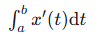chapter 5 Integral basics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
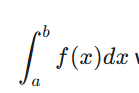
∫ ab f(x)dx will find the___
net area
What is the average value of f(x) from x=a to x=b ? (in other words, mean value theorem for integrals?)
1/(b-a) ∫ ab f(x)dx
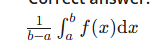
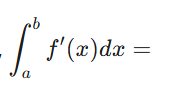
according to fundamental theorem of calculus, ∫ ab f’(x)dx = ?
f(b)-f(a)
why?
Total Change = Final Value - Initial Value
Total change = f(b) - f(a) The constant C cancels out. After all, F(x) = f’(x) , so it cancels out leaving f(x) ]b a
Area can ___ be negative
NEVER
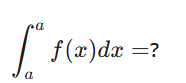
∫ aa f(x)dx =
zero
∫ ac f(x)dx = ___ + ____ ?
∫ b c f(x)dx + ∫ a bf(x)dx =
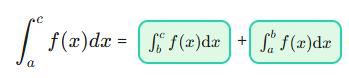
Net area is…
area above minus the area below
∫ ab f(x)dx will find
the area between the function above the x=axis and the x-axis minus the area between the function below the x-axis and the x-axis
in other words, positive area (area above x axis) minus negative area (area below x axis)
∫ ab f(x)dx = 10, then ∫ ba f(x)dx = ?
-10
becomes negative when limits of integrals are switched
d/dx ∫ 0x f(t)dt = ?
f(t)
bottom is constant, d/dx cancels out the integral
under vs over estimate: left hand and increasing
underestimate
under vs over estimate: left hand and decreasing
overestimate
right hand, increasing
overestimate
right hand, decreasing
underestimate
midpoint
if concave up, understimate (rectangle below curve)
if concave down, overestimate (rectangle above curve)
trapezoidal rule - over vs under estimate
concave up - overestimate, adds extra area
concave down - underestimate, misses area under curve
delta X ?
(b-a)/n where n is number of subintervals
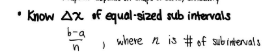
displacement:
change of position, includes negative velocity, distance beginning to end
ex. 2.0 feet, but walk back, -1.0 ft = 1.0 feet total
distance
includes all distance regardless of velocityies
2.0 ft, but walk back +1.0 = 3.0 feet
x(b) = x(a) + _____ (write as an integral expression)
∫ ab x’(t)dt