Microbial Genetics and Biotechnology Overview
1/385
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
386 Terms
Genetics
The study of genes, how they carry information, how information is expressed, and how genes are replicated.
Chromosomes
Structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information.
Genes
Segments of DNA that encode functional products (polypeptides or RNA).
Locus
The location of a gene on a chromosome.
Genome
All the genetic information in a cell.
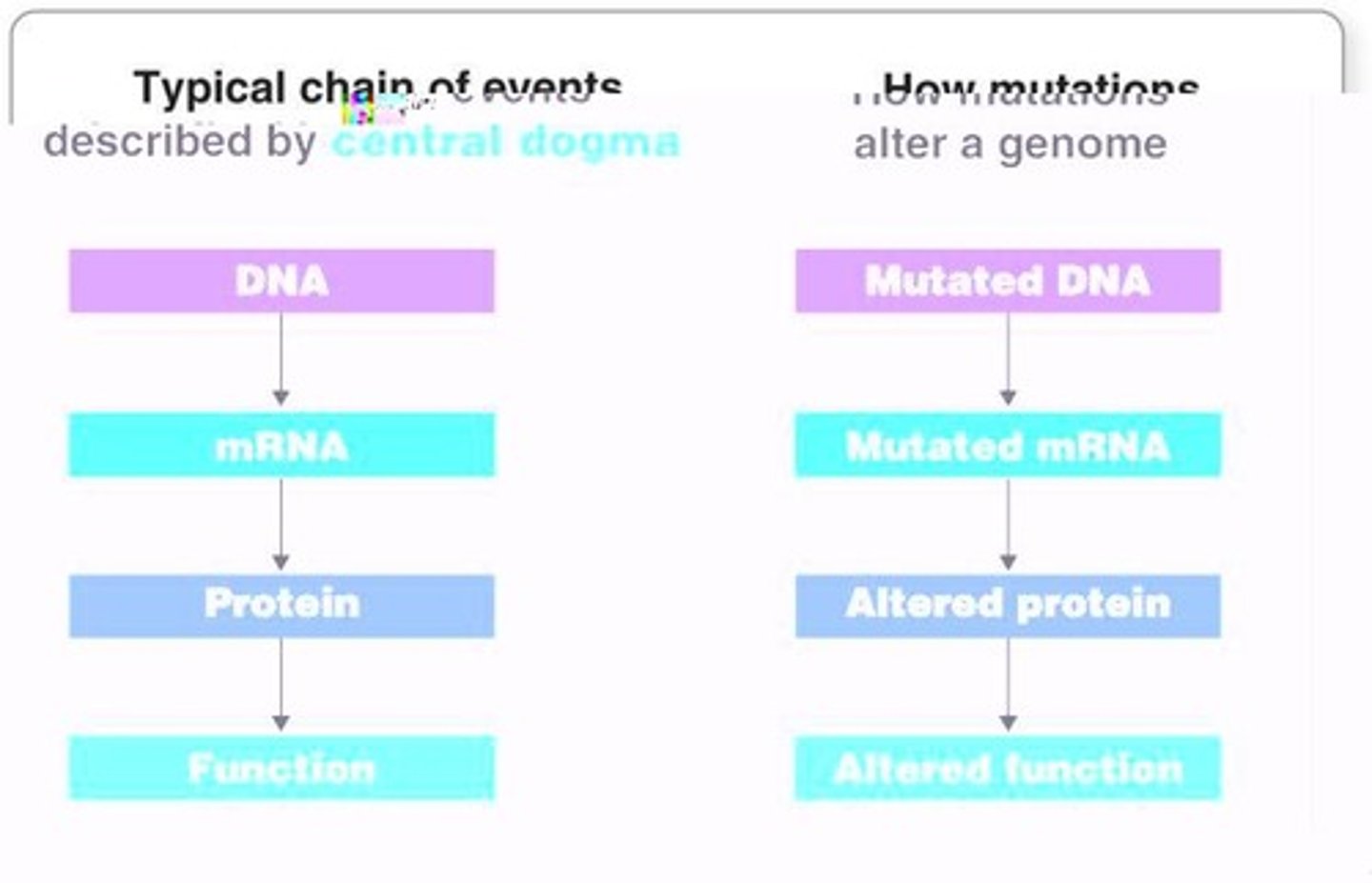
Central Dogma
Explains the flow of information moving from DNA to protein.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
Translation
The process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
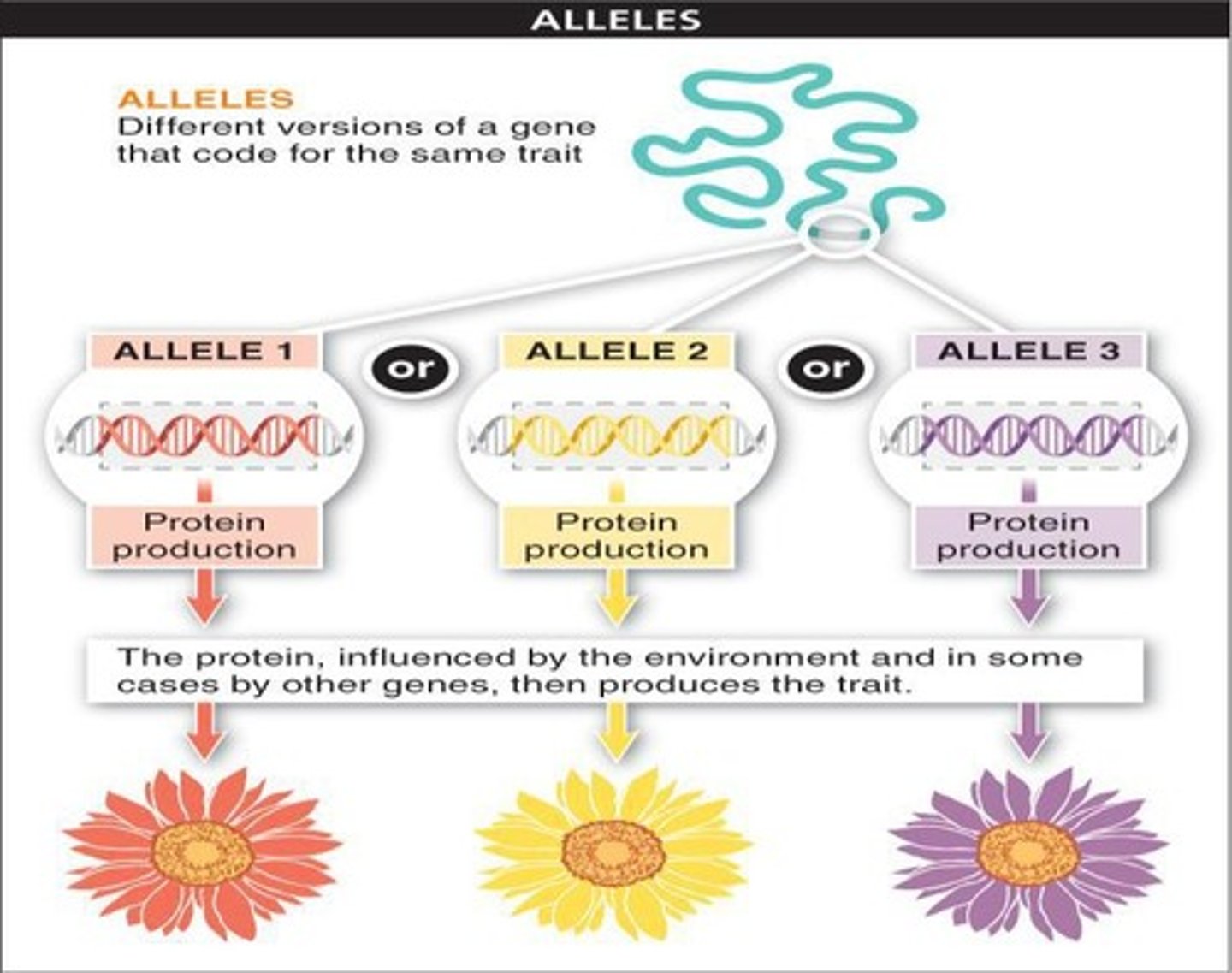
Alleles
Different versions of a gene.
Mutation
A change in a gene that can result in a different protein.
Blood Type Alleles
There are 3 alleles for blood type: A, B, and O.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
A nucleic acid that is a macromolecule storing information.
Nucleotides
Individual units that make up DNA, consisting of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base.
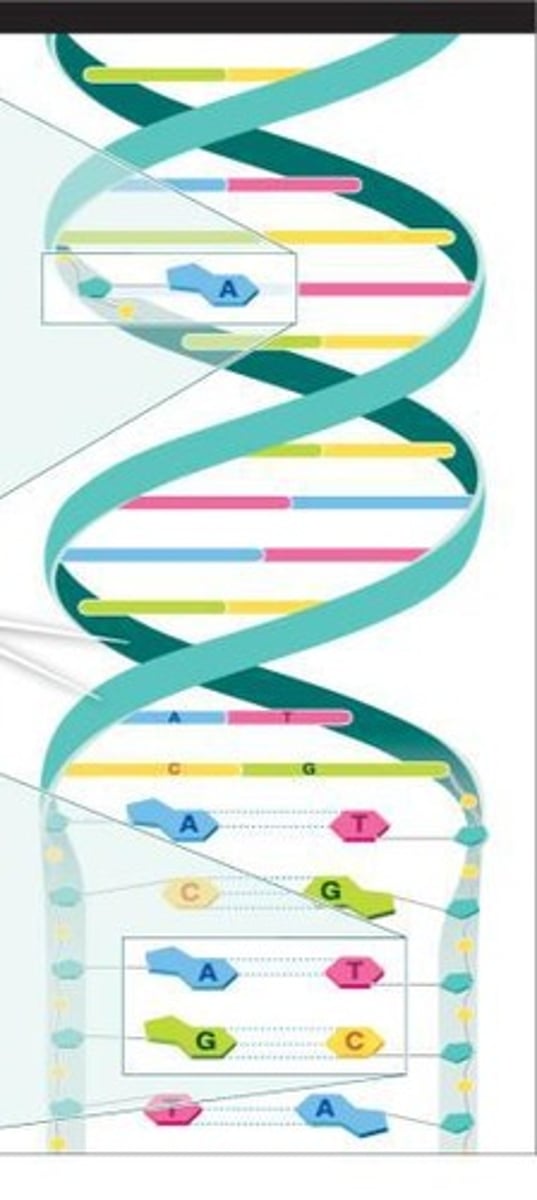
Double Helix
The physical structure of DNA, described as having two distinct strands.
Backbone of DNA
Made from two alternating molecules: a sugar and a phosphate group.
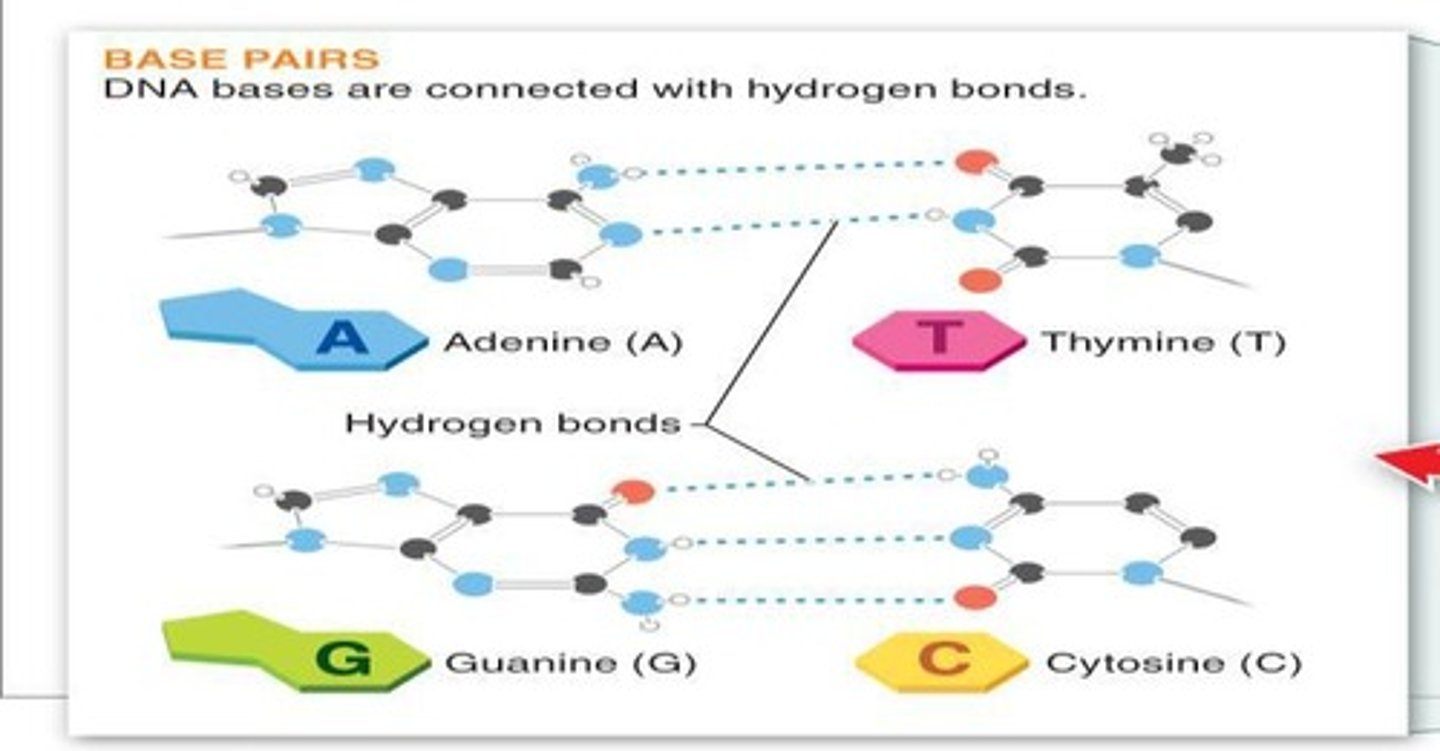
Nitrogen-containing Bases
The four types of bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
Covalent Bond
A strong bond in the backbone of DNA.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds between base pairs in DNA that allow the strands to open and close.
Non-Coding DNA
Regions of DNA that do not code for proteins; more prevalent in eukaryotes.
Introns
Non-coding portions of a gene that are removed during RNA processing.
Exons
Coding portions of a gene that are retained during RNA processing.
Semiconservative Model
The model of DNA replication where each offspring cell receives one copy of the DNA molecule.
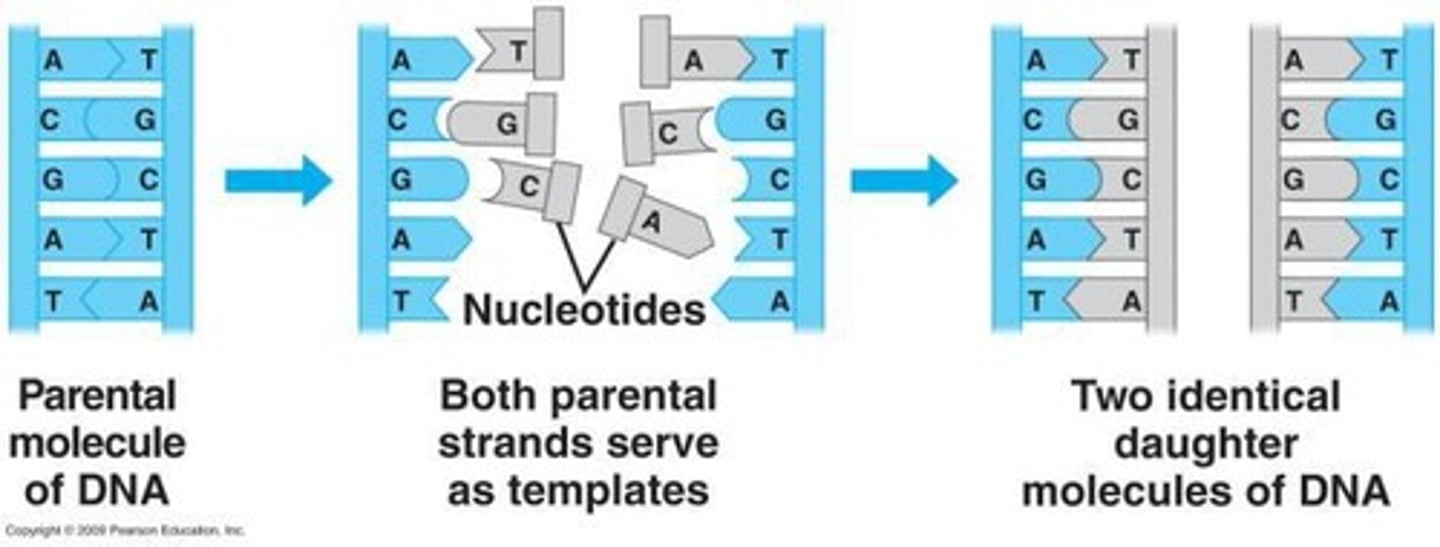
DNA Replication
The process by which DNA makes a copy of itself, typically bidirectional in bacteria.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that proofreads DNA during replication to ensure accuracy.
Transcription
Copy of a gene's base sequence is made.
Translation
The copy is then used to direct polypeptide sequence.
Polypeptide
Occurs in the ribosomes.
RNA Molecule
Ribonucleic acid that is single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries coded information from DNA to ribosomes.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Integral part of ribosomes.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transports amino acids during protein synthesis.
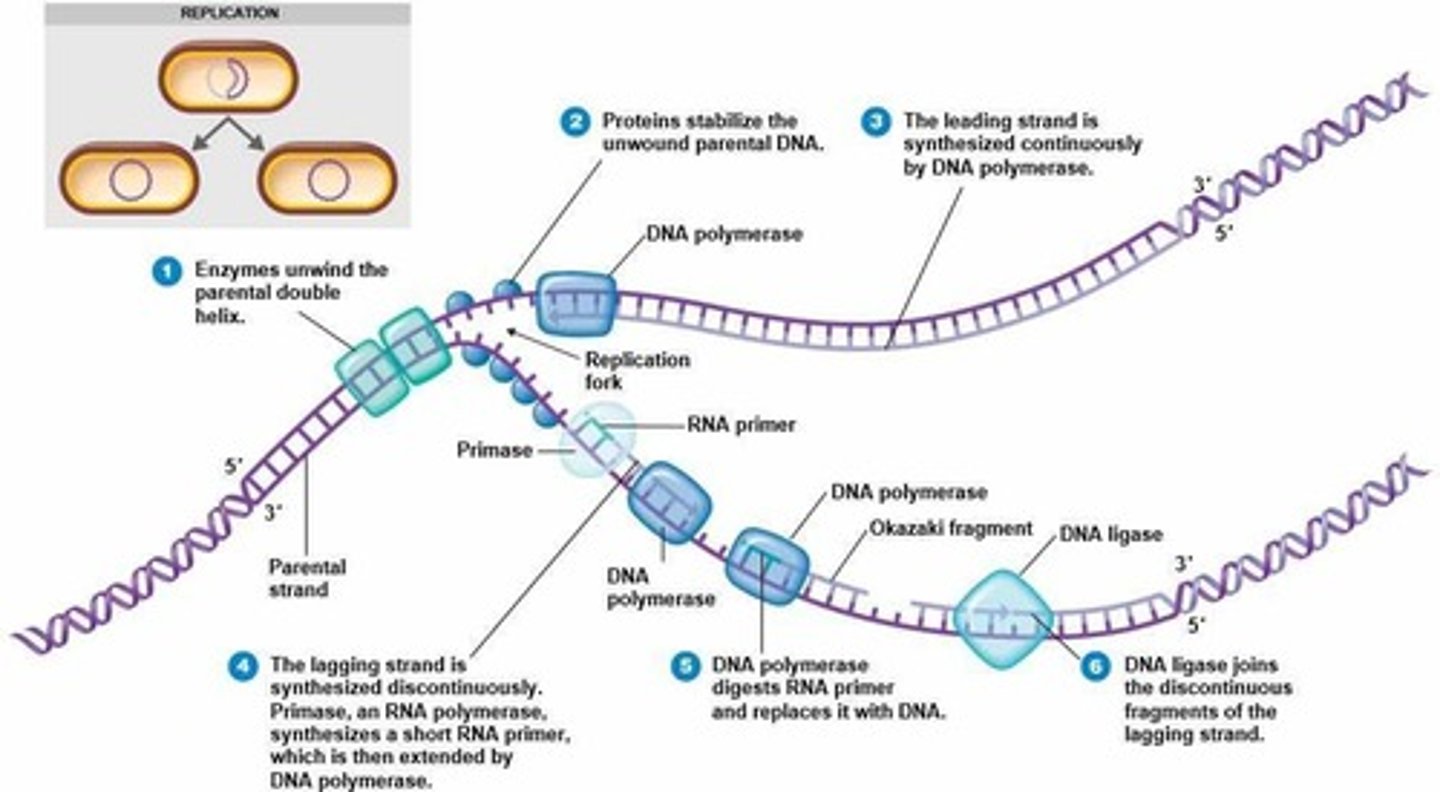
DNA Gyrase
Relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork.
DNA Ligase
Makes covalent bonds to join DNA strands; Okazaki fragments, and new segments in excision repair.
DNA Polymerases
Synthesizes DNA; proofreads and repairs DNA.
Endonucleases
Cut DNA backbone in a strand of DNA; facilitate repair and insertions.
Exonucleases
Cut DNA from an exposed end of DNA; facilitate repair.
Helicase
Unwinds double-stranded DNA.
Methylase
Adds methyl group to selected bases in newly made DNA.
Photolyase
Uses visible light energy to separate UV-induced pyrimidine dimers.
Primase
An RNA polymerase that makes RNA primers from a DNA template.
Ribozyme
RNA enzyme that removes introns and splices exons together.
RNA Polymerase
Copies RNA from a DNA template.
snRNP
RNA-protein complex that removes introns and splices exons together.
Topoisomerase
Relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork; separates DNA circles at the end of DNA replication.
Transposase
Cuts DNA backbone, leaving single-stranded 'sticky ends'.
Leading strand
Template strand where nucleotides are added from 5' to 3' and moves toward replication fork.
Lagging strand
At replication fork, primase adds RNA primer; builds DNA strand in 5' to 3' direction and moves away from replication fork.
Okazaki fragments
Fragments made on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
RNA primer
A starting line required by DNA polymerase to initiate DNA synthesis.
DNA ligase
The connecting enzyme that connects the fragments of DNA.
Nucleoside triphosphate
Building blocks of nucleic acids; when two phosphates are removed, energy is released for DNA synthesis.
Nucleotide
The basic building block of DNA and RNA, produced from nucleoside triphosphate.
DNA Replication
The process by which DNA is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules.
Energy for replication
Supplied by nucleotides; specifically, the hydrolysis of two phosphate groups on ATP.
Pyrophosphate
Released during the removal of a phosphate from triphosphate, providing energy for DNA replication.
Transcription
The synthesis of a complementary mRNA strand from a DNA template.
RNA polymerase
The main enzyme in transcription that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Promoter sequence
The specific DNA sequence where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Terminator sequence
The DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription.
Translation
The process of reading mRNA to synthesize proteins.
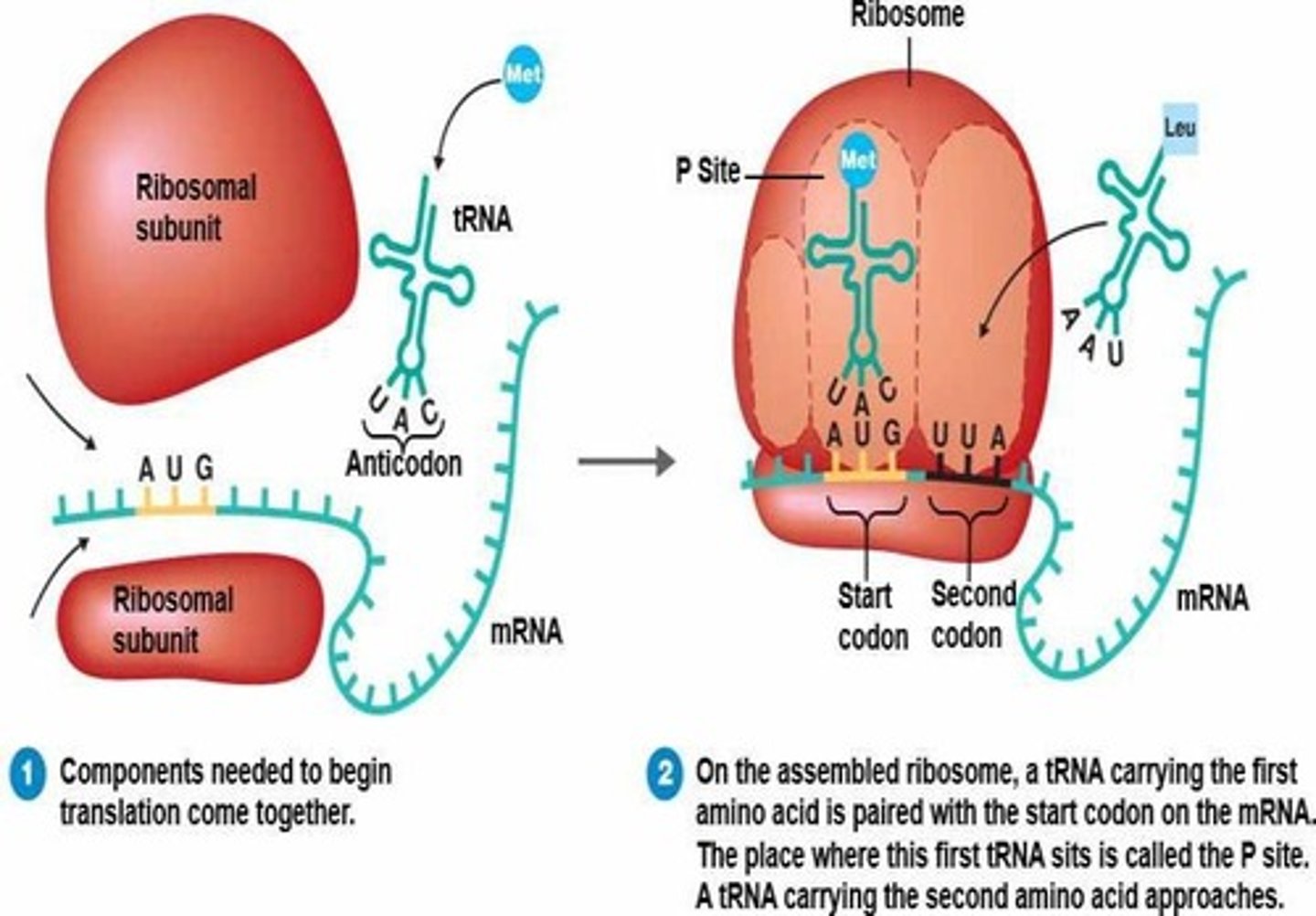
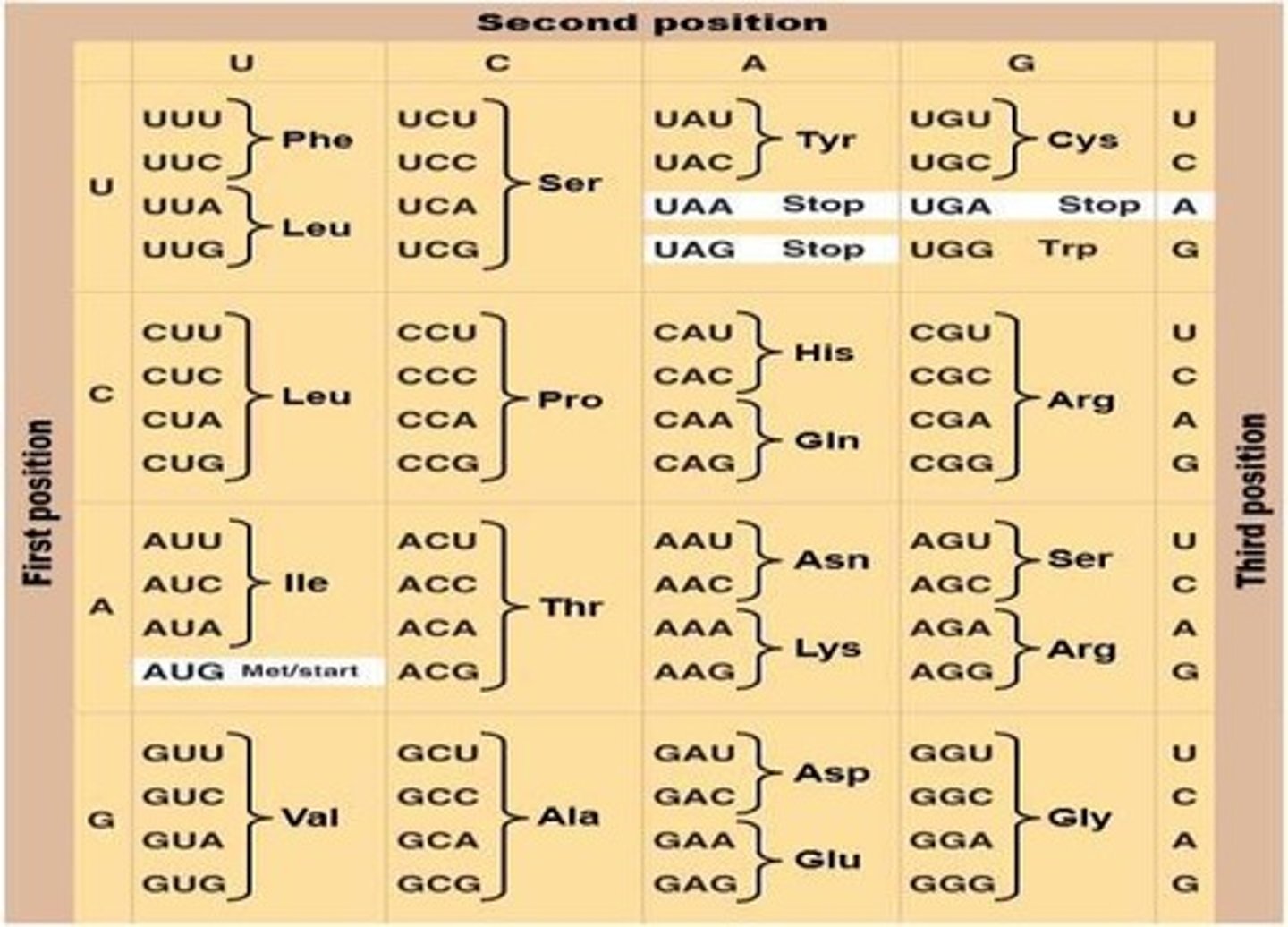
Codons
Groups of three mRNA nucleotides that code for a particular amino acid.
Sense codons
61 codons that encode the 20 amino acids.
Degeneracy
The genetic code property where multiple codons can encode the same amino acid.
Start codon
The codon AUG that signals the beginning of translation.
Nonsense codons
Codons that signal the termination of translation: UAA, UAG, UGA.
tRNA
Molecules that transport amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
Anticodon
A sequence on tRNA that base-pairs with the corresponding codon on mRNA.
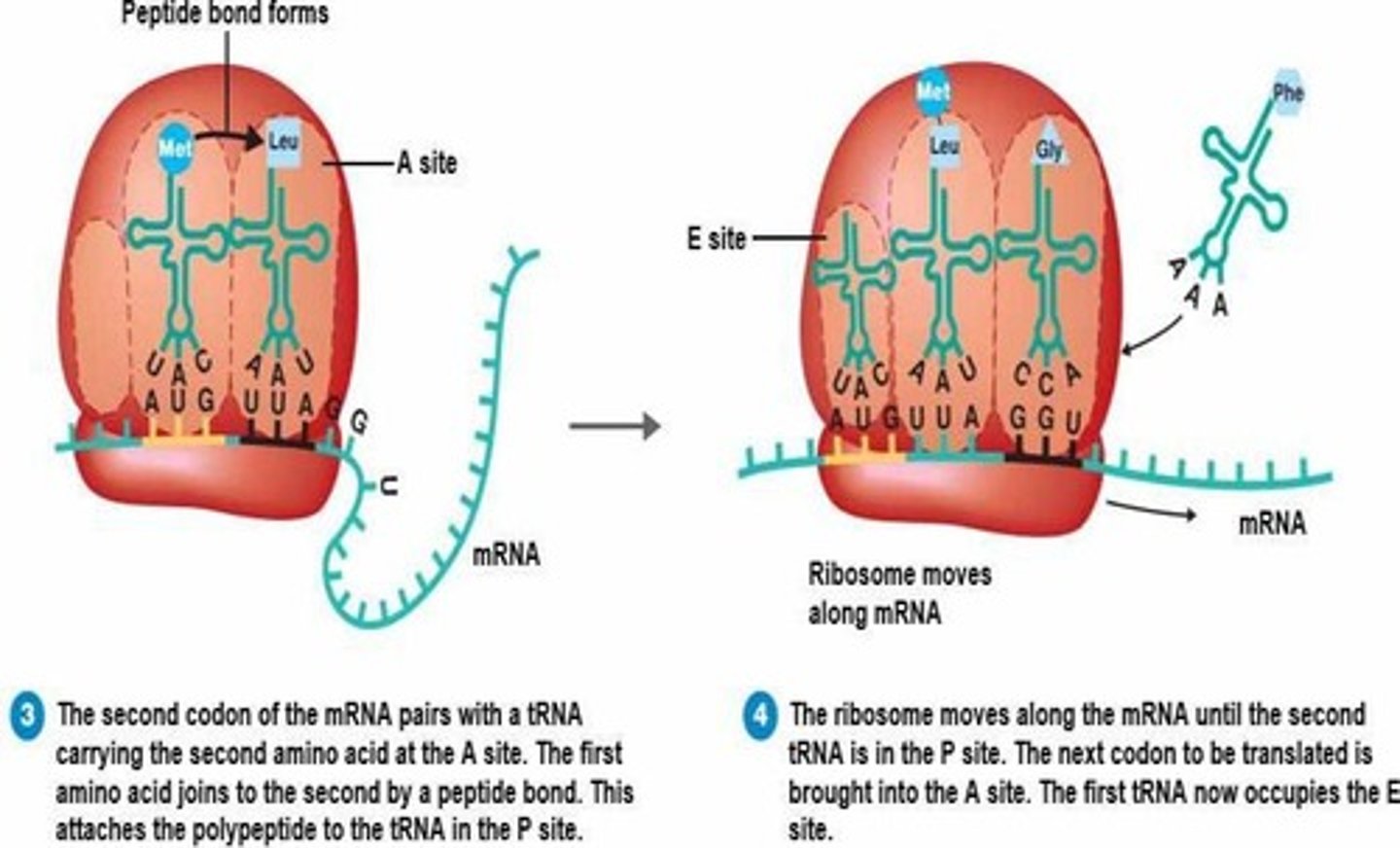
Peptide bonds
The bonds that join amino acids together in a protein.
Ribosome
The cellular structure where translation occurs.
mRNA
Messenger RNA that carries genetic information from DNA for protein synthesis.
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins, brought to the ribosome by tRNA.
5' to 3' direction
The direction in which RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA during transcription.
Gene replication
The combined processes of transcription and translation.
Anticodon
The reading device that corresponds to the codon of the mRNA molecule.
tRNA
Transfer RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
Peptide Bonds
Individual bonds that link amino acids together in a protein.
P Site
The site in the ribosome where the first tRNA molecule enters.
A Site
The site in the ribosome where other tRNA molecules enter.
E Site
The exit site where uncharged tRNA is released from the ribosome.
Start Codon
The codon that initiates translation, typically AUG.
Stop Codon
The codon that signals the end of translation.
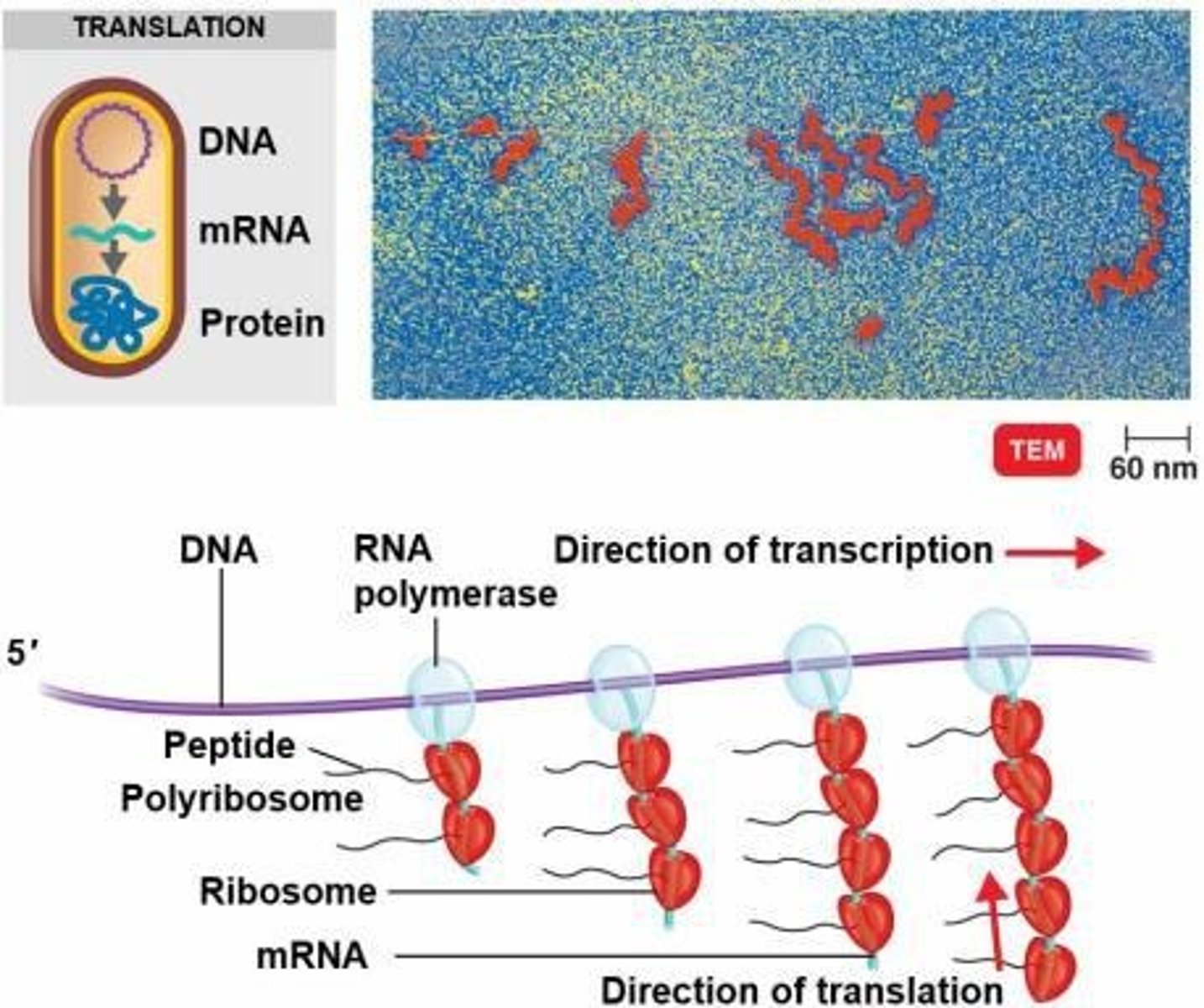
Simultaneous Transcription and Translation
The process in bacteria where translation begins before transcription is complete.
Eukaryotic Transcription
Occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
Eukaryotic Translation
Occurs in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Exons
Regions of DNA that code for proteins.
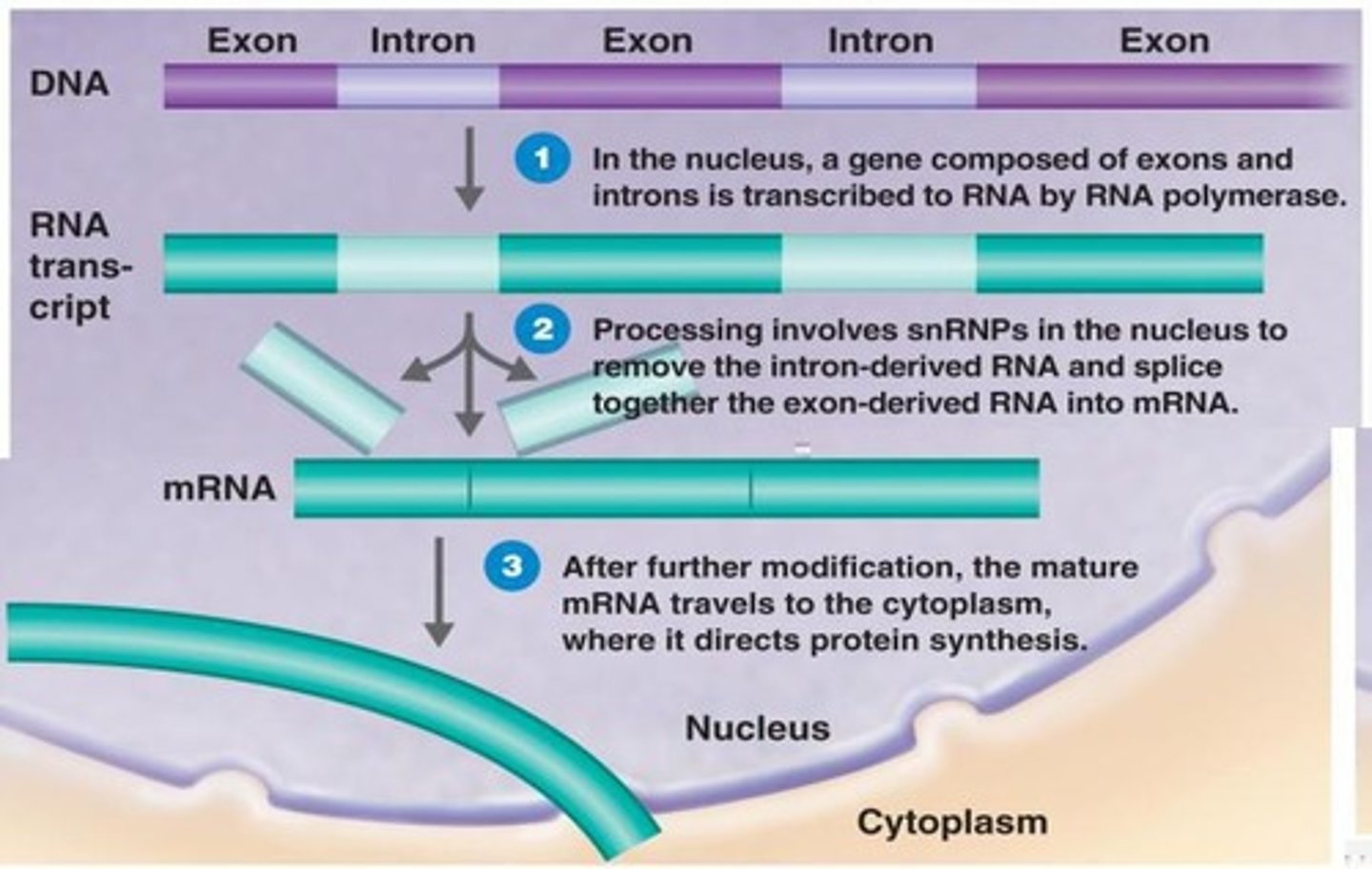
Introns
Regions of DNA that do not code for proteins.
snRNPs
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins that remove introns and splice exons together.
Constitutive Genes
Genes that are expressed at a fixed rate.
Inducible Genes
Genes that are expressed only when needed.
Repressible Genes
Genes that are typically on but can be turned off.
Repression
The process that inhibits gene expression and decreases enzyme synthesis.
Induction
The process that turns on gene expression.
Repressors
Proteins that block transcription.
Default Position of a Repressible Gene
Typically on, but can be turned off.
Default Position of an Inducible Gene
Typically off, but can be turned on.
Inducible operon
Structural genes are not transcribed unless an inducer is present.
Repressor
A protein that binds to the operator, preventing transcription.
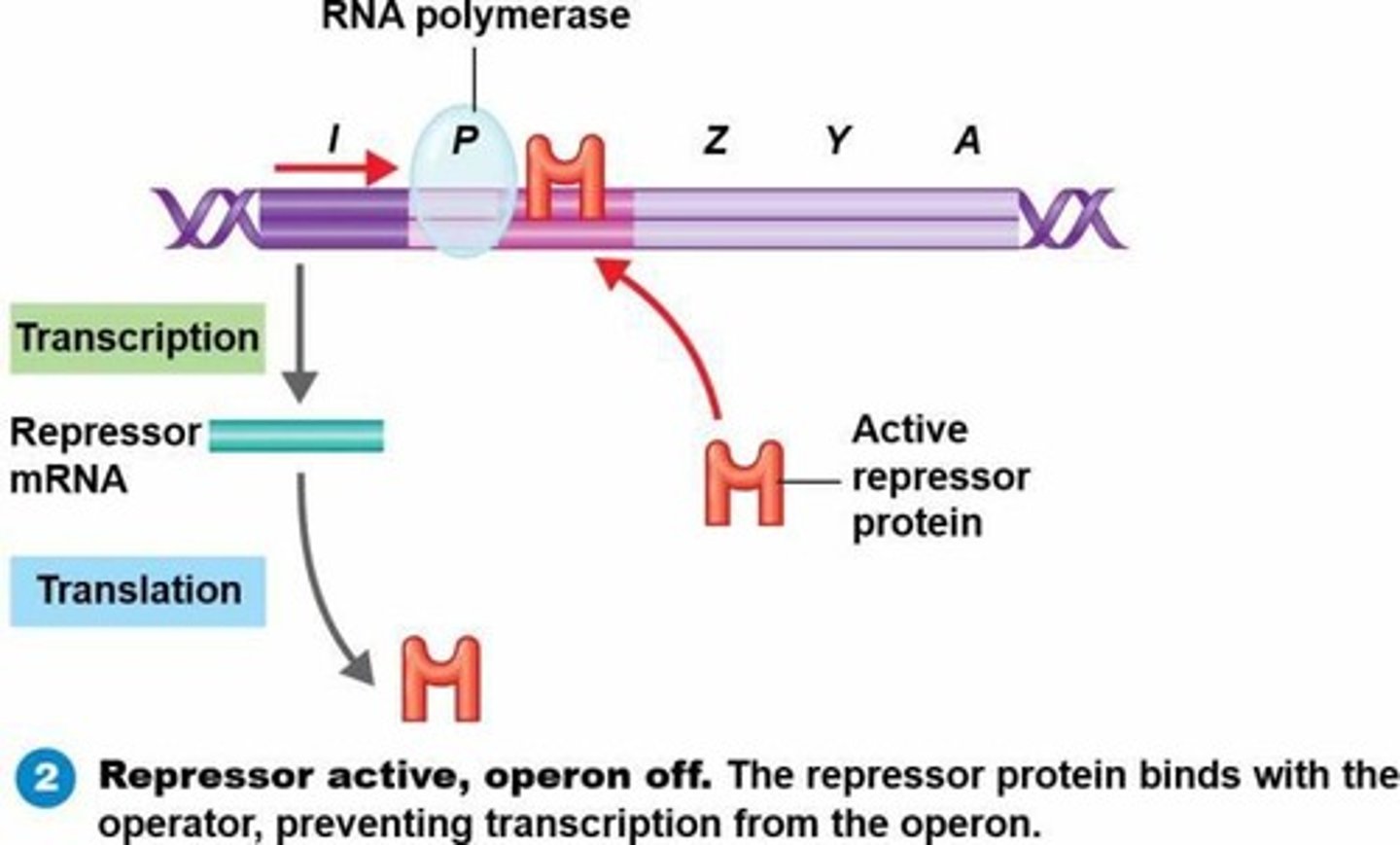
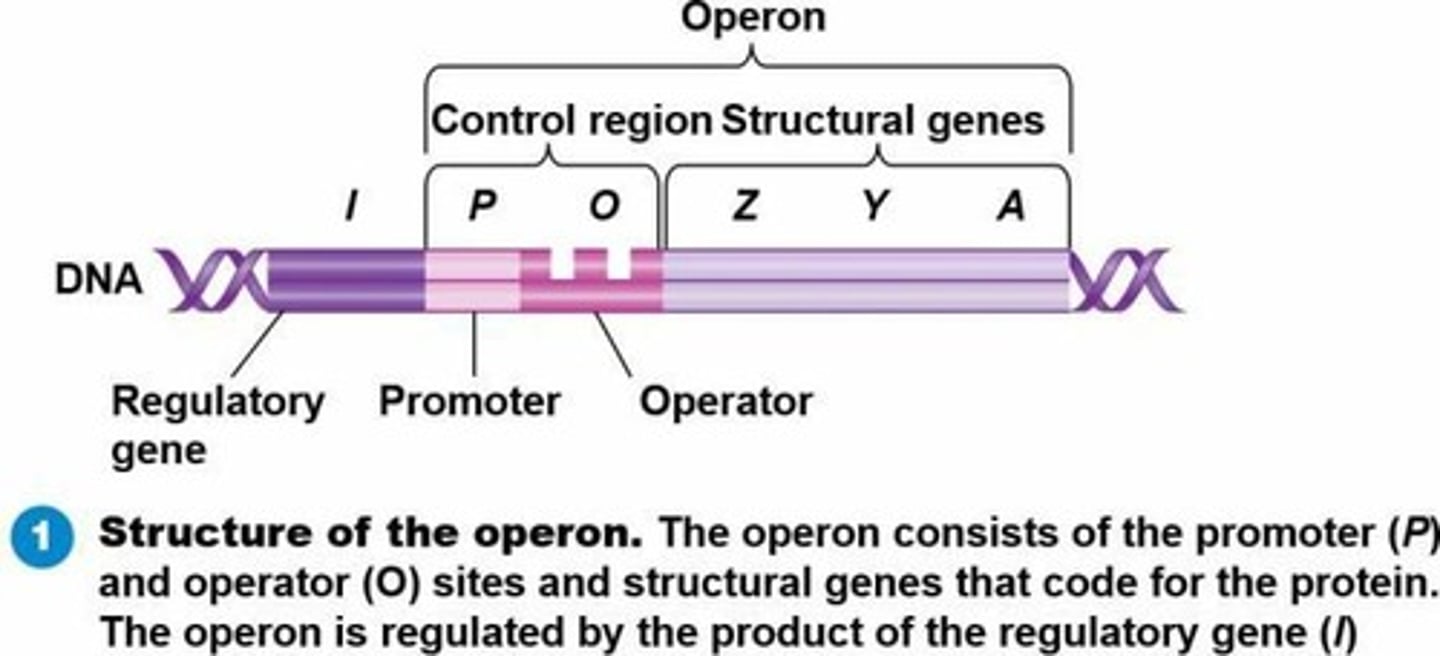
Operator
Segment of DNA that controls transcription of structural genes.
Promoter
Segment of DNA where RNA polymerase initiates transcription of structural genes.
Operon
Set of operator and promoter sites and the structural genes they control.