AP Biology Unit 1, AP Bio Unit 2: Cell transport, Ap bio Unit 3: cellular energetics
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
Hydrophilic
water loving (soluble in water)
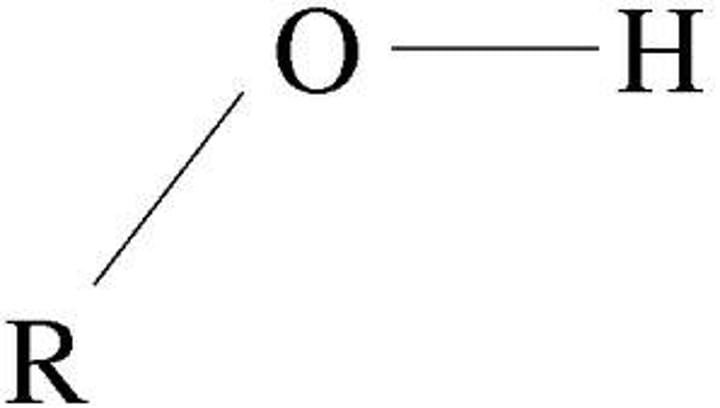
Hydroxyl Group
-OH
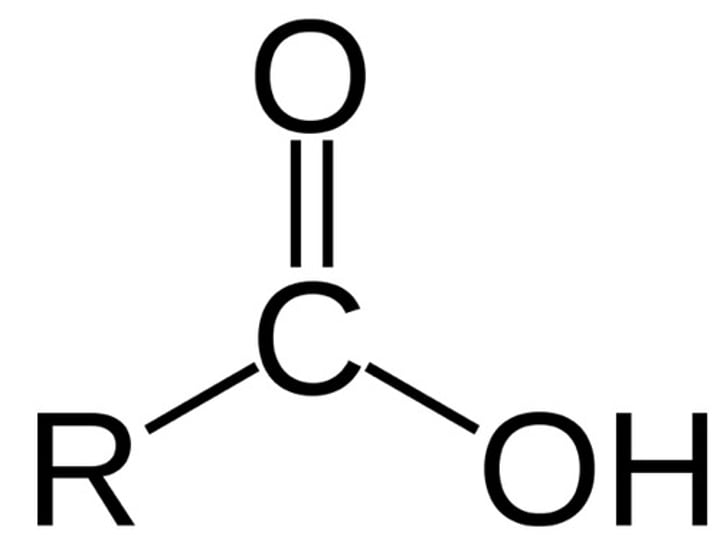
Carboxyl Group
-COOH
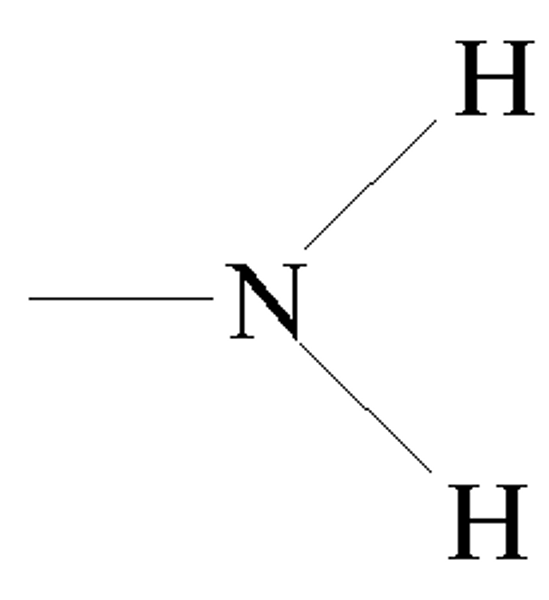
Amino Group
-NH2
Macromolecules
Large molecules such as: carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids
Polymers
a large molecule consisting of many monomers linked together
Monomers
one of the repeating parts of a polymer
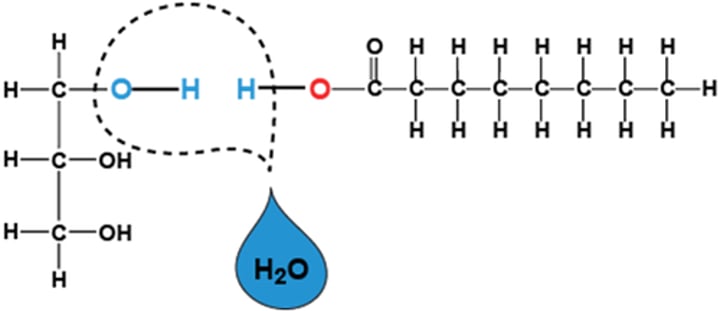
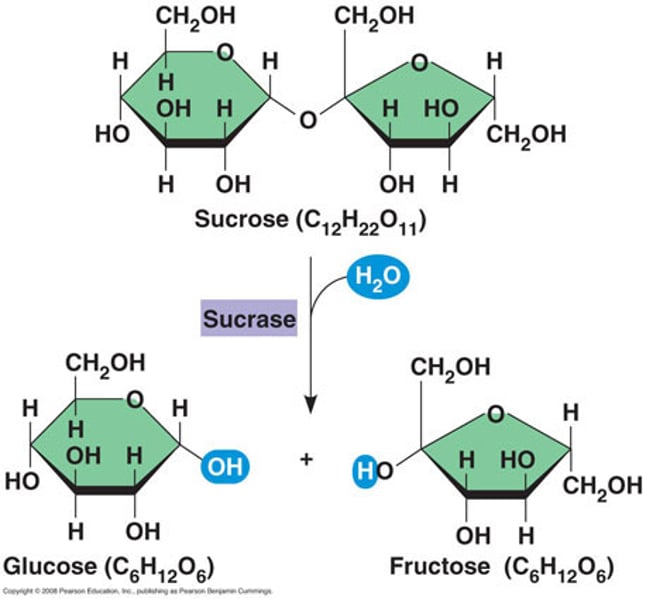
dehydration synthesis
a reaction that removes water and combines monomers into polymers
Hydrolysis
a reaction where adding water breaks up a polymer into monomers
Enzymes
specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells
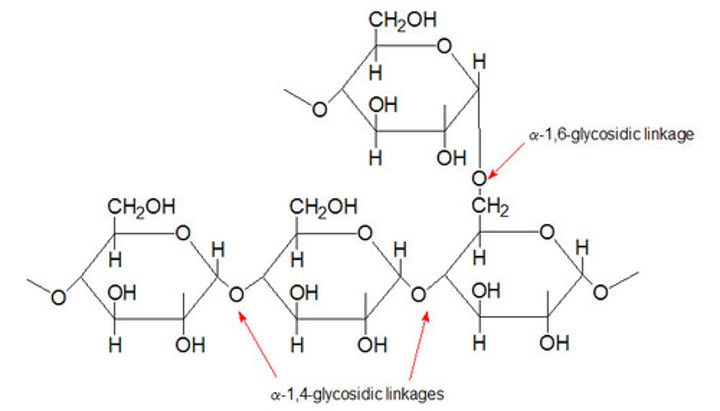
Carbohydrate
molecules ranging from the small sugar molecules to large polysaccharides like starches
Starch
a storage molecule used by plants
Glycogen
Molecule made by animals to store glucose
Hydrophobic
water fearing
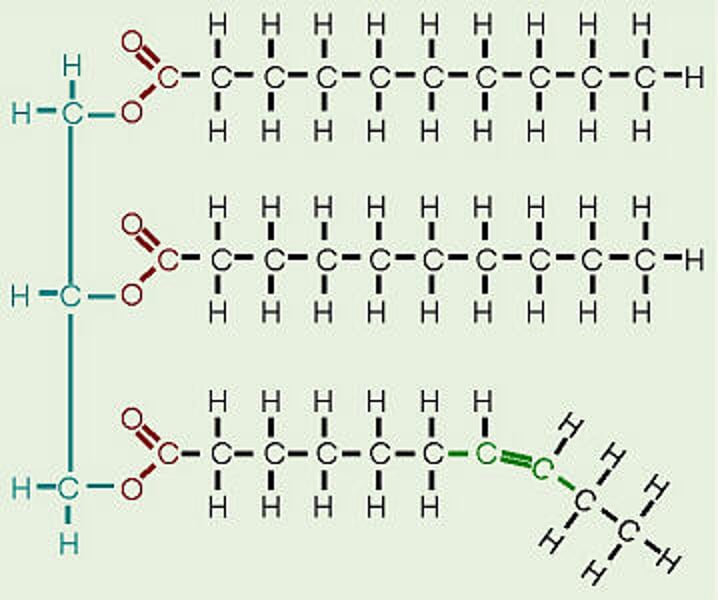
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid containing one or more double bonds - not saturated with Hydrogen
Saturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid containing only single bonds - full of hydrogens
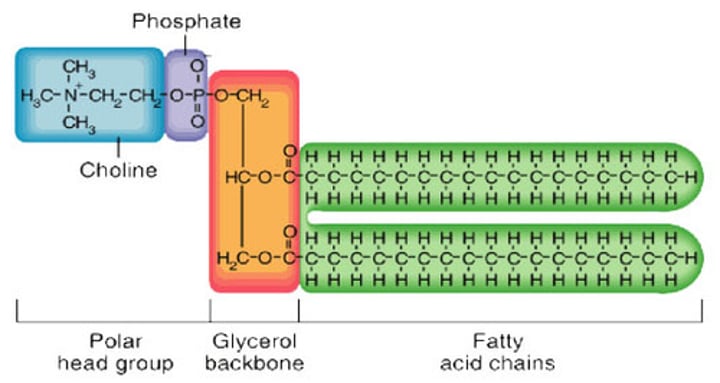
Phospholipids
contain a phosphate group and attach to 2 fatty acids rather than three - makes cell membranes
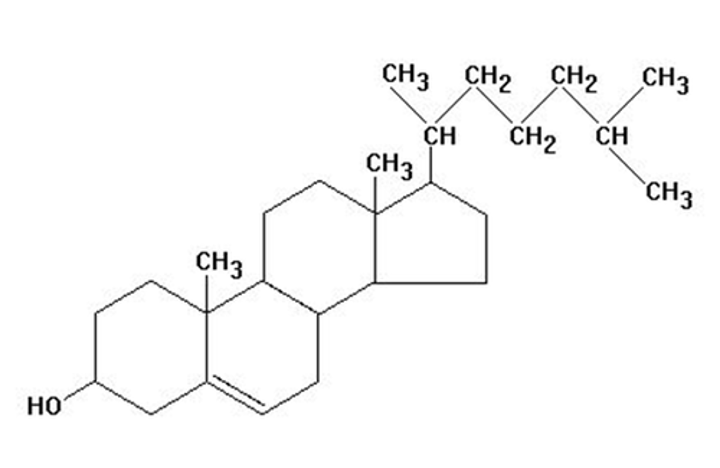
Steroids
lipids containing 4 fused carbon rings
Cholesterol
component in cell membranes - comes from animal fats
Protein
a molecule made of amino acids
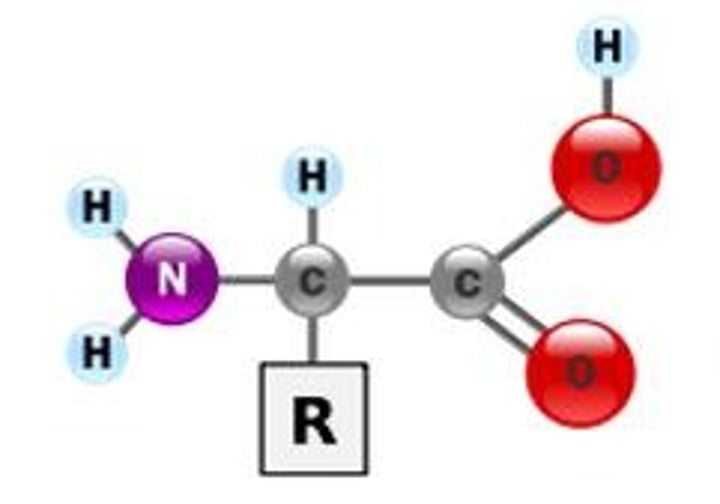
Amino Acids
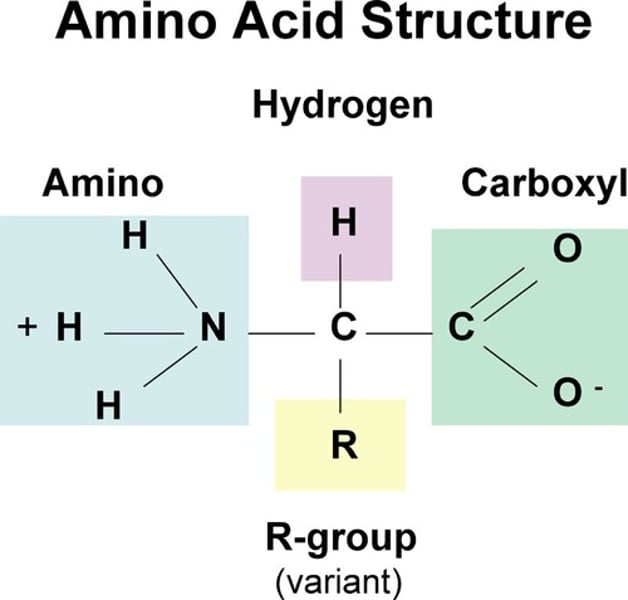
Monomers (building blocks) of proteins; amino group, hydrogen, and carboxylic acid group
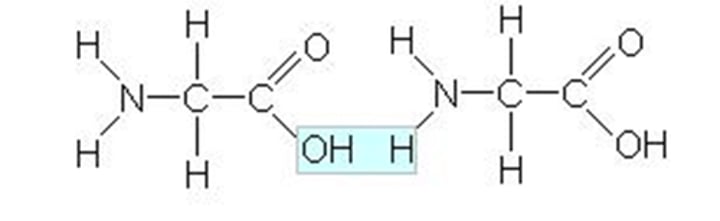
Peptide Bond
covalent linkage between peptides to form a poly peptide
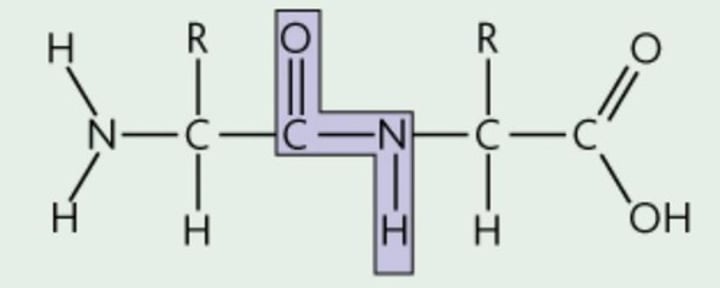
Polypeptide
a polymer made of peptides
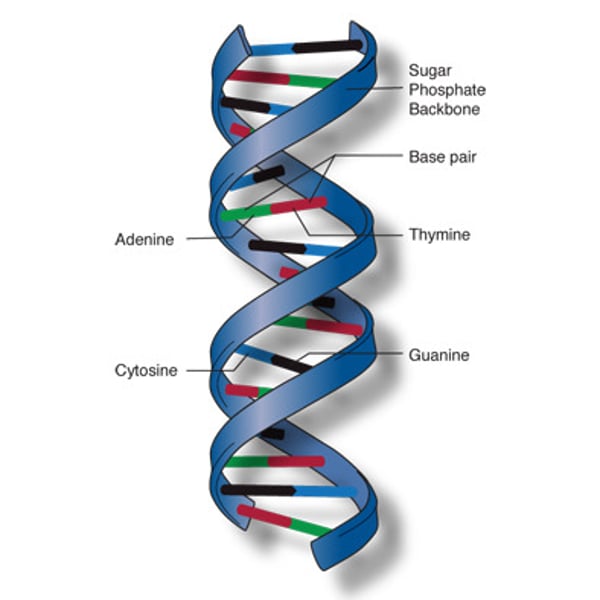
DNA
genetic inheritance polymer - Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid
Are most carbohydrates are hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
hydrophilic
Are fats and lipids are hydrophilic or hydrophibic?
hydrophobic
Denaturation
proteins or enzymes, lose their specific shape, and changes its function
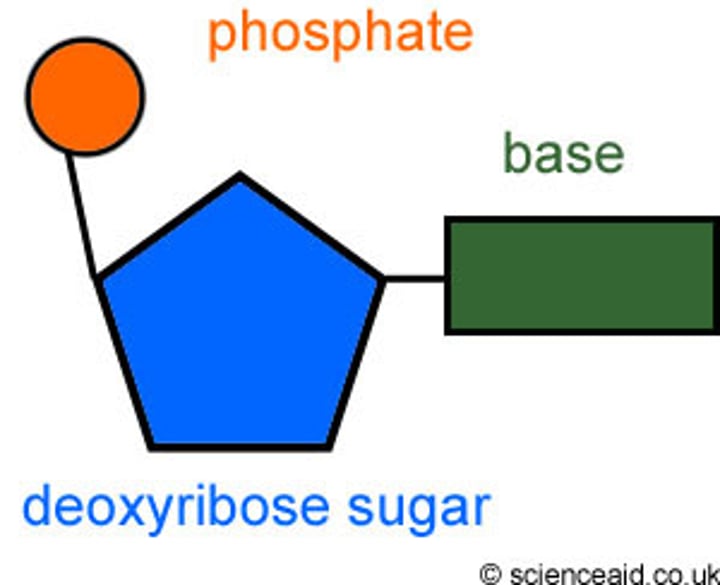
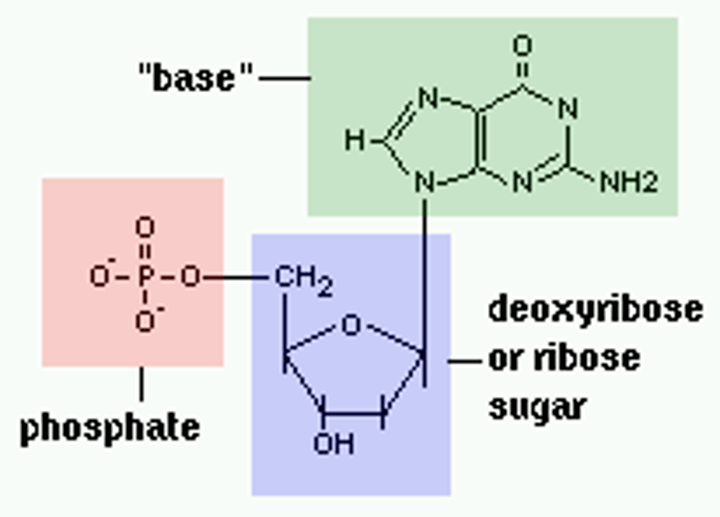
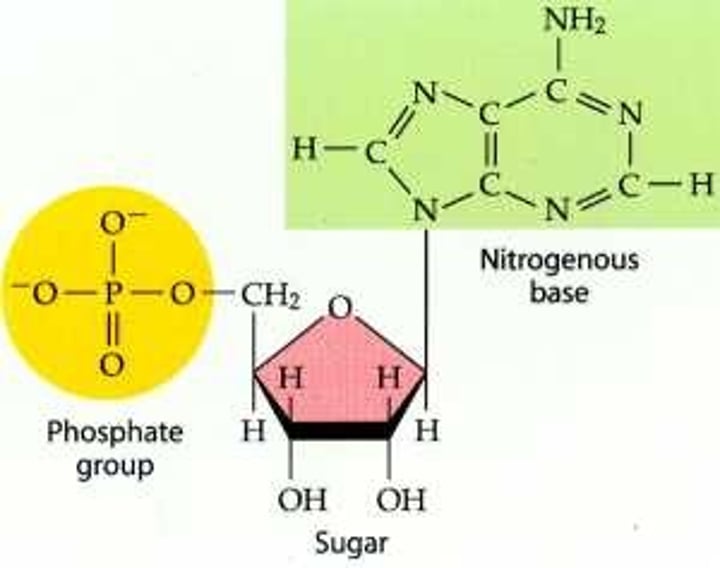
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Contains C, H, O
Carbohydrates and lipids
Contains C, H, O, N, and sometimes S
Proteins
Contains C, H, O, N, and P
Nucleic Acids
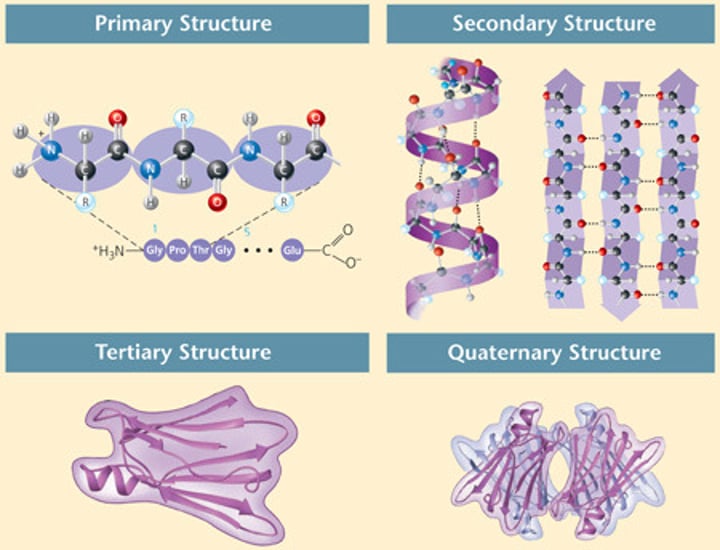
Primary Structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
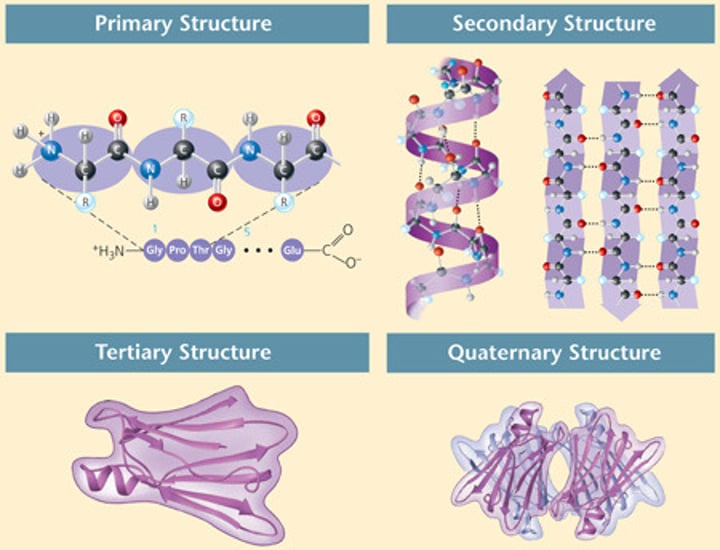
Tertiary Structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
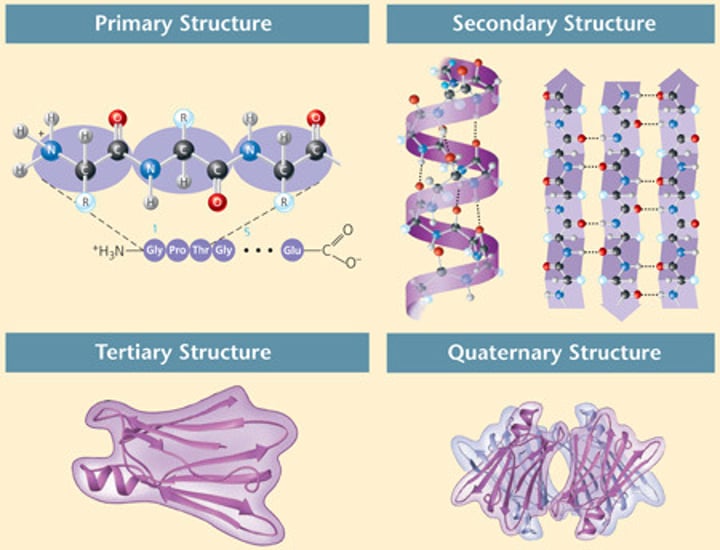
Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
peptide
Short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
buffer
A solution that minimizes changes in pH when extraneous acids or bases are added to the solution.
proton donors
Acids are
proton acceptors
bases are
acidosis
pH below 7.35
Alkalosis
pH above 7.45
nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
Triglycerides
three fatty acids attached to a glycerol
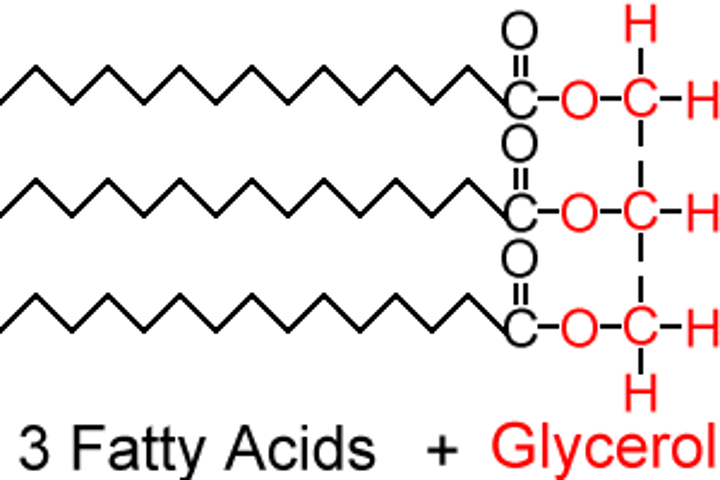
glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils.
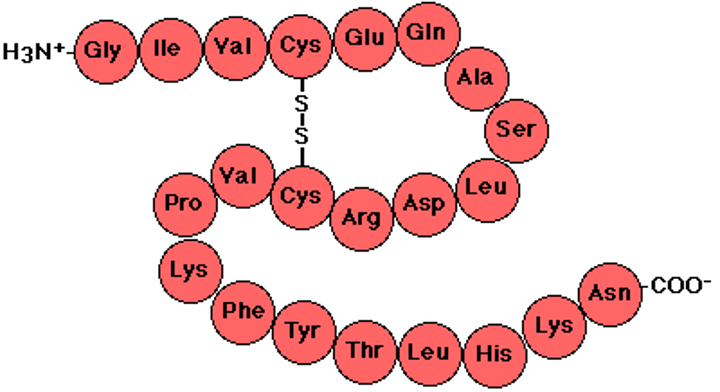
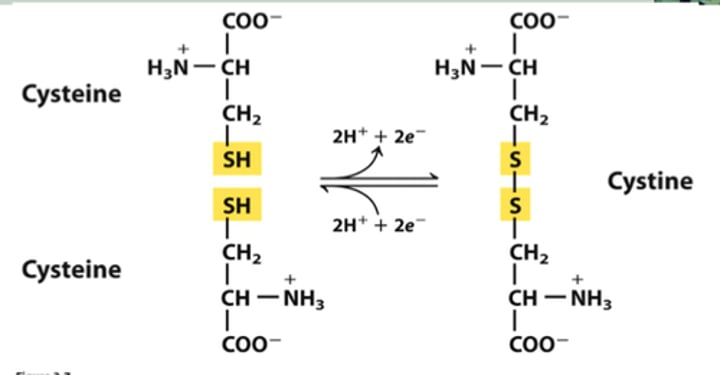
disulfide bridges
A strong covalent bond formed when the sulfur of one cysteine monomer bonds to the sulfur of another cysteine monomer.
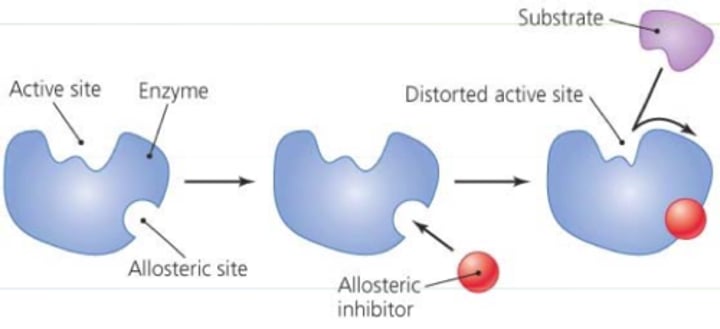
allosteric inhibitor
binds to the enzyme and induces the enzyme's inactive form
hydrogen bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule
bonds weakest to strongest
van der waals, hydrogen, ionic, covalent
water adhesion
water molecules stick to other kinds of substances (H bonding)
water cohesion
water molecules stick to each other (H bonding)
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius
evaporative cooling
The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation, a result of the molecules with the greatest kinetic energy changing from the liquid to the gaseous state.
nucleic acids
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
DNA and RNA
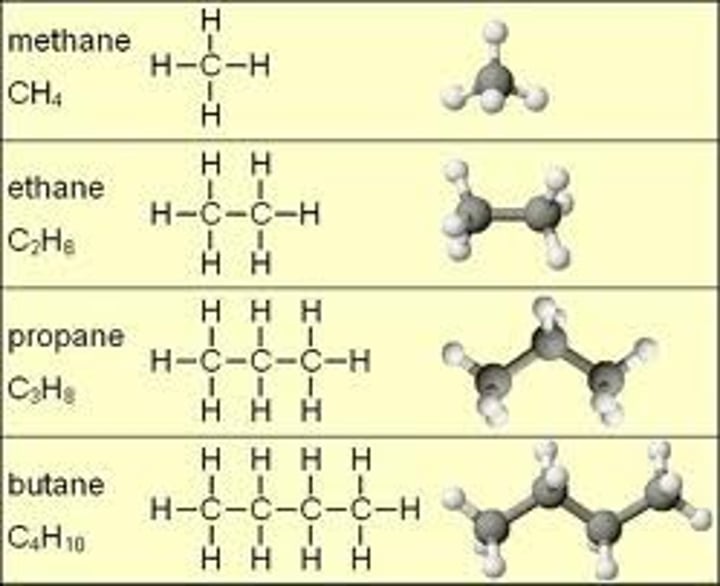
hydrocarbon
An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen.
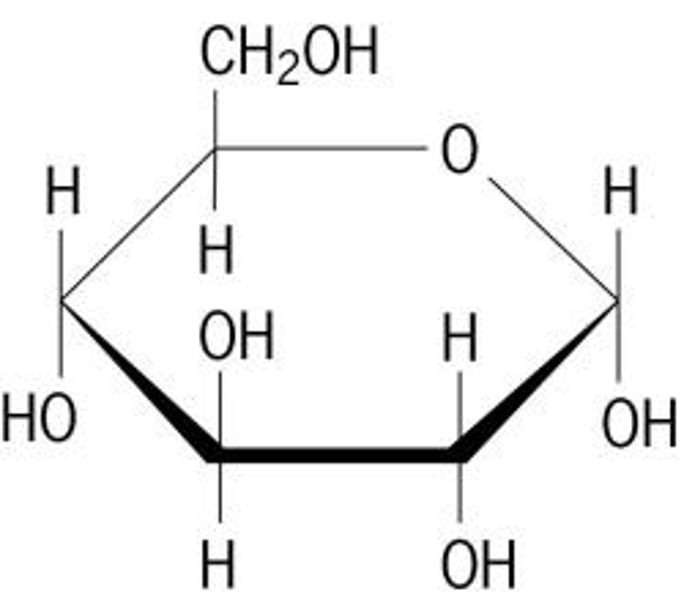
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
glucose, fructose, galactose
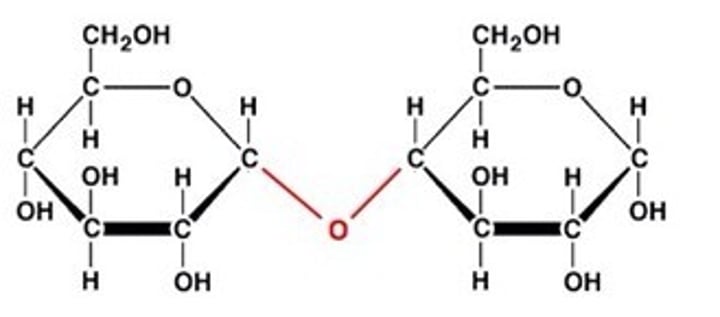
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
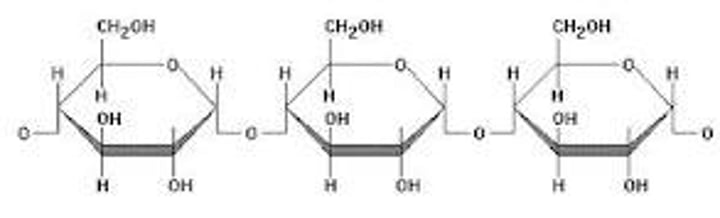
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
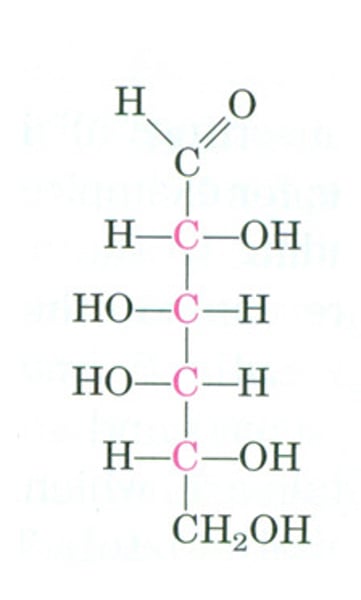
glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues.
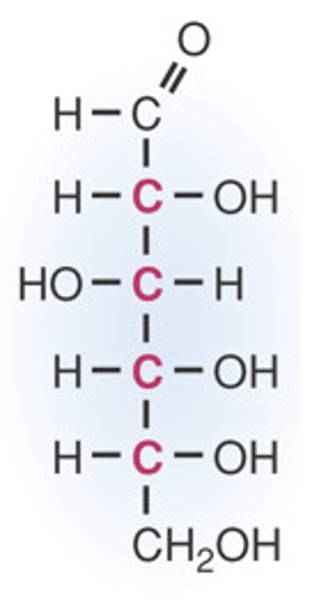
fructose
a hexose sugar found especially in honey and fruit.
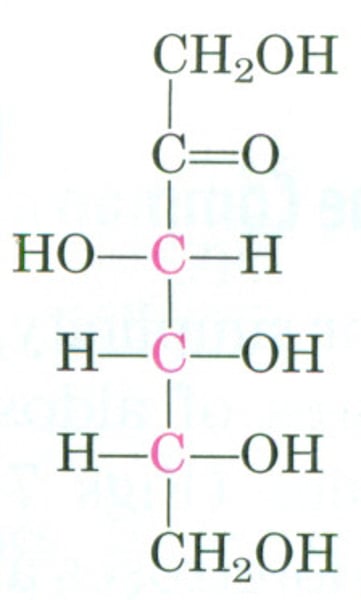
Galactose
a monosaccharide and has the same chemical formula as glucose
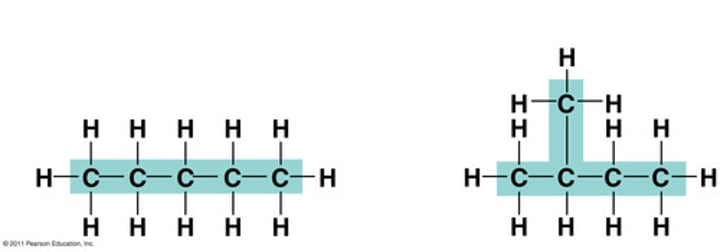
structural isomers
Two different molecules that have the same chemical formula
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
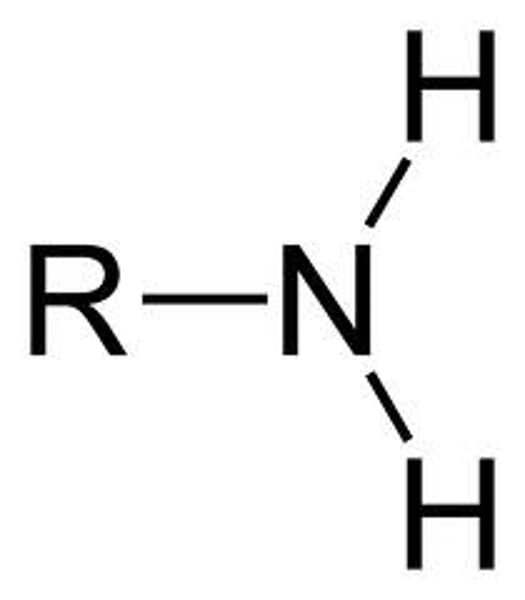
amine
nitrogen compound
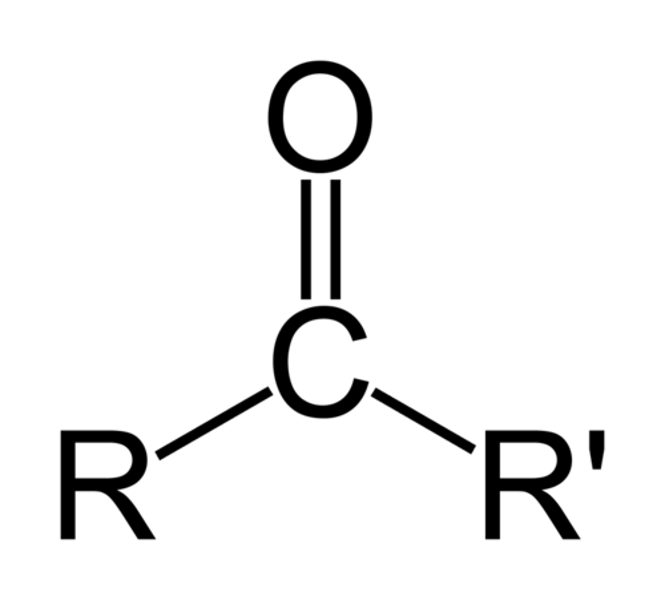
ketone
R-C=O-R
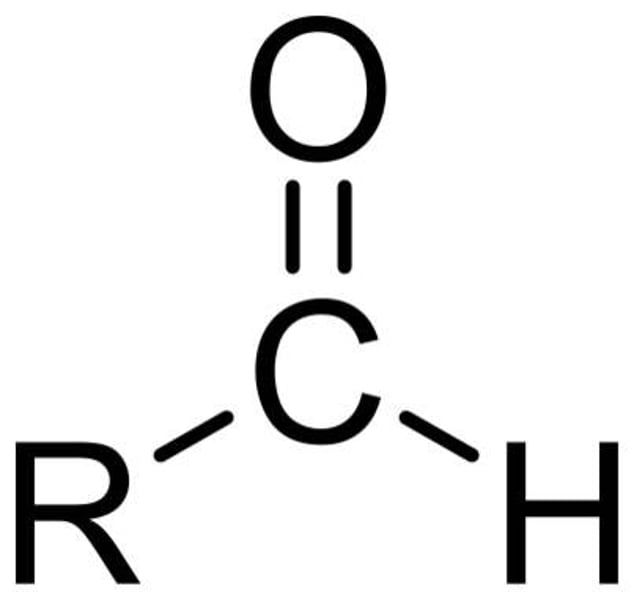
aldehyde
An organic molecule with a carbonyl group located at the end of the carbon skeleton.
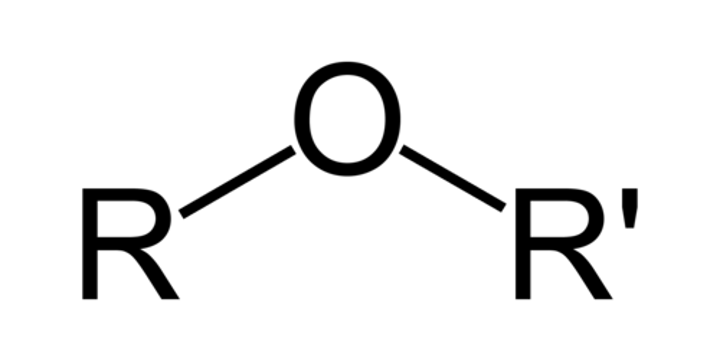
ether
have no hydrogen atom on the oxygen atom (that is, no OH group) R-O-R
alcohol
organic molecules assembled from carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms.
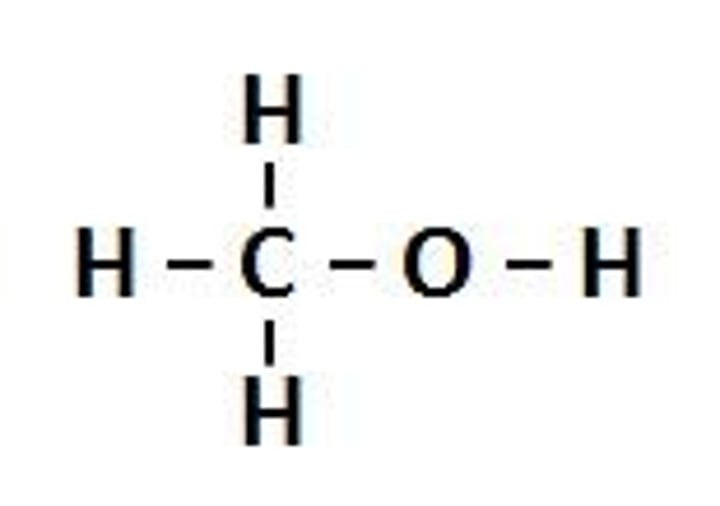
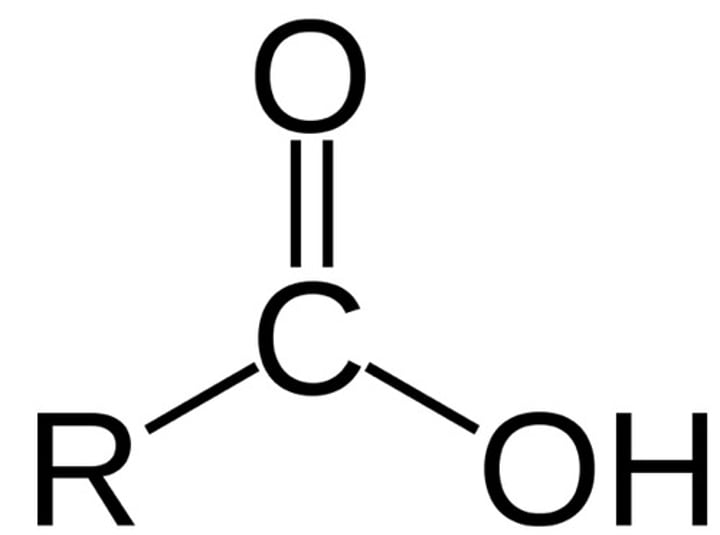
carboxylic acid
any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon (C) atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group (―OH) by a single bond
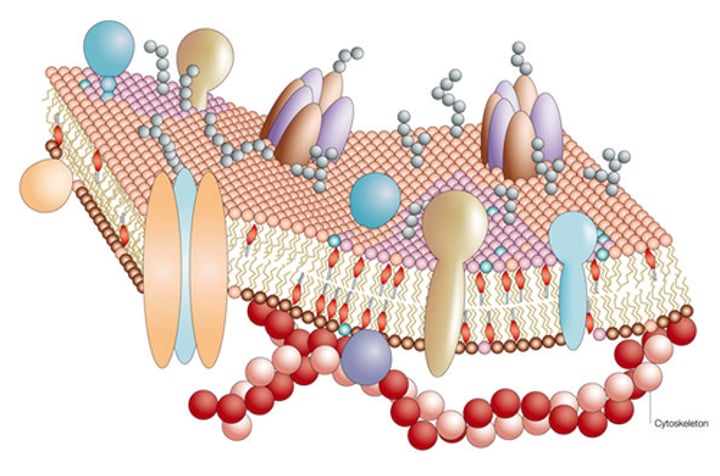
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
nuclear membrane
A highly-porous membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more carbohydrates covalently attached to it.
Glycolipid
a lipid with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates
facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins
ex. glucose transport
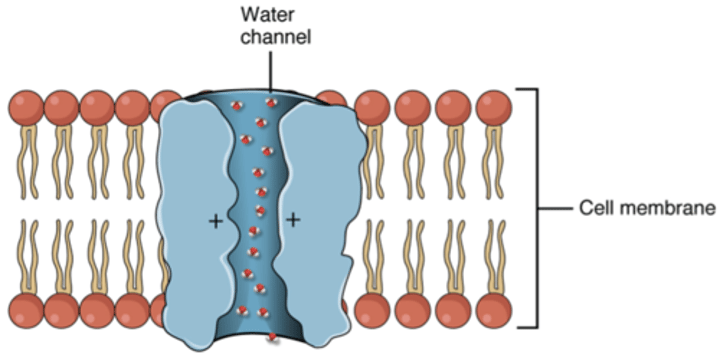
aquaporin
A membrane protein, specifically a transport protein, that facilitates the passage of water through channel proteins.
Compartmentalization
Membrane-bound organelles allow different parts of the cell to perform different functions at the same time
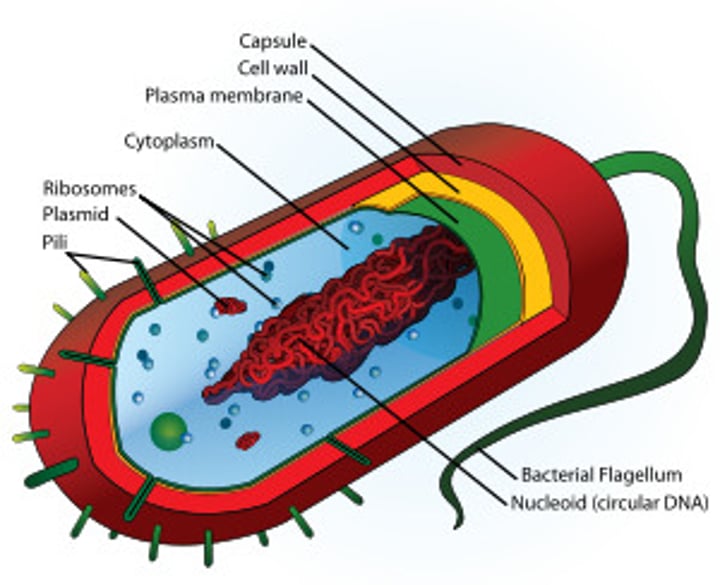
prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
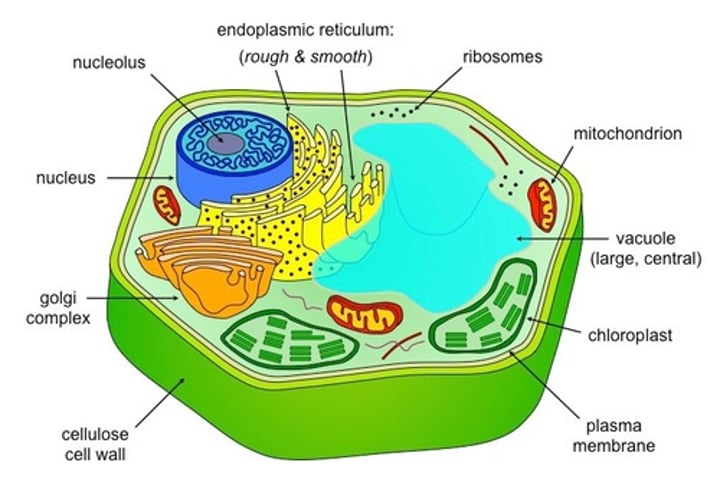
eurokaryotic cell
unicellular organism with membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
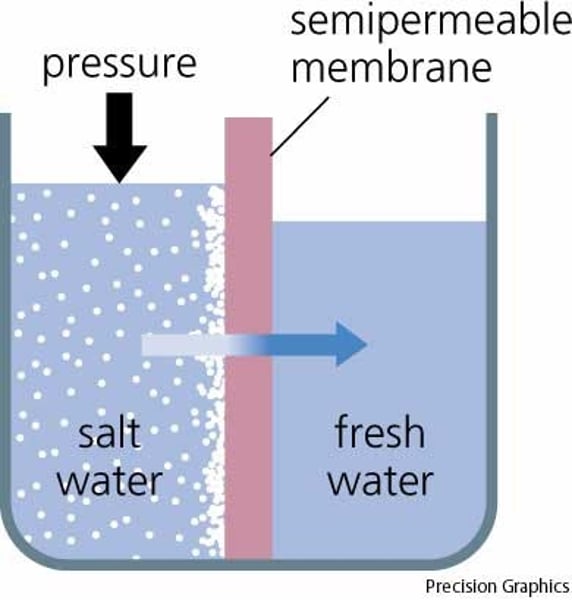
water potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure.
water potential formula
Ψ = Ψs + Ψp
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane; from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water
solute potential (ΨS)
iCRT
i= ionization constant
C= concentration in molarity
R= pressure constant -> 0.0831
T= temperature in K ( ___ C +273)
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
osomotic pressure
measure of the tendency for a solution to take up water when separated from pure water by a selectively permeable membrane; can be described as the amount of pressure required to prevent net movement of water into the solution
hypotonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
Co-transport
The transport of one substance coupled with the transport of another substance across a plasma membrane in the same direction through the same protein carrier.
phagosome
Intracellular vesicle containing material taken up by phagocytosis.
phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Integral Proteins
penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
lysed cell
Animal Cell that has burst in a high solute, low solvent environment
turgid cell
a plant cell that has absorbed water and has cytoplasm that is pressing outwards on the cell wall
flaccid cell
cell that lack water; is soft; causes plants to droop; closed stoma. If placed in higher solute concentration will undergo plasmolysis.
plasmolyzed cell
Plant cell that has been dehydrated
-Occurs when cell is placed in a hypertonic solution
electrochemical gradient
The diffusion gradient of an ion, representing a type of potential energy that accounts for both the concentration difference of the ion across a membrane and its tendency to move relative to the membrane potential.