C4.1 - Populations and communities
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is a population?
One species in a specific area at a given time. These species must be reproductively isolated
Why is it difficult to count all members of a population?
not enough time
Destructive - damages environment / habitat
motile animals move in and out
bias
How can population size be estimated?
Random quadrat sampling to estimate sessile populations (ones that cannot move)
Capture-Mark-Release-Recapture to estimate motile populations (ones that move) —> then estimated using lincoln index formula
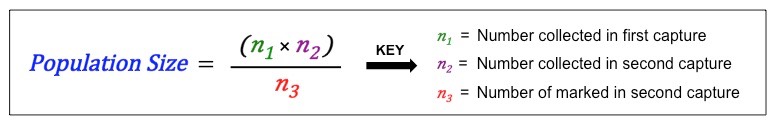
What is carrying capacity?
The maximum population size that an environment can long-term support
What factors affect carrying capacity?
Food and water
Shelter
Space
Predators
Climate
Disease
What are density dependent factors that affect population growth?
These are usually biotic, so living:
competition for resources
predators
disease
Usually, as population growth increases, so do density dependent factors, which in turn decreases the population again (negative feedback)
What are density independent factors that affect population growth?
These are not dependent or influenced by population density. These factors are usually abiotic:
Climate events and natural disasters
Habitat destruction
Seasonal changes
How is competition for resources, predators and disease an example of negative feedback loops?
Competition for resources —> if population density increases, there is more fight for resources. Better adapted animals win the fight, while the others die, decreasing the population
Predators —> if population density increases, there is more prey for predators, causing predator population to increase, so more animals which feed on prey, decreases the population size
Disease —> if population density increases, there is easier spread of diseases, but this causes more animals to die off, decreasing population size
What are factors affecting population growth?(Remember: Growth, not density!)
Natality → births
Mortality → deaths
Immigration → entering
Emigration → leaving
What is the formula for changes in population size?
Population size = (Natality + Immigration) - (Mortality + Emigration)
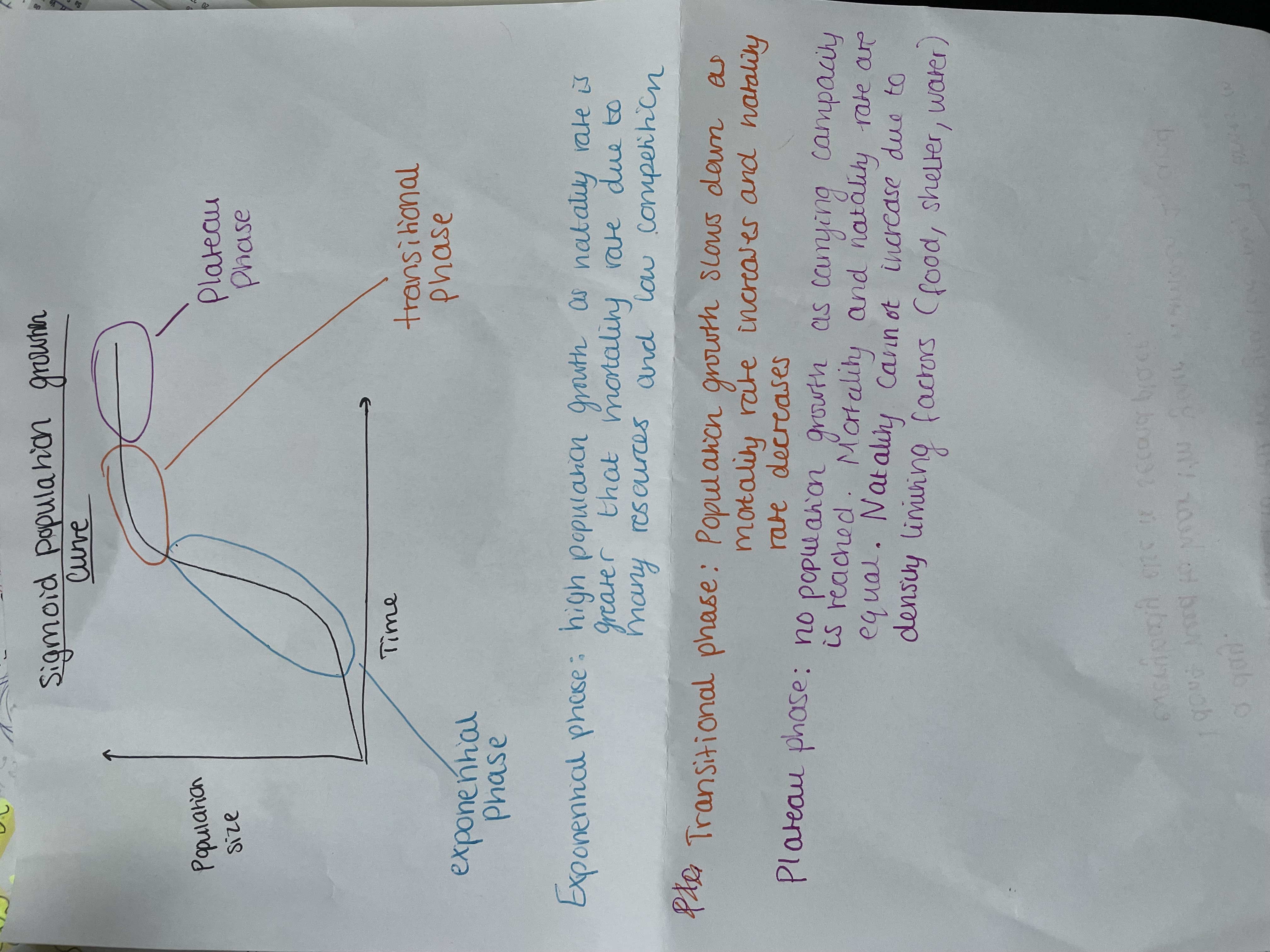
What is a sigmoid population growth curve?
A curve showing population growth, with an exponential increase, a transitional phase and then a plateau phase
Analyse the sigmoid population growth curve
What is intraspecific competition?
Competition for resources between members of the same species
Give examples of resources which animals of the same species compete for
Food and water
Shelter
Mates for reproducing
Social dominance
What is intraspecific cooperation?
When members of a species work together, such as group hunting or foraging, defense against predators and parenting.
What is a community?
Many different populations of species living and interacting with each other in an ecosystem
What are interspecific interactions and give examples?
These are interactions between different species within a community.
Herbivory - animals eating plants
Predation - animals killing other animals
Competition - when different species compete for the same resources
Mutualism - a close relationship between organisms of different species e.g., when bees pollinate plants (Mutualism benefits both species)
Parasites - when parasites harm animals
Pathogens - when pathogens harm animals