
The name of an ester contains the names of the ______ group from the alcohol
the carbon chain from the acid with _____ending
alkyl
-ate
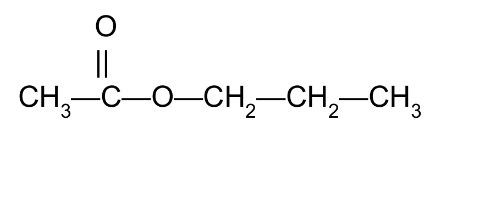
Give the IUPAC and common names of the following compound, which is responsible for the flavor and odor of pears:
Propyl ethanoate
Propyl acetate
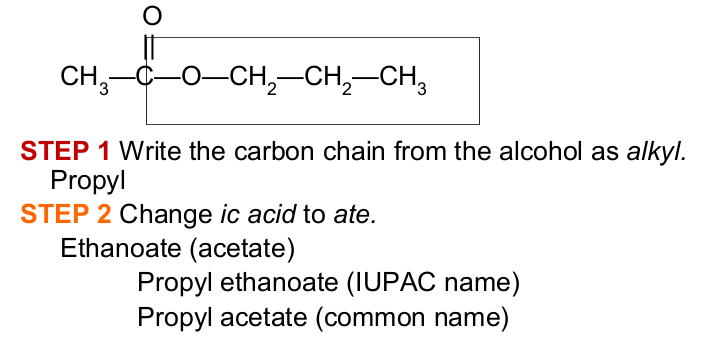
Name the following esters:
Methyl butanoate
Ethyl propanoate

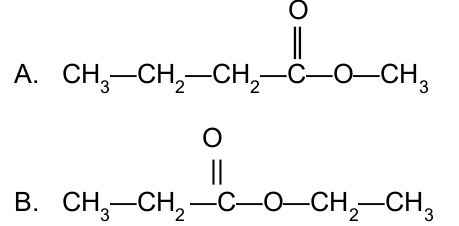
Draw the condensed structural formula of the following esters:
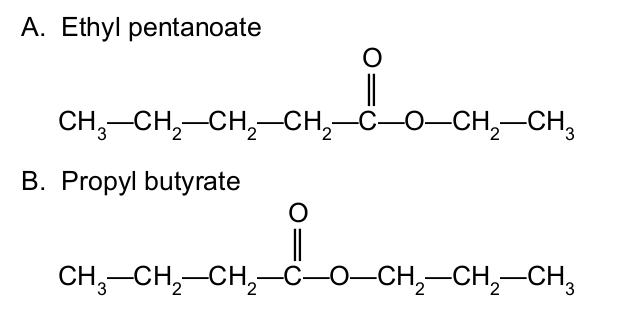
The boiling points of esters are (higher/lower) than alkanes of similar mass
higher
The boiling points of esters are (higher/lower) than alcohols and carboxylic acids of similar mass because esters cannot form hydrogen bonds
lower
In acid hydrolysis, an ester reacts with water to produce a __________ and an ___________;
___________ is also required
carboxylic acid, alcohol
acid catalyst
Base Hydrolysis (also called _______________)
is the reaction of an ester with a strong _________
produces the ______ of the carboxylic acid and an alcohol
Saponification
base
salt
The base hydrolysis of long chain fatty acids produces acid salts called “____________”
soaps
A soap contains a nonpolar end that dissolves in _____________ and a polar end that dissolves in ____
A soap forms groups of soap molecules called ____ that dissolve in water and are washed away
non polar fats and oils, water
micelles

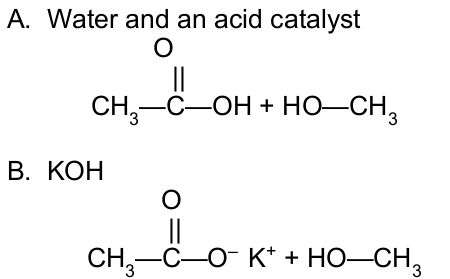
Write the condensed structural formulas of the organic products when methyl acetate reacts with:
_____ contain one or more alkyl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom
amines
Amines are classified by as _____, _______, and _______
primary, secondary, and tertiary
In a primary (1°) amine, ____ carbon group is bonded to the nitrogen atom.
A secondary (2°) amine has _____ carbon groups.
A tertiary (3°) amine has ___ carbon groups.
1
2
3
Simple amines are named with common names as ______
alkylamines
In naming of amines (IUPAC)
A.)
STEP 1 Name the longest carbon chain bonded to the N atoms as __________ by replacing -e of the alkane name with ________.
STEP 2 Number the carbon chain to locate the amine group and any substituents.
STEP 3 In a secondary or tertiary amine, use the prefix _____to name groups attached to the N atom.
alkanamines, -amine
N-
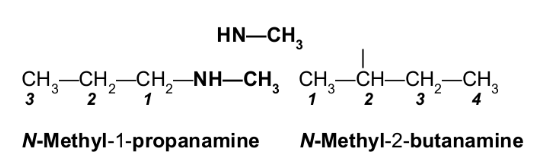
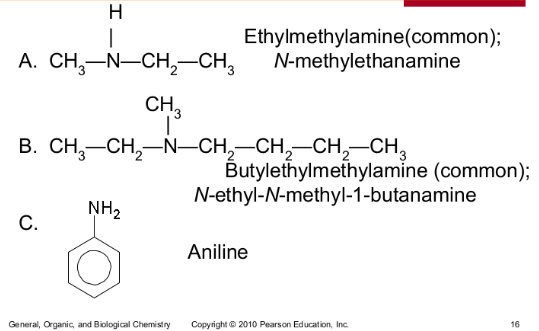
Give the common and IUPAC names, and classify each as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
1-Propanamine (IUPAC), 1°
Propylamine (common)
N,N-Dimethylethanamine (IUPAC), 3°|
Ethyldimethylamine (common)
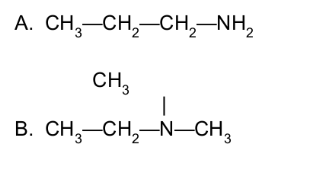
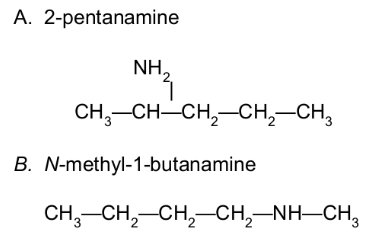
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following:
A. 2-pentanamine
B. N-methyl-1-butanamine
The amine of benzene is called _____
aniline
Amine of benzene may have alkyl groups attached to N that use the prefix ____ and the _____ name
N-, alkyl
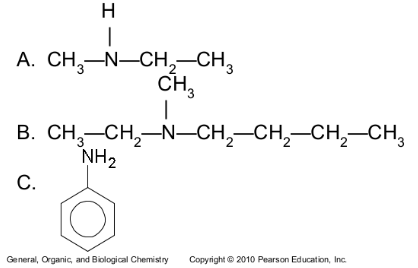
Give the common and IUPAC names for each of the following:
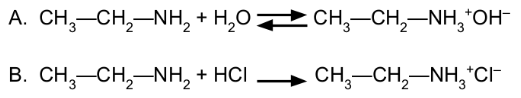
The boiling points of amines are
(higher/lower) than alkanes of similar mass
(higher/lower) than alcohols of similar mass
higher
lower
The polar N—H bond provides hydrogen bonding in ____ and ____ amines but not ____ amines classiifications
The polar N—-H bonds in amines (is/is not) as polar as the —OH in alcohols
primary, secondary, but not in tertiary
is not as polar
Amines are soluble in water if they have ______ carbons
and because the N atom in smaller amines forms _______ bonds with the polar O—H bond in water
1 to 5
hydrogen


Amines are ___________ bases that attract a H+ from H2O
to the N atom, and are (strong/weak) bases in water
Brønsted-Lowry
weak
it is formed when amine is neutralized by an acid
amine salt
amine salts are named by replacing the amine part of the name with _______ followed by the name of the negative ion
ammonium
Amine salts are
(solid/liquid/gas/vapor) at room temperature
(soluble/insoluble) in water and body fluids
the form used for _____
solid
soluble
gas
is sold illegally as an amine salt
Cocaine
Cocaine is reacted with ______ to produce the free amine form known as “crack”
NaOH

is a cyclic organic compound
has a five- or six-atom ring
contains one or more nitrogen atoms
heterocyclic amine
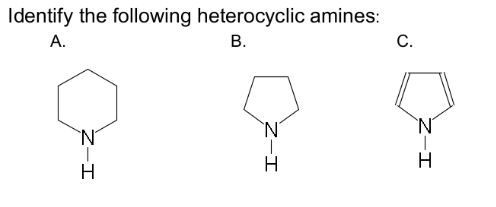
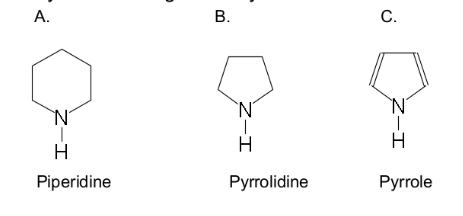
Piperidine
Pyrrolidine
Pyrolle
are physiologically active nitrogen-containing compounds; produced by plants
Alkaloids
used as stimulants, anesthetics, and antidepressants, often habit forming
Alkaloids