PT 710: Week 4 Review (GBS)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Guillain Barre Syndrome
Acute immune mediated demyelinating disorder affecting Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system
- AIDP most common variant in US
What is the most common type of acute paralytic neuropathy
GBS
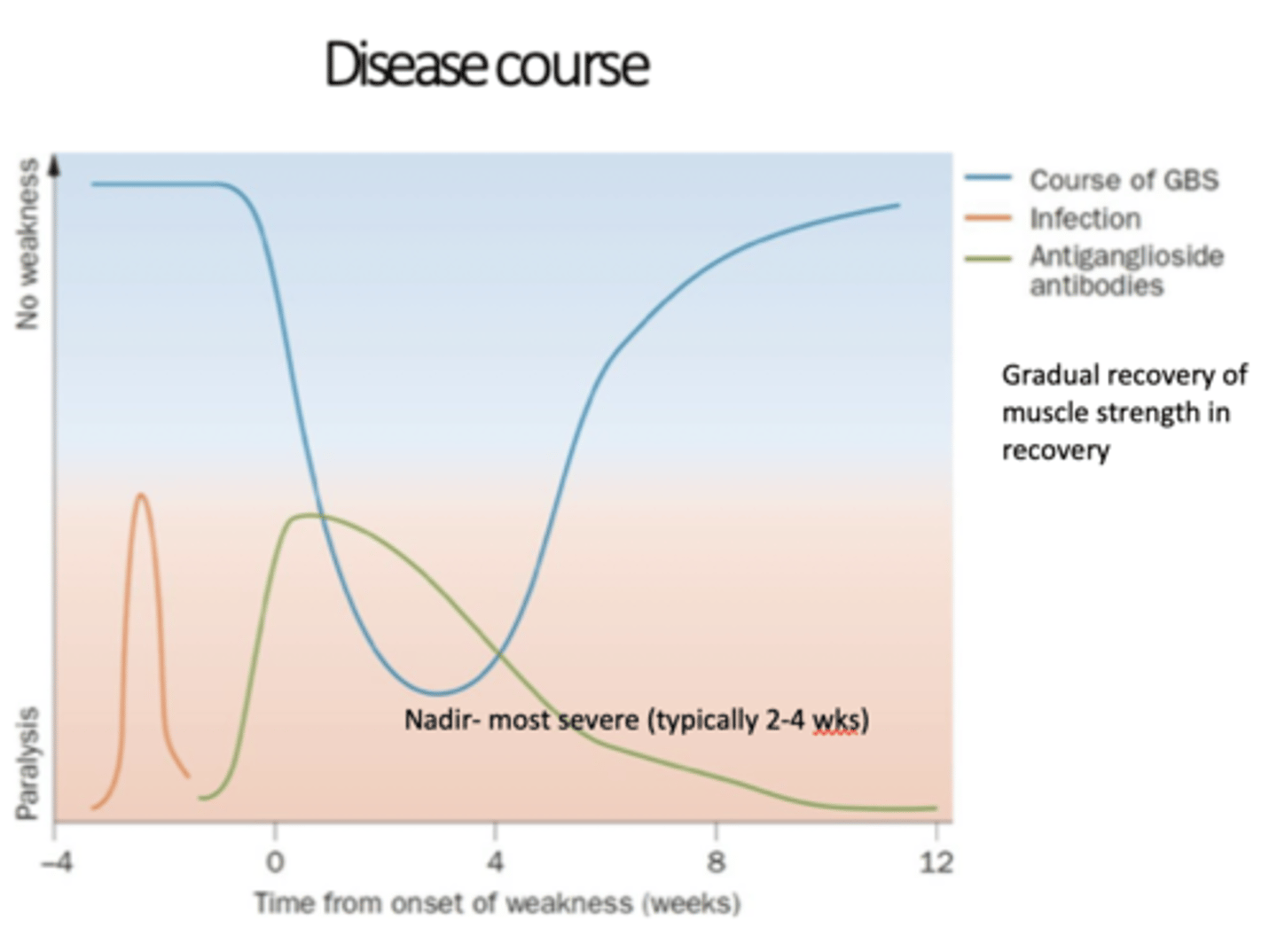
GBS disease course
GBS relation with protein levels
- Increased protein levels w/o pleocytosis
- Protein elevation notes in 90% of cases by 2nd week
Nerve conduction responses to GBS
- Reduced amplitude or absent distal motor AP
- Decreased conduction velocity
- Increased temporal dispersion
- Latency prolongation of F wave
- Nerve conduction block (axonal GBS)
What may show up on an MRI with GBS
- Enhancement and swelling/thickening of spinal nerve roots
Typical clinical presentation of GBS
- Motor weakness (rapidly progressive, symmetrical, usually distal to proximal)
- Hypo or areflexia
- Sensory symptoms
- Cranial nerve involvement
- Pain
- Progression of sx from 12 hrs to 28 days before plateau reached
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Respiratory difficulties (rq. ventilation)
REQUIRED features of GBS
- Progressive weakness of the legs and arms (sometimes initially only in the legs)
- Min-total paralysis of legs to total paralysis of all limbs, trunk, facial muscles
- Areflexia or decreased reflexes in weak limbs
In CIPD, the time to the nadir is typically...
>8 weeks
The following features make GBS diagnosis doubtful
- Sensory level loss of sensation below determined in neuro exam
- Marked, persistent asymmetry of weakness
- Bowel/bladder dysfunction at onset
- Severe pulmonary dysfunction with little to no limb weakness at onset
- Severe sensory signs with little or no weakness at onset
- Fever at onset
- WBC >50/mm3
What is CIPD
- Acquired immune mediated nerve d/o targets myelin sheaths of the peripheral nerve
- Defined by progression beyond 8 weeks
- Closely related to GBS
CIPD stands for
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Clinical manifestation of CIPD
- Symmetric motor involvement proximal and distal muscles
- Evolves over 2 months or more
- Reduced or absent reflexes
- Sensory impairment greater for vibration/prop than pain/temp
- Sensory involvement distal>proximal
Medical management of GBS if pt unable to walk 10m w/o assistance
1) IVIG
2) Plasma exchange
What is the 20/30/40 rule
Early intubation in pts w/autonomic dysfunction
- Vital capacity 15-20mL/kg
- MEP <40cm H20
- MIP <30 cm H20
Signs of respiratory failure
- Tachypnea
- Use of accessory muscles
- Paradoxical breathing w/inadequate effort
- Unable to complete sentences
- Weak cough or difficulty clearing secretions
Acute phase GBS
- Rapid progression of sx
- Sx peak between 2-4 wks
- 50% reach nadir w/in 1 wk, 70% by 2 wk, 80% by 3 wk
Plateau phase of GBS
- Characterized by stability of sx
- May only last days but can last months
Recovery phase of GBS
- Gradual improvement of sx
- Most pts show recovery of muscle strength 2-4 wks after plateau
- Sensory disturbances/fatigue may persist
Poor prognostic indicators w/GBS
1) Older age at onset >60
2) Severe muscle weakness on admission
3) Need for ventilatory support
4) Onset of sx (<7 days) prior to admission
5) An average distal motor response amplitude reduction to <20% of normal
6) Hx of GI (presence of diarrhea)
GBS specific T&M
1) GBS disability scale
2) Overall disability sum score (ODSS)
Considerations of functional retraining w/GBS
- Avoid stress to muscles w/o antigravity strength (use AD)
- Progressive functional exercises improves physical outcomes
Considerations of strengthening w/GBS
- AAROM to muscles w/MMT grade <3
- AROM and functional task training to muscles w/MMT grade >3
- Avoid eccentric exercises to weaker muscles
- Monitor for signs of overwork
Considerations for early aerobic conditioning w/GBS
- Low intensity aerobic conditioning (40-60% HR max)
- Energy conservation
- Careful monitoring resting and exertional vitals
Considerations for late aerobic conditioning w/GBS
- Submax (70-85% HR max) beneficial
- Gradually increase exercise times
- Monitor physiological responses
Organize these orthotics from most to least stable:
- Non-articulating/solid AFO
- PLS or FRO
- Articulating AFO
Most to least:
1) Non-articulating/solid AFO
2) Articulating AFO
3) PLS or FRO
Which of the following is true about CIDP?
A. More common in women than men
B. Defined by progression beyond 8 weeks
C. Motor involvement is asymmetric
D. Sensation loss if greater for pain and temp than vibration
B. Defined by progression beyond 8 weeks
Which of these is a positive prognostic indicator for GBS?
A. Age < 60 years
B. Preceding diarrheal illness
C. Severe muscle weakness of admission
D. Rapid progression beginning < 7 days prior to admission
A. Age < 60 years
The 20/30/40 rule is used to determine the need for what?
A. Intubation
B. Ability to ambulate
C. Level of sensory loss
D. Determination of plasmapheresis vs IVIG
A. Intubation
Medical intervention for GBS typically includes any of the following except...
A. Heparin and compression stocking for DVT prophylaxis
B. Intravenous immunoglobin (IVIG)
C. Plasmapheresis
D. Steroids
D. Steroids
Which of the following is true regarding the recovery phase of GBS?
A. There is a rapid progression of symptoms.
B. The nadir is the beginning of the recovery stage.
C. There is a gradual recovery of muscle strength.
D. Symptoms are stable neither improving or worsening.
C. There is a gradual recovery of muscle strength.
T/F: Pain in GBS occurs only due to neuropathic reasons.
False- musculoskeletal too
Which of the following is typical of the clinical presentation of GBS?
A. Slow progression of symptoms
B. Descending weakness
C. Hyporeflexia or areflexia
D. Absent sensation
C. Hyporeflexia or areflexia
All the following are true about mortality after GBS except...
A. Increased risk with ventilator dependence
B. Increased risk with age > 60 years
C. Is often due to infection
D. Occurs in grossly 30% of patients
D. Occurs in grossly 30% of patients (too high)
Which of the following is the most common variant of GBS?
A. Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP)
B. Acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN)
C. Acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN)
D. Miller Fisher Syndrome
A. Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP)
The medical diagnosis of GBS includes all of the following except?
A. Absence of fever at onset
B. Elevated CSF protein
C. Abnormal nerve conduction studies
D. Asymmetric motor weakness
D. Asymmetric motor weakness