Phylogeny II & the Species Concept (9)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
When allele frequencies change because of genetic drift, you expect _____. A. the average fitness of the population to increase
B. the average fitness of the population to decrease
C. the average fitness of the population to remain the same
D. the effect of drift on average fitness is not predictable
D: Genetic drift --> decrease in genetic variation --> can't predict what effect it will have on average fitness
Which of the following evolutionary mechanisms increases the amount of genetic variation in a population?
A. Genetic drift
B. Mutation
C. Sexual selection
D. Directional natural selection
E. Stabilizing natural selection
B: mutation adds alleles to population --> increases genetic variation
How do biologist classify life on Earth?
hierarchical classificaiton system
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus,
Species
What is the principle of Parsimony (Occam’s razor)?
used to construct PT
The simplest explanation is most likely to be correct (Unless other data suggest more complicated explanation)
Evolution of trait evolving twice is unlikely (emerging multiple times in a tree)
What is the simplest possible explanation?
tree with the fewest amount of evolutionary changes
fewest amount of traits appearing independently
What is Parsimony used to construct PTs?
Evolution of character twice is extremely unlikely
Evolutionary trees with derived characters appearing once are most parsimonious
What does parsimony minimize in PTs?
Minimize the number of evolutionary changes that must be assumed
fewest homoplasis
What are characters?
morphological, physiological, or molecular features that make up an organism
What are character states?
several observed conditions in characters
Simple: character is absent or present
wings in tetrapods, but not other vertebrates
More common: multiple character states
Petals on flower: character
State: arrangement of petals (helical, whorl, fused, etc.)
What are identified when constructing phylogenies?
derived traits
What kinds of traits are used to construct phylogenies?
• Morphological
Developmental
Paleontological
Behavioural
Molecular
what are the limitations of morphology in PT construction?
Comparing Distantly related things: very different looking things
Some morphological variation caused by environment: find source of variation
Some species show few morphological Differences:
wide spread butterfly in Brazil --> molecular work finds its 17 species that look identical
Sometimes always impossible
What are examples of morphological traits?
Features of the skeletal system in vertebrates
Floral structures in plants
External features of exoskeleton in insects
What can developmental traits reveal?
Similarities in development patterns may reveal evolutionary relationships
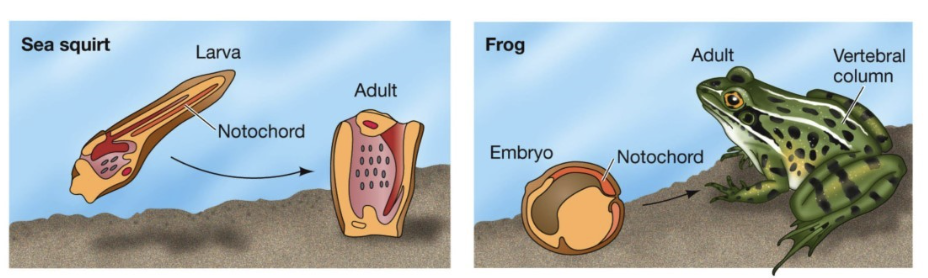
How do sea squirts and frogs show evolutionary relation?
Different morphology in adult form
In developmental stage: identify characteristic of Chordata
Two organisms are related because they share the notochord
What are the limitations to developmental traits?
complicated to quantify
What does paleontological traits show in PTs?
Fossils provide information about morphology of past organisms, and where and when they lived.
Why are paleontological traits important?
Important in determining derived and ancestral traits, and when lineages diverged.
What are the limitations of paleontological traits?
incomplete fossil record and rare to find
Morphology: live in present
Paleontological: mostly extinct organisms
Where do behavioral traits originate from?
Can be inherited but some are culturally transmitted.
Why are frog calls able to be used in phylogenic trees?
Frog calls are genetically determined
Genes responsible for call length
What is an example of a behavioral limitation for PTs?
Bird songs are often learned and may not be a useful trait for phylogenies.
Ex: European Starlings
Population in cities call louder than outside
Can mimic car sounds etc.
Environmental dependence on behavior --> be able to choose what are valuable
What are considered molecular characters?
DNA, RNA and amino acid changes reflect evolution
What are the advantages of molecular characters?
Abundant data
Easier comparison of distant or very close relations
No direct environmental effect
Effective at comparing very different species
What is the disadvantages of molecular characters?
Only four states in nucleotides, 20 in amino acids
Not very useful for comparing very closely related species
Base changes may have evolved independently
because there are so few bases
How do scientists use molecular data for PTs?
Can isolate region of DNA that we know is unique to clade in group and compare and contrast base pair sequence
Environment affects phenotype, but not accumulation of data in genotype
What is the molecular clock?
The number of changes, or mutations, which accumulate in the gene sequences of different species over time is relatively constant
What is mosiac evolution?
Each DNA sequence has a different clock tick
different parts of an organism, or different traits within a lineage, evolve at different rates.
"patchwork" of primitive and derived features rather than a uniform transformation of the entire body at once
What part of the molecular clock is used often?
Noncoding regions
Why are noncoding regions important for building PTs?
Coding regions creates proteins —> expressed
change less frequently but have a more constant ‘tick’
In DNA we accumulate mutations and all species collect mutations at constant rate in the noncoding region
Can measure time before species became two (index for divergence)
Why do noncoding regions change less frequently and are more stable?
In DNA there is redundancy --> not under as much selection
Coding for things that are redundant/repetitive/ basic recipes for material important in physiological process
if one altered, the others could produce something that could also work)
less important = mutations more likely to linger
Not under strong selection --> mutations collected there are more constant and variable
Noncoding DNA vs Important Coding DNA
Important coding DNA extremely important (could lead to death or major changes) and under strong selection --> resistant to change
How is the molecular clock used in PTs?
Molecular differences between pairs of species are proportional to the time of their separation and we can index the time of divergence between species
What part of molecular characters reflect evolutionary relationships?
DNA/RNA sequence of amino acids
nucleotide bases
How are DNA sequences used to find evolutionary relationships?
Different specific regions in DNA are relevent for different groups of organisms
Sequence of DNA must be lined up in the same positions of base pairs
Look for differences in ACGT
Find positions that have changed to different nucleotide state, deleted, or inserted
The more differences --> the more distantly related
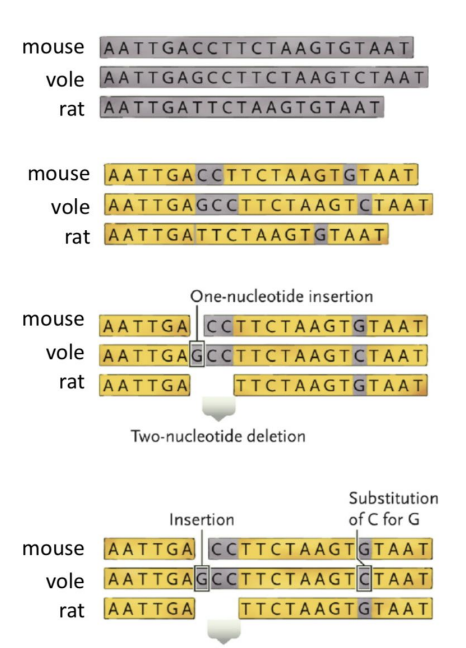
Why must sequences be aligned to the same position?
mutations can change length of DNA (computer programs, e.g., Clustal)
What has become the most widely used data for constructing PT trees?
DNA sequences
What kind of DNA is used?
Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is used as well as nuclear DNA, compared against reference database
What is Genomic Data?
All of the DNA
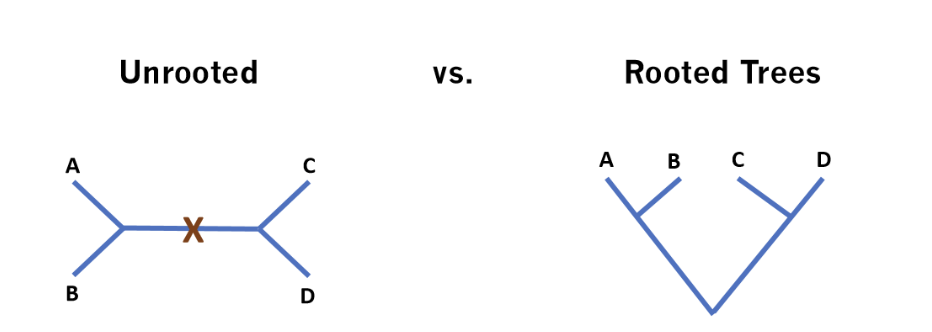
Unrooted vs. Rooted trees
Unrooted: tree doesn’t illustrate relatedness
too many different combinations possible to show relatedness
Rooted: shows related closeness
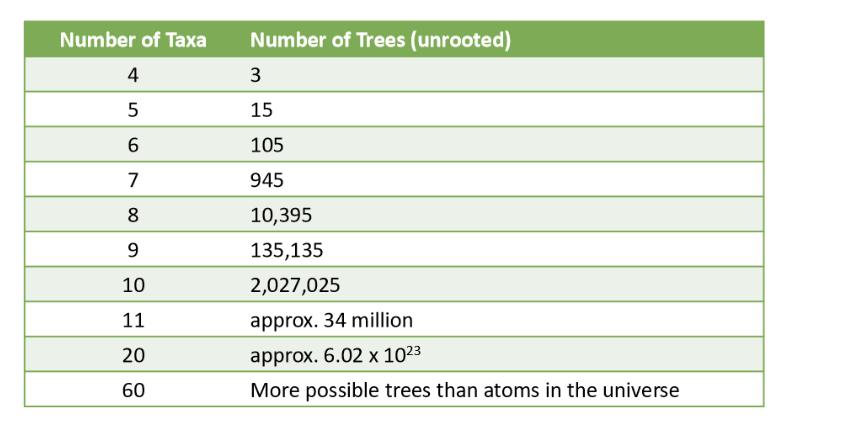
What is combinatorial explosion?
the more taxa that are compared —> the more unrooted tree possibilities
How are the # of PTs reduced?
computer software that uses principles of parsimony
What do we do when parsimony is not possible with the quality or quantity of data?
uses maximum liklehood and Bayesian-based tree (didn’t explain more)
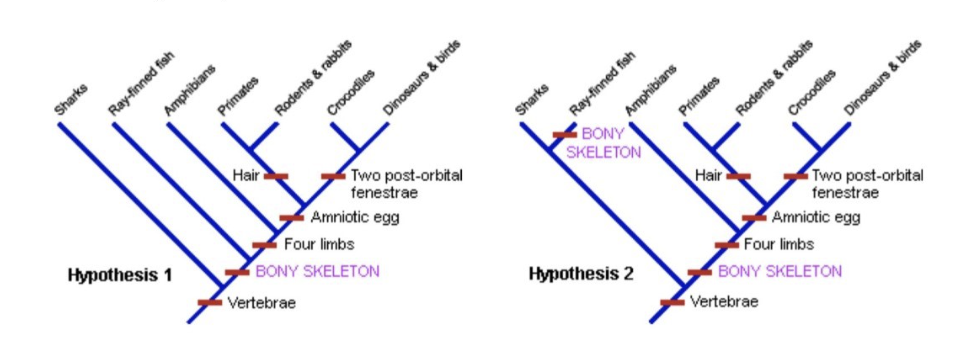
What is the most parsimonious tree?
Hypothesis 2 less parsimonious because same trait evolved two times
What does 0 represent in table of traits (characteristics)
traits that are the same as the outgroup
What does 1 represent in table of traits (characteristics)
a derived trait
How to construct tree based on graph?
Look for groups with the highest amount of derived traits
taxa that don’t have that derived trait most likely occur before the other taxa
What is a species?
Smallest independently evolving unit
Species follow independent evolutionary trajectories
definition is contentious
What does Pelage show us?
5 to 10 different subspecies of giraffes.
Distinctions partly based on geographic range and pelage pattern
There are abrupt transitions between pelage types in some areas not obviously associated with geographic barriers to the movement of giraffes
By analyzing DNA sequences, it has been established that giraffes show six genealogically distinct lineages
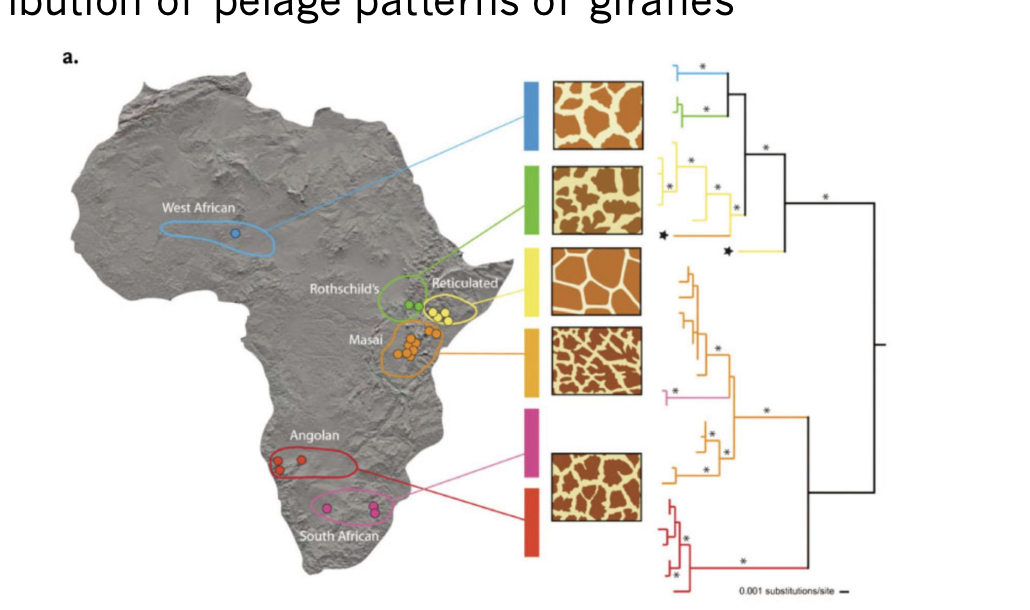
How does mating work with different pelage patterns?
can all interbreed, but Giraffes prefer to mate with those with the same pelage pattern
What is the morphological species concept?
Linnaeus
described/grouped species based on their appearance
Originated the binomial system of nomenclature (genus + species name)
morphospecies concept holds that members of the same species usually look alike
What is the basic thought behind morphological species concept?
Members of species look alike because they share many alleles.
What does the morphological species concept also extend to outside of phentype?
members of the same species usually have similar DNA sequences that are distinct from those of other species.
What is a barcode?
Under morphological species concept
every species has a unique signature in a certain region of DNA
What are the limitations of the morphological species concept
• But males and females may not look alike.
Ex: sexual dimorphism
Immature individuals may not look like their parents.
Other types of information must be used to determine species
What is the biological species concept?
A species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
members of same species capable of producing offspring together
members of diff species incapable of producing offspring together
One we traditionally use
members of different species are reproductively isolated from one another.
Why is the Asian and Sri Lankan elephant the same species?
They can potentially interbreed
never have to because of geographical separation
What kind of gene bool is a species according to BSC?
closed gene pool
alleles shared among members of species but not with members of others
What are the issues with biological species?
Closely related species hybridize and may produce offspring
Plant cultivars
Excludes Asexual organisms
do not interbreed, instead asexual reproduction
Why can testing BSC be difficult?
unnatural circumstances could impact animal behavior/mating
What are plant cultivars?
plants cultivated to suit human use
can breed and are the same species, but look very different
What are hybrid offspring under BSC?
first pair of populations represents two species, whereas the second pair represents just one
What is hybridization often caused by?
incomplete reproductive isolation
In one location, the two groups may be reproductively isolated from each other, while in another location, they interbreed
What kind of organisms is reproductive isolation common?
plants
Ex: different species of willow, oak, and dandelion than exchange genes and produce hybrids
But, species maintain distinct appearance rather than a single merged population —> NS discriminates against hybrid offspring
What can become an issue with hybridization?
Example: western and Eastern meadowlark have differentient themselves by calls
In Areas they overlap and interact with each other —> they mate
Why they mate--> produces hybridization--> different call --> no one wants to mate with him
often don't survive and don't become a new species)
What does a horse and donkey mating create?
creates infertile mule (hybridization)
Why is a mule infertile?
has uneven set of chromosomes
may reproduce but creates errors in zygote formation that can lead to death
What is an Androdioecous species?
Reproductive system characterized by the coexistence of males and hermaphrodites
asexual species
What is a Gynogenetic species?
Embryo contains only maternal chromosomes due to activation of an egg by sperm that degenerates without fusing with the egg nucleus
asexual species
decreases genetic diversity more than androdioecious species
How do killfish show limitations of biological species?
Androdioecous species
Killfish live in Low oxygen areas and dries out quickly and sporadic (temporal habitats) --> only has males and hermaphrodites
Can produce generation by itself because of crazy conditions
Individual can lay eggs and produce their own sperm to create clone of itself
Males also persist --> can provide sperm --> increases genetic variation --> recombination can occur
How does the amazonian molly show limitations of biological species?
All female population
Produce eggs (clones of themselves)--> mate with closely related species that enacts that process
Will go extinct some day
What is the ecological species concept?
A species is a group of organisms that share a distinct ecological niche
Different species use ecological resources differently, to become divergent in behaviour and location, leading to isolation from one another as a species.
Why. is the ecological species concept not used
states that niches are unique own species —> a one-to-one correspondence between a species and its niche
But niches can have variation
ex: fundamental niche
full range of environmental conditions and resources within which a species could survive and reproduce in the absence of limiting factors
What is the phylogenetic species concept?
A species is a group of organisms bound by a unique ancestry (single common ancestor)
emphasizes that members of a species all share a common ancestry and a common fate

Limitations of phylogenetic species concept
Does not specify scale that should be used
Ex: thousands of mammals that evolved since long-ago common ancestor
What is the phylogenetic species concept more useful for?
asexual species
Don’t breed with different individual
What is introgression?
on path of diff species has collapsed back into each other
Ex: Ravin in Artic Vs. California
Artic: separate in space and have not bred with the one in California —>on path to become new species
But, there is a bridge between them
DNA tested and genetic details —> of Olarghic (Artic) population stronger —> traits of weaker species may be lost during introgression
Why is there controversy around species?
Species are dynamic, evolving individuals, but we attempt to force them into rigid classes
Nature does not conform to our boundaries or classification
Species are real evolutionary groups and not categories which are created as a direct function of perceived distinction
Taxa may be at various stages of divergence