Bio Test
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
allele
gene variations that arise by mutation and exist at the same relative locations on homologous chromosomes
autosomes
any of of the non-sex chromosomes
dihybrid
result of a cross between two true-breeding parents that express different traits for two characteristics
dominant
trait which confers the same physical appearance whether an individual has two copies of the trait or one copy of the dominant trait and one copy of the recessive trait
epistasis
antagonistic interaction between genes such that one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another
F1
The first filial generation in a cross; the offspring of the parental generation
F2
second filial generation produced when F1 individuals are self-crossed or fertilized with each other
Genotype
underlying genetic makeup, consisting of both physically visible and non-expressed alleles, of an organisme
heterozygous
having two different alleles for a given gene on the homologous chromosome
homozygous
having two identical alleles for a given gene on the homologous chromosome
law of independent assortment
genes do not influence each other with regard to sorting of alleles into gametes; every possible combination of alleles is equally likely to occur
law segregation
paired unit factors (ie genes) segregate equally into gametes such that offspring have an equal likelihood of inheriting any combination of factors
monohybrid
result of a cross between two true-breeding parents that express different traits for only one characteristic
P0
parental generation in a cross
phenotype
observable traits expressed by an organism
Punnett square
visual representation of a cross between two individuals in which the gametes of each individual are denoted along the top and side of a grid, respectively ,and the possible zygotic genotypes are recombined at each box in the grid
recessive
trait that appears “latent” or non-expressed when the individual also carries a dominant trait for that same characteristic; when present as two identical copies, the recessive trait is expressed
reciprocal cross
paired cross in which the respective trait of the male and female in one cross become the respective traits of the female and male in the other cross
sex-linked
any gene on a sex chromosome
test cross
cross between a dominant expressing individual with an unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual; the offspring phenotypes indicate whether the unknown parent is heterozygous or homozygous for the dominant trait
trait
variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic
x-linked
gene present on the X, but not the Y chromosome
helicase
during replication, this enzyme helps to open up the DNA helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds
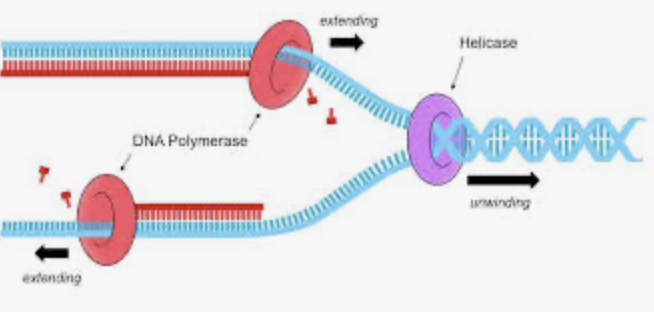
lagging strong
during replication, the strand that is replicated in short fragments and away from the replication fork
leading strand
strains that is synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction, which is synthesized in the direction of the replication fork
ligase
enzyme that catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester linkage between the 3’ OH and 5’ phosphate ends of the DNA
Okazaki fragment
DNA fragment that is syntheseized in short stretched on the lagging strand
primase
enzyme that synthesizes the RNA primer; the primer is needed for DNA pol to start synthesis of a new DNA strand
primer
short stretch of nucleotides that is required to initiate of replication, in the case of replication, the primer has RNA nucleotides
replication
Y-shaped structure formed during initiation of replication
single-strand binding protein
during replication, protein that binds to the single-stranded DNA; this helps in keeping the two strands of DNA apart so that they may serve as templates
topoisomerase
enzyme that prevents overwinding of DNA when DNA replication, is taking place