GEN. BIO. 11: Earliest Microscopic Observations + The Cell & Its Beginning
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All information was taken from Ma'am Evelyn's PPT and the book. As of 02/01/26, information is still incomplete as the discussion has not finished yet. If you wish to study only specific chapters from this huge topic, please star it and choose the option to study starred terms only. I know there are a lot of terms to take in but I made it into 1 flashcard set out of convenience, so I hope you understand. Thank you!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Robert Hooke (1635 – 1703)
He devised the earliest microscopes that could magnify materials.
His commemorative work came from a thin slice of cork from the bark of an oak tree.
He described the perforated and porous surface as honeycomb and later called it cellulae, using the Latin word for “small room.”
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
A Dutch naturalist credited to be the first to study magnified cells.
He gave the name animalcules,” meaning little animals, because he saw them moving in the pond.
He was the first to observe living cells.
Resolution
Indicates the clarity of an image.
Micrograph
It specifies the type of microscope used to produce the image as well as the magnification value of the image.
Magnification
It is the measure of optical instruments for an object to appear larger than its actual size.
Resolution
It indicates the clarity of an image.
Compound Microscope
A type of microscope that is commonly used in schools and is equipped with lenses to enlarge objects up to several hundred times, with the most powerful one having a magnification up to 2000x. This microscope is used to examine cells and sections of tissues with the use of sunlight or artificial light to illuminate the object being examined.
Stereo Microscope
A type of microscope that is used to examine the external structure of a specimen such as insects.
Phase-contrast Microscope
A type of microscope that is used to examine highly transparent objects such as unstained cell.
Electron Microscope
A type of microscope that uses streams of electrons to enlarge objects approximately 10,000,000x.
Fluorescent Microscope
A type of microscope that illuminates objects stained with fluorescent dyes that glow in the dark.
Confocal Scanning Microscope
It is used to examine the three-dimensional structure of an organelle without cutting the specimen into sections. It uses a beam to scan across the specimen.
Matthias Jakob Schleiden (1804 – 1881)
A German botanist who concluded that all plants are made of cells.
Theodor Schwann (1810 – 1862)
A German physician and physiologist who examined animal cells and concluded that all animals are composed of cells.
Rudolf Carl Virchow
A German physician
Stated that all cells come from other cells through the process of cell division
All organisms are composed of cells
Cells are the smallest and basic units of structure and function in organisms
Cells arise from previously existing cells
Cells
The fundamental units of life and the smallest structural and functional units in all living organisms.
All plants are made up of these units (Matthias Jakob Schleiden, 1804–1881).
All animals are made up of these units (Theodor Schwann, 1810–1862).
They arise from previously existing units through the process of division (Rudolf Virchow, 1821–1902).
They make up the bodies of living organisms and carry out essential life functions.
Cell Division
It is the fundamental biological process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, essential for growth, repair, and reproduction. It involves duplicating DNA and splitting cellular components, occurring primarily through mitosis (identical body cells) or meiosis (sex cells).
Mitosis
A type of cell division that produces two identical diploid cells, maintaining the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, and is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that produces four genetically different haploid cells, with half the number of chromosomes as the parent, and is used for sexual reproduction.
Miller-Urey Experiment
An experiment that provided the first evidence that organic molecules needed for life could be formed from inorganic components. Some scientists support the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that the first life was self-replicating RNA.
Aleksandr Oparin
He proposed that organic molecules might have been assembled in the Earth’s primitive atmosphere in the presence of strong energy (volcanic eruption, meteorites, isotopes, lightning, uv light)
They excluded oxygen from the mixture of gases in their experiment, as they knew that oxygen would prevent the formation of organic molecules from inorganic molecules. There is solid empirical evidence that the Earth's atmosphere has always had significant levels of oxygen.
What was missing from the Miller-Urey experiment?
Organic Chemical Evolution
It says that the first form of true living cells have evolved from protocells.
Nucleic Acids
They are known as the main information-carrying molecules of the cell, as well as leading the process of protein synthesis.
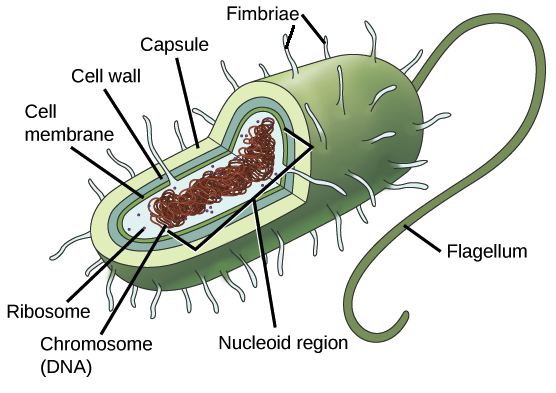
Prokaryotic Cells
Came from the Greek words pro, meaning “before,” and karyon, meaning “nut.”
Simple organisms with small size and simple structures
Examples include bacteria, blue-green algae, and archaea (bacteria that live in extreme environments)
Reproduce quickly and can be found in air, soil, water, and even inside the bodies of living organisms
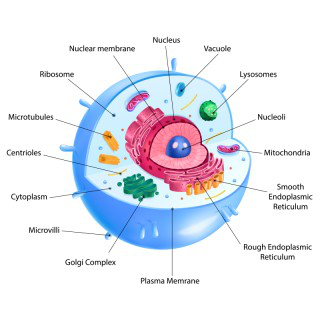
Eukaryotic Cells
Came from the Greek words eu, meaning “true,” and karyon, meaning “nut.”
Complex type of cell possessed by fungi, plants, animals, and protists.
Genetic material (DNA) is enclosed within a nucleus.
Cells contain membrane-bound compartments.
Organelles are neatly arranged.
Plasma Membrane
A semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Cell Wall
A rigid layer surrounding the plasma membrane that maintains the cell’s shape and protects it from environmental stress.
Capsule
A protective outer layer made of polysaccharides, present in some prokaryotic cells, that shields the cell from harmful conditions.
Nucleoid Region
An irregularly shaped area in prokaryotes where the cell’s DNA is stored, since they lack a true nucleus.
Cytoplasm
The fluid inside the cell where cellular components are suspended; not organized into distinct compartments in prokaryotes.
Ribosomes
Small structures scattered in the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesized.
Plasmid
A small, circular DNA molecule separate from chromosomal DNA that can provide genetic advantages such as antibiotic resistance.
Flagellum
A tail-like appendage that enables bacterial movement; it rotates like a whip to propel the cell.
Pili
Short, hair-like structures on the cell surface used for transferring DNA between bacteria and for cell-to-cell communication.
Nucleoid
A region in prokaryotic cells where DNA is located; it is not enclosed by a membrane.
Nucleus
A membrane-bound organelle that contains DNA and controls the cell’s activities.
Mitochondria
Organelles that produce energy for the cell through cellular respiration. It is known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
A membrane network with ribosomes attached that helps produce and transport proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER)
A membrane network without ribosomes that helps make lipids and detoxify chemicals.
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport.
Lysosome
A sac containing enzymes that break down waste materials and worn-out cell parts.
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant cells that carries out photosynthesis to produce food using sunlight.
Vacuole
A storage sac that holds water, nutrients, or waste; large and central in plant cells.
Cytoskeleton
A network of protein fibers that maintains cell shape and assists in movement and transport inside the cell.
Centrosome / Centrioles
Structures that help organize cell division in animal cells.