Biology Chapter 3 McGrawHill
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
cell
smallest unit of life that can function independently
2
New cards
cell theory
the ideas that all living things consists of cells, cells are the structural and functional units of life, and all cells come from preexisting cells.
3
New cards
Ribosome
a structure built of RNA and protein where mRNA anchors during protein synthesis.
4
New cards
Cell membrane
the boundary of a cell, consisting of proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer; also called the plasma membrane.
5
New cards
cytoplasm
the watery mixture that occupies much of a cell's volume; in eukaryotic cells, it consists of all materials, including organelles, between the nuclear envelope and the cell membrane.
6
New cards
cytosol
the fluid portion of the cytoplasm.
7
New cards
prokaryote
a cell that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bounded organelles; bacteria and archaea
8
New cards
eukaryote
organism composed of one or more cells containing a nucleus and other membrane-bounded organelles.
9
New cards
Bacteria
one of two domains of prokaryotes
10
New cards
Archaea
one of two domains of prokaryotes
11
New cards
Eukarya
domain containing all eukaryotes
12
New cards
nucleoid
the part of a prokaryotic cells where the DNA is located.
13
New cards
cell wall
a rigid boundary surrounding cells of many prokaryotes, protists, plants, and fungi.
14
New cards
flagellum (flagella)
a long, whip-like appendage that a cell uses for motility
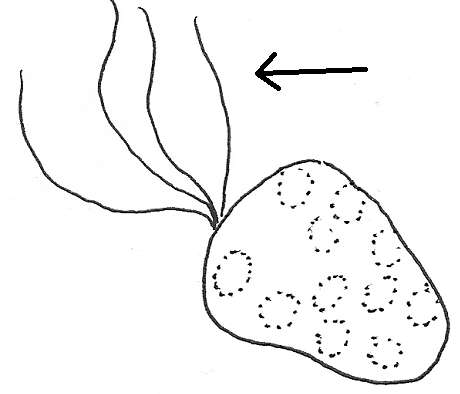
15
New cards
Organelle
a compartment of a eukaryotic cell that performs a specialized function.
16
New cards
phospholipid
molecule consisting of glycerol attached to two hydrophobic fatty acids and a hydrophilic phosphate group.
17
New cards
phospholipid bilayer
double layer of phospholipids that forms in water; forms the majority of a cell's membranes.
18
New cards
fluid mosaic
the two-dimensional structure of movable phospholipids and proteins that form biological membranes
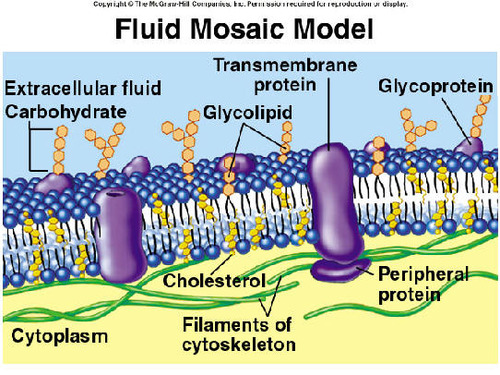
19
New cards
endomembrane system
eukaryotic organelles that exchange materials in transport vesicles.
20
New cards
vesicle
a membrane-bounded sac that transports material within a cell
21
New cards
nucleus (cell)
the membrane-bounded sac that contains DNA in a eukaryotic cell
22
New cards
nuclear pore
a hole in the nuclear envelope.
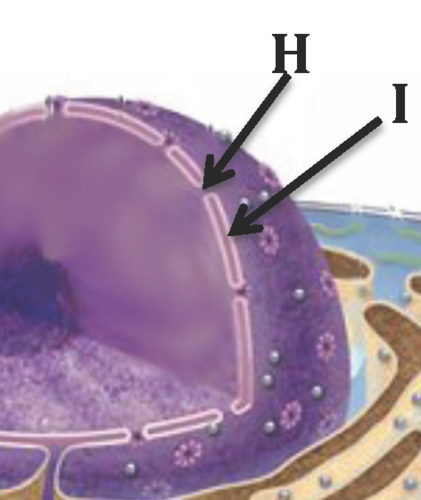
23
New cards
nuclear envelope
the two membranes bounding a cell's nucleus
24
New cards
nucleolus
a structure within the nucleus where components of ribosomes are assembled
25
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
interconnected, membranous tubules and sac in a eukaryotic cell.
26
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
a ribosome-studded portion of the ER where secreted proteins are synthesized.
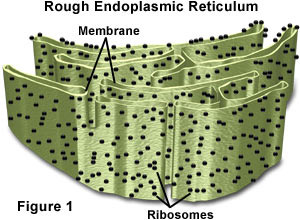
27
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
a portion of the ER that produces lipids and detoxifies poisons.
28
New cards
Golgi apparatus
a system of flat, stacked, membrane-bounded sacs that packages cell products for export.
29
New cards
lysosome
organelle in a eukaryotic cell that buds from the Golgi apparatus and enzymatically dismantles molecules. bacteria, and worn-out cell parts.
30
New cards
vacuole
membrane-bounded storage sac in a cell, especially the large central vacuole in a plant cell.
31
New cards
peroxisome
membrane-bounded sax that houses enzymes that break down fatty acids and dispose of toxic chemicals.
32
New cards
mitochondrion
organelle that houses the reactions of cellular respiration in eukaryotes.
33
New cards
crista (cristae)
fold of the inner mitochondrial membrane along which many of the reactions of cellular respiration occur.
34
New cards
chloroplast
organelle housing the reactions of photosynthesis in eukaryotes
35
New cards
cytoskeleton
framework of protein rods and tubules in eukaryotic cells
36
New cards
microfilament
component of the cytoskeleton; made of the protein actin
37
New cards
intermediate filament
component of the cytoskeleton; intermediate in size between a microtubule and a microfilament.
38
New cards
microtubule
component of the cytoskeleton; made of subunits of the protein tubulin
39
New cards
centrosome
part of the cell that organizes microtubules
40
New cards
cilium (cilia)
one of many short, movable protein projections extending from a cell.
41
New cards
tight junction
connection between two adjacent animal cells that prevents fluid from flowing past the cell.
42
New cards
anchoring (or adhering) junction
connection between two adjacent animal cells that anchors intermediate filaments in a single spot on the cell membrane.
43
New cards
gap junction
connection between two adjacent animal cells that allows cytoplasm to flow between them.
44
New cards
plasmodesma (plasmodesmata)
connection that allows cytoplasm to flow between adjacent plant cells.
45
New cards
transport proteins
Embedded in phospholipids bilateral creates passageways through which ions, glucose, and other polar substances pass into or out of the cell
46
New cards
Recognition proteins
carbohydrates attached to cell surface proteins serve as "name tags" that help the body's immune system recognize its own cells
47
New cards
Adhesión proteins
These membrane proteins enable cells to stick to one another
48
New cards
receptor proteins
bind to molecules outside the cell and trigger a response inside the cell, called signal transduction
49
New cards
amphipathic phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules. This means that they have a hydrophilic, polar phosphate head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails.
50
New cards
animals extracellular matrix
animal cells release materials into the extracellular space, creating a complex meshwork of proteins and carbohydrates
51
New cards
One property that is present in cells in domain Eukarya but absent from those in domain Bacteria is
Membranous organelles
52
New cards
What chemical property of phospholipids is key to the formation of the cell membrane ?
The hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
53
New cards
Within a single cell, which of the following is physically the smallest?
phospholipid molecule
54
New cards
A human nerve cell that has an abnormal shape most likely has a defective
cytoskeleton
55
New cards
What type of cellular junction prevents stomach acid from leaking into the abdomen and digesting internal organs?
tight junctions
56
New cards
Light microscopes can reveal
True-color views of living or preserved cells, specimen must be transparent and thinly sliced, and two types are compound and confocal
57
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a sample, coated with metal atoms, to study details of its topography.
58
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the internal structure of thinly sectioned specimens.
59
New cards
Electron microscopes can reveal
Greater magnification and resolution, and use electrons for microscope