rp6 + other tests for functional groups
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
other tests from oxidation of alcohols topicc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
describe the test for an alcohol and a +ve result:
add solution you are testing to clean, dry test tube
place small piece of metallic sodium into test tube
conduct ‘squeaky pop’ test - place lit splint into test tube - if squeaky pop is heard, hydrogen has been produced, indicating the presence of an alcohol
OR w/o squeaky pop test: Na shows effervescence
describe the test for an aldehyde using Fehling’s solution and a +ve result:
add equal volumes Fehling’s solution A and B to a clean, dry test tube - this should form a dark blue solution
add 5 drops of this solution and some anti bumping granules to a different clean, dry test tube
add solution you are testing into test tube
prepare a water bath and place test tube inside, bringing water to boiling
leave contents of test tube to stand for a few minutes
if aldehyde present → brick red precipitate
(if ketone present → no change)

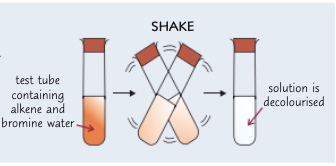
describe a test for an alkene using bromine water and a +ve result:
add 2 cm³ of solution you are testing to a clean, dry test tube
shake w/ 2 cm³ of bromine water
if solution changes from orange → colourless, C=C bonds are present, highlighting the presence of an alkene
describe a test for an alkene: using acidified potassium manganate and a +ve result
to approx 1 cm³ of the solution you are testing in a test tube, add an equal vol of acidified potassium manganate solution
shake contents well
solution should go from purple to brown as brown precipitate forms
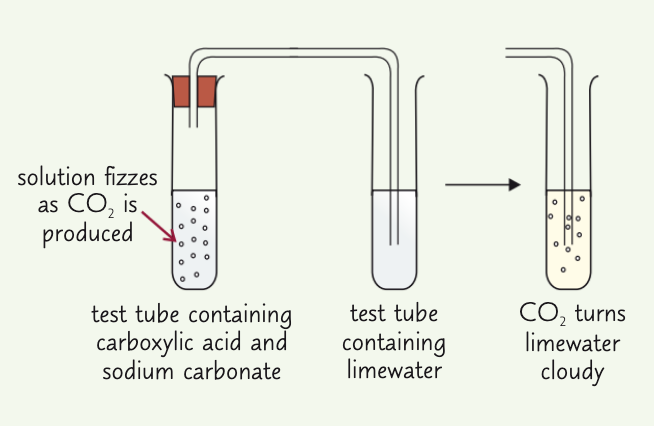
describe the test for a carboxylic acid and a +ve result:
add 2 cm³ solution you are testing to clean, dry test tube, then add 2 cm³ sodium carbonate solution (or a small spatula of solid sodium hydrogencarbonate)
if successful, effervscence of CO2 being produced should occur, highlighting the presence of a carboxylic acid
OR CO2 produced turns limewater cloudy
(note that this test shows a +ve result for all acids!)
give the general eqn for the test for (carboxylic) acids:
(carboxylic) acid + carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water
describe the test for a haloalkane and a +ve result:
add solution you are testing to NaOH solution in a test tube
prepare a water bath at approx 60oC and place the test tube and its contents into water bath
add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution (acidifies solution)
if a haloalkane is present, a cream precipitate should form
how can we test for 1o alcohols? give a +ve result:
add 10 drops alcohol to 2 cm³ acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
warm gently in hot water bath
if 1o: solution goes from orange → green as an aldehyde forms
we must repeat this and distill the product to separate it and carry out a further test to find out whether it is actually a aldehyde and so whether or not the alcohol was 1o
how can we test for 2o alcohols? give a +ve result:
add 10 drops alcohol to 2 cm³ acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
warm gently in hot water bath
if 2o: solution goes from orange → green as a ketone forms
we must repeat this and distill the product to separate it and carry out a further test to find out whether it is actually a ketone and so whether or not the alcohol was 2o
give the eqn for and explain the colour change of 1o/2o alcohols when added to acidified potassium dichromate (VI):
Cr2O72- → Cr3+ + e-
orange
how can we test for 3o alcohols? give a +ve result:
add 10 drops alcohol to 2 cm³ acidified potassium (VI) dichromate
warm gently in hot water bath
if 3o: nothing happens
summarise the process of oxidising a 1o/2o alcohol to distill the product (aldehyde/ketone - respectively)
add XS alcohol to 2 cm³ acidified potassium (VI). dichromate solution in a round bottom flask
set up flask as part of distillation apparatus
gently heat flask - alcohol will be oxidised and product will be distilled to be collected
what are the 2 tests we can use to distinguish between an aldehyde and ketone after distillation? what happens if a ketone is present?
Fehling’s solution test (same as aldehyde test in RP6)
Tollen’s reagent test
if a ketone is present for both: no change
describe the Tollens’ reagent test and a +ve result:
make Tollens’ reagent:
add 2 cm³ 0.1 mol dm-3 silver nitrate solution to a test tube
add a few drops of dilute NaOH solution - light brown precipitate should form
add drops of dilute ammonia solution until brown precipitate completely dissolves
test:
place test tube containing Tollens’ reagent into hot water bath and add 10 drops of aldehye/ketone
wait for a few minutes
if aldehyde present - silver mirror forms on test tube walls
if ketone present - nothing happens :(
suggest why a water bath may be used to heat the mixture in a test tube test:
most organic compounds (specific) flammable
give and explain the equation for the formation of the silver mirror in the presence of an aldehyde in the Tollens’ reagent test:
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)
aldehyde reduces Ag+ to silver ions
give the eqn for and explain the colour change when 1o/2o alcohols are added to acidified potassium dichromate (VI):
orange dichromate (VI) ion is reduced to the green chromium (III) ion
Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O