Equilibrium
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:04 AM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
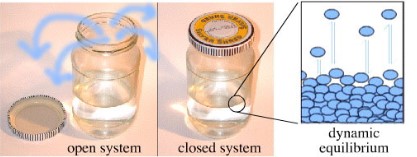
dynamic equilibrium
In a chemical system, when the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are balanced and the reactions are occurring at the __same rate__.
It is changing at a ***molecular level*** while its ***macroscopic properties*** (an observable or measurable property such as concentration, colour, temperature, pressure, and pH) remain __***constant***__.
* System must be **closed**.
* Three main types that can occur.
It is changing at a ***molecular level*** while its ***macroscopic properties*** (an observable or measurable property such as concentration, colour, temperature, pressure, and pH) remain __***constant***__.
* System must be **closed**.
* Three main types that can occur.
2
New cards
reversible reaction
A chemical reaction that proceeds in both the forward and reverse directions.
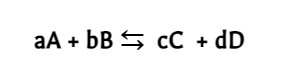
3
New cards
phase equilibrium
A physical change of state.
* Evaporating, etc.
* Evaporating, etc.
4
New cards
solubility equilibrium
The dissolving process (solutions).
5
New cards
chemical equilibrium
For any reversible reaction (the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are occurring at the same rate).
6
New cards
The Law of Equilibrium
In a chemical system at equilibrium, there is a __constant ratio__ between the __concentrations of the products__ and the __concentrations of the reactants__.

7
New cards
Equilibrium Constant Expression
**K***eq*
The ratio of equilibrium concentrations for a particular chemical system at a particular temperature.
The ratio of equilibrium concentrations for a particular chemical system at a particular temperature.
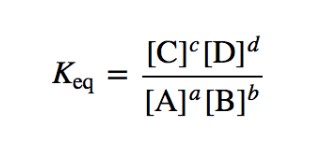
8
New cards
homogeneous equilibrium
A chemical system in equilibrium in which all of the components are in the same physical state.
9
New cards
heterogeneous equilibrium
A chemical system in equilibrium in which the components are in different physical states (the components do not have to be the same substance).
10
New cards
Le Chatelier’s Principle
When a system at equilibrium is put under stress, the system will shift to relieve the stress and re-establish equilibrium.
11
New cards
inert gas
* Do **not** react with other gases
* Increasing pressure affects reactants and products **equally**
* There is **no effect** on the position of equilibrium
* Increasing pressure affects reactants and products **equally**
* There is **no effect** on the position of equilibrium
12
New cards
catalyst
* Decreasing the activation energy speeds up both the forward and reverse reaction rates **equally**
* The system reaches equilibrium **faster**
* There is **no effect** on the position of equilibrium
* The system reaches equilibrium **faster**
* There is **no effect** on the position of equilibrium
13
New cards
changing concentration
Shift occurs to use up added species __or__ produce more of removed species.
* Keq = no change
* Keq = no change
14
New cards
changing temperature
Depends on if the reaction is endothermic __or__ exothermic.
* Keq = changes (will increase or decrease)
* Keq = changes (will increase or decrease)
15
New cards
changing pressure by changing volume
Shift occurs to reduce the number of gas molecules __or__ increase the number of gas molecules.
***NOTE****: only for gas systems!!!*
* Keq = no change
***NOTE****: only for gas systems!!!*
* Keq = no change
16
New cards
1000 Rule
If the concentration to which “*x*“ is added or subtracted from is **1000x or more greater** than the value of K (when K is small!), then we can **cancel out** ***x*** and assume that \[initial\] = \[equilibrium\].
\
**[initial] >> 1000 x K then [initial] = [equilibrium]**
\
**[initial] >> 1000 x K then [initial] = [equilibrium]**
17
New cards
Solubility-product Constant
For slightly soluble ionic compounds; determined __experimentally__.
* The magnitude of Ksp is a measure of how much solid dissolves to form a saturated solution (unitless).
* The magnitude of Ksp is a measure of how much solid dissolves to form a saturated solution (unitless).
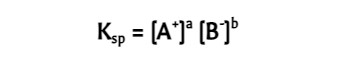
18
New cards
solubility
The maximum amount of **solute** that can dissolve in a given quantity of **solvent** at a particular temperature.
19
New cards
molar solubility
The amount (in moles) of solute in 1L of a saturated solution (molarity/concentration of the solution).
20
New cards
unsaturated solution
A solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved.
* Qsp < Ksp
* More solute dissolves
* Qsp < Ksp
* More solute dissolves

21
New cards
saturated solution
A solution with solute that dissolves until it is unable to dissolve anymore, leaving the undissolved substances at the bottom.
* Qsp = Ksp
* No more solute dissolves
* Qsp = Ksp
* No more solute dissolves

22
New cards
supersaturated solution
A solution that contains more than the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved at a given temperature.

23
New cards
soluble ionic compounds
When **soluble** ionic compounds (salts with high solubility) dissolve in water, they dissociate **completely** into ions (i.e. NaCl).
24
New cards
slightly soluble ionic compounds
For **slightly soluble** ionic compounds (salts with low solubility), only a **small amount** dissolves in water (i.e. AgCl). When the solution becomes **saturated**, the __solid__ reaches **equilibrium** with the dissociated ions.
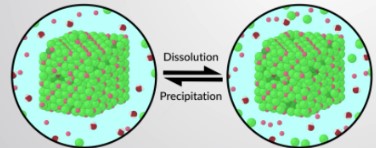
25
New cards
Common Ion Effect
The equilibrium of a system containing ions can be **shifted** by dissolving it into a **common ion** or a **compound that reacts** with one of the ions already in solution. This follows from **Le Chatelier’s Principle**. T__his will affect how we construct our ICE Tables__ (ion molarity is __**NOT ZERO initially**__).
* When the solubility of an ionic compound is lowered as a result of the addition of a common ion; reaction will shift towards the solid.
* When the solubility of an ionic compound is lowered as a result of the addition of a common ion; reaction will shift towards the solid.
26
New cards
precipitate
An insoluble product formed in a reaction between two soluble ionic compounds.
For solutions of slightly soluble ionic compounds, we can compare Qsp and Ksp values to determine if this forms.
For solutions of slightly soluble ionic compounds, we can compare Qsp and Ksp values to determine if this forms.
27
New cards
Solubility Quotient
Used to describe the current state of an aqueous solution and to **predict** whether a **precipitate forms or not**. If it is less than Ksp, then more solid can be dissolved. But if it is larger than Ksp, the solid will precipitate at the bottom of the solution.