Class of Compounds Unit 2a CHM2210 Broward College online Organic Chemistry 1
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Summer C 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
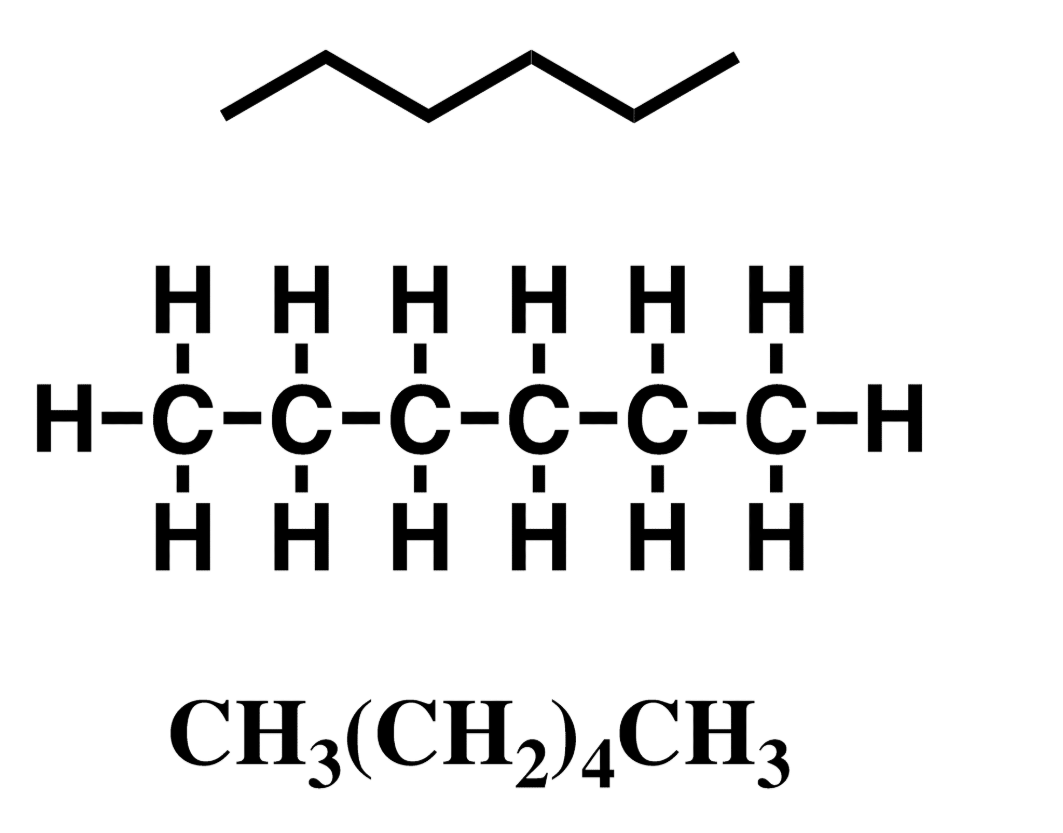
Alkane, hydrocarbon
c-c single bonds only, saturated
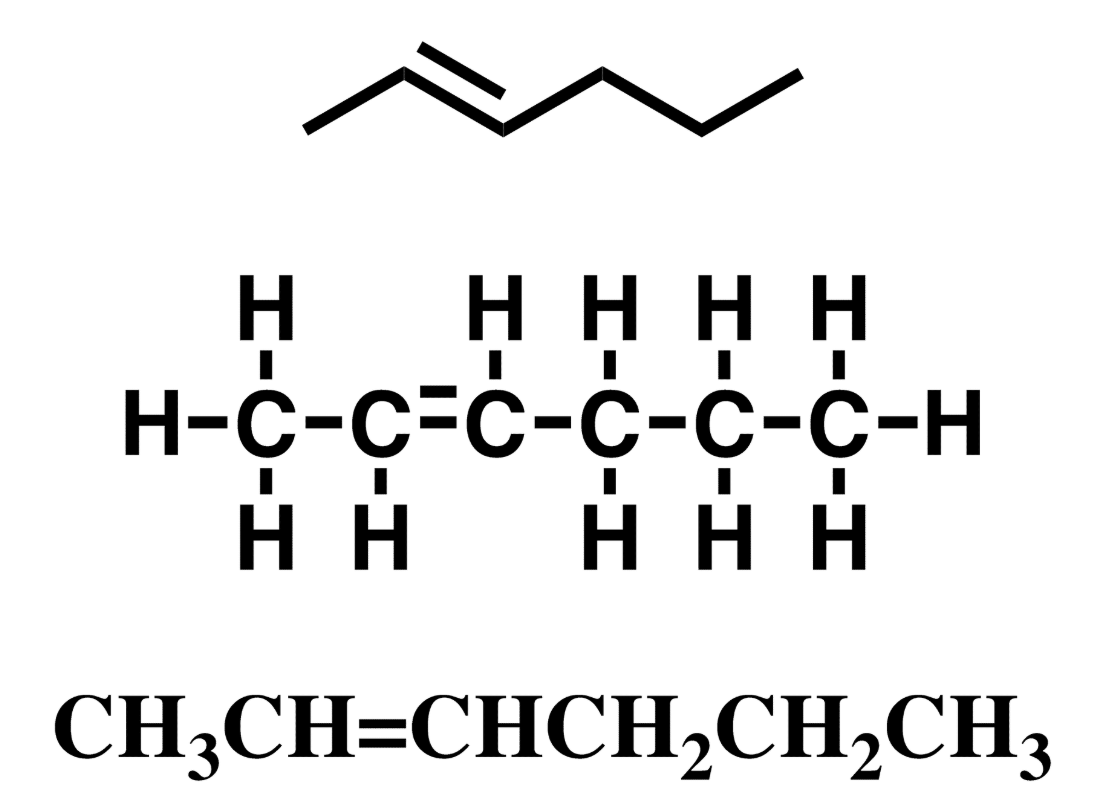
Alkene, hydrocarbon
contains at least one c=c (carbon-carbon double bond.) Unsaturated.
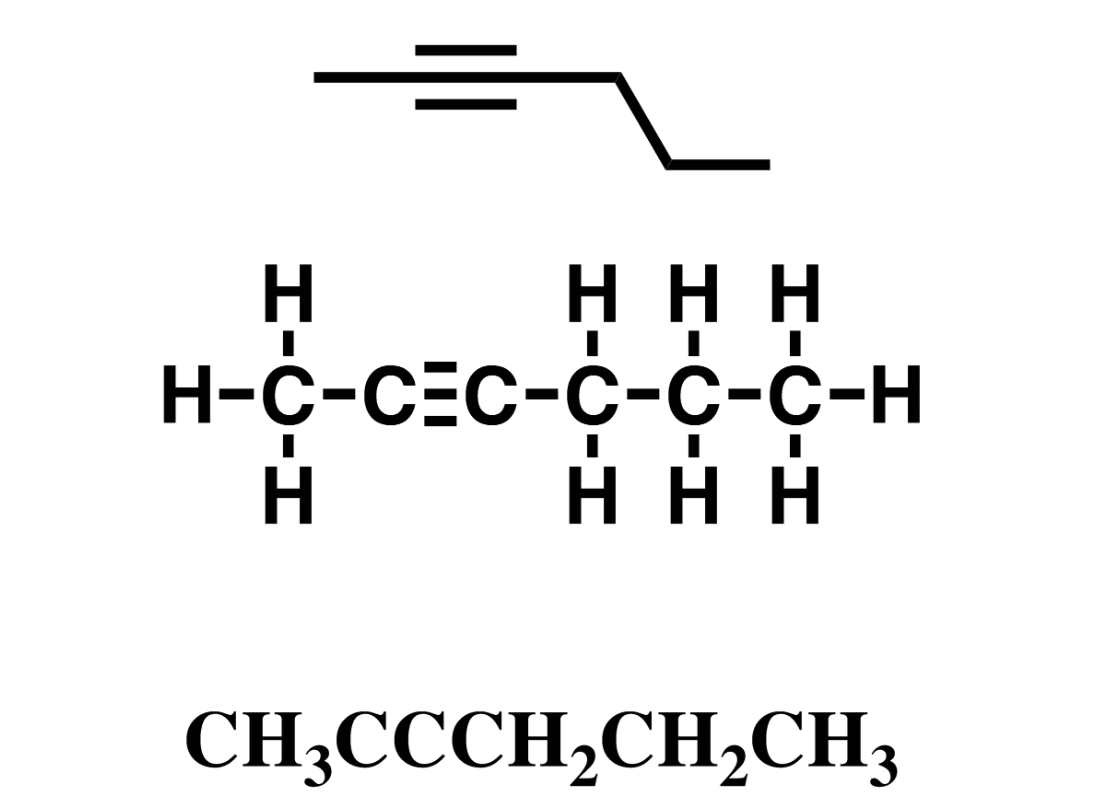
Alkyne, hydrocarbon
contain at least 1 carbon to carbon triple bond. Unsaturated.
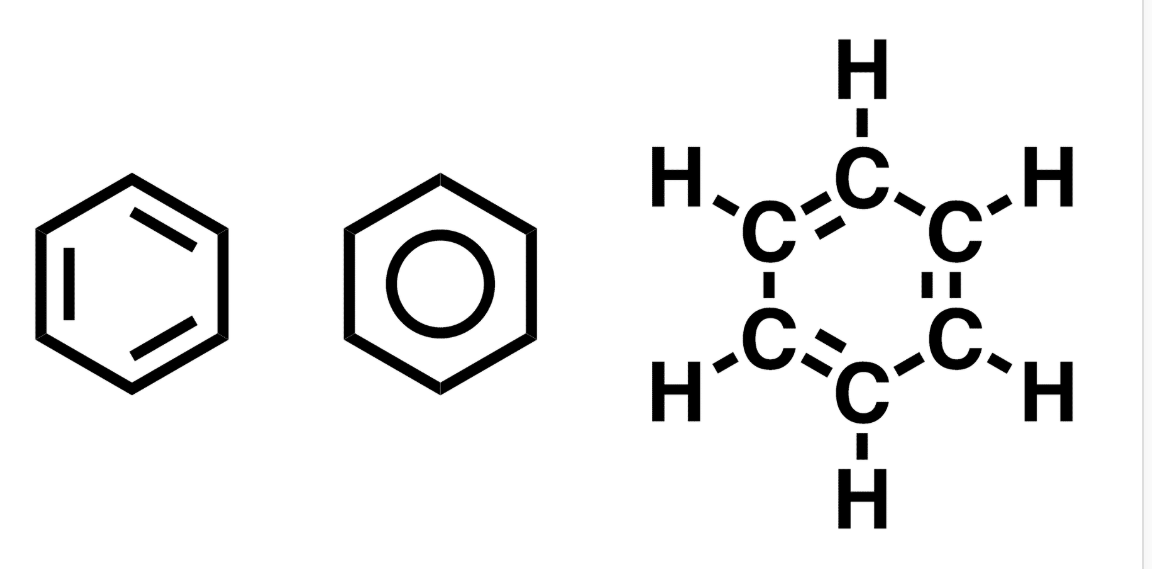
Aromatic, hydrocarbon
6-carbon ring w/ alternating double bonds
Hydroxyl
H-O. The oxygen is then bonded to a carbon/
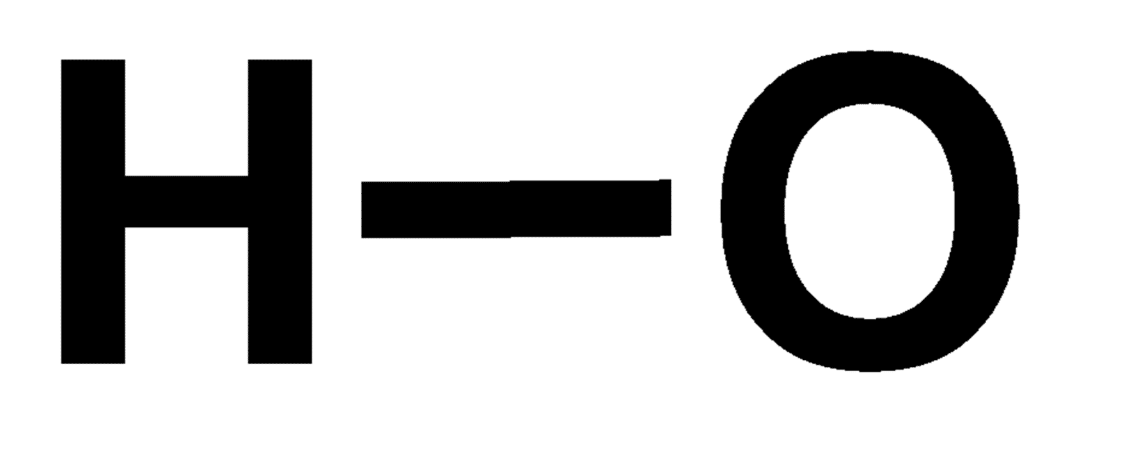
Carbonyl
C=O. Oxygen double bonded to a carbon
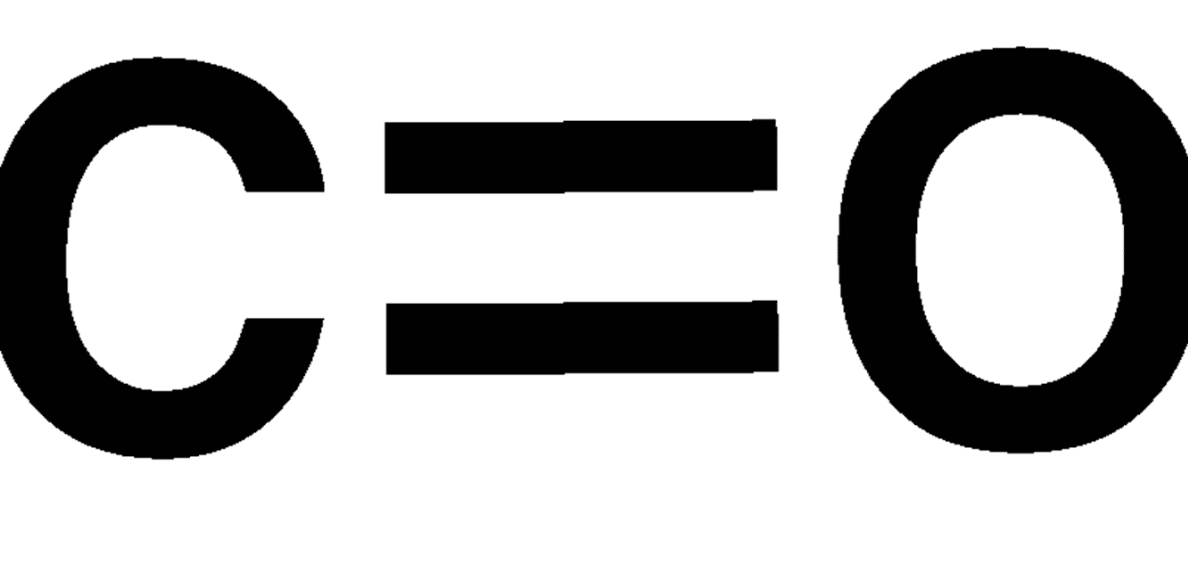
Alcohol
Hydroxyl group connected to an R group. R group is never hydrogen.
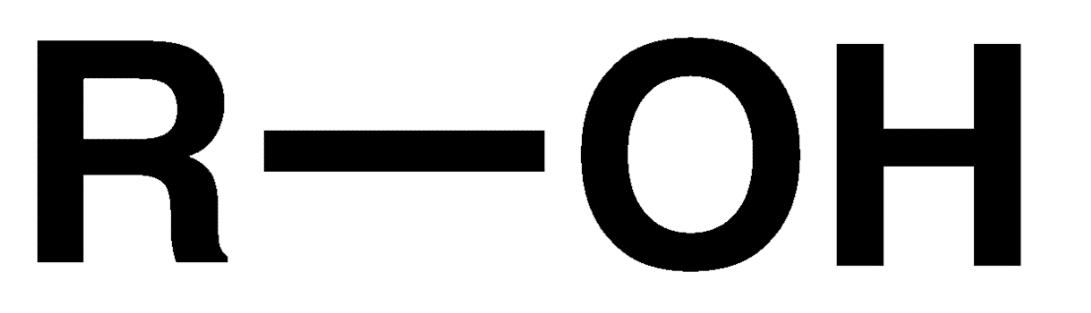
Primary alcohols (1 degree)
A hydroxyl attached to a carbon w/ 2 hydrogens and 1 other carbon
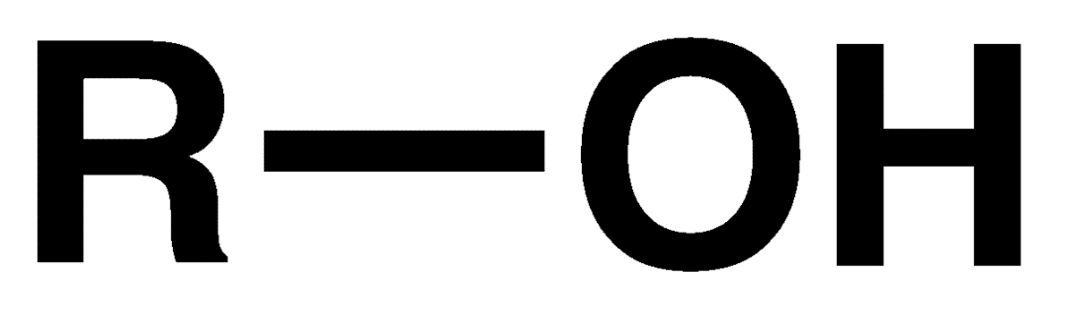
Secondary alcohols (2 degree)
A hydroxyl attached to a carbon w/ 1 hydrogen and 2 other carbons
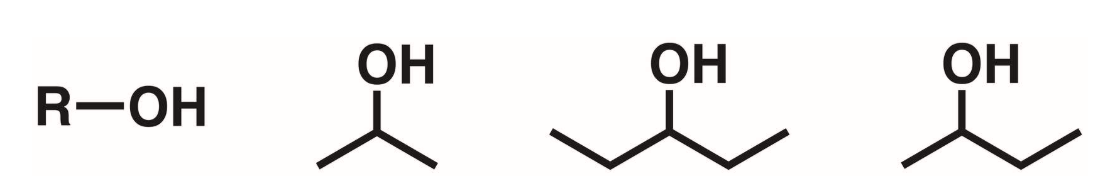
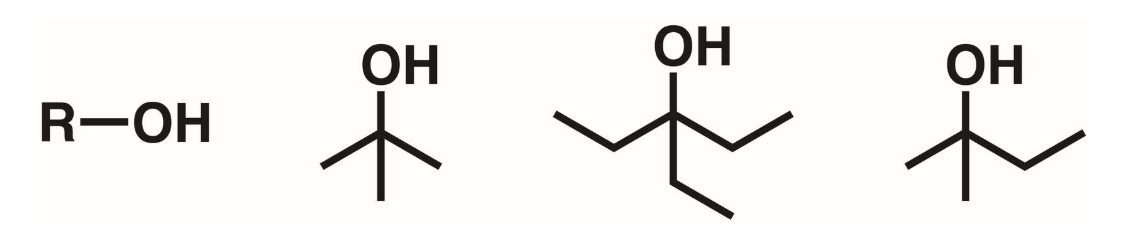
Tertiary alcohols (3 degree)
A hydroxyl group attached to a carbon w/ 0 hydrogen and 3 other carbons
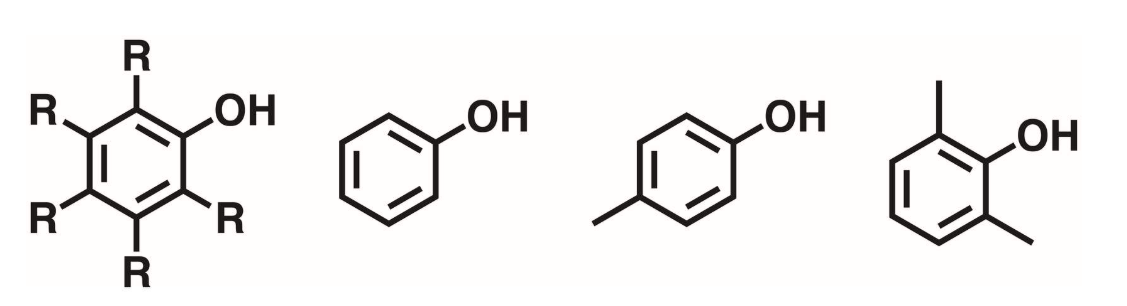
Aromatic Alcohol
Contains a hydroxyl group bonded directly to an aromatic ring
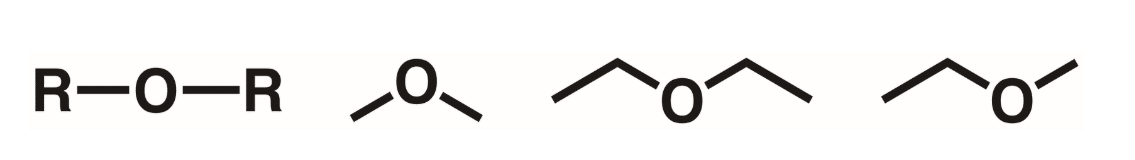
Ether
An oxygen atom flanked by R groups on either side. R cannot be hydrogen.
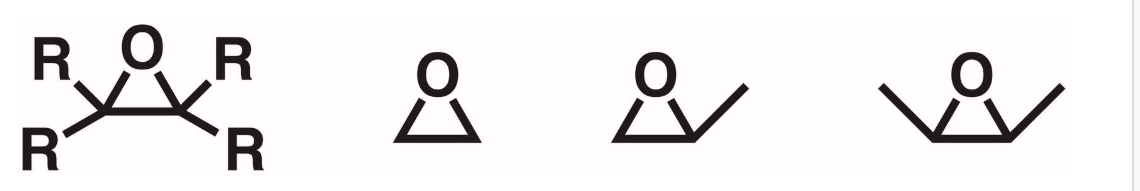
Epoxide
An ether that’s part of a 3 membered ring
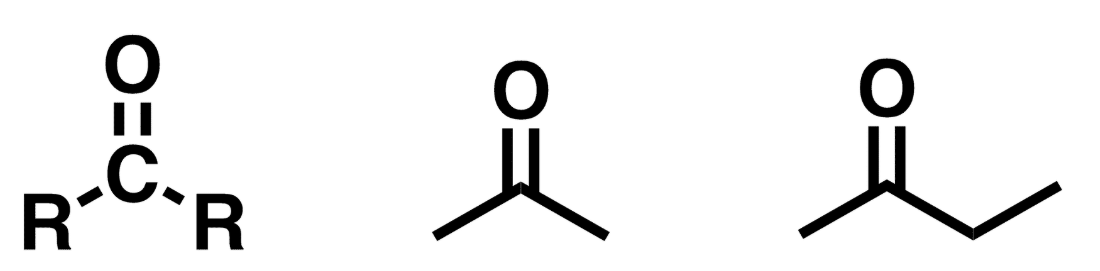
Ketone
C=O (carbonyl) flanked by R groups on either side of the carbonyl carbon. R groups are not hydrogen.
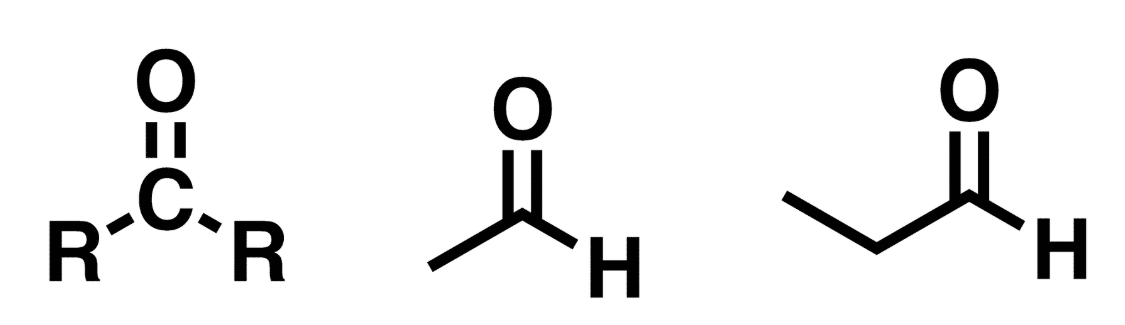
Aldehyde
C=O (carbonyl) w/ R groups attached to the carbonyl carbon. At least 1 of the R groups must be hydrogen
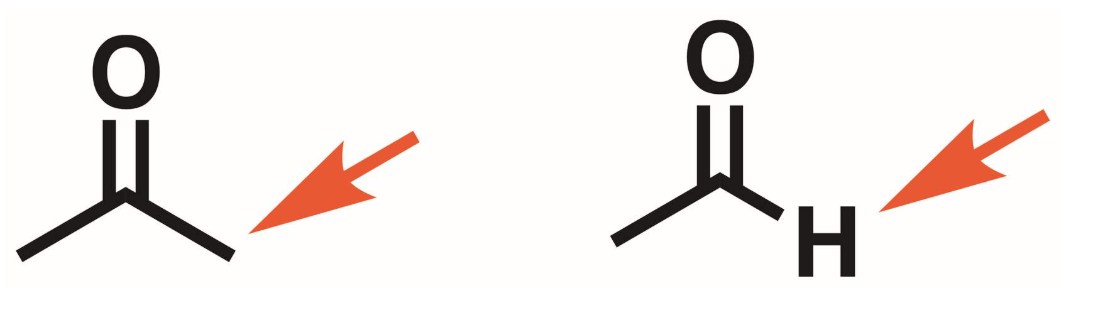
Ketone vs aldehyde
aldehyde has H directly bonded to the carbonyl carbon, ketone does not
Carboxylic acids
Contains C=O (carbonyl) flanked by 1 side of an O-H (hydroxyl) and the other side is an R group (that is a carbon group or hydrogen
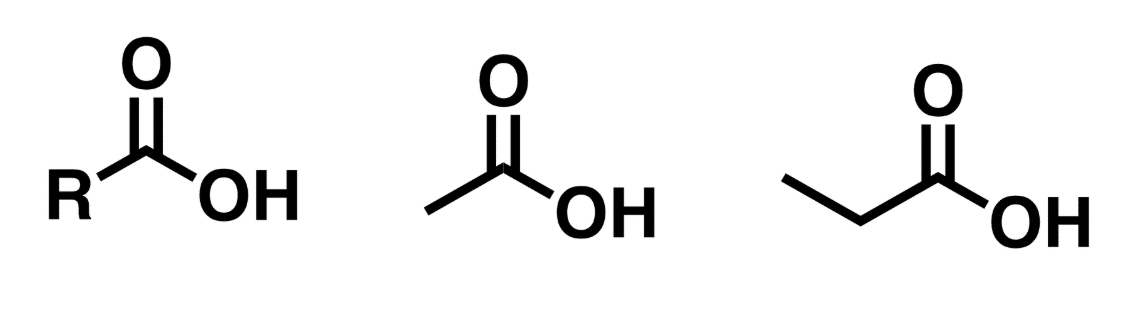
Esters
Similar to carboxylic acid, but the H on the hydroxyl group is replaced by a C group
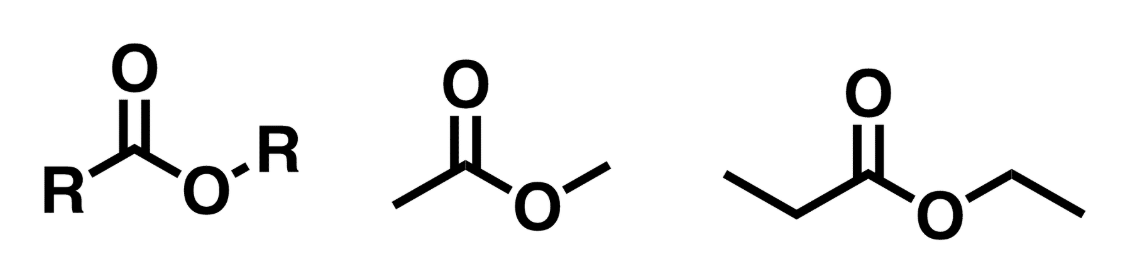
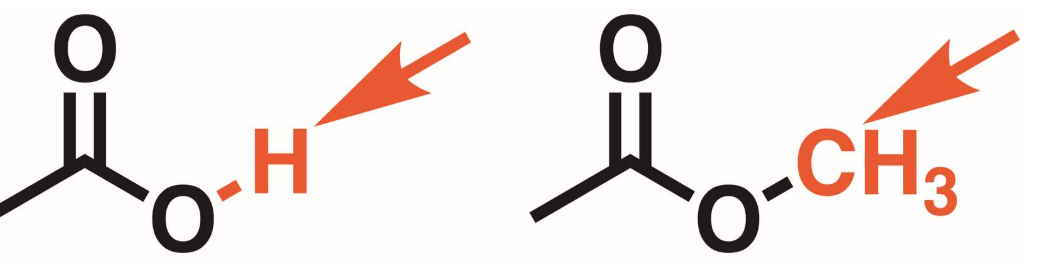
Esters vs Carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acid has a hydrogen atom on the oxygen adjacent to the carbonyl. In that place on esters it is a carbon group. Arrows point to structural differences.
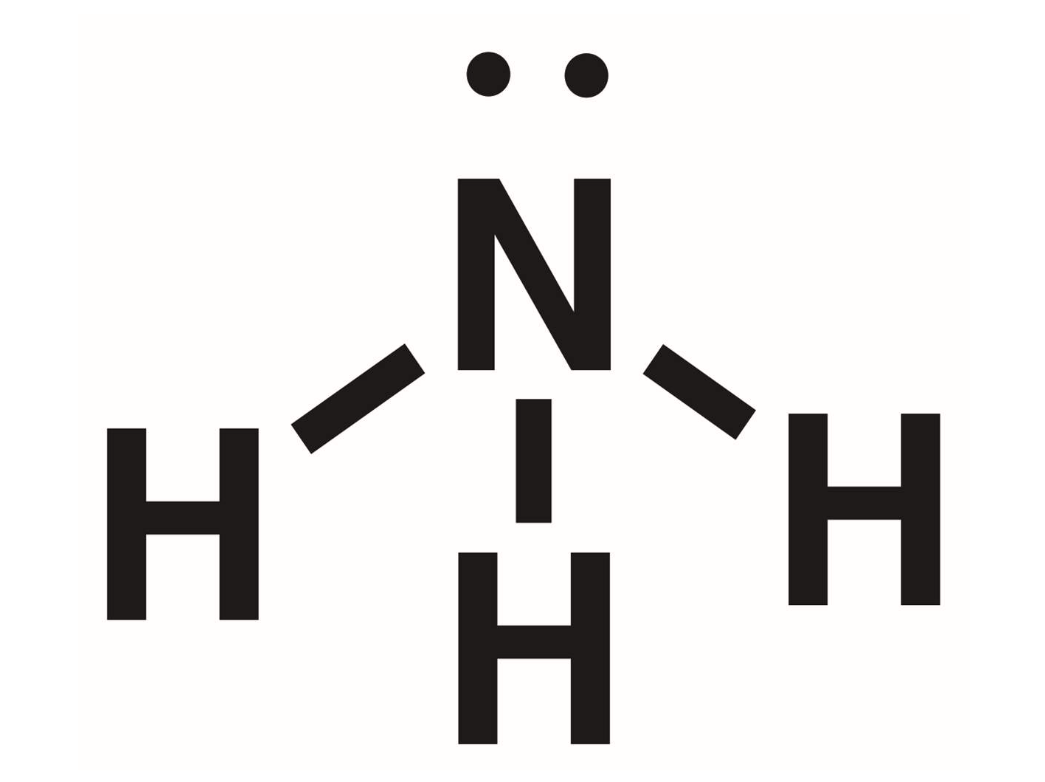
Ammonia
NH3. Amines are derivatives of this inorganic compounds. Defined to be an amine if 1 or more of the hydrogens are replaced by an R group.
Primary amines (1 degree)
1 of the hydrogen in ammonia replaced with an R group
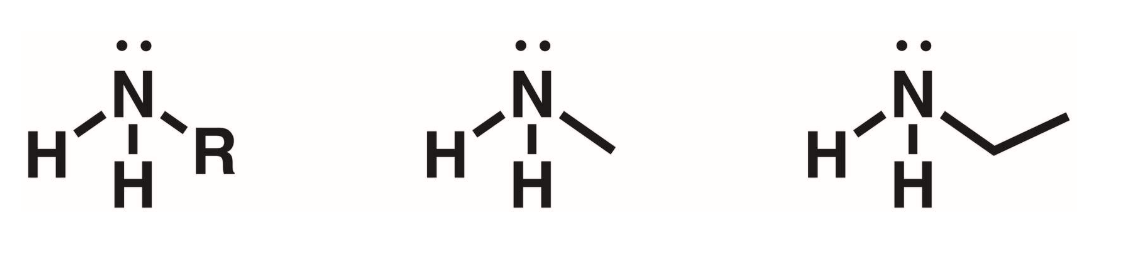
Secondary Amines (2 degree)
2 of the hydrogens of ammonia replaced with R groups
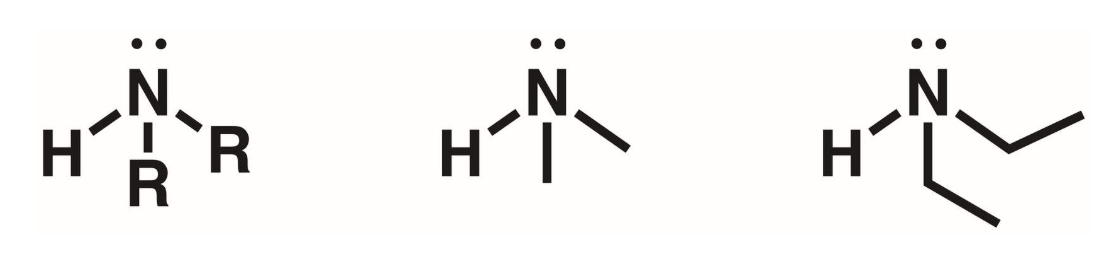
Tertiary amines (3 degree)
3 of the hydrogens of ammonia replaced with R groups
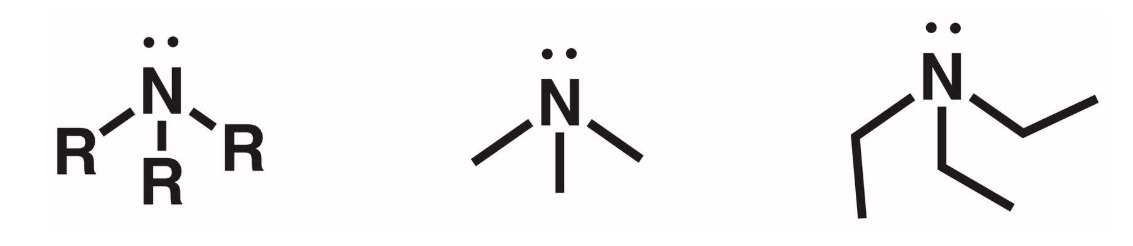
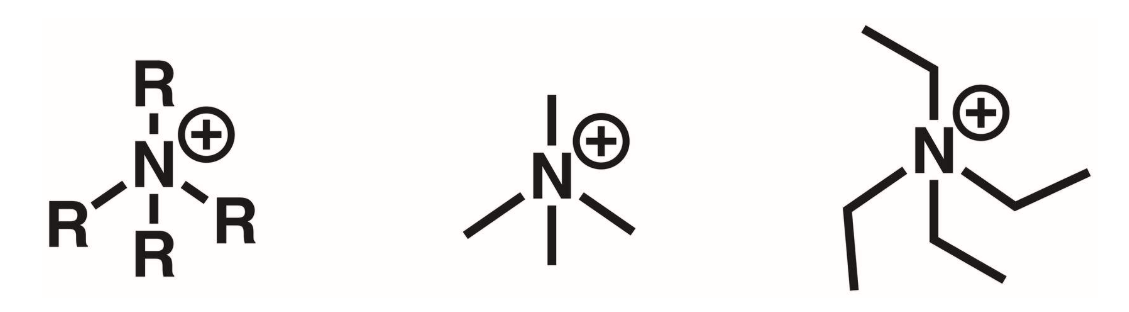
Quaternary amines (4 degree)
N atom surrounded by 4 R groups. The N is +
Nitrile
C N triple bond. R group can be a carbon group or hydrogen

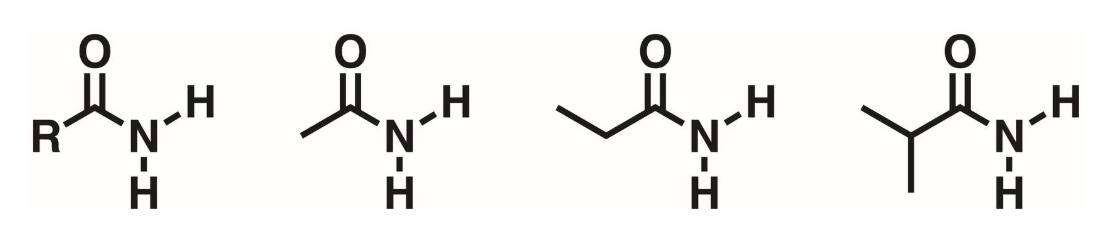
Primary amides (1 degree)
Carbonyl flanked by a nitrogen. N must have 2 hydrogens
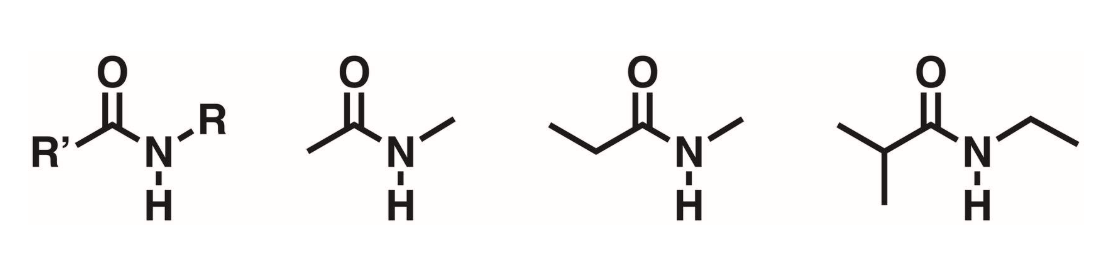
Secondary amides (2 degree)
A carbonyl flanked by a nitrogen. N must have 1 hydrogen
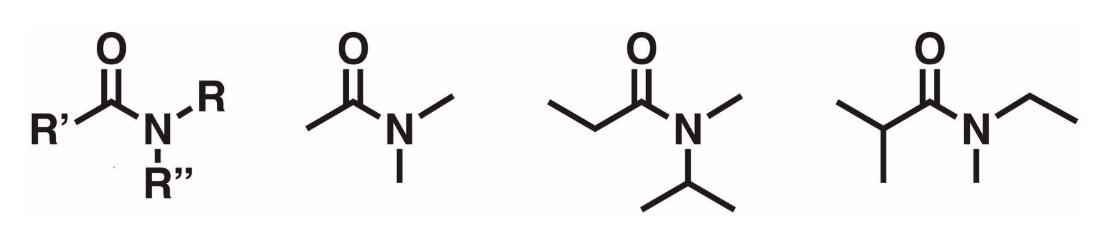
Tertiary Amides (3 degree)
Carbonyl flanked by a N. The N does not have any hydrogens
Nitro Alkanes
O-N=O. A nitrogen atom double bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to a second oxygen. The N is positively charged and 1 of the oxygens is negatively charged.
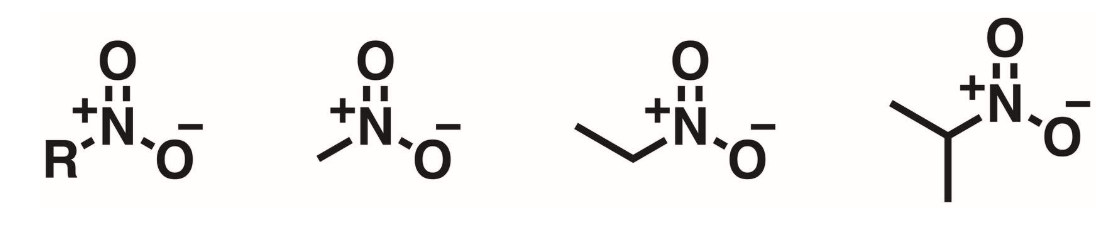
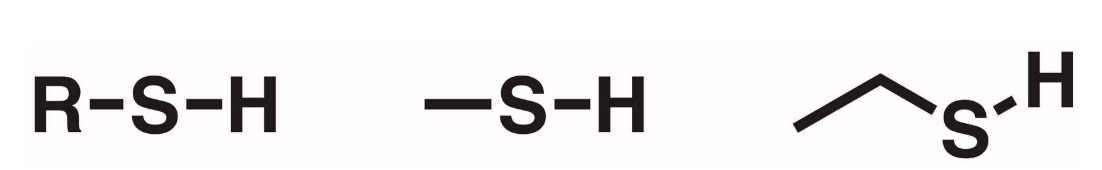
Thiol
H-S. A hydrogen directly bonded to a sulfur.
Disulfide
R-S-S-R. 2 sulfur atoms bonded w/ R groups on either side.
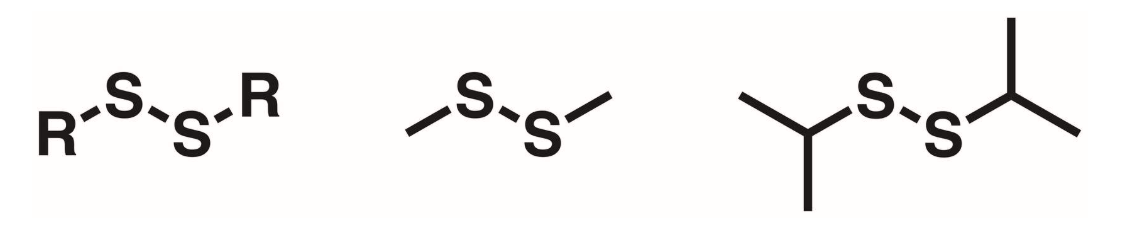
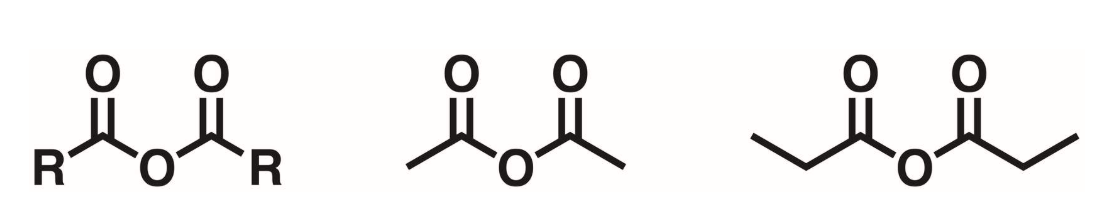
Anhydride
An oxygen flanked on either side by carbonyl groups
Peroxyacid
Carbonyl bonded to a peroxide followed by a hydrogen