Neoplasia FLASHCARDS🦀
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
What is neoplasia?
Neoplasia is an abnormal mass of tissue growth.
2
New cards
What are the hallmarks of cancer
* self-sufficiency in growth signals
* insensitivity to anti-growth signals ( because they don’t have receptors)
* evading apoptosis( telomeres)
* sustained angiogenesis
* limitless replicative potential
* invasion and metastasis
* escaping immune surveillance (checkpoint inhibitors)
* variation in population of cells
* heritable: Mutations in DNA, chromosomes, methylation pattern
* insensitivity to anti-growth signals ( because they don’t have receptors)
* evading apoptosis( telomeres)
* sustained angiogenesis
* limitless replicative potential
* invasion and metastasis
* escaping immune surveillance (checkpoint inhibitors)
* variation in population of cells
* heritable: Mutations in DNA, chromosomes, methylation pattern
3
New cards
What are the different tissue types associated with cancer?
* **carcinoma** → epithelial cells
* **sarcoma** → connective tissue
* **leukemia** → circulatory or lymphatic
* **sarcoma** → connective tissue
* **leukemia** → circulatory or lymphatic
4
New cards
What are the different cell types associated with cancer?
* **adenomatous cells** → ductal or glandular cells
* **squamous cells** → flat cells
* **myeloid** → blood cells
* **Lymphoid** → lymphocytes or macrophages
* **squamous cells** → flat cells
* **myeloid** → blood cells
* **Lymphoid** → lymphocytes or macrophages
5
New cards
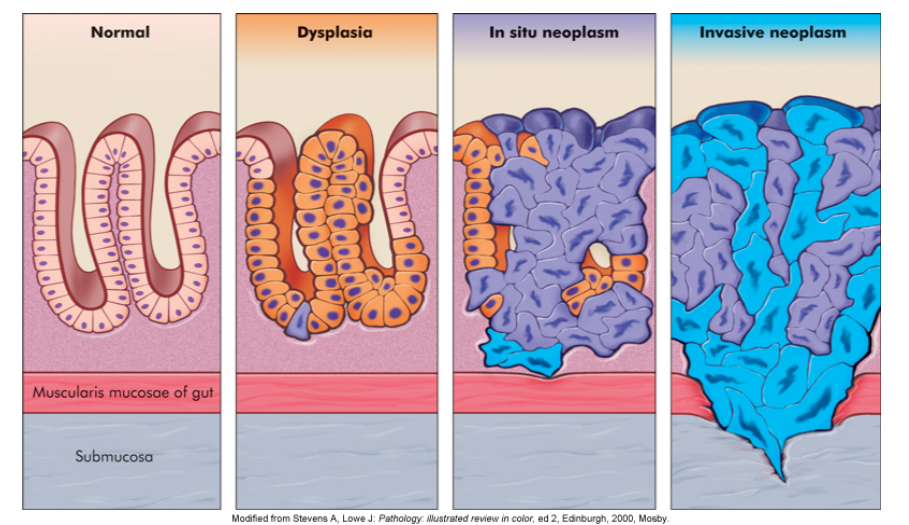
What are carcinoma in situ (**CIS**)?
* epithelial malignant tumors that have *not* broken through or invade the surrounding stroma (can be cut out cleanly)
6
New cards
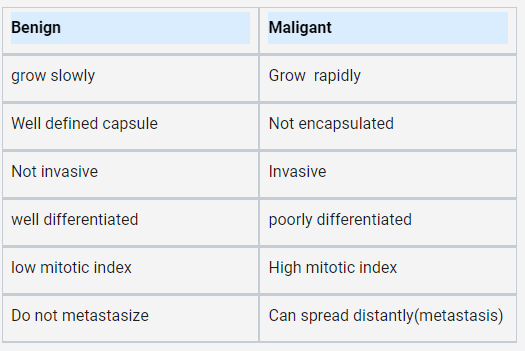
What is the difference between benign and malignant tumors?
==**Benign**== tumors ==grow slowly==, have a ==well-defined capsule==, are ==not invasive==, are ==well-differentiated==, have a ==low mitotic index==, and ==do not metastasize==. ^^**Malignant**^^ tumors ^^grow rapidly^^, are ^^not encapsulated^^, are ^^invasive^^, are ^^poorly differentiated^^, have a ^^high mitotic index^^, and can ^^spread distantly through metastasis^^
7
New cards
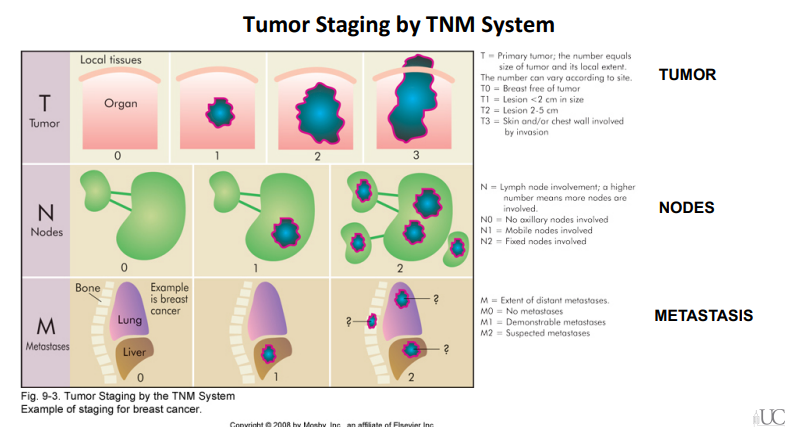
What is the TNM system used for in cancer staging?
The TNM system is used to stage malignant tumors based on the tumor size and invasiveness, the number of lymph nodes affected, and the presence of distant metastasis.
8
New cards
What are tumor markers
Tumor markers are biological markers produced by cancer cells
* enzymes
* genes
* Antigens ( PSA -prostate-specific antigen are associated with prostate cancer)
* antibodies
* enzymes
* genes
* Antigens ( PSA -prostate-specific antigen are associated with prostate cancer)
* antibodies
9
New cards
What bacteria is linked to stomach cancer
Helicobacter pylori is a type of bacteria that has been linked to the development of stomach cancer
10
New cards
What is the paradox associated with fast-growing tumors?
Fast-growing tumors are paradoxically easier to treat because they are more responsive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy
11
New cards
What is a pap smear? and how should it look like its helathy tissue or tumours tissue?
* **PAP smear**- cervical l screaming via a swab, the smear is histologically analyzed and checks if to dysplasia
* ==red stained cells== are dysplasia or cancer
* could also show cells is mitosis and multiple nuclei
* blub that starts to grow → lesion
* HPV causes cancer in basal cells( because they proliferate the most)
* due to the alteration of genome of the host develops cancer
* HVP produced proteins that block p53( hallmark in cancer) if the p53 build-ups and it does not function the cell does not go into apoptosis
* ^^blue + purple^^ stained cells are normal
* ==red stained cells== are dysplasia or cancer
* could also show cells is mitosis and multiple nuclei
* blub that starts to grow → lesion
* HPV causes cancer in basal cells( because they proliferate the most)
* due to the alteration of genome of the host develops cancer
* HVP produced proteins that block p53( hallmark in cancer) if the p53 build-ups and it does not function the cell does not go into apoptosis
* ^^blue + purple^^ stained cells are normal
12
New cards
What 2 DNA viruses is linked cancer? What is a RNA virus and association cancer?
* hepatitis B → liver cancer
* EBV → kissing disease ( mononucleosis) + Burkitt lymphoma
\
* HIV → cervical cancer, caner of mouth, throat, anus
* EBV → kissing disease ( mononucleosis) + Burkitt lymphoma
\
* HIV → cervical cancer, caner of mouth, throat, anus
13
New cards
what is the APC gene and what is its assosiation with cancer ?
The APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene is a **tumor suppressor gene** that plays a role in **regulating cell growth and division**. **Mutations** in the APC gene can lead to the development of familial adenomatous polyposis (**FAP**), a hereditary condition characterized by the **formation of numerous polyps in the colon and rectum**, which can progress to colon cancer.
14
New cards
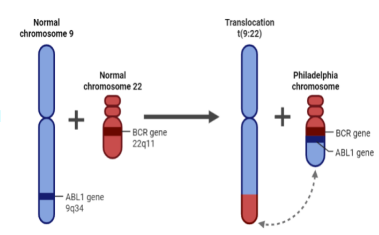
what is the Philadelphia Chromosome in Myeloid Leukemia
* genetic abnormality that is commonly found in myeloid leukemia → translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, leading to the fusion of the BCR (breakpoint cluster region) gene on chromosome 22 and the ABL1 (Abelson tyrosine kinase 1) gene on chromosome 9.
* what does it cause?: produces a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that promotes uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation
* what does it cause?: produces a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that promotes uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation
15
New cards
what is the RAS gene and what is it associations with cancer?
* RAS gene is a family of genes that encode proteins involved in **cell signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, and survival**
* mutation causes: constitutively active, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation. This can result in the formation of tumors and the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
* mutation causes: constitutively active, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation. This can result in the formation of tumors and the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
16
New cards
what is the NMYC gene an its association with Neuroblastomas?
The NMYC gene is a **proto-oncogen**e that encodes for the N-Myc protein, a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in **neural development**. In normal cells, the NMYC gene is tightly regulated, but in some cases, **it can become amplified or overexpressed, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division.**
NMYC amplification is frequently found in **neuroblastoma**, a type of **cancer** that arises from immature nerve cells in the adrenal gland, neck, chest, or spinal cord. In neuroblastoma, the NMYC gene is often amplified, leading to high levels of N-Myc protein expression. This amplification is associated with aggressive tumor growth and a poor prognosis, particularly in high-risk neuroblastoma.
NMYC amplification is frequently found in **neuroblastoma**, a type of **cancer** that arises from immature nerve cells in the adrenal gland, neck, chest, or spinal cord. In neuroblastoma, the NMYC gene is often amplified, leading to high levels of N-Myc protein expression. This amplification is associated with aggressive tumor growth and a poor prognosis, particularly in high-risk neuroblastoma.
17
New cards
what is the TP53 gene
the ^^TP53 gene^^ is **a tumor suppressor gene** that plays a crucial role in preventing the development and progression of cancer. It **encodes a protein called p53**, which acts as a **transcription factor to regulate the expression of other genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, apoptosis, and cellular senescence.** Mutations in TP53 are found in a **wide range of human cancers** and are associated with an **increased risk of cancer development.** The loss or dysfunction of p53 protein can lead to **uncontrolled cell proliferation, genomic instability, and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, thereby promoting cancer growth and metastasis.**
18
New cards
APC gene and caner?
The APC gene is a tumor **suppressor gene that helps prevent the development of cancer by controlling cell growth and division**. Mutations in the APC gene can disrupt this control and lead to the **formation of tumors, particularly in the colon and rectum (colorectal cancer).** The APC gene is also associated with other types of cancer, such as **pancreatic cancer and stomach cancer.**
19
New cards
what is metastais in cancer?
Metastasis → **cancer cells spread from the primary tumor to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.**
* Seeding within body cavities → A direct seeding of body cavities and surfaces
* Lymphatic spread→ They enter the lymphatic
* Hematogenous spread → the transfer of tumor cells from the primary tumor with the bloodstream.
* Seeding within body cavities → A direct seeding of body cavities and surfaces
* Lymphatic spread→ They enter the lymphatic
* Hematogenous spread → the transfer of tumor cells from the primary tumor with the bloodstream.
20
New cards
what is anaplasia and the assoscitaion to cancer ?
Anaplasia is a term used to describe **a lack of differentiation or abnormal differentiation of cells in cancer**→ when cells become **less specialized and lose their normal appearance and function**. This lack of differentiation makes **cancer cells more aggressive**, as they can grow and divide more rapidly and invade surrounding tissues more easily.
21
New cards
Local invasion and metastasis are two different processes in cancer progression, what is the diffrnece?
local invasion refers to the spread of cancer cells to nearby tissues, while metastasis refers to the spread of cancer cells to distant sites in the body
22
New cards
what are oncogenes?
Oncogenes are normal genes that control cell growth and division. However, when mutations occur in these genes, they can become overactive and promote excessive cell growth and division, leading to the development of cancer.