BIOL 2173 Human Physiology Final
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
What is the function of blood?
Mass transport from one part of the body to another
What are the functions of plasma proteins?
- blood clotting
- defense of foreign invaders
- carriers for steroid hormones, cholesterol, drugs and certain ions as a Fe2+
- Some act as hormones or extracellular enzymes
What type of cells increases during parasitic, viral, and bacterial infection?
Parasitic: eosinophils
Bacterial: neutrophils & monocytes
Viral: lymphocytes
What is leukemia?
abnormal growth and development of WBCs
What is thrombocytopenia?
decreased platelets
What is anemia?
decreased RBCs
What is neutropenia?
few WBCs
What is thrombopoiesis?
growth and maturation of megakariocytes (parent cell of platelets)
What is leukopoiesis?
production and development of leukocytes
What is erythropoiesis?
regulation of erythrocyte production
What are the functions of the different cytokines involved in hematopoiesis?
Erythropoietin: produced in kidneys, influences RBCs
Thrombopoietin: produced in liver, influences megakaryocytes
Colony-stimulating factors, interleukins, stem cell factor: produced in endothelium and fibroblasts of bone marrow, leukocytes. influences all types of blood cells & mobilizes hematopoietic stem cells
What is Hemostasis, and what steps are involved in this process?
- process of keeping blood within a damaged blood vessel (opposite of hemorrhage)
1) vasoconstriction (decreased blood flow and pressure)
2) temporary blockage by a platelet plug (platelet adhesion)
3) coagulation (seals the hole until tissues are repaired)
What is the function of coagulation?
seal the hole until tissues are repaired
What are the pathways involved in coagulation?
intrinsic pathway: damage tissue exposes collagen
extrinsic pathway: damage tissue exposes tissue factor III
What is fibrinolysis?
breaking down of a clot in the body to maintain healthy blood flow and prevent blockages. can be natural or induced by meds/conditions.
What is the role of thrombin in the common pathway of coagulation?
fibrin production
What initiates the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway of coagulation?
intrinsic: collagen
extrinsic: tissue thromboplastin
role of vWF (VonWillebrand Factor) in coagulation:
Regulates level of factor VIII
Vitamin K role in Coagulation:
Needed for synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, X
role of Fibrinogen and Fibrin in coagulation:
From insoluble fibers that stabilize platelet plug.
What is the function of calcium ions in the coagulation cascade?
factor IV, required for several steps of coagulation cascade
What are the functions of heparin
block factors IX, X, XI, and XII
What are the functions of prostacyclin and NO?
eiconasoid that blocks platelets adhesion (normal endothelial cells)
What are the functions of RBCs?
facilitate oxygen transport from the lungs to cells and carbon dioxide from the calls to lungs
What are the functions of platelets?
blood clotting
What causes hemophilia?
Factor VIII deficiency
What is Immunity?
the body's ability to protect itself against infectious diseases
basophils & mast cells functions
release chemicals that mediate inflammation and allergic responses (histamine)
neutrophils function
ingest and destroy invaders (fever causing pyrogens)
eosinophils functions
destroy invaders, particularly antibody-coated parasites
monocytes & macrophages function
ingest and destroy invaders. antigen presentation (remove old RBCs dead neutrophils)
lymphocytes & plasma cells function
specific responses to invaders, including antibody production
dendric cells function
recognize pathogens and activate other immune cells by antigen presentation
What are the two components of the immune system?
1.
lymphoid tissues
2. various types of immune cells (chemical signals that coordinate responses)
What are the functions of the spleen in an immune response?
- secondary lymphoid tissue
- create an open framework that supports the blood vessels and lymphoid tissue
What are the functions of the lymph nodes in an immune response?
filter lymph fluid, trap foreign substances, and initiate immune responses by activating and deploying immune cells to fight off infections
What are the functions of the thymus in an immune response?
- primary lymphoid tissue
- produce T lymphocytes & peptides (thymosin, thymopoietin, thymulin)
What are the two lines of defense in our body?
1. physical chemical and mechanical barriers
2. Internal Immune response
What are antigens and antibodies?
antigen: substances that trigger immune response: a toxin or other foreign substance
antibodies: protein secreted by certain immune cells, bind antigens and make them more visible to the immune system
What is innate immunity?
Innate:
- non-specific
- responds to a range of signals
- present from birth
- immediate response
What is acquired immunity?
- specific
- attacks a specific pathogen or antigen
- slower but stronger response
- cell-mediated (cell contact- cytotoxic lymphocytes)
- humoral immunity (antibodies)
What are allergies?
an inflammatory response to a nonpathogenic antigen
What are the responses of the immune system against allergens?
massive release of histamine and other cytokines causes vasodilation, circulatory collapse, and bronchoconstriction.
What are the functions of T and B lymphocytes?
T lymphocytes: specialized to defend against intracellular pathogens.
B lymphocytes: differentiated in to specialized cells that secrete antibodies
What are the functions of the different antibodies (immunoglobulins Ig) in acquired immunity?
IgG: give infants immunity.
• IgA: external secretions, (saliva, tears, intestinal and bronchial mucus,breast milk) and bind to pathogen and flag them for phagocytosis.
• IgEs: target gut parasites and are associated with allergic reactions.
• IgM: react to red blood antigens.
• IgD: surface of B lymphocytes
What is an autoimmune disease?
- immune system does not normally react against "Self" antigens, in a process called self-tolerance
- autoimmune diseases occur when self-tolerance fails
- autoimmune diseases are usually restricted to specific tissues or organs
What is the function of the membrane attack complex?
forms pores in the plasma membrane of pathogens or targeted cells, leading to osmolysis
What is a cytokine and what types of cytokines are produced in response to viral infections?
- peptides or proteins released from one cell that affect the growth or activity of another cell.
- erythropoietin: kidney cells, influence growth of red blood cells
- thrombopoietin: liver, influences megakaryocytes
- Colony-stimulating factors, interleukins, stem cell factor: endothelium and fibroblasts of bone marrow, leukocytes. influences all types of blood cells, mobilizes hematopoietic stem cells
What are PRRs, and PAMs?
PRR: pattern recognition receptors. Receptors on immune cells that recognize PAMs
PAMP: pathogen-associated molecular pattern. Molecular structures found on pathogens recognized by PRRs
(combined they kill or ingest microorganisms)
What are the functions antibodies
- antigen clumping
- inactivation of bacterial toxins
- ac as opsonins to tag antigens for phagocytosis
- trigger degranulation
- activate complement
- activate B lymphocytes
What are the functions of interferons
Interferon α and β promote synthesis of antiviral proteins.
Interferon γ, activates macrophages and other immune cells.
What are the functions of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) proteins
Class I: found on all nucleated cells of the body. recognized by cytotoxic T cells
Class II: found only on antigen-presenting cells (macrophages or dendritic cells). recognized by helper T cells
What are the functions of helper T cells (TH) and cytotoxic T cells (Tc)?
TH: regulate other immune cells
Tc: attach and destroy virus infected cells
What is inflammation? What are the roles of inflammation in fighting infections?
- the hallmark reaction of innate immunity
1. attracting immune cells and chemical mediators to the site
2. producing a physical barrier (retard the spread of infection)
3. promoting tissue repair (once that the infection is controlled)
When do primary and secondary immune responses occur?
The primary immune response occurs on first exposure to an antigen
secondary immune response occurs upon re-exposure to the same antigen
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
1. Exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood.
2. Homeostatic regulation of body pH(lungs can alter body pH by selectively retaining or excretingCO2).
3. Protection from inhaled pathogens and irritating substances.
4. Vocalization (air moving across the vocal cords creates vibrations).
What is the function of the mucociliary escalator?
move mucus layer toward pharynx, removing trapped pathogens and particulate matter
Tidal Volume
volume of air that moved during respiratory cycle
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
Volume you inspire above the tidal volume
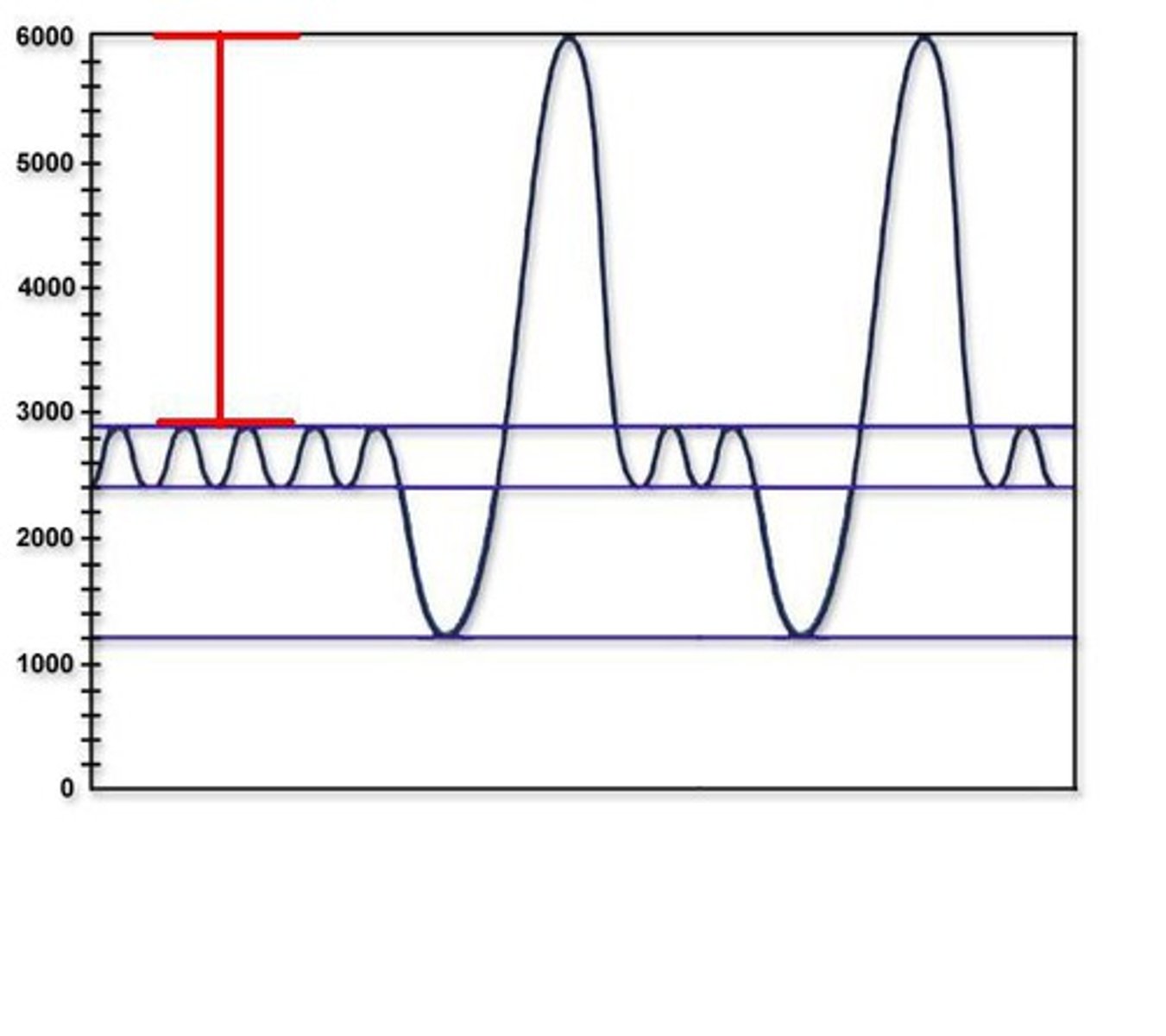
Expiratory Reserve Volume
the amount of air forcefully exhaled after the end of a normal respiration
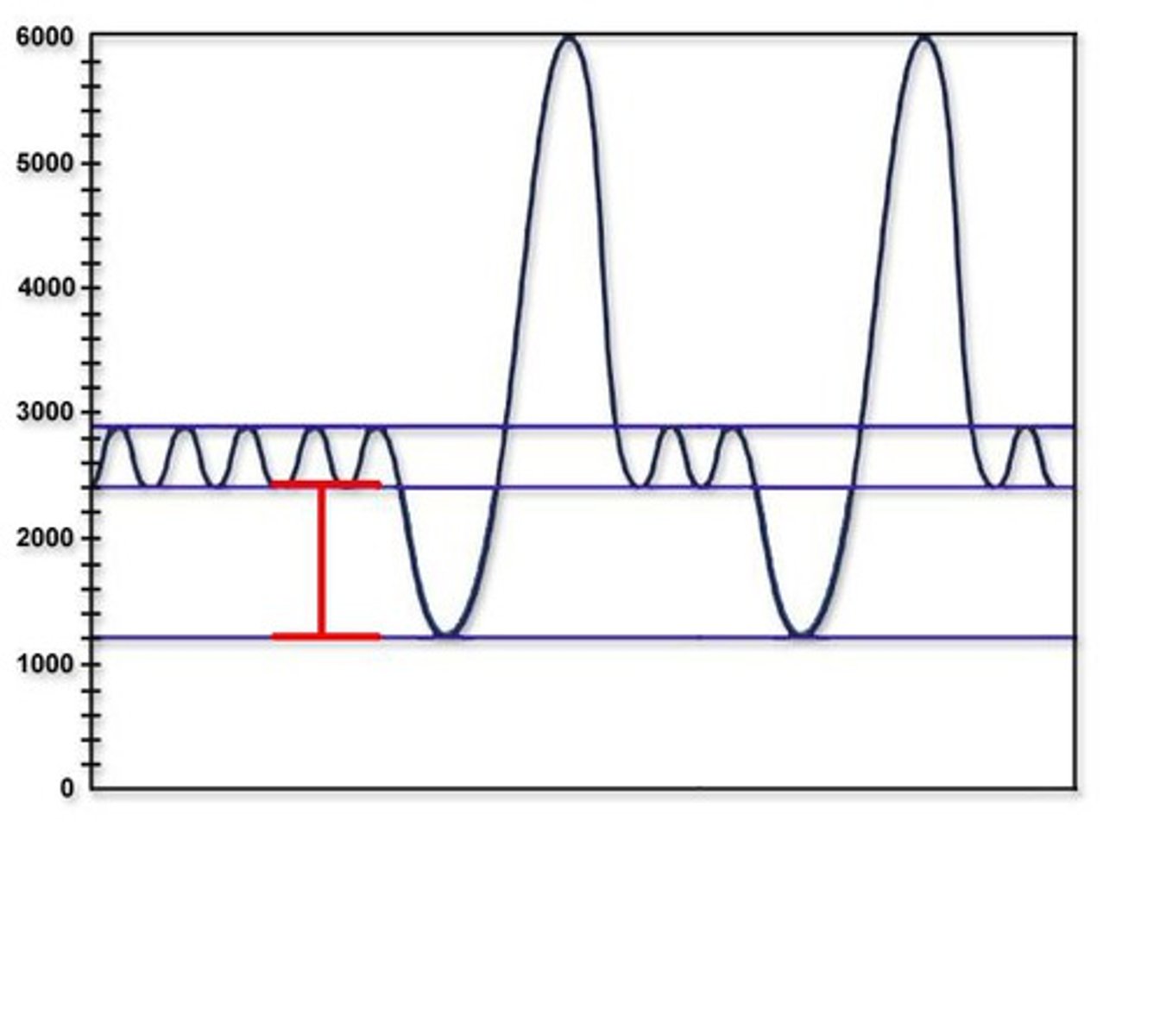
Residual Reserve
volume of air in the respiratory system after maximal exhalation
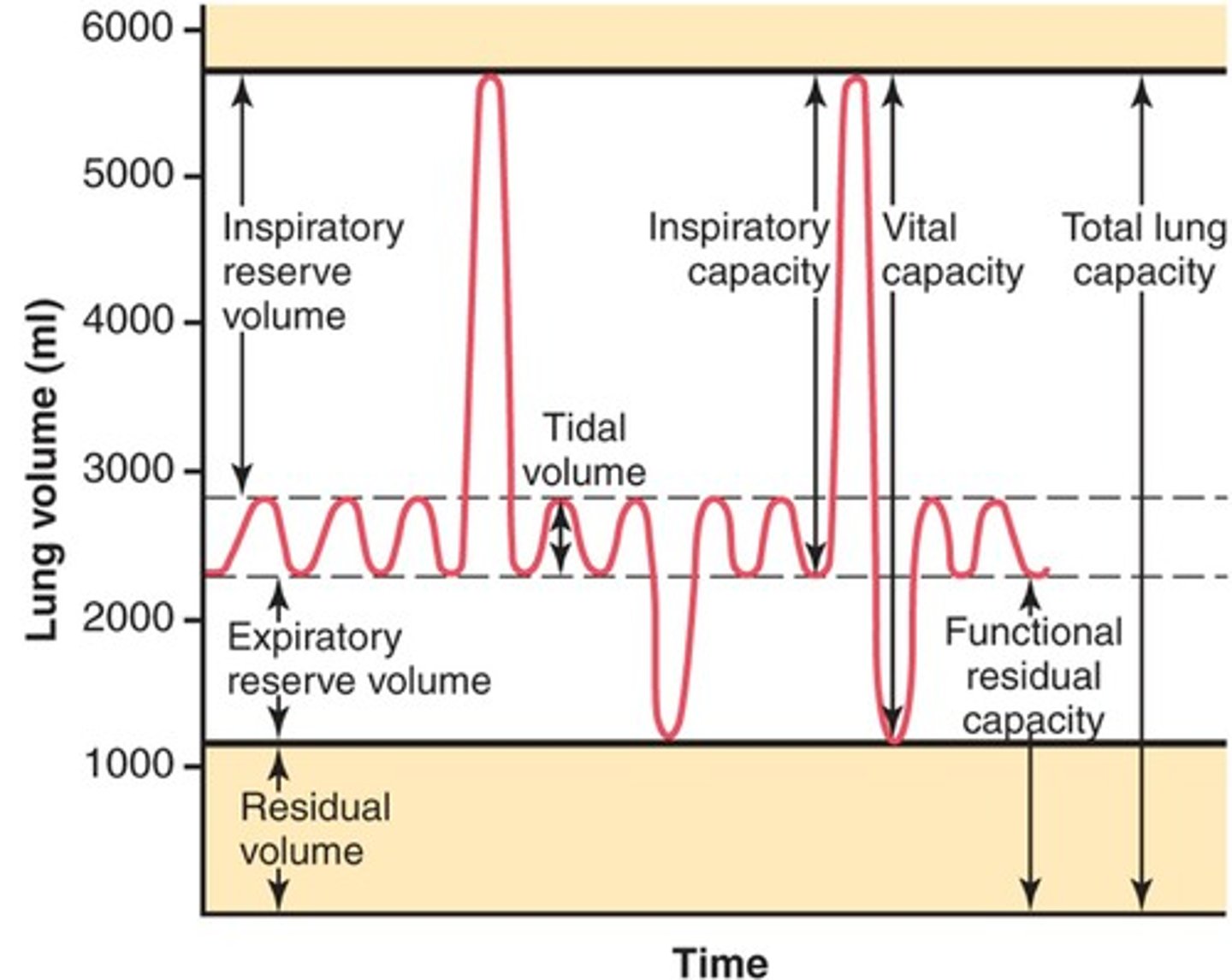
What are lung capacities?
the sum of two or more lung volumes
vital capacity
- maximum amount of air that can be voluntarily moved into or out of the respiratory system with one breath
- IRV + ERV + TV
total lung capacity
VC + residual volume
inspiratory capacity
TV + IRV
Functional Residual Capacity
ERV + RV
What is the function of ventilation?
requires that lungs move in association with the expansion and relaxation of the thorax
What are the functions of Type I and II alveolar cells?
Type 1: exchange gases CO2 and O2
Type 2: produce surfactant (molecules that disrupt cohesive forces between water molecules on the alveolar surface)
What is the function of glomus cells in respiration?
release neurotransmitter when PO2 decreases
oxyhemoglobin
the amount of oxygen binding to Hemoglobin
carbaminohemoglobin
carbon dioxide bound to hemoglobin
hypoxia
- Low oxygen
- can by caused by: emphysema, fibrotic lung disease, pulmonary edema, asthma
hypercapnia
too much CO2 in blood
pneumothorax
results in collapsed lung that cannot function normally
dyspnea
difficulty breathing (a subjective feeling sometimes described as "air hunger" )
hyperpnea
increased respiratory rate and/or volume in response to increased metabolism
hyperventilation
increased respiratory rate and/or volume without increased metabolism
compliance
ability of the lung to stretch
elastance
ability to resist being deformed
apnea
cessation of breathing
eupnea
normal quiet breathing
What is the function of surfactants?
molecules that disrupt cohesive forces between water molecules on the alveolar surface
Describe the Bohr effect.
A shift in the Hb saturation curve from a change of pH
How is carbon dioxide transported by red blood cells?
Binding to Hb once oxygen leaves
Know the normal ventilation values in Pulmonary medicine.
Total pulmonary: 6 L/min
Total alveolar: 4.2 L/min
Max voluntary: 125-170 L/min
Respiration: 12-20 breaths/min
What is alveolar ventilation? Know how to calculate it.
- volume of fresh air that reaches the alveoli each minute
ventilation rate x (tidal volume - dead space volume)
What pathologies are associated with problems of oxygen diffusion?
- emphysema: destruction of alveoli (less surface area for gas exchange)
-fibrotic lunch disease: thickened alveolar membrane slows gas exchange. loss of of lung capacity
- pulmonary edema: fluid in interstitial space increases diffusion distance
- Asthma: increased airway resistance decreases alveolar ventilation
How do pH, PCO2, DPG, temperature, and Hb structure affect the affinity of hemoglobin foroxygen?
- pH (Bohr Effect): Lower pH decreases affinity.- PCO₂: Higher CO₂ decreases affinity.- DPG (2,3-Diphosphoglycerate): Higher levels decrease affinity.- Temperature: Higher temperature decreases affinity.- Hb Structure: Variants like fetal hemoglobin (HbF) have higher affinity.
What are the functions of the VRG, DRG, and pre-Bötzinger complex?
VRG (of medulla): contains pre-botzinger complex. nerve fibers keep upper airways open
PRG (pons): coordinate smooth respiratory system
Pre-botzinger complex: neurons that act as a pacemaker of the respiratory rhythm
What are the functions of peripheral and central respiratory chemoreceptors?
Peripheral: located in carotid and aortic arteries sense changes of PO2, pH, and PCO2
Central:
respond to changes of CO2 in CSF. receptors lie on the ventral surface of the medulla close to neurons involve in the respiratory control
What is the function of the Hering-Breuer inflation reflex in humans?
plays a role in limiting ventilation volume
What are the functions of the kidneys?
1. Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure.
2. Regulation of osmolarity. Blood osmolarity 290 mOsM.
3. Maintenance of ion balance. Balancing dietary intake with urinary loss
.4. Homeostatic regulation of pH. If ECF becomes acidic, the kidneys remove H+ and conserveHCO3-
5. Excretion of wastes
6. Production of cytokines Kidney cells synthesize erythropoietin, renin.
What is the function of nephrons
filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion
What are the functions of the proximal tubule?
Isosmotic reabsorption of organic nutrients, ions, and water. Secretion of metabolites and xenobiotic molecules such as penicillin.
What are the functions of renal corpuscle
filtration of mostly protein-free plasma from the capillaries into the capsule
What are the functions of loop of Henle?
reabsorption of ions in excess of water to create dilute fluid in the lumen. countercurrent arrangements contributes to concentrated interstitial fluid in the renal medulla
What are the functions of distal nephron?
regulated reabsorption of ions and water for salt and water balance and pH homeostasis
Describe the following processes that occur in the nephron: excretion, filtration, reabsorption, and secretion
excretion: out and away
filtration: of plasma in kidney tubule is first step in urine formation
reabsorption: allows kidneys to selectively return ions and water to the plasma
secretion: separate something from its source
Describe the three barriers involved with the filtration of plasma in the renal capsule.
- Endothelial Cells: Fenestrated capillaries.
- Basement Membrane: Prevents large molecules from passing.
- Podocytes: Specialized cells with filtration slits.
What is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)? and what conditions would cause an increase and decrease in GFR?
- the volume of fluid (plasma) that filters into bowmans capsule per unit time
- increase: increased resistance of efferent arteriole
- decrease: vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole