Physics Y10
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Transverse wave
A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. Still is a wave with amplitude, frequency and wavelength.
Longitudinal waves
a wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave. Still is a wave with amplitude, frequency and wavelength.
ElectroMagnetic wave
a wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which radiate outward at the speed of light. Does not need a medium to travel always travels the same speed.
Crest
the highest point of a wave
Through
Lowest point of a wave
Compression
The part of a wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
Rarefaction
The part of a wave where the particles of the medium are far apart
Wave Formula
Velocity= frequency times wavelength
Interference
result of the combination of two or more waves of the same type and frequency in which the amplitude of the resulting wave is equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the combining waves
Constructive
Increase of amplitude in interference
Destructive
Decrease of amplitude in interference
principle of superposition
When two or more waves overlap the resulting displacement is the result of algebraicly sum of their individual disturbances.
Disturbance
Refers to any change from the equilibrium state that travels through the medium, carrying energy without permanently displacing the medium itself. It can be a variation in pressure, density, or displacement of particles in the medium.
Angle of incidence
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal to a a surface
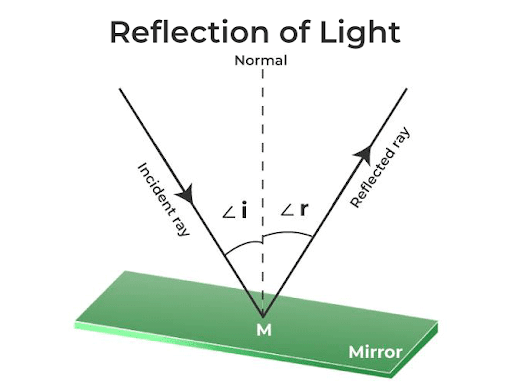
Angle of reflection
From the angle of normal in a surface and the reflection ray
Incident ray
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. It is the incoming ray before it undergoes reflection, refraction, or absorption.
Refraction
Bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, caused by a change in its speed. this can be observed in glass as light is a bit slower in glass.
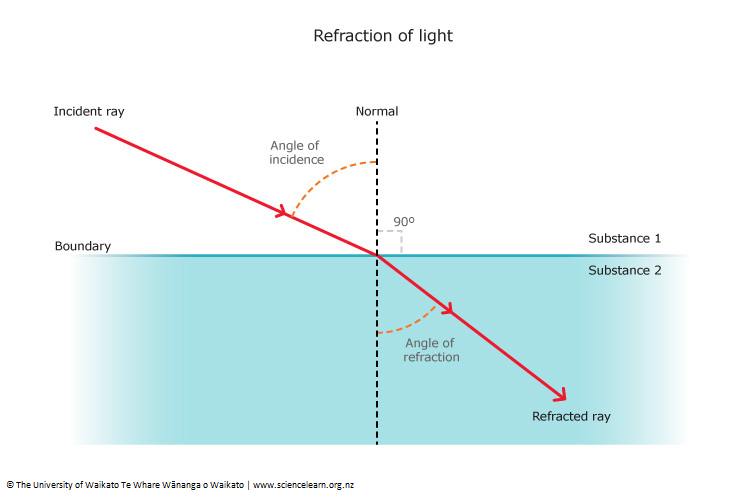
Normal
90 degree angle form the medium
Reflected ray
A reflected ray is the light ray that bounces off a surface, obeying the law of reflection, where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Laws of reflection
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
All lie on the same plane.
Snell Laws
N1 sin (beta)1=n2 sin (beta)
Index of refraction
1.0 for air which is same for vacuum. For different transparent materials it’s different meaning light can go at different speeds. To know what speed you divide it by the vacuum speed of light
speed of sound
341 +0.6 x Celsius
Resonant frequency
Natural frequency where the medium vibrates at the highest amplitude