ESCI 274 Lecture 10 + 11 Mental Health & Psychology + Citizen Science
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 11 + 12 in class
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Links between Nature & Mental Health
* Nurtured by nature
* Environment: A natural remedy for mental ill-health
* Mental Health Benefits of the outdoors
* Research suggests that mood disorders can be lifted by spending more time outdoors
* Environment: A natural remedy for mental ill-health
* Mental Health Benefits of the outdoors
* Research suggests that mood disorders can be lifted by spending more time outdoors
2
New cards
Climate & Mental Health
* Medical & Physical Health: Changes in fitness and activity level, heat-related illness, allergies, increased exposure to waterborne and vector-borne vector
* Mental Health: stress, anxiety, depression, grief, sense of loss, strains on social relationships, substance abuse, PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder)
* Community Health: increased interpersonal aggression, increased violence and crime, increased social instability, decreased community cohesion.
* Mental Health: stress, anxiety, depression, grief, sense of loss, strains on social relationships, substance abuse, PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder)
* Community Health: increased interpersonal aggression, increased violence and crime, increased social instability, decreased community cohesion.
3
New cards
Eco-Anxiety (12)
* Hopelessness
* Anger/Frustration
* Existential dread
* Guilt or Shame about your carbon footprint
* PTSD after experiencing a climate disaster
* Depression, Anxiety, Panic
* Grief & Sadness
* Obsessive thoughts about climate
* Sleep problems
* Apatite changes
* Difficulty Concentrating
* Direct mental health consequences of climate change
* Anger/Frustration
* Existential dread
* Guilt or Shame about your carbon footprint
* PTSD after experiencing a climate disaster
* Depression, Anxiety, Panic
* Grief & Sadness
* Obsessive thoughts about climate
* Sleep problems
* Apatite changes
* Difficulty Concentrating
* Direct mental health consequences of climate change
4
New cards
Today’s Generation vs Natural Disasters
Today’s kids will have to live through 3x more climate disasters than their grandparents
5
New cards
Types of Climate related disasters
* Floods, Wildfires, Dam collapses, heat waves, droughts.
* Distresses can persist for years, especially among vulnerable groups
* Example: Hurricane Katrina (Category 5, 2005), Fort McMurray Wildfire (2016)
* Distresses can persist for years, especially among vulnerable groups
* Example: Hurricane Katrina (Category 5, 2005), Fort McMurray Wildfire (2016)
6
New cards
Risk Factors
* Low social capital or support
* Physical injury
* Property loss
* Witnessing others with illness or injury or in pain or dying
* Loss of family
* Displacement
* Pre-existing history of psychiatric illness
* Children may be at special risk
* Physical injury
* Property loss
* Witnessing others with illness or injury or in pain or dying
* Loss of family
* Displacement
* Pre-existing history of psychiatric illness
* Children may be at special risk
7
New cards
Protective Strategies
* Strengthen social support before/after disasters
* Post disaster mental health services
* Prompt insurance compensation for loss
\
* Taking action can maintain some semblance of control
* Post disaster mental health services
* Prompt insurance compensation for loss
\
* Taking action can maintain some semblance of control
8
New cards
Indirect mental health impacts of climate change
* Climate change degrades environments
* Causes a sense of loss, stress, mental distress
* More pronounced in Arctic
* Indigenous peoples place high cultural value on place attachment
* Causes a sense of loss, stress, mental distress
* More pronounced in Arctic
* Indigenous peoples place high cultural value on place attachment
9
New cards
Impacts of Displacement
* Climate change degrades environments
* Populations can be forced to relocate - acute disasters, scarce resources
* Most well documental is droughts
* Could displace 1.2 billion people by 2050 reports warn
* Populations can be forced to relocate - acute disasters, scarce resources
* Most well documental is droughts
* Could displace 1.2 billion people by 2050 reports warn
10
New cards
War, Refugees, Population Dislocation
* Climate related disasters
* Overwhelmed by undernutrition and stress
* Refugees face public health threats, violence, sexual abuse, and mental illness
A growing body of evidence links climate change and violence - instability often results in conflict
* Overwhelmed by undernutrition and stress
* Refugees face public health threats, violence, sexual abuse, and mental illness
A growing body of evidence links climate change and violence - instability often results in conflict
11
New cards
Climate “Refugees”
“We are on the cusp of a major environmental change that is going to redistribute populations on a planetary scale”
\
Only recently are there protections for climate refugees
\
Only recently are there protections for climate refugees
12
New cards
Ecological
13
New cards
Solastalgia
“The homesickness you have when you are still as home”
* Pandemic of earth-related distress….
* Either we face a pandemic of solastalgia and related negative psychoterratic syndromes as a result of the havoc created by unsustainable development and climate change, or we use our intelligence and creativity to give rise to a world where our positive psychoterratic emotions can thrive”
* Pandemic of earth-related distress….
* Either we face a pandemic of solastalgia and related negative psychoterratic syndromes as a result of the havoc created by unsustainable development and climate change, or we use our intelligence and creativity to give rise to a world where our positive psychoterratic emotions can thrive”
14
New cards
Stress leads to other conditions
It may…..
* Negatively impact blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes
* Result in cardiovascular disease
* Increase risk of developing some forms of cancer
* Or lead to progression of cancer in those fighting already
* Strained relationships
* Negatively impact blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes
* Result in cardiovascular disease
* Increase risk of developing some forms of cancer
* Or lead to progression of cancer in those fighting already
* Strained relationships
15
New cards
Who is at Risk
* Some are more susceptible than others
* Children
* Elderly
* Women (esp pregnant & post-partum)
* Individuals w/ pre-existing mental illness
* Economically disadvantage
* Homeless
* First Responders
* Communities reliant on natural environment for food and livelihood
* Communities in areas more susceptible to specific climate change events
* Children
* Elderly
* Women (esp pregnant & post-partum)
* Individuals w/ pre-existing mental illness
* Economically disadvantage
* Homeless
* First Responders
* Communities reliant on natural environment for food and livelihood
* Communities in areas more susceptible to specific climate change events
16
New cards
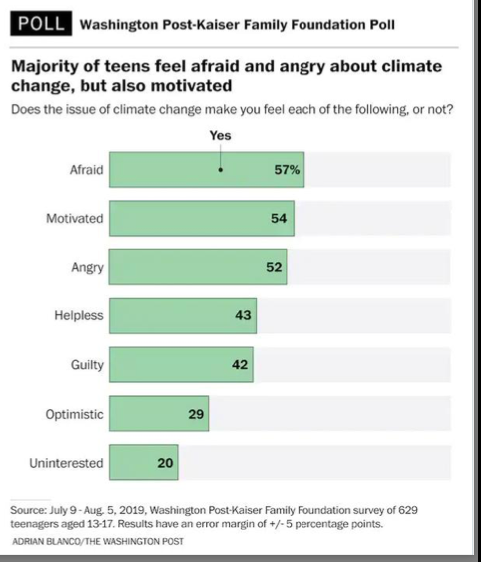
Pre-Traumatic Stress
see slides (Lecture 10, Week 11)
17
New cards
Climate Anxiety
see slides (Lecture 10, Week 11)
18
New cards
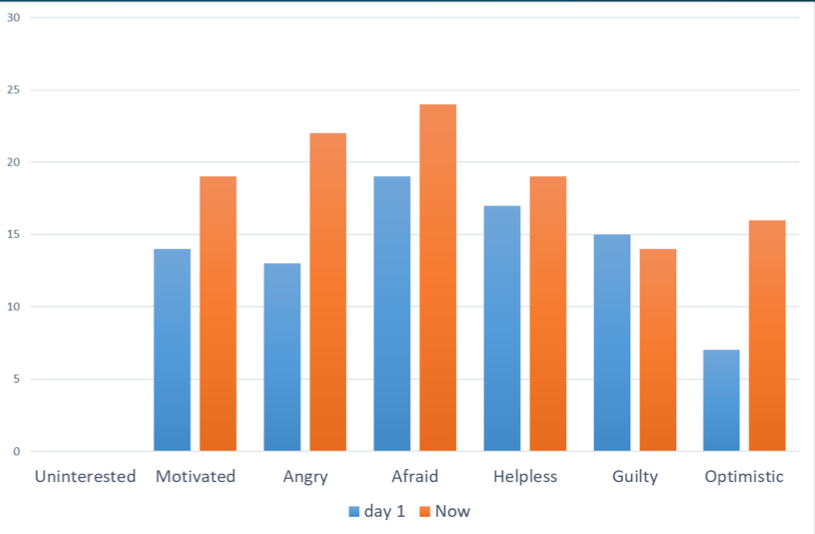
ESCI 274 Feelings
* More ‘response; last week than week 1
* (Comparison to early semester vs late semester)
* (Comparison to early semester vs late semester)
19
New cards
Climate change & Mental Health (3)
* Immediate: PTSD, anxiety, depression, self-harm, substance abuse
* Gradual: Chronic stress, late-onset PTSD
* Indirect: loss of connection with self, community, traditional lifeways, increased social and domestic issues
* Gradual: Chronic stress, late-onset PTSD
* Indirect: loss of connection with self, community, traditional lifeways, increased social and domestic issues
20
New cards
Deficit Model
* Audience lacks facts, just need to supply facts you can make them feel as you do
This approach usually fails in risk of communication
Ineffective way to change peoples attitudes
Appeals to reason… but reason is not what drives human behaviour
Facts alone (without broader context) are meaningless
We don't worry about risks that don’t feel personally threatening
We also worry more about risks that threaten us sooner than risks that threaten us later
We worry less about risky behaviours if those behaviours carry tangible benefits
This approach usually fails in risk of communication
Ineffective way to change peoples attitudes
Appeals to reason… but reason is not what drives human behaviour
Facts alone (without broader context) are meaningless
We don't worry about risks that don’t feel personally threatening
We also worry more about risks that threaten us sooner than risks that threaten us later
We worry less about risky behaviours if those behaviours carry tangible benefits
21
New cards
What Resonates
* Risk communication that acknowledges and respects the emotions and psychology of people will have a greater impact
* Words matter: Climate change
* Messages not about facts (can get lost in the science) but about personal fear
* Frame the issue in terms of personal and immediate fear of a future that promises more harm than benefit
* Words matter: Climate change
* Messages not about facts (can get lost in the science) but about personal fear
* Frame the issue in terms of personal and immediate fear of a future that promises more harm than benefit
22
New cards
Reasons for Hope (5) (END OF LECTURE 10)
* The global economy is growing faster than emissions
* Energy efficiency is moving from the margins toward a new normal in the products we use
* The price of solar and wind power has plunged
* The supply of clean energy resources is growing at the same time pries have declined
* State and local Leaders set building and energy-use regulations
* Energy efficiency is moving from the margins toward a new normal in the products we use
* The price of solar and wind power has plunged
* The supply of clean energy resources is growing at the same time pries have declined
* State and local Leaders set building and energy-use regulations
23
New cards
Citizen Science (START OF LECTURE 11)
* Voluntary public collection of scientific data- any age, ability, background
* National Parks, government agencies, academic institutions, etc.
* becoming popular and is easier with technology and is sometimes short lived
* National Parks, government agencies, academic institutions, etc.
* becoming popular and is easier with technology and is sometimes short lived
24
New cards
Citizen Science Benefits (8)
* Free labour for researchers
* Maximizes researcher analysis times
* Public has good ideas and a tie to the area
* Maximizes public outreach (education 7 engagement)
* Enhances public appreciation for their area
* Empowers citizens
* “Democratizes the research process”
* Encourage critical thinking
* Maximizes researcher analysis times
* Public has good ideas and a tie to the area
* Maximizes public outreach (education 7 engagement)
* Enhances public appreciation for their area
* Empowers citizens
* “Democratizes the research process”
* Encourage critical thinking
25
New cards
Citizen Science Complications (6)
* Non-expert data quality: accidental or purposeful data sharing
* Data sharing
* Intellectual property: Misappropriating what research is used for
* Government opposition
* Conflict of interest
* Exploitation of citizen scientists
* Data sharing
* Intellectual property: Misappropriating what research is used for
* Government opposition
* Conflict of interest
* Exploitation of citizen scientists