Global Climate Change and Its Impacts
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Earth System
Interconnected components of Earth's environment.
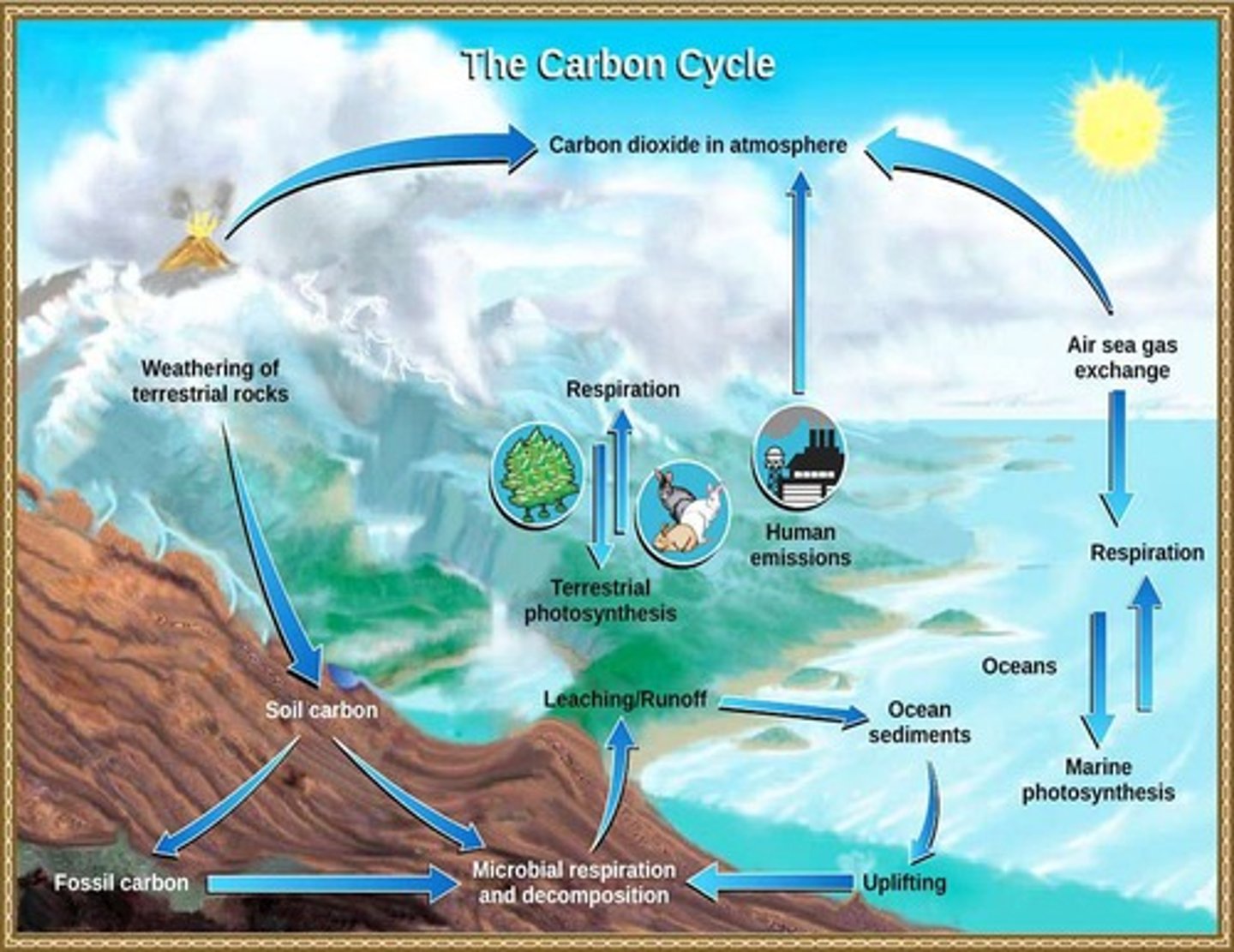
Carbon Cycle
Process of carbon movement between Earth systems.
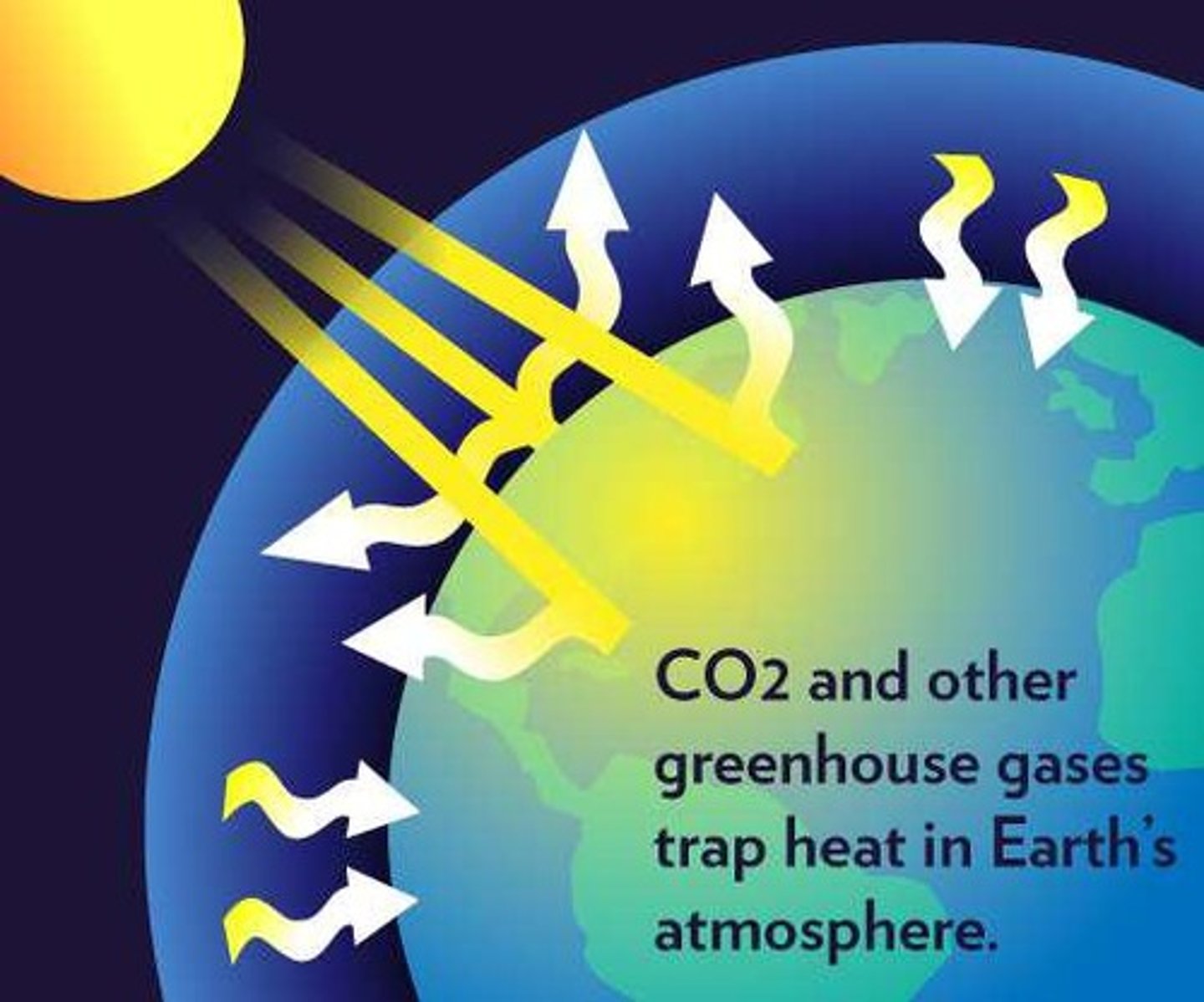
Greenhouse Effect
Heat retention by greenhouse gases in atmosphere.
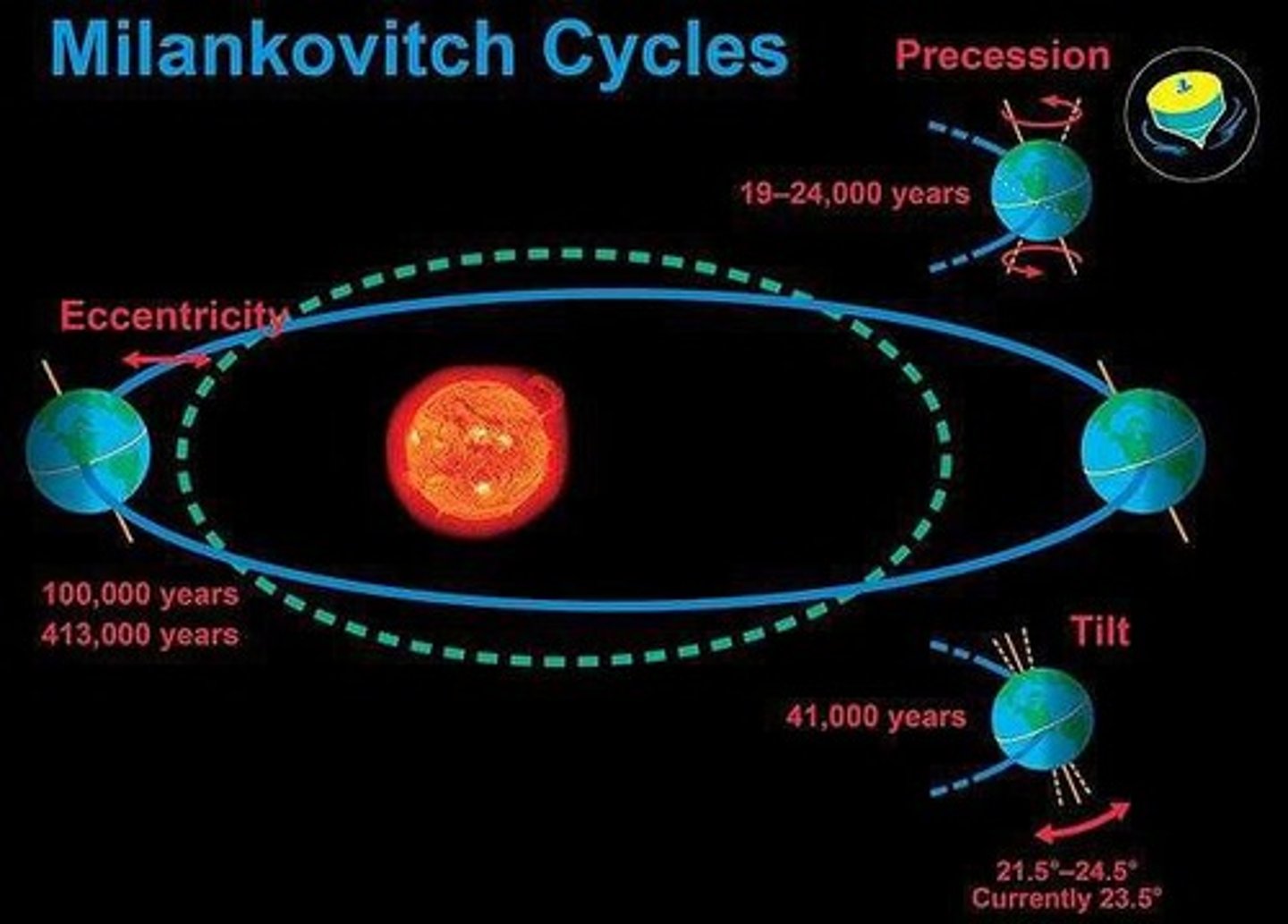
Milankovitch Cycles
Long-term climate changes due to Earth's orbital variations.
Feedback Mechanisms
Processes that amplify or diminish climate change effects.
Proxy Indicators
Evidence used to infer past climate conditions.
Weather
Short-term atmospheric conditions over days or weeks.
Climate
Long-term average of weather patterns in a region.
Geosphere
Solid Earth, including rocks and soil.
Atmosphere
Gaseous envelope surrounding the Earth.
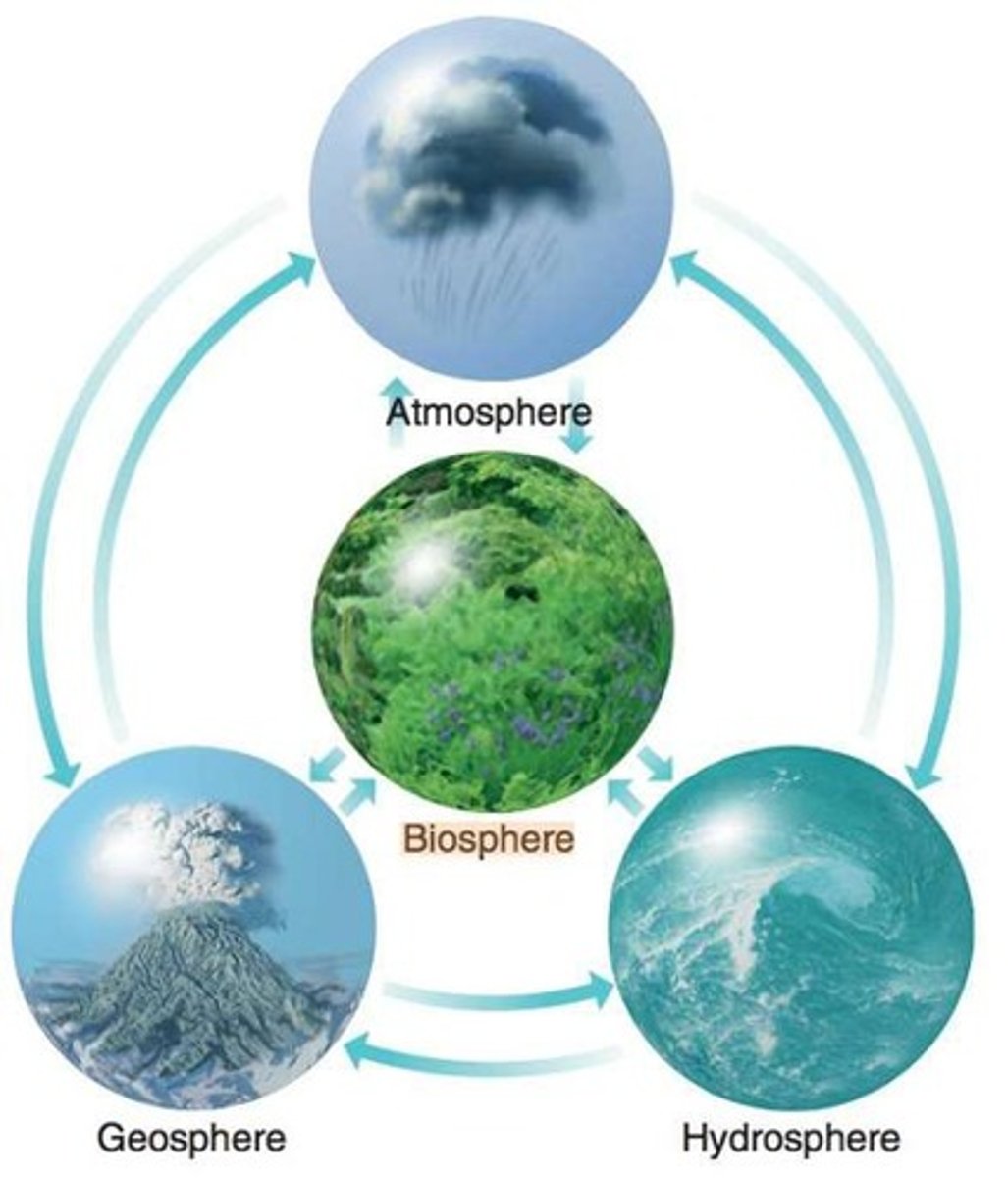
Biosphere
All living organisms on Earth.
Hydrosphere
All water bodies on Earth.
Cryosphere
Frozen water components, including ice and snow.
Biological Carbon Cycle
Carbon cycling through living organisms via photosynthesis.
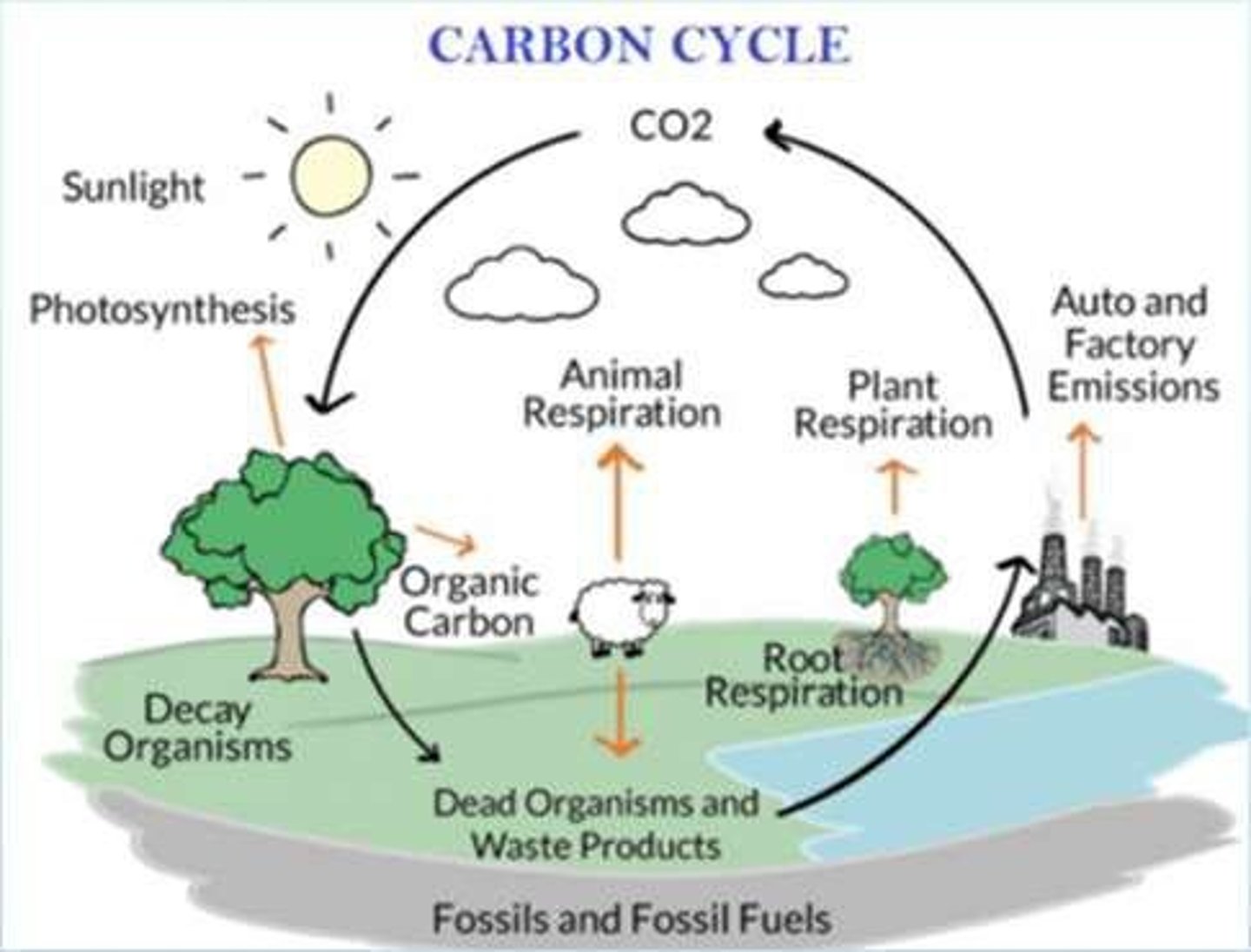
Geologic Carbon Cycle
Long-term carbon storage in geological formations.
Dissolved Bicarbonate
Form of carbon stored in ocean water.
Carbonate Rocks
Rocks formed from calcium carbonate over millions of years.
Volcanic Outgassing
Release of CO2 from Earth's interior to atmosphere.
Anthropogenic Emissions
Carbon emissions resulting from human activities.
Greenhouse Gases
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere.
Trace Components
Minor gases in the atmosphere, including CO2 and methane.
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed from sediment accumulation over time.
Greenhouse Effect
Trapping of heat by greenhouse gases.
Milankovitch Cycles
Earth's orbital variations affecting solar radiation.
Feedback Mechanisms
Responses within Earth System to climate forcings.
Proxy Indicators
Evidence of past climates from natural records.
Solar Radiation
Energy from the Sun, including UV and IR.
Thermal Radiation
Heat emitted by Earth's surface as infrared.
Energy Budget
Balance of incoming and outgoing energy on Earth.
Albedo Effect
Reflectance of sunlight by surfaces like ice.
Positive Feedback
Amplifies the original cause or effect.
Negative Feedback
Suppresses the original cause or effect.
Eccentricity
Shape of Earth's orbital path, cycles every 100k years.
Obliquity
Tilt angle of Earth's axis, cycles every 41k years.
Precession
Direction of Earth's axis rotation, cycles every 23k years.
Volcanic Activity
Natural process affecting greenhouse gas concentrations.
Rock Weathering
Natural process that buries CO2 in sediments.
GHG Concentrations
Levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration in Earth's climate patterns.
Direct Measurements
Current climate data from instruments and records.
Paleo Climate Change
Historical climate changes inferred from proxies.
Thermal IR
Infrared radiation emitted from Earth's warmed surface.
Solar Heat
Energy received from the Sun influencing temperatures.
Climate Proxy Indicators
Natural records used to infer past climate conditions.
Proxy Indicators
Indirect records of past climate conditions.
Fossils
Remains of ancient organisms indicating climate.
Stable Isotopes
Isotope ratios used to infer past temperatures.
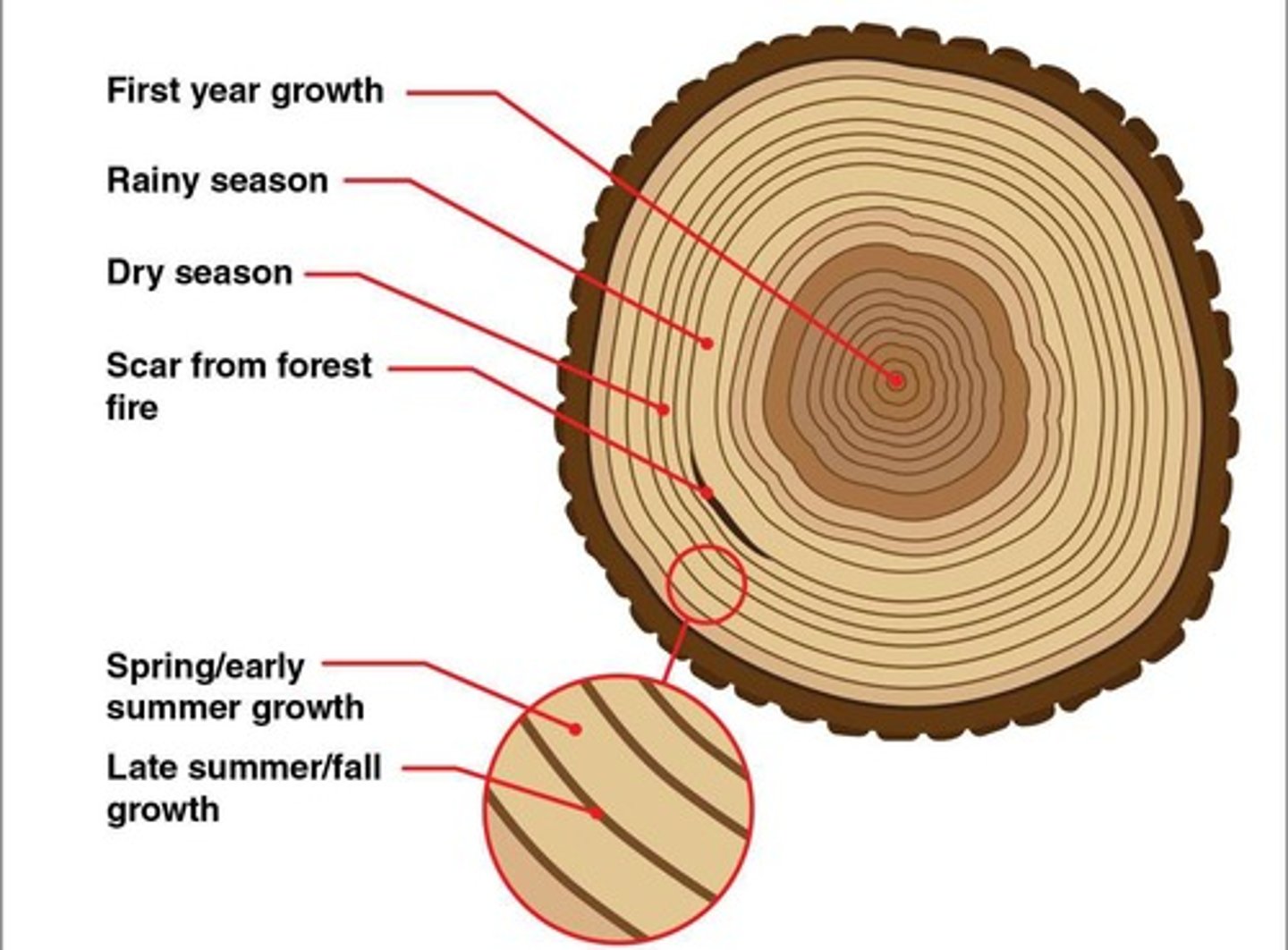
Tree Rings
Annual rings indicating climatic conditions.
Pollen
Plant pollen indicating ancient climates and environments.
Sediment Cores
Layers of sediment revealing historical climate data.
Oxygen Isotope Ratio
Ratio of 18O to 16O indicating temperature.
Deep-Sea Sediment
Sediment containing microfossils for climate analysis.
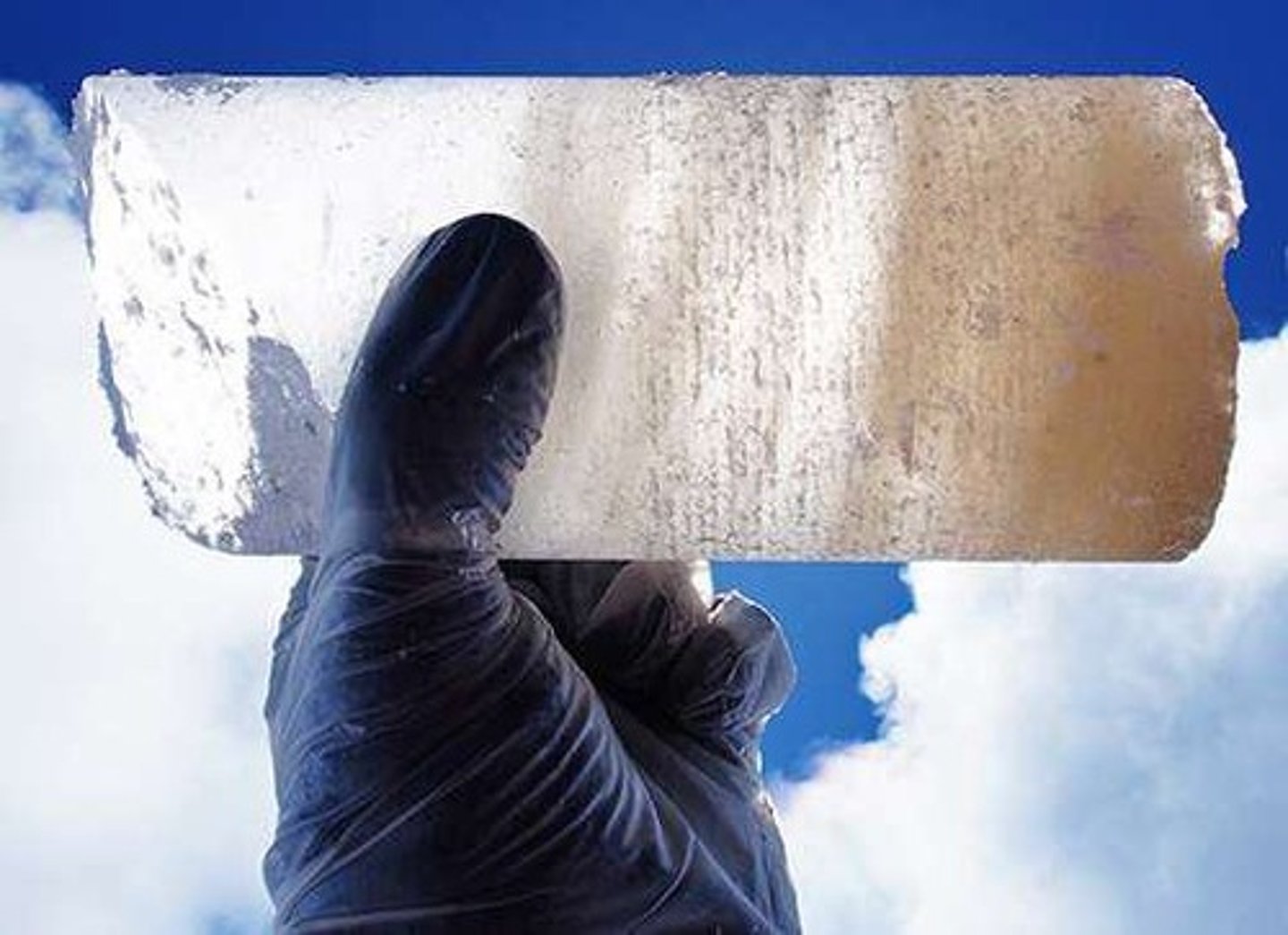
Ice Cores
Layers of ice trapping ancient atmospheric gases.

Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
Warm period before Cenozoic cooling.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
Current affecting global climate patterns.
Global Temperature Rise
Increase in average temperatures since ~1900.
Changes in Weather Patterns
Alterations in storm frequency and intensity.
Greater Moisture Capacity
Increased atmospheric moisture leading to extreme weather.
Microorganisms
Tiny organisms used in paleoclimate studies.
Cave Carbonates
Sediments in caves indicating past climate conditions.
Colder Times
Periods with more pine tree pollen.
Warmer Times
Periods with less pine tree pollen.
Bubbles in Ice
Trapped gases revealing ancient atmospheric composition.
δ18O
Oxygen isotope ratio used in climate studies.
Glacial Features
Geological evidence of ancient ice sheet extents.
Chemical Records
Stable isotopes indicating climate change.
Global average air temperature
Overall temperature of Earth's atmosphere over time.
Ocean warming
Increase in ocean temperatures due to climate change.
Extreme weather events
Severe weather occurrences linked to climate change.
Confirmed weather disasters
24 disasters in 2024, each over $1 billion.
Annual average disasters (1980-2023)
Average of 8.5 climate disasters per year.
Ocean acidification
Decrease in ocean pH due to CO2 absorption.
Carbonic acid formation
CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid.
Marine organism impact
Shellfish and corals suffer from acidified waters.
Melting glaciers
Alpine glaciers are retreating and thinning rapidly.
Ice sheet mass loss
Greenland and Antarctica ice sheets decreasing in mass.
Rate of ice loss
Tripled in the past decade.
Rising sea level
Sea level rise doubled compared to the last century.
Global mean sea level rise
10 cm increase since 1992.
Thermal expansion
Water volume increases as temperatures rise.
Atmospheric CO2 measurements
Continuous CO2 data from Mauna Loa since 1958.
Current CO2 concentration
419.3 ppm in 2024, highest in 400,000 years.
CO2 increase rate
~100 ppm increase in CO2 over 60 years.
Photosynthesis role
Consumes CO2 during summer months.
Decomposition role
Releases CO2 during winter months.
Greenhouse gases (GHG) correlation
GHG concentrations rise with global temperatures.
Milankovitch cycles
Natural cycles affecting Earth's climate over thousands of years.
Anthropogenic CO2 emissions
Human activities increasing atmospheric CO2 levels.
Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations
Increased by fossil-fuel burning since 1900s.
13C/12C Ratio
Indicates source of carbon in the atmosphere.
Fossil Fuels
Millions of years old organic matter used for energy.
14C
Radioactive carbon isotope absent in fossil fuels.
Negative Enrichment
Atmospheric carbon shows more 12C than 13C.
Terrestrial Plants
Primary source of carbon fingerprints in fossil fuels.
14C Decay Rate
Fast decay rate leads to low 14C in fossil fuels.
Ocean Circulation Changes
Influences climate by redistributing heat globally.
Ocean Conveyor Belt
Driven by temperature and salinity differences.
Younger Dryas
Abrupt climate change event 14,500-11,500 years ago.
Sea Level Rise
Estimated 216-foot rise if all land ice melts.
Temperature Change
Regions experience varying warming and cooling trends.