Exam 3
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
spirometry
Measures volume & speed of air inhaled or exhaled as a function of time
FEV1 – Forced expired volume in 1st second
FVC – Total volume of air exhaled from maximal inhalation to maximal exhalation
FEV1/FVC% - The ratio of FEV1 to FVC, expressed percentage.
Based on gender, size, race and age there are values (diagnosing severity) and predicts obstruction
Below 70% indicated obstruction
PEFR – fastest flow gas from lungs
COPD treatment
Relieve symptoms
Bronchodilators
Short acting - rescue drug
Beta agonist
sama
Long acting - daily relief
Lama
Laba
how COPD meds are prescribed
Step 1
Quick acting bronchodilator
Short Acting Beta agonist (SABA)
Short Acting Muscarinic antagonists (SAMA)
Step 2
Add long-acting bronchodilator
Long-Acting Muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) or
Long-Acting Beta agonist (LABA)
Step 3
Add 2nd long-acting bronchodilator
Long-Acting Beta agonist (LABA) or
Long-Acting Muscarinic antagonists (LAMA)
bronchodilators
Rapid, short-acting (4-8o)
Albuterol (SABA)
Ipratropium (SAMA)
Long-acting
Antimuscarinic (LAMA)
Tiotropium (24o), Aclidinium (12o)
Long-acting b2-agonist (LABA)
Salmeterol (12o), Indacaterol (24o)
inhaled steroid
Last line treatment
Fluticasone
Budesonide
What are their effects
Oral thrush
Need to rinse mouth afterwards
Hoarse voice
Cough
Throat irritation
Long term
Adrenal insufficiency
Cataracts
Osteoporosis
Bruising
hyperglycemia
inhalers
Pressurized (MDI)
Propelled by gas
Dry Powder (DPI)
Drug inhaled as Powder
using a DPI
Open it so you can see the mouthpiece.
Slide the lever until it clicks (loads medication).
Gently breathe out.
Do not exhale into the device
Can clog it
Seal lips around the mouthpiece.
Inhale rapidly and deeply
Hold breath 10 sec. to deposit
Remove device from mouth, exhale.
Check if powder is gone; if not repeat.
Wait 1 min between puffs
being less SOB
Pursed Lips Breathing
Inhale via nose with mouth closed
Exhale over 4-6 seconds thru pursed lips
Use when experience dyspnea
Prevents air trapping
Keeps airways open longer
Creates PEEP
tripod position
arms forward - raises clavicles and increases lung expansion
pulmonary rehab
Strengthens upper arm muscles and improves muscle tone
Helps with ADLs
Teaches Self- Management
How to use equipment (inhaler, O2)
How to exercise, less dyspnea
Stress reduction
Keeps pts active
when to give O2
sats below 88%
green zone
doing well
usual activity and exercise level
usual amounts of cough and sputum
sleeping well at night
appetite is good
actions
take daily meds
use O2 as prescribed
continue regular diet/exercise plan
avoid cigarette smoke, inhaled irritants
yellow zone
COPD flare
more breathless
less energy
increase, change in consistency, and/or color of sputum
poor sleep
medications not wokring
actions
continue medications
use quick relief inhaler
use O2
used pursed lip breathing
call provider if no improvement
red zone
Need urgent medical care
severe SOB even at rest
cannot tolerate any activity
cannot sleep at all
feeling confused or very drowsy
coughing up blood
fever or chills
actions
call 911
asthma
Airway hyperresponsiveness through many things
Exercise, mold, allergens
Release inflammatory mediators
allergic asthma
Allergen exposure
Antibodies are synthesized and secreted and bind to mast cells and whenever they are exposed again the mast cells will secrete mediators, histamines, leukotrienes, etc that give asthma side effects
non allergic asthma triggers
results from encounter trigger
Strong odors
Air pollution
Chemical
Exercise
Same sxs allergic asthma
peak flow meter
Measure speed gas leaves lungs
Provides # for self-management
Three zones
Green = 80-100%
Yellow – 50-80%
Red = < 50%
How to use
Move dial to bottom
Stand up
Deep breath
Blow into device hard & fast
Record value
Repeat X 3
Use highest value
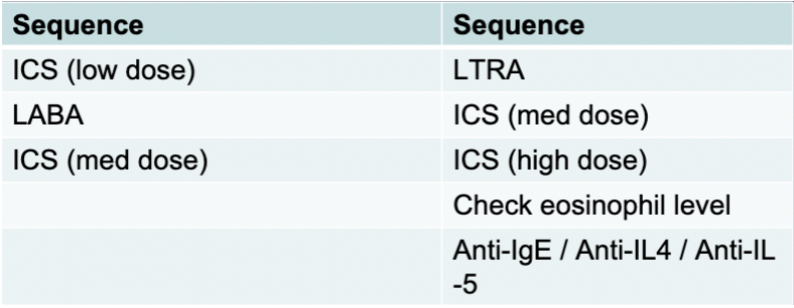
asthma symptom control
No SAMA for asthma
Relievers (onset 1 minute, last 4-6 hours)
Dilate airways
Short acting bronchodilator (SABA)
Standard Controllers (onset 5 minutes, last 12-24 hours)
Reduce / prevent chronic inflammation
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS)
Dilate airways
Long-acting bronchodilators (LABA)
Prevent release of mediators
Leukotriene antagonists (LTRA)
Biologic Controllers (last 2-4 weeks)
Reduce effects IgE / eosinophils
Anti-IL-5 / Anti IgE
asthma vs copd symptom control
What is missing versus COPD?
Muscarinic antagonists
What is added versus COPD?
LTRAs
Anti-IgE
What is different about the sequence?
Start with ICS
black box warning
Pt with asthma should not take a long acting beta agonist (LABA) without also taking an inhaled corticosteroids
Silent chest phenomenon / asthma exacerbation
Wheezing and exacerbation → 30 min later no wheezing but a lot of tightness = silent chest phenom
Risk factors for sleep apnea
Men more than women
Post menopausal women higher incidence
Fat distribution in tongue - closes off airway
Anatomy
Small upper airway
hypopnea index
Amount of times they quit breathing within an hour
<5 is normal
5-15 is mild
15-30 is moderate
>30 is severe
sleep apnea test
Polysomnography (PSG) Sleep Study
in lab diagnostic sleep study
records brain waves, heart rate, oxygen levels, and breathing
at-home sleep test
wearable device used to determine if someone has OSA
sleep apnea treatment
Positive airway pressure → keeps airway open bc positive pressure
Cpap
Bipap
Different on inspiration and expiration
Apap
Automatically titrate to pt needs
sleep apnea symptoms
Loud snoring
Partner reports apnea
Excessive daytime sleepiness
Memory, learning, mood problems
Impotence
pneumatic air splinting
must be used daily
most effective REM sleep (last night)
devices are portable, quiet, comfortable
very effective ↓ sx
adherence is poor
mandibular jaw advancement
Apnea (↑ CO2)
Arousal
Tongue moves
Muscles airway dilate
Device moves tongue and jaw forward
Not as effective as pos airway pressure
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation
In sleep
muscles pharynx relax, airway obstructs
Tongue position major factor
base tongue falls to back airway
New technique
Impulse generator
Sensor intercostal muscle
Electrode stimulates hypoglossal nerve
hiatal hernia symptoms
Often asymptomatic
Usually do not need treatment
Pyrosis (heart burn)
Dysphagia
Regurgitation
S/S – paraoesophageal
Fullness in chest
paraesophageal hiatal hernia
stomach moves into diaphragm next to the esophagus
hiatal hernia management
Small frequent meals
Elevate hob
Sit up for 1 hr post food
Smoking cessation
GERD risk factors
Asthma
Pregnancy
Obesity
Sedentary lifestyle
Smoking
GERD causes
Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter
Increased gastric volume (increased BMI increases gastric volume)
Delayed gastric emptying
Potency of refluxed material
Hiatal hernia
GERD symptoms
Burning in esophagus
Dyspepsia (indigestion)
Dysphagia and pain with swallowing
Hypersalivation
Esophagitis
GERD management
Smoking cessation
Dietary restrictions – avoid trigger foods
Sit up for 1 hour after eating
Do not eat for 3 hours before sleeping
PPIs: esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole
H2RAs: famotidine, ranitidine
Prokinetic agents: domperidone, metoclopramide (increases GI motility)
Bethanecol to increase lower esophageal sphincter tone
Cytoprotective agents: sucralfate
Nissan fundoplication
Peptic ulcer disease causes
Increased secretion of gastric acid
Damaged mucosa – decreased mucus secretion
Damaged mucosa predisposes to H. pylori infection
70-90% of ulcers
Produces ammonia, cytotoxins, mucous eroding enzymes → impaired bicarbonate production
ASA, NSAIDS
30% upper GI bleeds
30% deaths r/t ulcers
Stress, smoking, alcohol use
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Hypersecretion of gastric acid and multiple tumors resistance to medical treatment
Peptic ulcer disease risk factors
Age 40 – 60
H. pylori infection (most common cause)
ASA or NSAID use (second most common cause)
Increased gastric acid secretion
Peptic ulcer disease symptoms
Dull, gnawing pain or burning sensation in mid epigastrium or back
Pain relieved by eating or talking an alkali
Heartburn
Vomiting
Constipation or diarrhea
Bleeding and perforation
Belching
Bloating
Peptic ulcer disease diagnosis
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Biopsy
Tests for H. pylori - urea breath test, serologic and stool testing
peptic ulcer disease management
2 antibiotics plus PPI x 10-14 days if ulcer caused by H. pylori
Patient education: take full course of antibiotics
PPIs, H2RAs
Smoking cessation
Dietary modification
Surgical management
Vagotomy
Antrectomy
Biliroth I – gastroduodenostomy
Biliroth II – gastrojejunostomy
post op GI nursing interventions
Check gag reflex
Anytime you have surgery in stomach area don’t manipulate ng tube
Could damage suture line and make it bleed
GI hemorrhage
complication of PUD
S/S: hematemesis, hematochezia, melena, pallor, fatigue
PUD accounts for 50-80% of GI hemorrhage
bariatric surgery
Restrictive
reduce diameter of stomach lumen; capacity adjusted by silicone band
Laparoscopic banding
band placed around stomach to create pouch
Roux en y
Staple off part of stomach and bypass duodenum
Decrease in food intake and at risk for dumping syndrome
High protein and fiber complex carb diet
Want to not give oral fluids with food → 30 min between
Cholelithiasis risk factors
Age
Native American, Northern European
Family history
Obesity
Rapid weight loss (bariatric surgery)
Liver secretes extra cholesterol
Can prevent proper emptying
Female > male
Pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives
Hormones increase cholesterol levels
Diet
High in calories and refined CHO
Low in fiber
Cholelithiasis symptoms
Epigastric pain
pain that could radiate to shoulder and back
n/v with meals high in fat
inflammation of gallbladder
blockage of common bile duct
billiary obstruction
Elevated direct/conjugated
If liver is doing its job but there is a blockage in the gallbladder
Elevated indirect or unconjugated bilirubin
Due to liver disease
Elevated direct conjugated bilirubin bc liver is conjugating the bilirubin but can’t excrete it
cholecystitis management
morphine/opioid
Antiemetics
Antibiotics
NPO → low fat diet
Cholesterol stone dissolution with ursodiol (Actigall) or chenodiol
ERCP
E = endoscopic
R = retrograde
C = cholangio
P = pancreatography
direct visualization of the common duct-can via an endoscope to retrieve stones & place stents
Check for gag reflex
cholecystitis surgical management
Removal of gallbladder
Post op
Pain relief
Bile leak
Incisional care
Low fat diet when discharged
Abdominal assessment
Ileus, bile leak
Pulmonary toilet-CDB, incentive spirometry, AMBULATE
Incisional care
T-tube (choledochotomy)
For inflammation until swelling goes down
appendicitis symptoms
Mcburney point
Acute onset of pain
Starts in umbilical area and then radiates down to RLQ
Increase temp
Rebound abdominal pain
Push on abdomen - pain is when you let go
Pain with defecation and urination
appendicitis test
Labs
WBC increase
Ultrasound
Appendiceal diameter > 6mm
CT scan
Appendiceal diameter >6mm
Occluded lumen
Thickening of appendix wall
pre op appendicitis
NPO
Fluid electrolyte monitoring
No laxatives and No enemas
Do not want to stimulate the bowel to avoid rupture
antibiotics
post op appendicitis
Look at incision sites
Abdominal assessment
Antibiotics
24hours
NPO advance as tolerated
Semi fowlers
Moving
IS
Observe for complications
Bowel leak
Peritonitis
Pain
In shoulder due to CO2 from procedure
peritonitis symptoms
PAIN
Movement aggravates it
Fever
Abdominal distention
“board like” abdomen
Extremely hard
Shifting of extracellular fluids into peritoneal cavity
Diminished or absent bowel sounds
Nausea and vomiting
Hypovolemia and shock
From shift of fluids
Hiccups
Irritation to phrenic nerve
peritonitis
Acute inflammation of the peritoneum (serous membrane that lines abdominal cavity & covers visceral organs) leads to abscess formation and adhesions
peritonitis treatment
prevent extension of inflammation
correct fluid and electrolytes
minimize bowel obstruction
Do not want adhesions
NG tube with continuous suction to rest GI
Antibiotics IV and place them in cavity
Complex wound care
Semi fowlers
peritonitis complications
Abscess formation
Septicemia
Septic shock
Hypovolemic shock (fluid loss)
Adhesions (bowel obstruction)
Mortality
Overall, 40%
Younger and with less contamination < 10%
diverticular disease risk factors
Western world diet
Low fiber
Age
Constipation
Decreased physical activity
Laxative abuse
diverticulosis treatment
Due to deficient dietary fiber
Increase in intraluminal pressure
high fiber diet
diverticulosis symptoms
Asymptomatic when not inflamed
Episodic pain in LLQ
Narrow stool
Weakness and fatigue
diverticulosis interventions
Increase fiber to 25-30mg a day
Bowel retraining
Fiber supplements
Avoid laxatives
Drink 8 glasses of water a day
Increase activity
Diverticulitis vs diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
multiple diverticula are present without inflammation
Diverticulitis
Diverticula become inflamed
diverticulitis symptoms
Increased defecation
constipation
N/V
Fever
Increase WBC
Abdominal distention
Ribbon like stool
Blood in stool
diverticulitis treatment
different from diverticulosis
start with low fiber then build
diverticulitis interventions
Antibiotics
Bowel rest
Initially NPO -> clear liquids -> soft low fiber -> and continue
Back to high fiber once infection is gone
Hydration
Pain relief
No morphine
Increases intralumal pressure
NO laxatives
Antispasmodics
bentyl
Diet
diverticulitis complications
Perforation
Peritonitis
Abscess/fistula formation
Bowel obstruction
Urethral obstruction
Bleeding (hematochezia)
diverticulitis surgery
Resect area with diverticulitis
Hartmann's procedure
Temporary colostomy
Reversed once infection is gone
Peritonitis
Abscess
Failure to respond to medical treatment
Hemorrhage
UC vs Crohn’s
UC
Mucosa and submucosa
Colon
Stool
Bloody and mucosy
tenesmus
Chron’s
Multiple layers
Anywhere
No blood in stool
UC
Affects
Only the large intestine
Involves
Only the mucus and submucosa
Not every layer
Exacerbations
Mild to severe
unpredictable
Manifestations
LLQ pain
Bloody diarrhea with mucus
Tenesmus
Pressure feeling of needing to pass a BM but dont have to
Weight loss
Anemia
Low albumin
Bleeding
Megacolon
Dilation of colon
Leads to perforation
Crohn’s
Seen in any age but usually younger people
Affects
Anywhere
Mouth
Commonly in ileum and colon
Small ulcers
Involves
Entire thickness of bowel
Manifestations
Diarrhea
Non bloody
Fatigue
RLQ pain
Anemia
Weight loss
Malnutrition
Low albumin
Crohn’s disease of mouth
X-ray
Shows cobblestone effect
managment of IBD
Nutritional treatment (TPN)
Bowel Rest (Severe)
Medications
Antibiotics
Cipro
Immunosuppressants
Methotrexate
prednisone
Amino salicylates
Change the way cells release certain chemicals (cytokines)
Apriso
Rowara enema
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor
Slow progression of inflammation
Humera
Janus Kinase Inhibitors
Single transmission pathways for cytokines
Anti-diarrheal
Surgery
IBD nursing care
Pain relief
Maintain hydration
Maintain optimal nutrition
Promote rest
Reduce anxiety
Prevent skin breakdown
Medication education
Fewer, firmer stools
ostomy post op
Post op monitor fluid and electrolyte balance
Ascending - liquid
Transverse - slightly firmer
Sigmoid - formed
How it looks depends on ostomy placement
characteristics of stoma
Rose to brick red
Purple to black = emergency
pale - anemia
ostomy interventions
Clear liquid diet once ordered (+flatus, +BS)
Pain management
Activity
IS
SCD use
Provide private time for patient to discuss self-image and sexual concerns
Aseptic technique for dressing changes
Ostomy care
ostomy complications
Prolapse
Can have issues with keeping appliance on
Can be repaired
Retracted stoma
Keeping ostomy appliance on is difficult
Ileostomy and colostomy diet
May start out with low fiber/low residue diet until intestinal swelling resolves
Advance to regular diet with balanced dietary fiber.
Take vitamin supplements as directed by physician
Add new foods gradually to determine tolerance
Try foods several times before eliminating them
Eat at regular intervals (may benefit from more frequent and smaller meals)
Do not skip meals
Lactose intolerance is common
peripheral artery disease
Atherosclerosis most common chronic arterial disorder
Deposit of fat and fibrin obstructs and hardens arteries
5 P’s (Signs and Symptoms of Acute Limb Ischemia)
Pain
Pulselessness
Poikilothermic
Pallor
paresthesia
Most common cause of amputations
peripheral vascular disease risk factor
Men
African American
Family history
Smoking
HTN
DM
Metabolic syndrome
age
peripheral vascular disease prevalence
70 or older
40s if they have another risk factor
intermittent claudication
Pain when walking
From calf muscle
Increase in oxygen demand -> increase lactic acidosis -> increase pain
Dependent limbs can help with pain
PVD intervention
keeping legs warm bc they will vasoconstrict if they get cold
varicose veins treatment
Conservative
Compression stocking (augment muscle pumping action of legs)
Leg elevation
Toes above the nose
Exercise
Ablation Therapy
Heated catheter
Laser or radiofrequency
Heated catheter creates scare tissue and causes vein to close
Sclerotherapy
Vein Stripping
Cut the vein above the affected area and below
Rip it out
Gotten away from
varicose veins
Heaviness and discomfort in legs
DVT symptoms
Dull, aching pain
tenderness
warmth
erythema
Edema (Increase in extremity circumference)
Could be asymptomatic and pulmonary emboli is first sign
DVT risk factors
Hospitalized, immobile
Surgery – 20% increase
50% increase for orthopedic surgery
Obesity
Smokers
Oral contraceptives
Central Venous Catheters
DVT diagnosis
Doppler
IV heparin therapy
Baseline PT/PTT, Anti-Xa, H/H and Platelet count required before therapy is initiated
Platelet count and H/H QD
Assess for “HIT” (Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia)
Report Plt count <150,000 or a 30-50 % reduction
start on different anticoagulant
Assess for signs of bleeding
stool guiac
hematuria
Reversal agent
Protamine Sulfate
Management-Warfarin
Coumadin is given simultaneously with heparin until Coumadin is therapeutic and then Heparin is discontinued.
Coumadin should be given same time every day
On Coumadin 3- 6 months usually
INR monitored frequently
INR range that is therapeutic is 2-3 usually
Patient education essential - safety
Dietary instruction
Vitamin K reversal agent
need consistent level
Do not take any over the counter medication or herbal supplements without consulting MD first
Wear a med alert bracelet
No smoking
No alcohol
Obtain blood work as ordered
Take precautions to avoid bleeding
Report to ED for episode of bleeding
Careful with G herbal supplement
Anticoagulants
Factor Xa Inhibitors
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Apixaban (Eliquis)
Does not effect platelet aggregation
Short half-life so can discontinue 2 days before surgery and resume 6-10 hours post-surgery
Interacts with many meds and over the counter herbals
Contraindicated in renal impairment (CrCl < 30ml/min) and Hepatic impairment
aneurysms
If asymptomatic and <5.5 cm → typical treated medically w bp control and serial imaging
Once 5.5 then go in and surgery on it
AAA management
Medical Management
If asymptomatic
Aggressive BP control
Serial imaging
Surgery when ≥ 5.5 cm
Surgical Management
Two types
Endovascular grafting (EVSG or EVAR)
Up through the groin and place a stent
Avoids pressure on the weakened wall
Open approach
Clamp above and below aneurysm
Mortality
≤ 5% elective; 40% emergent
AAA patient teaching
BP control and surveillance
aortic dissection
Type A
Ascending aorta
Emergent surgery
High risk for life threatening complications
Only contraindication for surgery is if presence of comorbidities impact survival to one year or less
Type B
Descending aorta
Surgery reserved for development of complications related to dissection
If uncomplicated generally managed medically
Medical management
Blood pressure control
Imaging surveillance
HIV
Specific type of virus (a retrovirus)
Carries genetic information as RNA
Enters body, infects cells CD4 antigen
Uses enzyme to convert RNA to DNA
DNA is duplicated in cell division
Can remain inactive years
Creates antibodies (seroconversion)
Detected as early as 2 weeks to 4 weeks
HIV Stages
Stage 1
Transmission and Seroconversion
Short, flu-like illness or no symptoms
Highly contagious at this time
Seroconversion detected:
2-4 weeks
Stage 2
Clinical Latency Period
Lasts for average 8-10 years
Usually no symptoms
May be swollen glands
Level HIV blood drops to very low levels
HIV antibodies are detectable in the blood
Stage 3
AIDS
The immune system weakens
Illnesses become more severe leading to an AIDS diagnosis
HIV nursing care
Changes over course of disease
Early stages
Preventive health measures
Health maintenance activates
Education
Psychosocial support
Disease progresses
Physical symptom management
Education on infection prevention
Continued psychosocial support
tuberculosis symptoms
Pulmonary issues
Cough
Fever
Weight loss
Anorexia
Night sweats
tuberculosis treatment
Airborne isolation
Antitubercular meds
Admin of 4 drugs over 6 month course
Infection control and med compliance