Unit 4: The Circulatory System
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
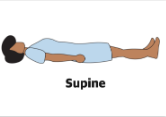
Supine
face/palm up
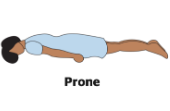
Prone
face/palm down
What is the position of the hand during hand blood draws?
Prone position
What is the position of the hand during arm blood draws?
Supine Prosition
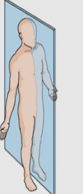
What plane is this?
Sagittal
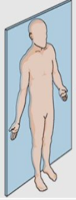
What plane is this?
Frontal
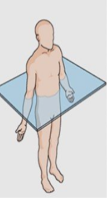
What plane is this?
Transverse
What cavities does the dorsal side of the body contain?
cranial & spinal
What cavities does the ventral side of the body contain?
thoracic, abdominal, pelvic
What separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities?
the diaphram
What does anterior mean?
Towards the back of the body
What does posterior mean?
Towards the front of the body
What does superior mean?
The higher part of the body
What does inferior mean?
The lower part of the body
What does proximal mean?
nearest to the center of origin
What does distal mean?
farther to the center of origin
What does medial mean?
toward the midline
What does lateral mean?
towards the side
What does midsagittal mean
splitting the body into EQUAL left and right halves
Pulmonary circulation
circulation specific to gas exchanged within the heart and lungs
Systemic circulation
circulation throughout the body
What are the steps of blood flow throughout the heart?
Superior vena cava, right atria, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs (gas exchange), pulmonary veins, left atria, bicuspid valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta, body
What is the SA node?
the pacemaker of the heart
Where is the SA node located
at the back wall of the atrium
How is the SA node triggered
filling up of blood in the atria
What does the atrial node trigger
atrial contraction
Where is the AV node located
bottom of right atria
What does the SA node do
pauses the impulse from SA node to allow the atria to empty
Where is the bundle of His located
top of septum/ventricular system
What does the bundle of his do
relays the impulse from the AV node through purkinje fibers
What does the bundle of his trigger
ventricular contraction
What does the bundle of his branch into
right and left bundle branches and perkinge fibers

What is the p wave
SA Node firing, atrial contraction, and depolarization

What is the QRS wave
ventricular contraction and depolarization

what is the T wave
repolarization/relaxation
what is the sac that protects the heart
the pericardium
What is the tunica intima
1st innermost layer of veins and arteries: endothelium
What is the elastic tissue
2nd layer of veins and arteries
what is the tunica media
the 3rd layer of veins and arteries: smooth muscle
what is the tunica advertitia
the 4th layer of veins and arteries: connective tissues
Arteries
carry O2 rich blood away from heart, thick smooth muscle, smaller lumen
Veins
carry O2 poor blood towards heart, thinner smooth muscle, thicker lumen, valves to prevent backflow of blood
What are capillaries made of
one cell walls
where is the cephalic vein located
on the radial (thumb) side
where is the median cubital located
in the center
where is the basilic vein located
on the ulnar (pinky) side
What shape veins do the majority of people have
H shape
what 3 veins does H shape contain
Cephalic, medial cubital, and basilic
what are the choices for blood drawing on H shape (best to worst)
median cubital, cephalic, hand, basilic
why should you avoid taking blood from the basilic vein
the vein is located over the brachial artery and nerves
What replaces the median cubital in the M pattern
median cephalic and median basilic
What is the first choice for a blood draw on a M pattern
median cephalic
What is blood composed of
plasma and formed elements
What does non clotted blood separate into
plasma, buffy coat, and formed elements
what percent of blood volume is plasma
55%
what is the composition of plasma
91% water 9% solute
How many liters of blood are in the body
5 liters
What are the three types of formed elements
erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes
What are erythrocytes
red blood cells
what do erythrocytes do
carry oxygen
What are immature erythrocytes
reticulocytes
What are leukocytes
white blood cells
what do leukocytes do
attack bacteria and infections
what are granulocytes
easily visible white blood cells when stained
what are agranulocytes
white blood cells with no granules or very fine when stained
What are the three types of granulocytes
eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils
What do eosinophils do
create an immune response to allergies and parasitic infections
What do neutrophils do
most numerous white blood cells that is present when there is a bacterial infection
What do basophils do
least numerous white blood cell that causes an inflammatory response
What are the two types of agranulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes
what are the two types of lymphocytes
T-lymphs and B-lymphs
what do t-lymphs do
directly attack infected cells
what do B-lymphs do
produce antibodies
what is the second most numerous agranulocyte
lymphocytes
what is the largest white blood cell
monocytes
what do monocytes do
destroy Pathogens through phagocytosis
what does the anticoagulant become after being spun
a buffy coat
which type of blood separates when spun or not
clotted blood
What is clotted blood separated into
serum and clotted blood (sometimes separator gel)
what are thrombocytes
the smallest formed element, first on the scene when injury occurs
What does plasma have that serum does not
fibrinogen
What is hemeostasis
body’s response to injury
what are the two phases of hemeostasis
platelet plug, then coagulation cascade that solidifies plug into clot
what determines blood type
antigens
what antigens does type AB have
both antigens
what antigens does type O have
neither
what is Rh factor
D antigen
What type of blood are you in the presence of D antigen
+
If you cant find a vein on the antecubital fossa where can you resort to
the feet
to draw blood from the feet you must
have doctors orders
what region of the arm is most preferred for blood drawing
antecubital fossa