4.2.2. How the macroeconomy works: the circular flow of income, aggregate demand/supply analysis and related concepts
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is national income and what does it measure?
national income = total value of goods and services a country produces over a year
GDP, GNI and NNP
What is the equation to measure real national income?
Nominal NI/average price level
What are the three methods of measuring flow of new output in an economy?
these always equal each other
NI = measured income received by different factors of production
NO = measures actual goods and services produced by the economy
NE= shows the spending of these incomes on the goods and services produced by the economy
explain NI=NO=NE:
If you are selling bread:
NI-wages received at each stage of production, adds together to the total value of the bread
NO- sale of bread added to NI
NE- price paid for finished product
What is the circular flow of income?
Model that shows how money flows between the key components of the economy
Draw the circular flow of income:
Label key components
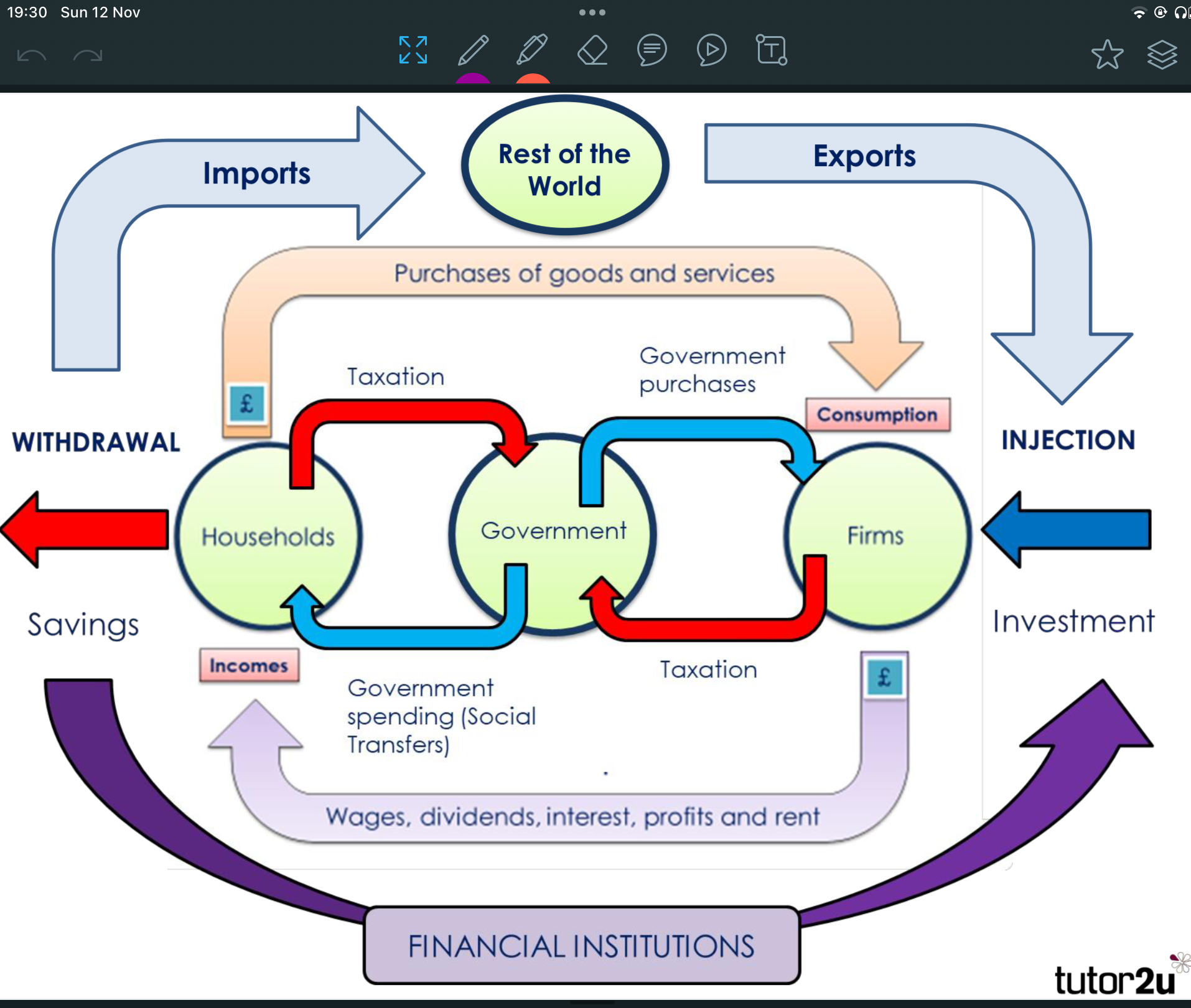
Define the word injection in terms of the CFOI:
money entering the circular flow of income
Injections include investment, government spending and exports
Define the word withdrawals in terms of the CFOI:
leakage of spending power out of the CFOI
Withdrawals include savings,taxation and imports
What does this mean?
S + T + M = I + G + X
National income is in equilibrium
What does this mean?
S + T + M> I + G + X
Net withdrawal/leakage of demand out of the CFOI occurs causing NI to fall
What does this mean?
S + T + M < I + G + X
Net injection of demand into the CFOI, National income rises
What does aggregate demand mean?
Measurement of the totals amount of demand for all finished goods and services produced in an economy
What is the equation for aggregate demand?
What do each of the components mean?
AG = C + I + G + (X-M)
C= Expenditure by households on UK produced goods and services
I = Expenditure by firms on capital equipment
G=Expenditure by government to include capital spending eg building hospitals and current spending e.g. teachers wages
X=Expenditure by overseas consumers and firms on UK produced goods and services
M= Expenditure by UK consumers and firms on overseas produced goods and services
Draw an Aggregate demand curve
Correctly labelling the X and Y axis
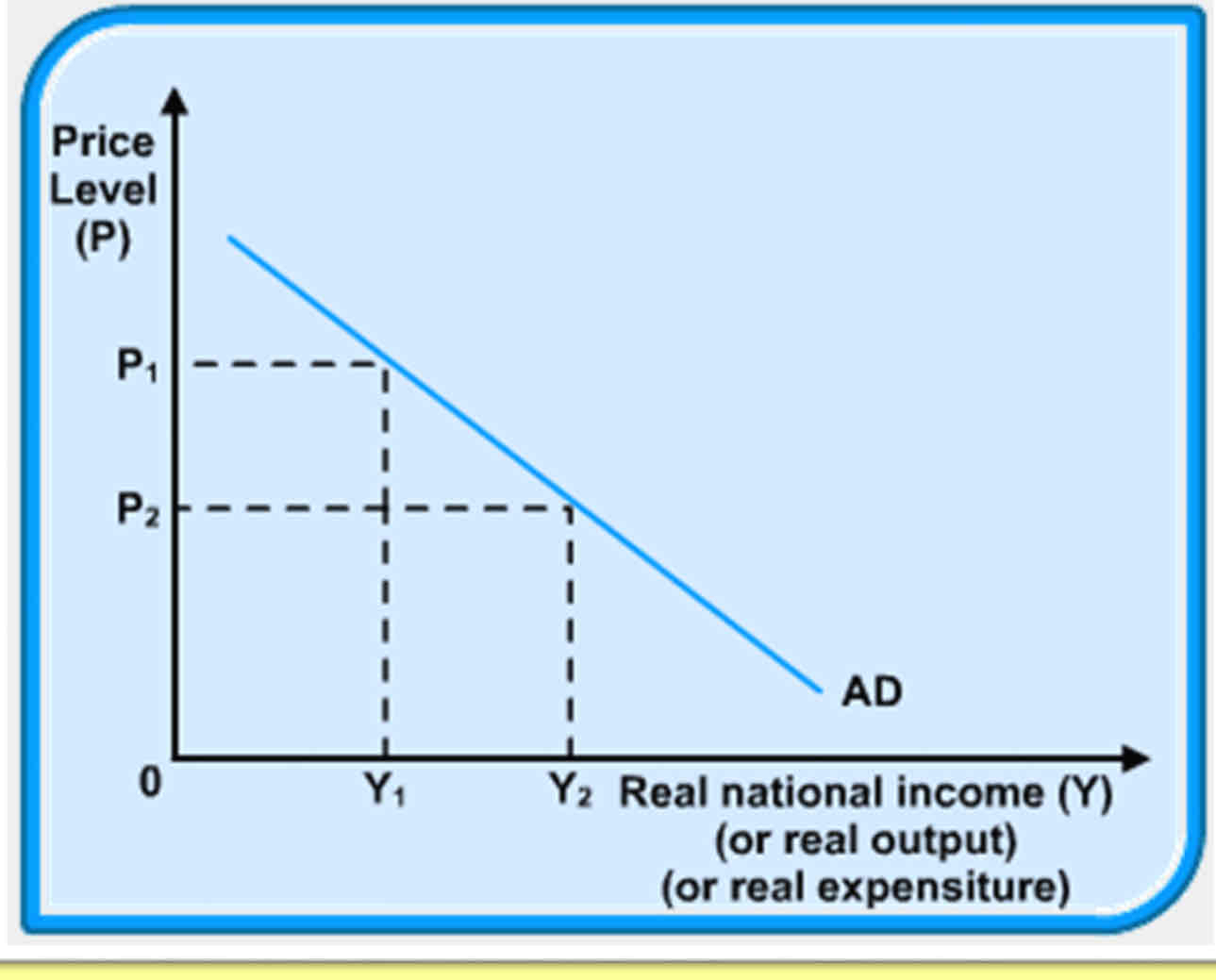
What is key about the AD curve?
What causes a fall and rise in AD?
curve has the familiar downward slope.
At a higher price level (P) the demand for real national income will be relatively low (Y) vice versa
Fall:
Fall in exports
Cut in GS
Higher interest rates
Decline in household wealth
Rise:
Depreciation of the exchange rate
Cuts in direct and indirect taxes
Increase in house prices
Expansion of supply of credit and lower interest rates
What is aggregate consumption?
combined spending of all households in an economy
What factors influence consumption/ consumer spending?
interest rates
Wealth
Level of income
Expected future income
Consumer confidence
Availability of credit
Distribution of income
Expectation of future inflation
What is the opposite of consumption?
The opposite of consumption is savings. If consumption decreases savings increase and vice versa.
What does investment mean in economics?
planned demand for capital goods in an economy
Investment is a flow while capital is a stock. Investment needs to be measured over a period of time and not at a point in time.
What are the two types of investment ?
Replacement:
replacing old capital
Maintains current size
Net:
adds to the capital stock
Increases productive potential
What factors influence investment ?
Predictions on future sales
Price of labour/capital
Interest rates
Predictions on future costs/profit
Technical progress
Gov policies
How do you calculate the savings ratio for an economy?
Actual personal saving/personal disposable income
What does government spending mean in economics?
The government can choose to spend money in the economy. This is called Fiscal spending.
What does Exports/Imports mean?
This is known as Net Exports . Exports add to AD of an economy while Imports deduct from an economy.
What factors influence Exports/Imports?
relative cost of the good
Exchange rate
Trade barriers
Ability to produce a good
What causes a shift in the AD curve?
an increase in any of the AD components
What does government spending mean in economics?
The government can choose to spend money in the economy. This is called Fiscal spending.
What factors influence government spending?
how the economy is performing
Budget
Party in charge
Expectations about the future
What is SRAS?
amount of goods and services that businesses are prepared to produce assuming capital is fixed
A rise in the general price level should stimulate an expansion of supply
When prices are falling, production may contract
Draw an AS curve:
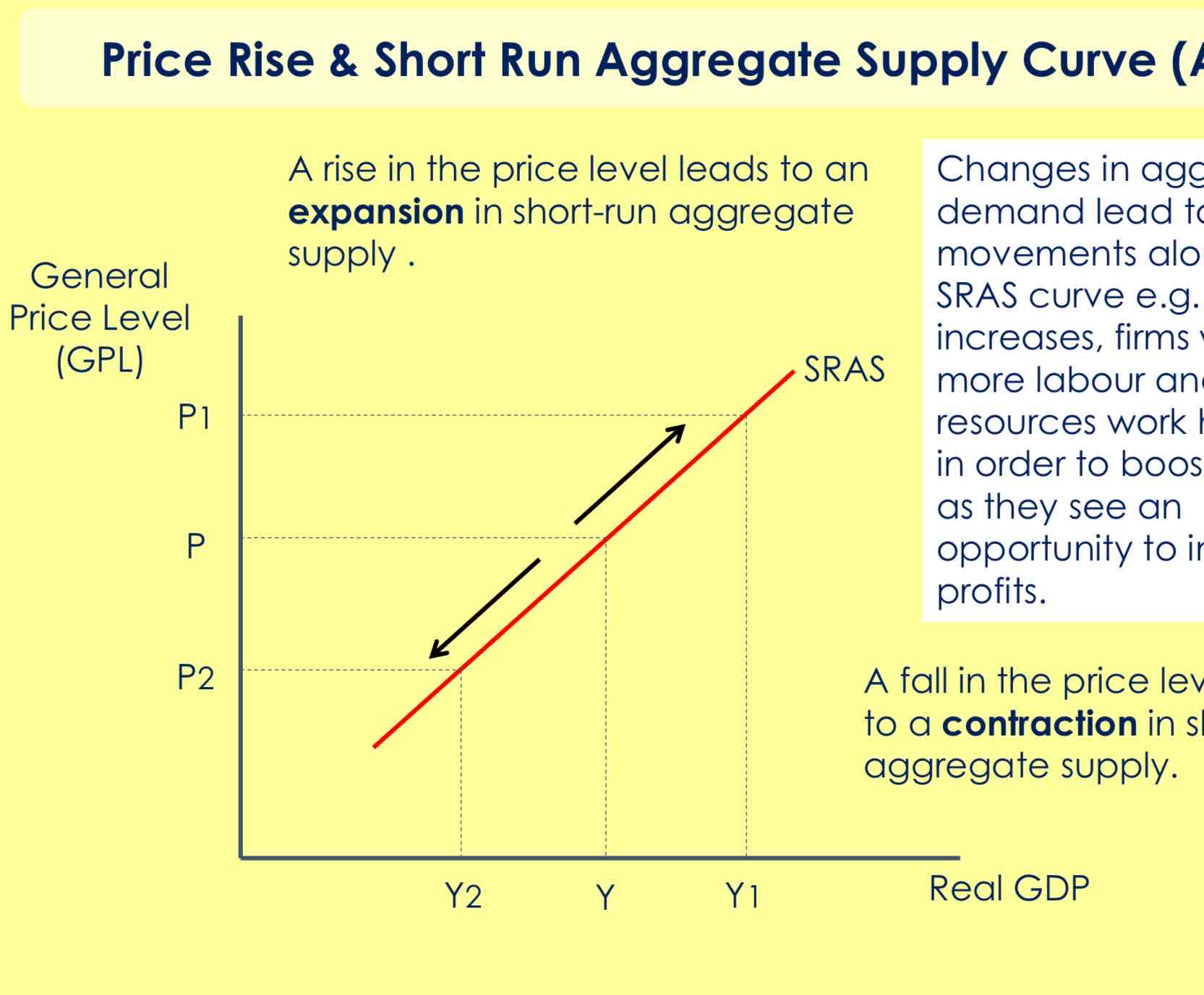
What causes a shift in SRAS?
Wages - if wage rates increase forms may substitute labour for capital
Labour productivity (higher efficiency ceteris paribus lowers unit costs)
Raw material and component prices such as glass, cement, rubber - if prices increase, firms cost of production increase and reduce SRAS
Taxes and subsidies - an increase in business tax rates increases costs of production = SRAS decreases
Increase in business subsidies lowers COP lowers SRAS
Exchange rates and imports - many businesses import raw materials, if currency strengthens, this makes purchasing raw materials relatively cheaper and SRAS will increase
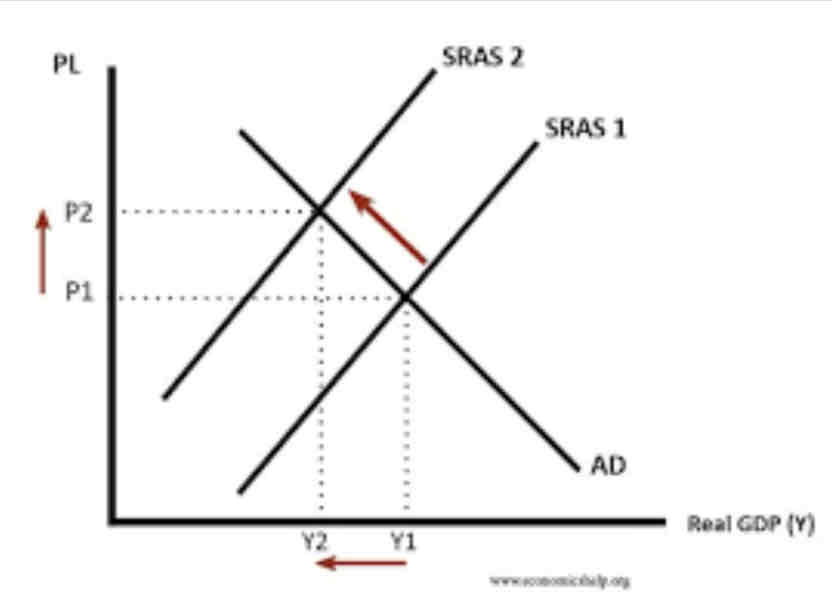
Supply shock
Draw an aggregate supply curve to show the impacts of a supply shock
Draw an aggregate supply curve to show the impacts of falling oil prices
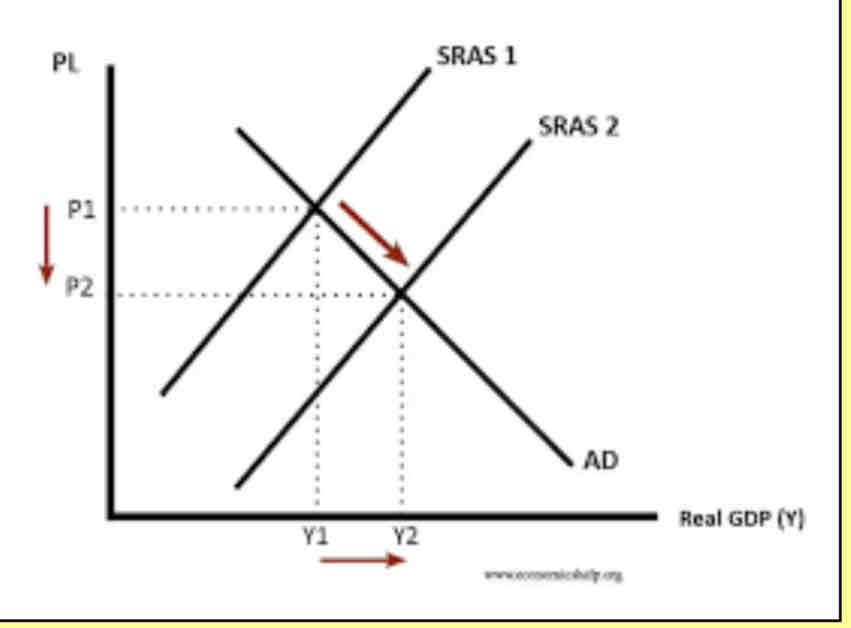
What does LRAS mean?
goods and services that can be produced in an assuming the level of capital is variable
This is when all the available factors of production are employed and producing at their normal capacity level of output
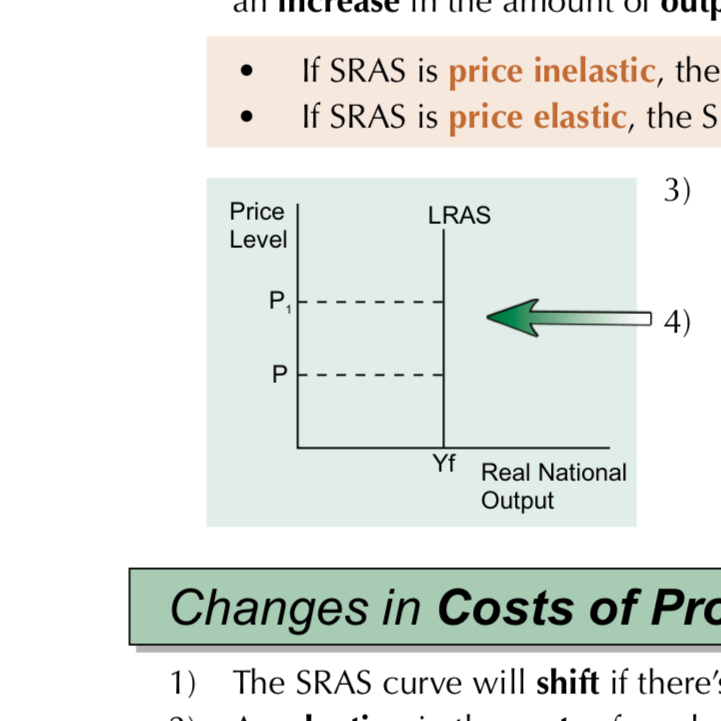
What does a LRAS curve show?
The LRAS curve is vertical. An increase in the price level (e.g. to P1) won’t cause an increase in output because the economy is running at full capacity so it can’t create any more output.
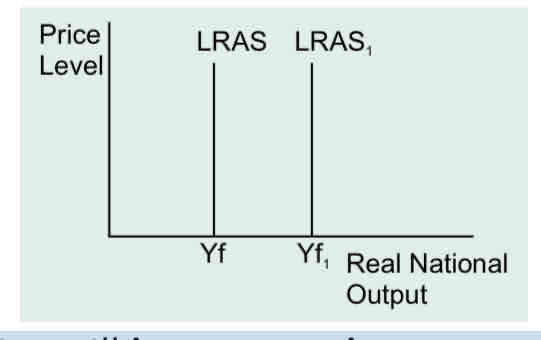
What causes the LRAS curve to shift?
Long run aggregate supply is determined by the factors of production — the LRAS curve will shift if there’s a change in the factors of production which affects the capacity of the economy.
2) An improvement in the factors of production increases the capacity of the economy
3) E.g. investment that leads to advances in technology and more efficient production will increase maximum output.
What does an outward shift of LRAS show?
rise in productive potential
What is the difference between gross and net investment?
Gross = total investment on capital goods
Net = gross investment adjusted for capital consumption
What is a supply shock?
unexpected event that changes the supply of a product or commodity, resulting in a sudden change in its price.
What is role of AD in influencing the level of economic activity?
the higher the level of AD, the higher the level of EA
A large part of government economic activity is designed to stimulate the various components of AD
Any increase in the components will shift the AD curve to the right, and will increase the level of real national output
What is the multiplier effect?
occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a larger final increase in the level of real national income/output
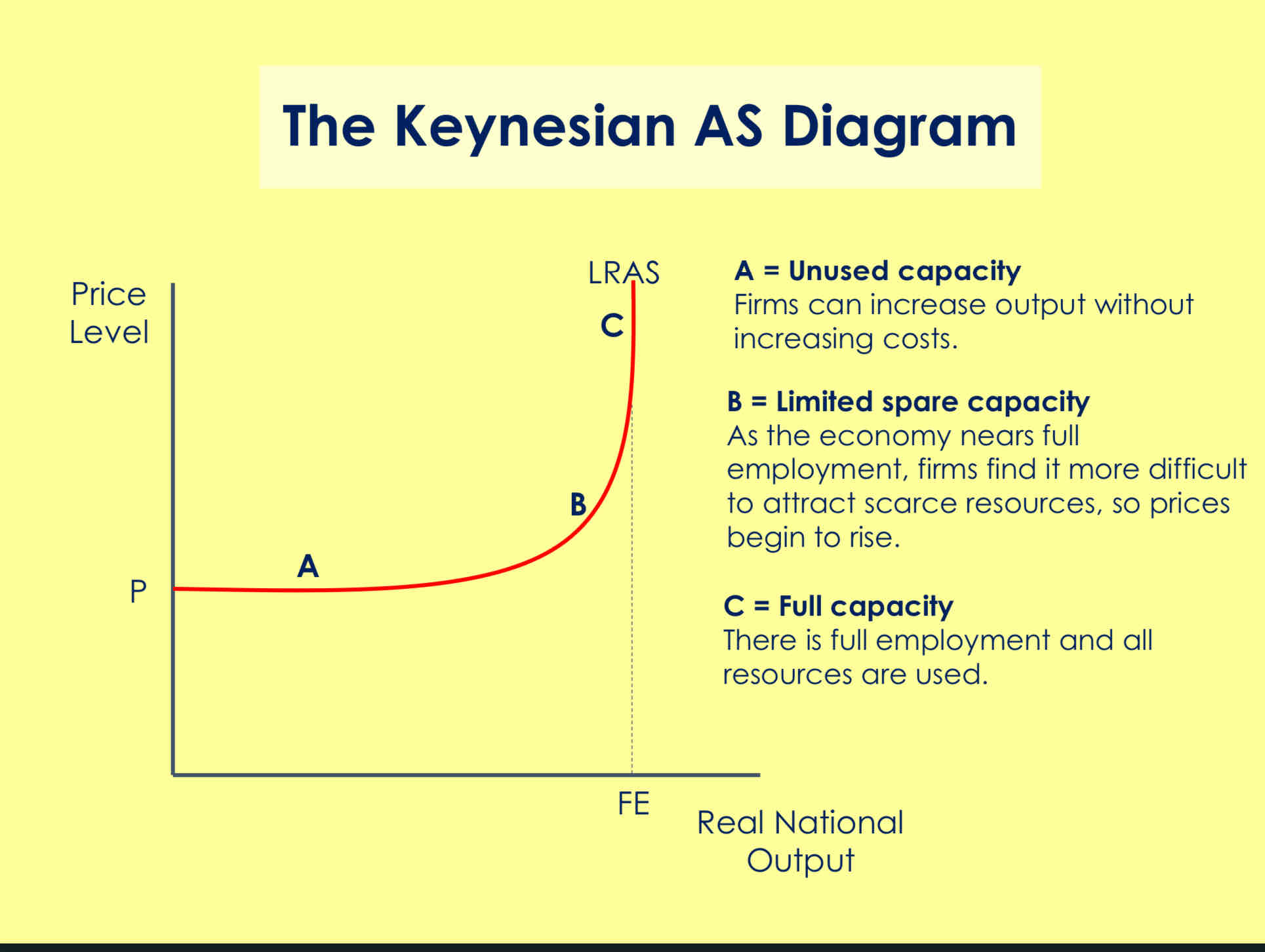
What does the Keynesian AS curve show?
Draw it and label it
concluded that the LRAS curve was upward sloping, and has a vertical section (like the classical LRAS curve), but at times an economy could settle at a level of output below full employment
What is the equation for calculating the multiplier?
Change in national income/ initial change in government spending
or
K = 🔼Y/ 🔼J
J = injections
What is the negative multiplier?
can happen in reverse due to a withdrawal from the economy
Cuts in spending and increases in tax lead to a negative multiplier and a fall in GDP
What factors affect the multiplier?
interest rates - if they’re high, consumption might not rise as much as consumers might save money
Tax rates - withdrawal from the CFOI, if they’re high = less disposable income
Imports - if disposable income increases, but is spent on imported goods, this counts as a withdrawal from the CFOI
Spare capacity- any increase in AD may not be able to be met by firms, as a result the multiplier effect will be limited and inflation might occur
What is the accelerator theory of investment?
increase in (GDP) results in a larger rise in investment spending.
What is MPC? (Marginal propensity to consume)
change in consumer spending following a change in investment
What is MPS?(marginal propensity to save)
Percentage of disposable income