Cardiovascular
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
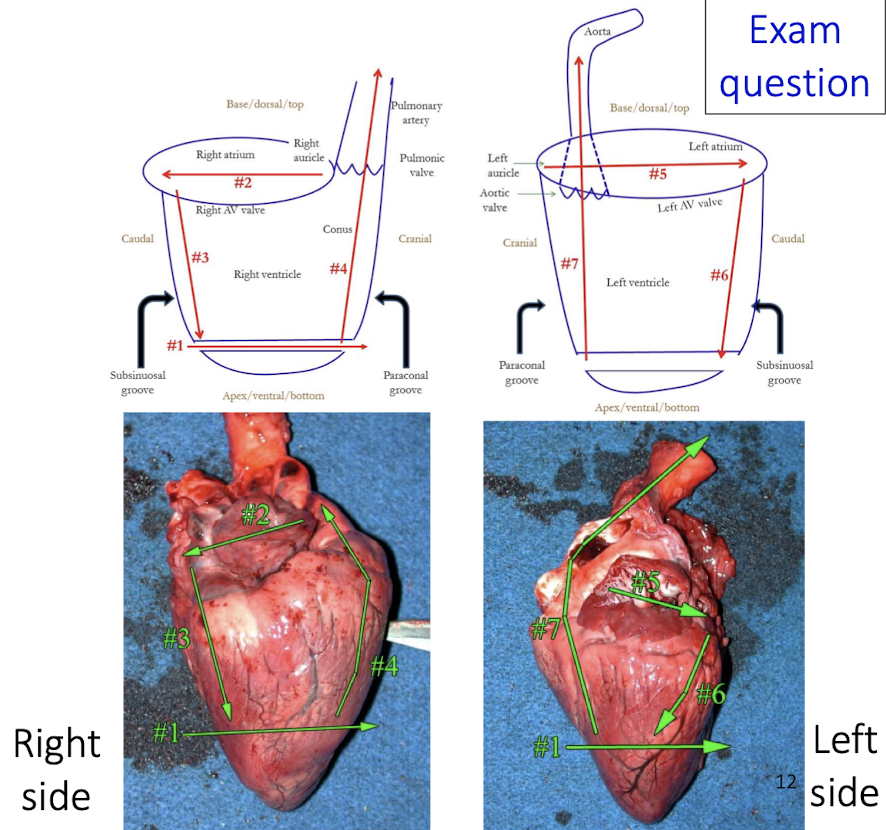
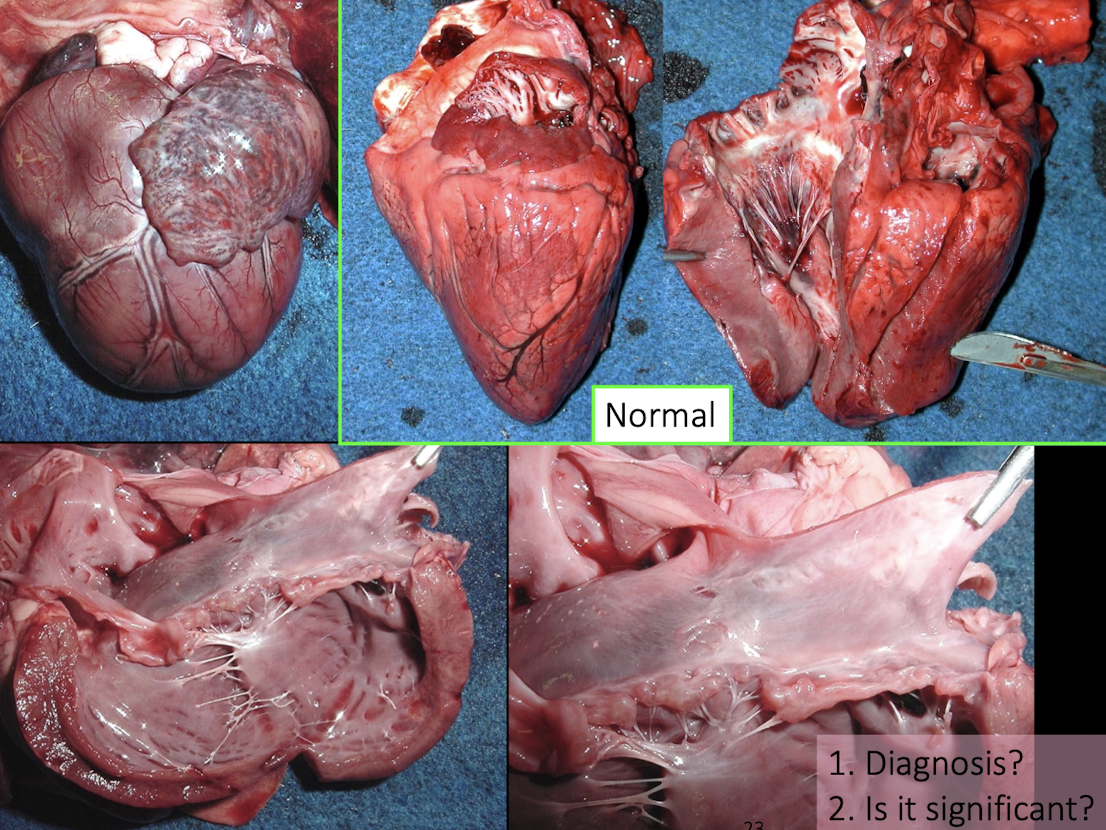
What is the most important principle when examining the heart at necropsy?
Observation comes before protocol and sampling — carefully orient and assess the heart before cutting.
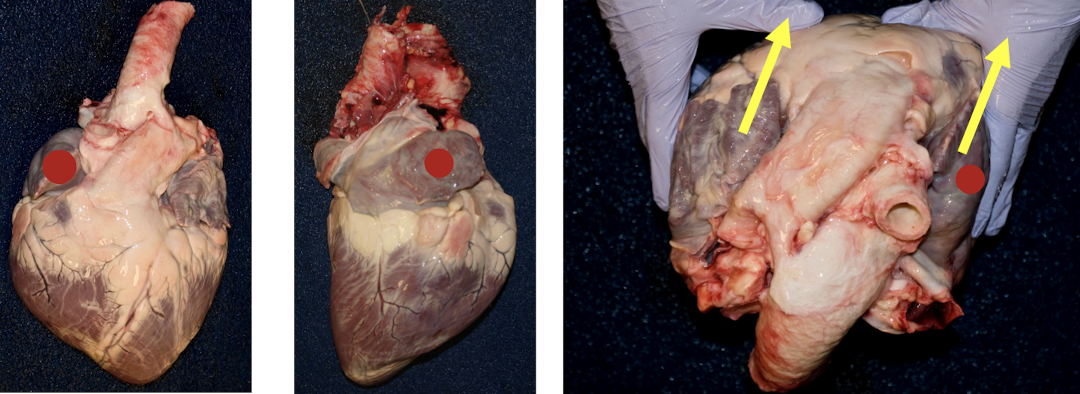
What structure is used for orientation of the heart?
The right auricle is the key landmark for orientation
What chamber features must always be assessed?
Size of the atria
Wall thickness
Chamber volume
Why is the septum important during examination?
The septum is your guide to distinguishing left vs right sides and assessing symmetry or hypertrophy
What is the correct directional flow to follow when examining chambers?
Atria → inflow → outflow
What learning tools are emphasized for mastering heart examination?
Courselink videos
Necropsies
Why is external orientation critical before cutting?
Incorrect orientation can lead to misidentification of chambers, vessels, or lesions
What are the two key external grooves used to orient the heart?
Subsinuosal groove
Paraconal groove
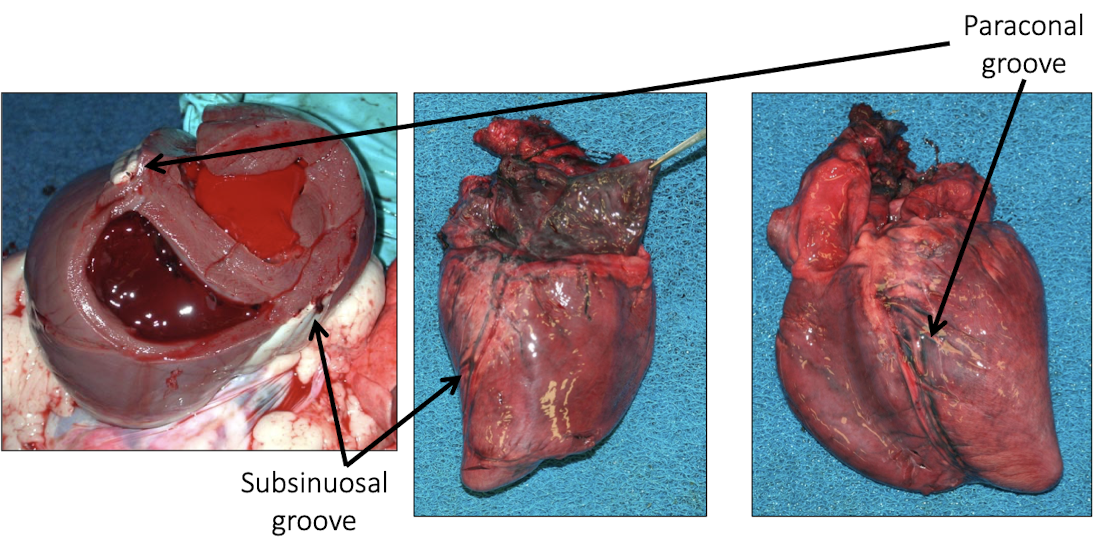
They correspond to interventricular septal orientation and help distinguish right vs left ventricular surfaces
Which groove on the heart is typically visible on the right side?
The subsinuosal groove
Which groove on the heart is typically visible on the left side?
The paraconal groove
What core steps should you mentally follow in an exam setting when identifying heart anatomy?
Locate the right auricle
Identify right vs left side
Assess atria size
Compare wall thickness and chamber volume
Use septum as guide
Follow atria → inflow → outflow
prevents random guessing and ensures systematic identification of lesions and chambers
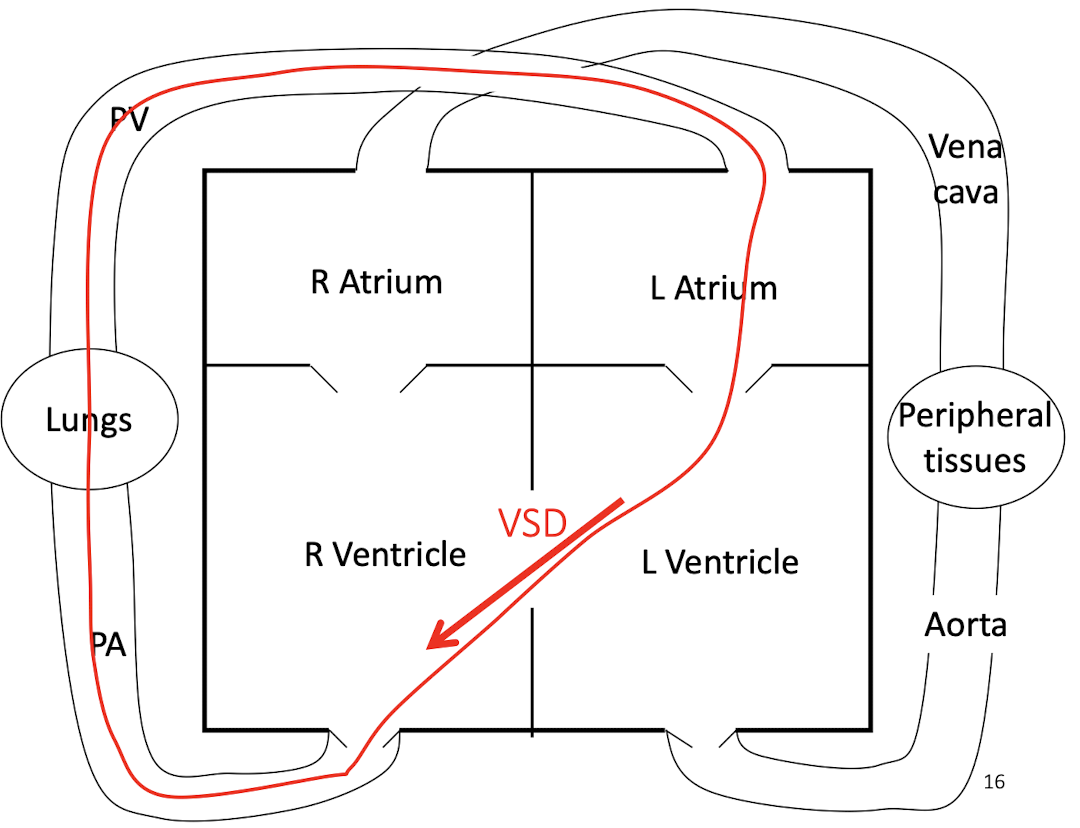
What does a VSD cause physiologically?
Left-to-right shunt, increased pulmonary blood flow, volume overload
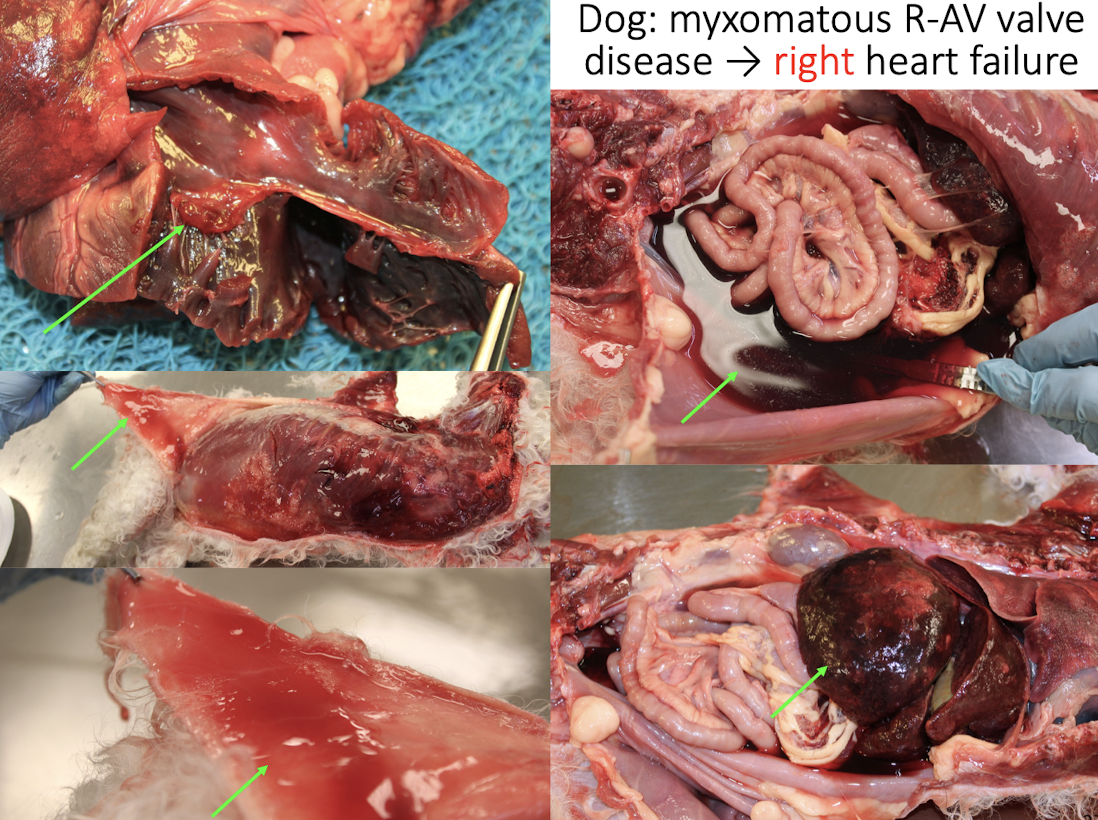
What are the two major endocardial diseases?
Endocardiosis (degenerative)
Endocarditis (infectious) → inflammation + thrombosis
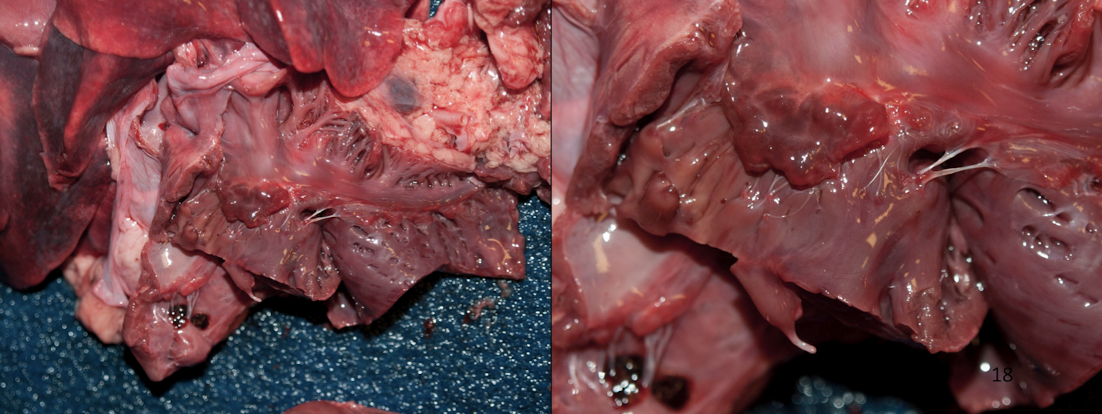
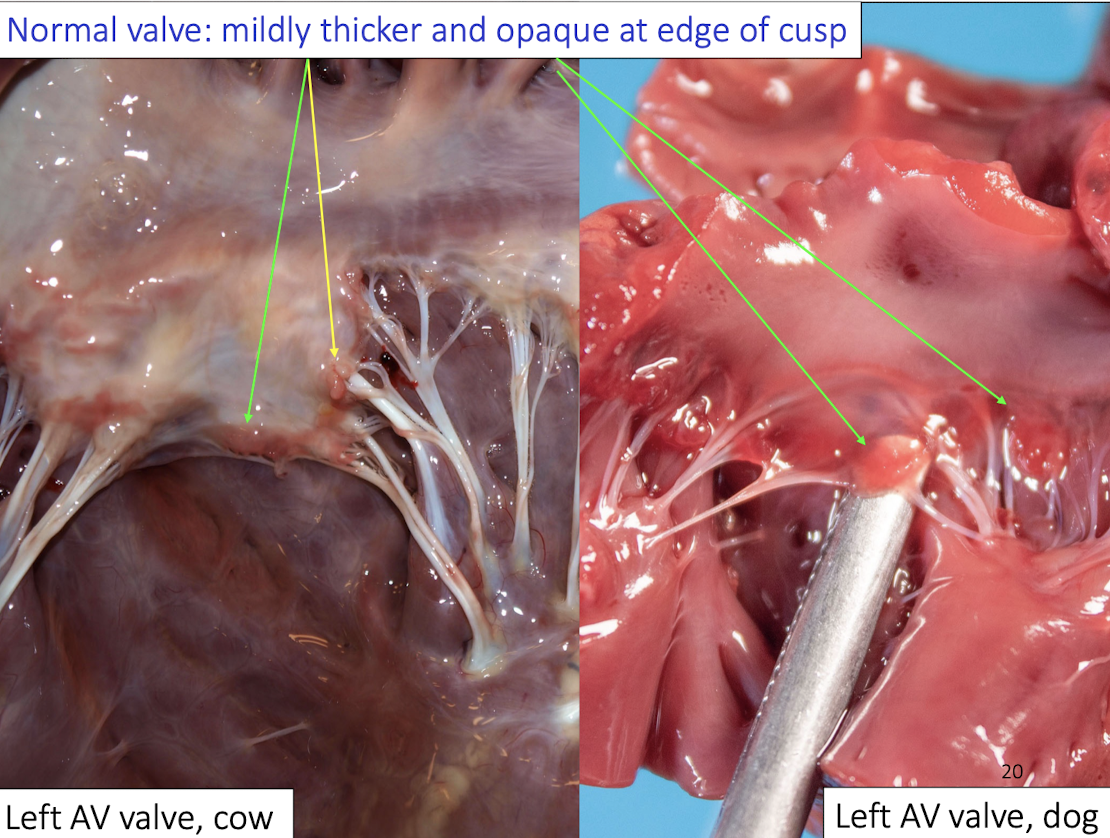
What is endocardiosis (MMVD)?
Chronic degenerative disease of cardiac valves, especially mitral → Very common in dogs
Shiny, smooth nodules → fibrous tissue over the valve
Valve distortion
Valvular incompetence → volume overload
How do you tell if valvular disease is significant?
Look for secondary changes:
Atrial dilation
Ventricular hypertrophy
Congestion or edema
Normal structures of the dog aortic valve
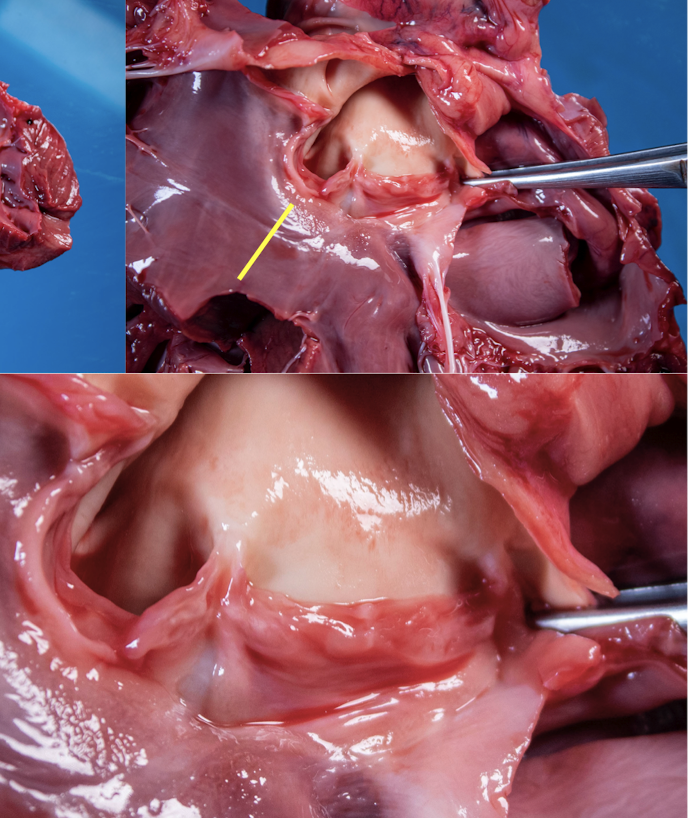
Nodule in centre
of each cusp
Ventricular
outflow: all muscle
until annulus of
valve cusp
L atrium is larger → functionally significant, regurge of blood
L ventricle is very big
shiny nodules on valve
jet lesion
outside the heart → pulmonary congestion and edema, heart failure cells, effusion
Lesions of LEFT heart failure?
Pulmonary edema & congestion
Heart failure cells
Pleural effusion (cats, both)
Lesions of RIGHT heart failure?
Ascites
Congested/enlarged liver
Subcutaneous edema
Pleural effusion
Pulmonary Congestion
What findings indicate compensation (not failure)?
Atrial dilation
Eccentric or concentric hypertrophy
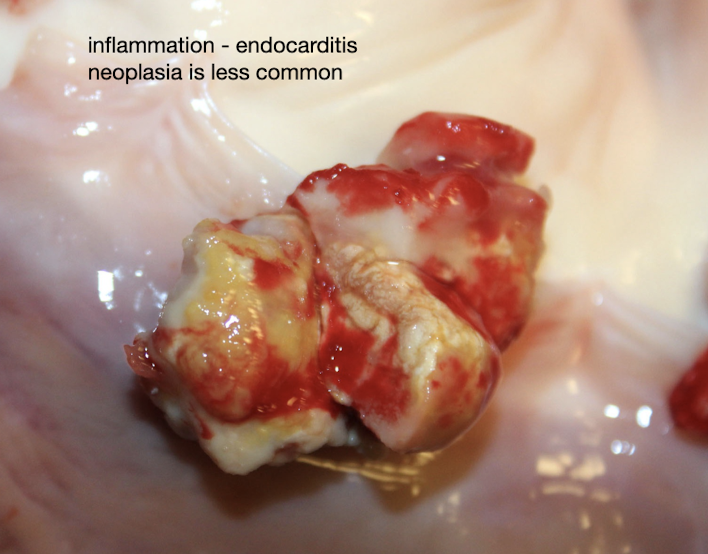
What is endocarditis?
Bacterial infection of valves with thrombosis and neutrophilic inflammation
Gross appearance
Rough, dull, irregular vegetations
Sequelae
Valvular insufficiency
Septic emboli
Heart failure
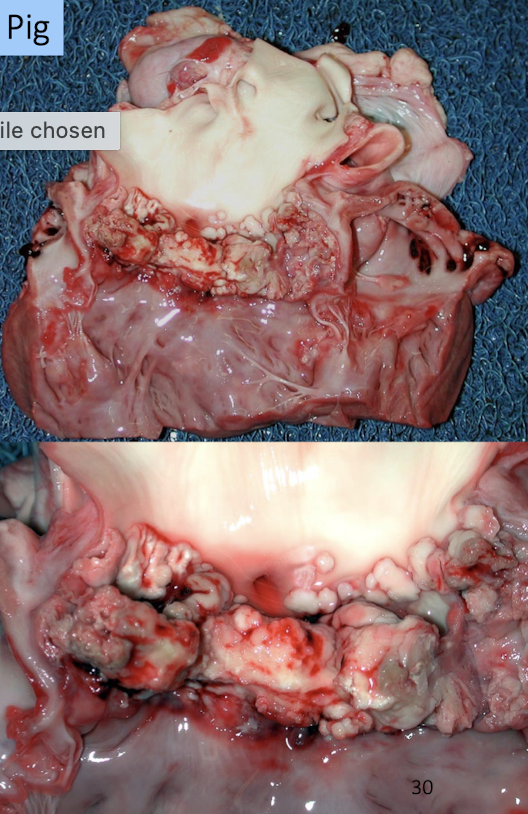
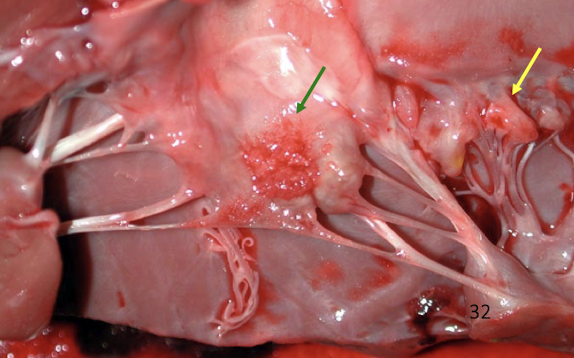
What is the lesion
Endocarditis in the dog → less severe
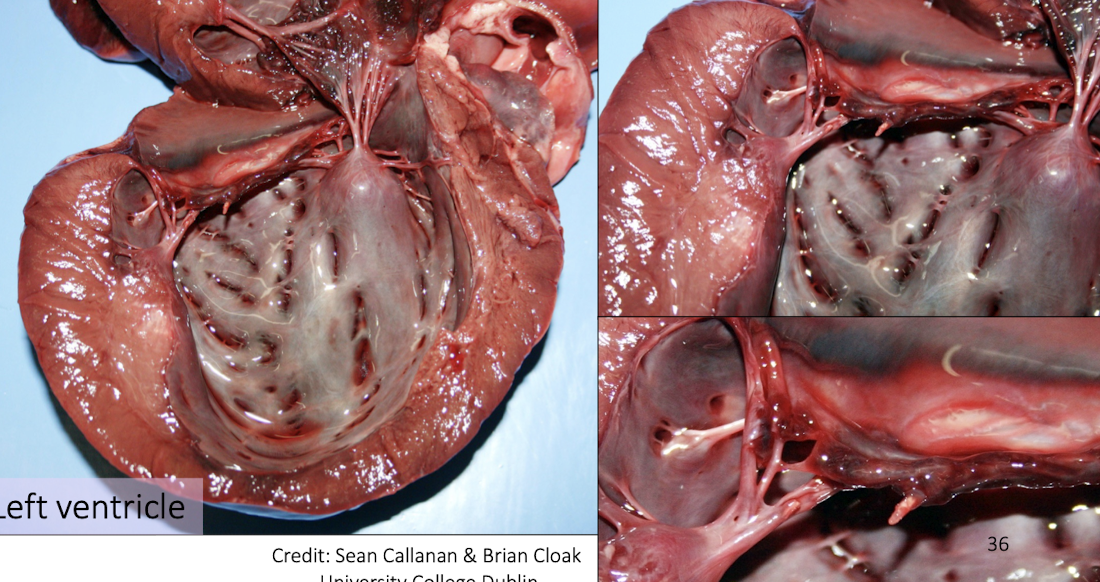
Causes of acute worsening in chronic heart failure?
Myocardial ischemic necrosis
Ruptured chordae tendineae
Left atrial dilation, rupture, hemopericardium, tamponade
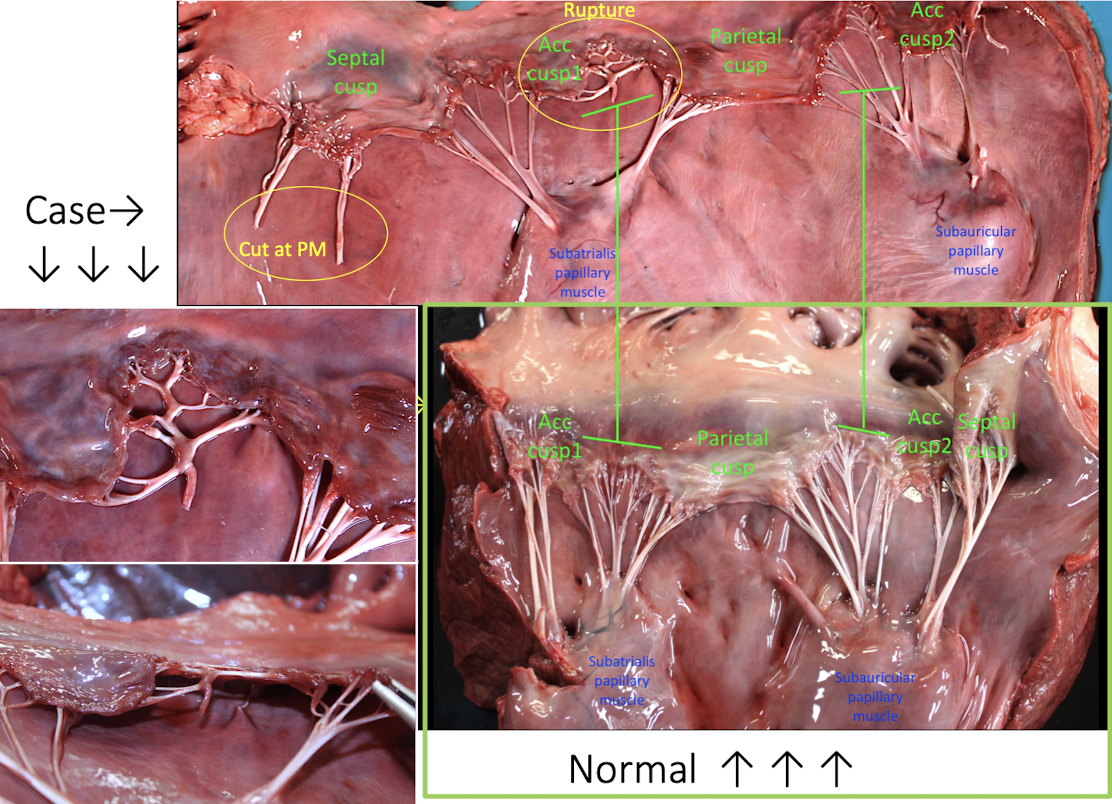
Ruptured vs. Cut chordae tendineae
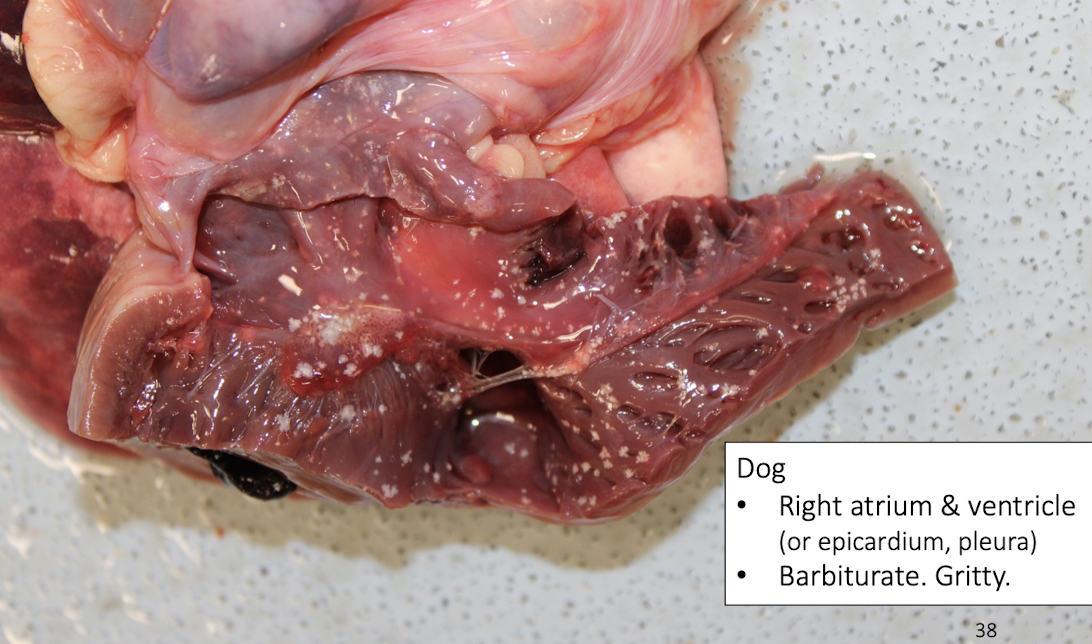
What causes gritty endocardial lesions in dogs?
Barbiturate euthanasia artifact
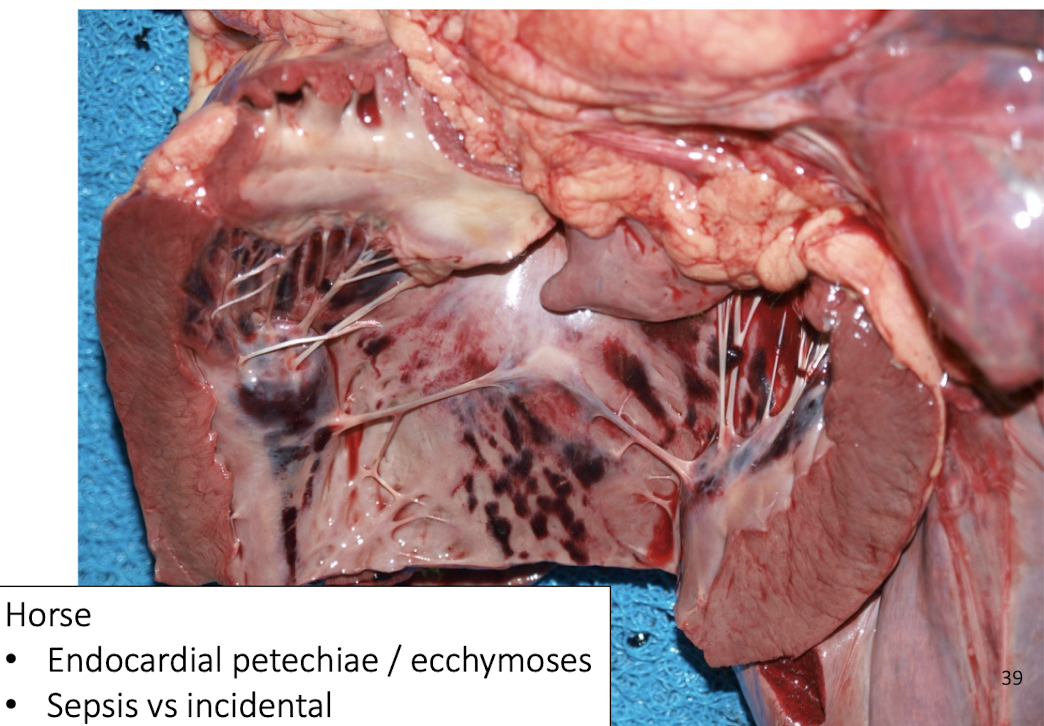
Endocardial hemorrhages in horses indicate?
Often incidental, consider sepsis context.
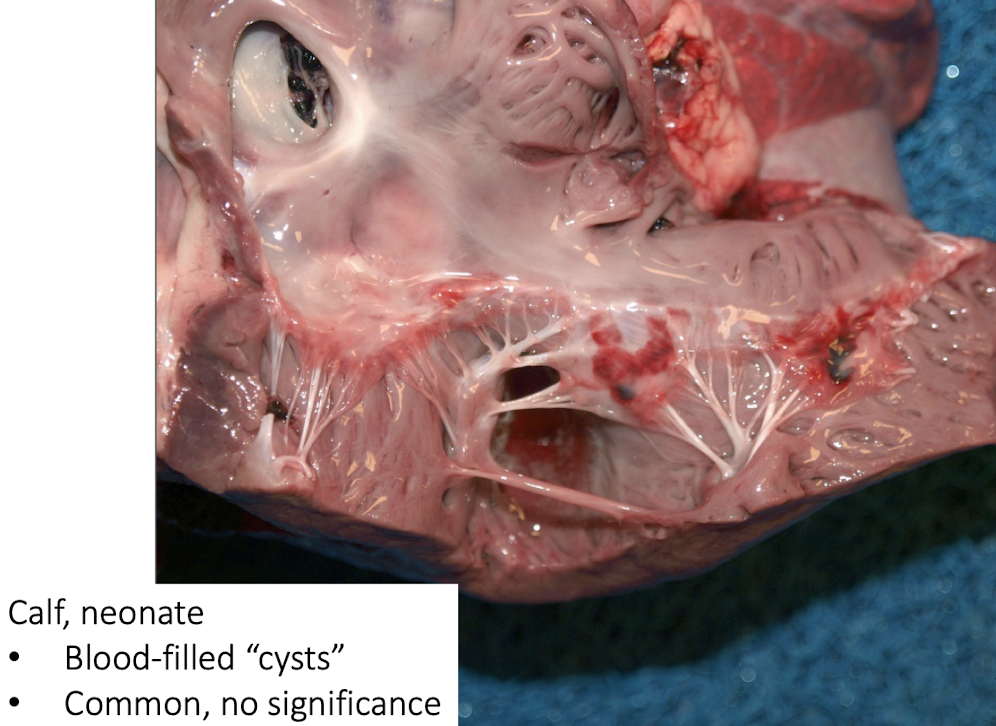
Blood-filled cysts in neonatal calves?
Common and insignificant
How does myocardium compensate?
↑ Stroke volume → ↑ chamber size
↑ Heart rate
↑ Contractility → myocardial hypertrophy
↑ Sodium/water retention
Why is myocardium compensation inefficient?
↓ Diastolic filling
↑ Myocardial work
↓ Perfusion
What happens when myocardial compensation fails (decompensation)?
Decompensation leads to myocardial ischemia, resulting in:
Decreased contractility, reducing cardiac output
Ventricular dilation due to volume overload
Atrial enlargement, secondary to impaired ventricular filling
Venous congestion and edema, producing clinical heart failure signs
This marks the transition from adaptive hypertrophy to pathologic heart failure.
How do pressure overload and volume overload differ in their effects on myocardial hypertrophy?
Pressure overload (e.g. subaortic stenosis, pulmonic stenosis, pulmonary hypertension):
Causes concentric hypertrophy
Wall thickness increases without chamber dilation
Reduces ventricular compliance → diastolic dysfunction
Volume overload (e.g. valvular insufficiency, shunts):
Causes eccentric hypertrophy
Wall thickness increases with chamber dilation
Leads to systolic dysfunction over time
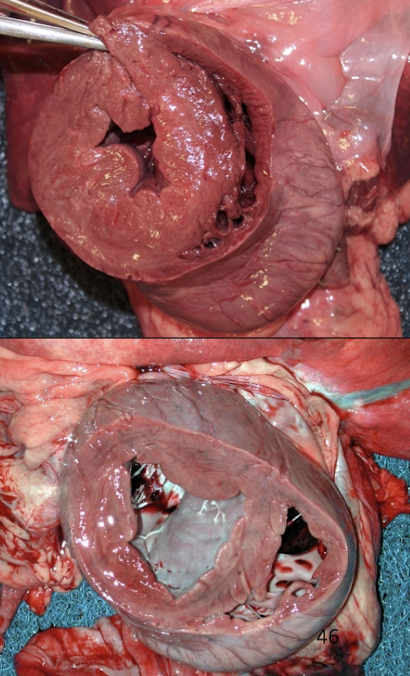
How does a ventricular septal defect (VSD) alter cardiac blood flow and workload?
A VSD causes left-to-right shunting due to higher left ventricular pressure, resulting in:
Increased pulmonary blood flow
Volume overload of the left heart
Progressive eccentric hypertrophy
Eventual pulmonary hypertension and heart failure if severe or chronic
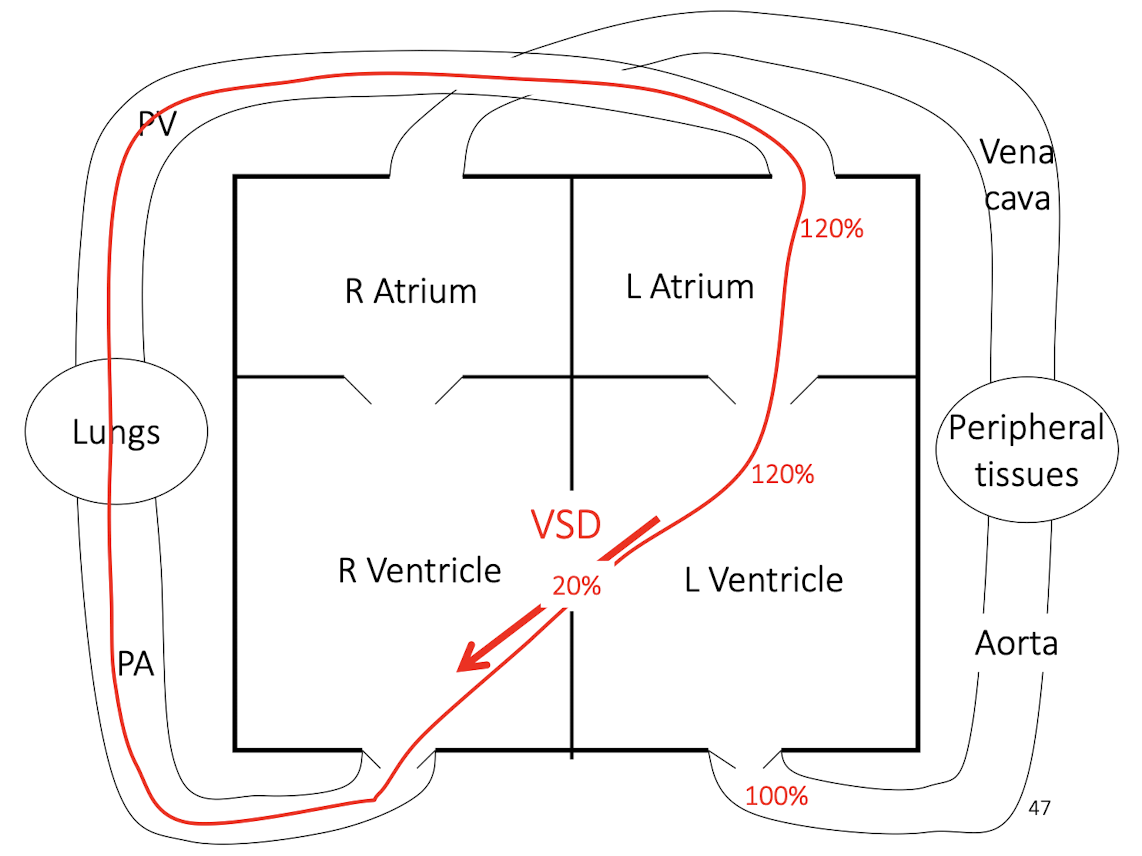
How do compensation and left heart failure differ in myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD)?
Compensated MMVD:
Atrial dilation
Eccentric ventricular hypertrophy
Maintained cardiac output
Decompensated MMVD (left heart failure):
Pulmonary congestion and edema
Reduced forward output
Clinical respiratory distress
This slide emphasizes staging of disease, not just lesion presence
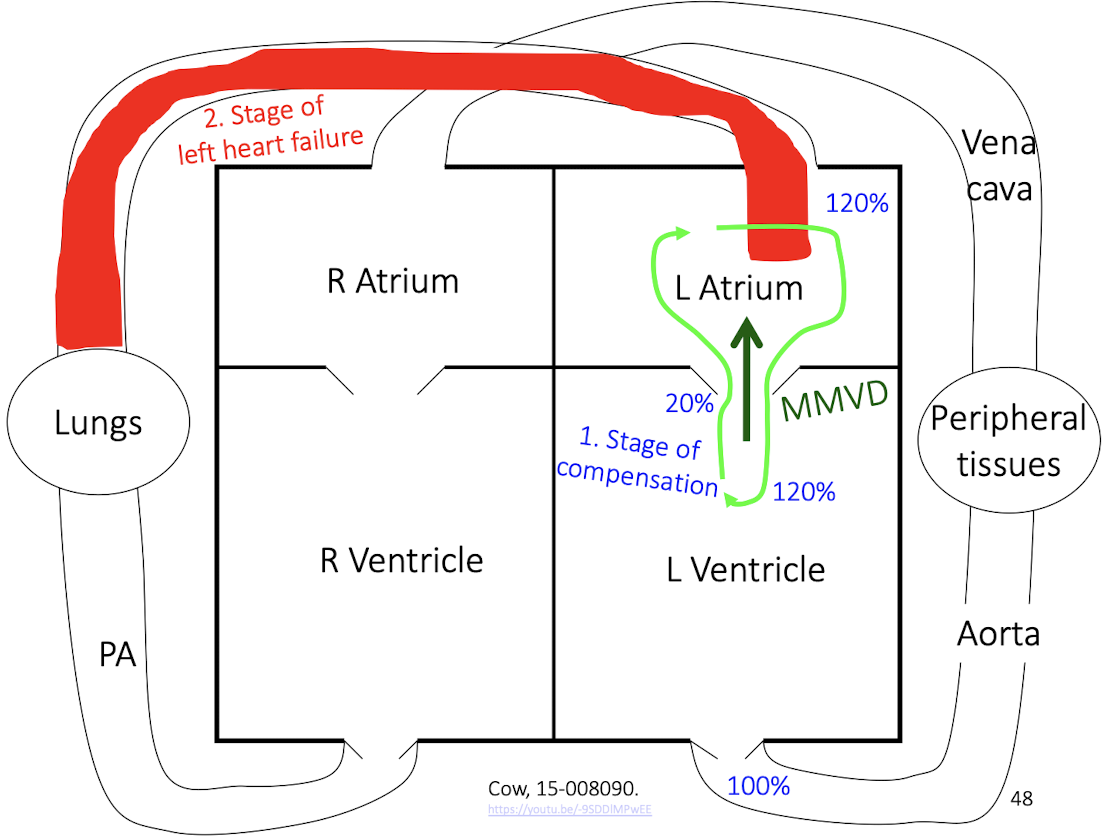
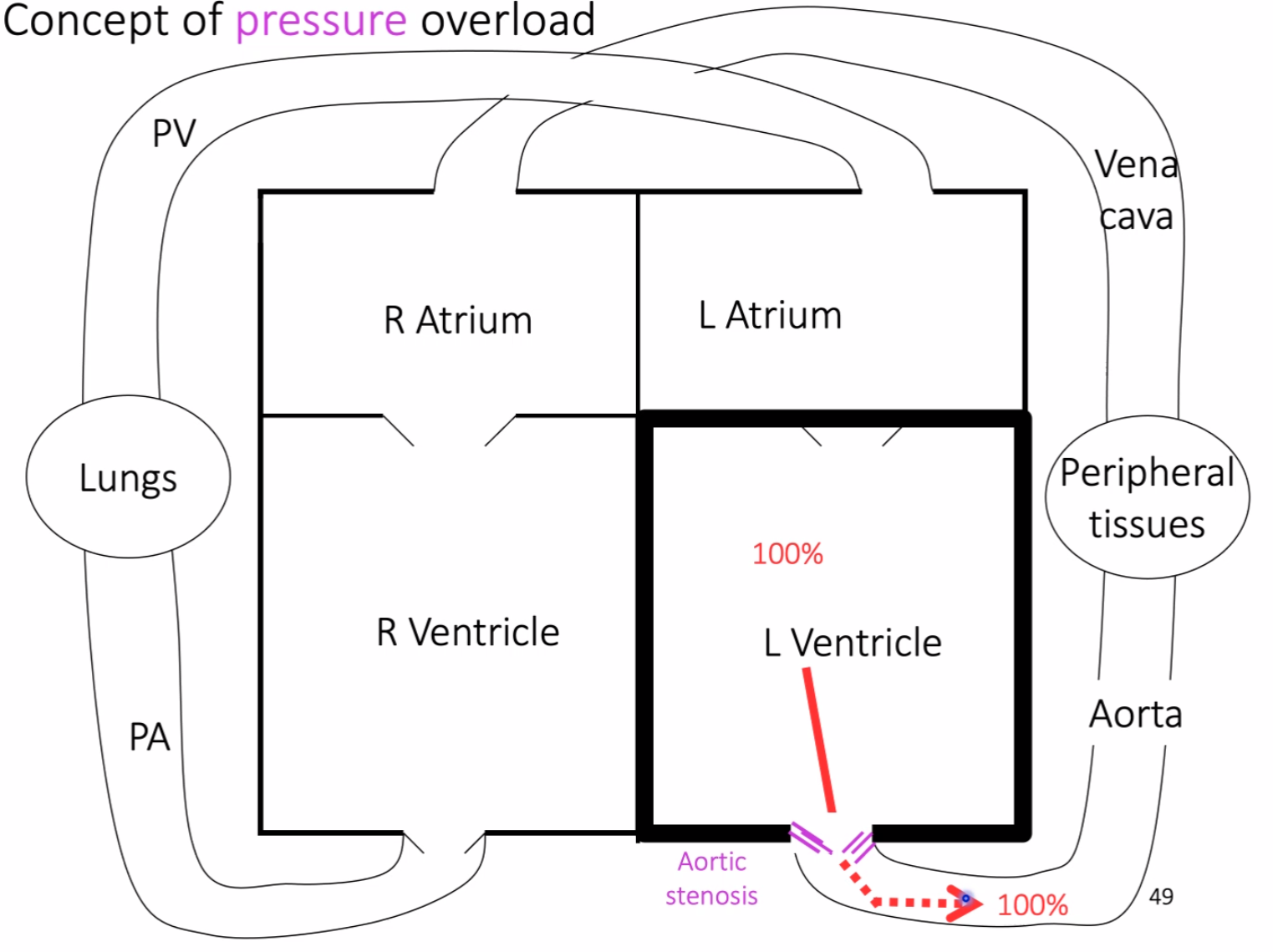
aortic stenosis causing pressure overload, where the left ventricle must generate abnormally high pressure to maintain normal cardiac output, leading to concentric hypertrophy
What is cardiomyopathy, and how are primary and secondary forms distinguished?
Primary cardiomyopathy:
Intrinsic disease of cardiac myofibers
Often idiopathic or inherited
Secondary cardiomyopathy:
Myocardial changes secondary to another condition
Causes include hyperthyroidism, nutritional deficiency, hypertension, congenital anomalies, or chronic heart failure
Major categories:
Hypertrophic
Dilated
Restrictive
Unclassified
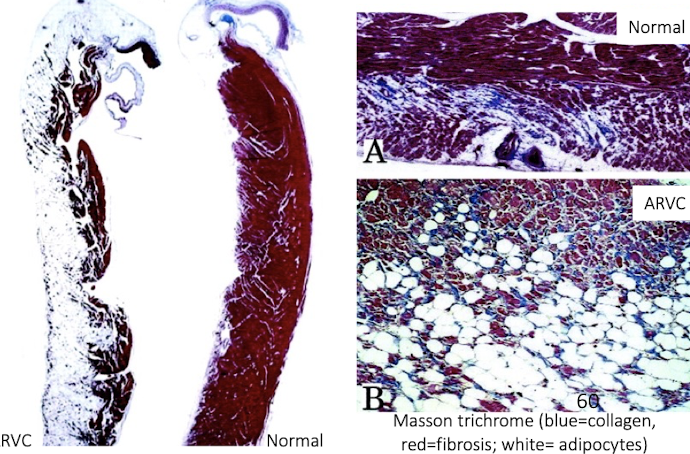
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
What defines hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and which species is most affected?
HCM is characterized by concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle, involving:
Thickening of the free wall and interventricular septum
Reduced ventricular compliance
R/O hyperthyroidism, hypertension, subaortic stenosis, hypersomatotropism
Heterogeneous >1 disease, clinical or subclinical
It is most common in cats, and uncommon in other species.
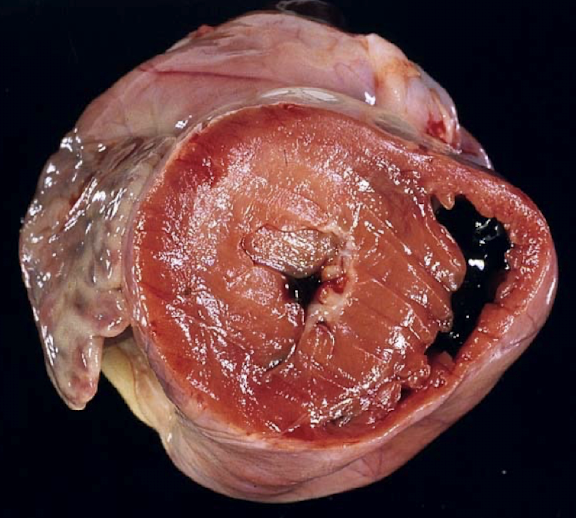
Why must hyperthyroidism be ruled out before diagnosing primary HCM?
Hyperthyroidism causes secondary concentric myocardial hypertrophy due to:
Increased metabolic demand
Chronic sympathetic stimulation
Increased heart rate and contractility
This produces a phenotype indistinguishable grossly from primary HCM.
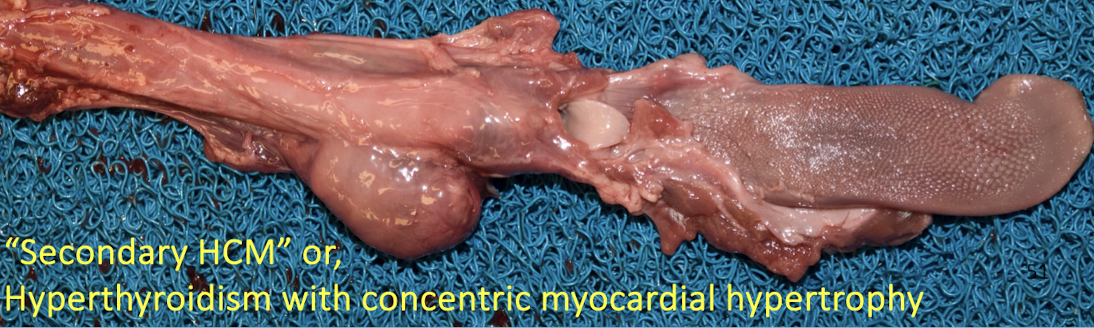
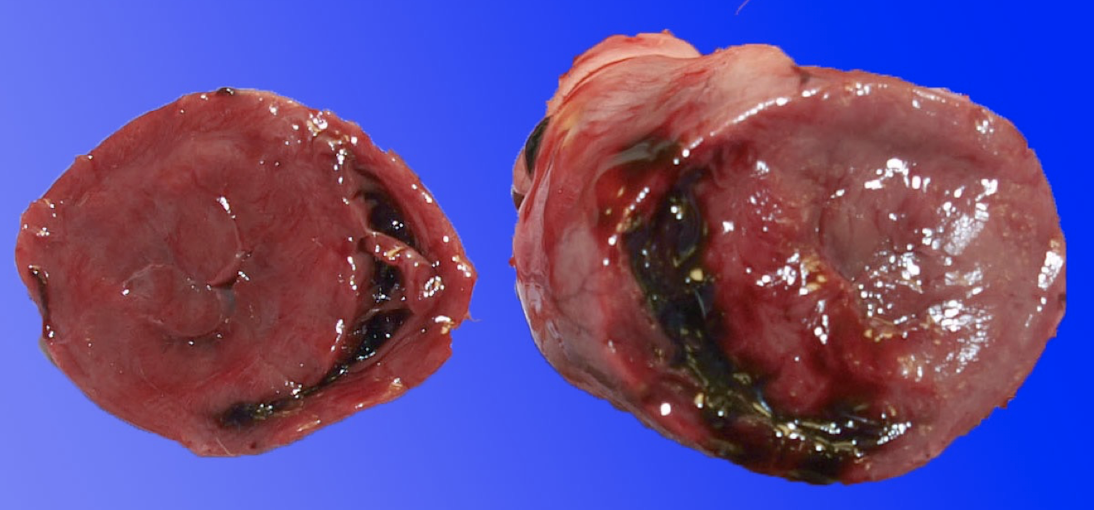
What are the gross and histologic lesions of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Gross lesions:
Marked left ventricular hypertrophy without dilation
Increased heart weight
LV : RV wall ratio >3:1 (often ~5:1)
± Left atrial dilation
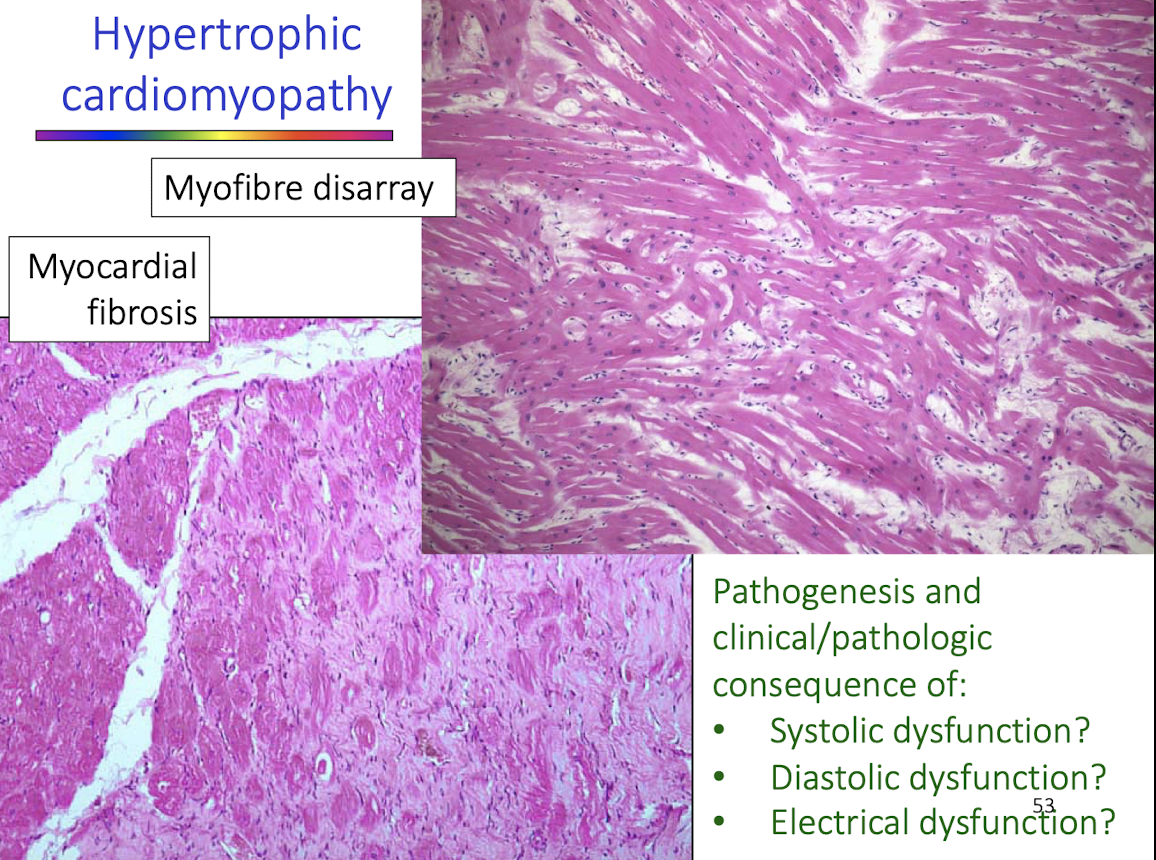
Histologic lesions:
Myocardial fibrosis
± Myofiber disarray
Vascular changes contributing to ischemia
What functional impairments result from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Diastolic dysfunction due to stiff ventricular walls (most important)
Electrical instability, predisposing to arrhythmias
Myocardial ischemia, from reduced capillary density and increased oxygen demand
Systolic function is often initially preserved
Why is myofiber disarray significant in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Myofiber disarray:
Disrupts coordinated contraction
Increases electrical instability
Predisposes to fatal arrhythmias
Is a key histologic hallmark of primary HCM
How is restrictive cardiomyopathy defined and distinguished from HCM and DCM?
Not on exam
RCM is defined by restricted ventricular filling during diastole with:
Normal ventricular wall thickness
Marked atrial dilation
Endocardial fibrosis ± synechiae
Unlike HCM or DCM, ventricles are neither thickened nor dilated
What are the causes of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Secondary causes: look for other gross and histo lesions, test levels in blood or diet
Volume overload
Myocarditis
Myocardial necrosis
Shunts
Nutrition → Taurine or carnitine deficiency
Primary (idiopathic) DCM:
Common in Dobermans, giant breeds, English Cocker Spaniels, and cats
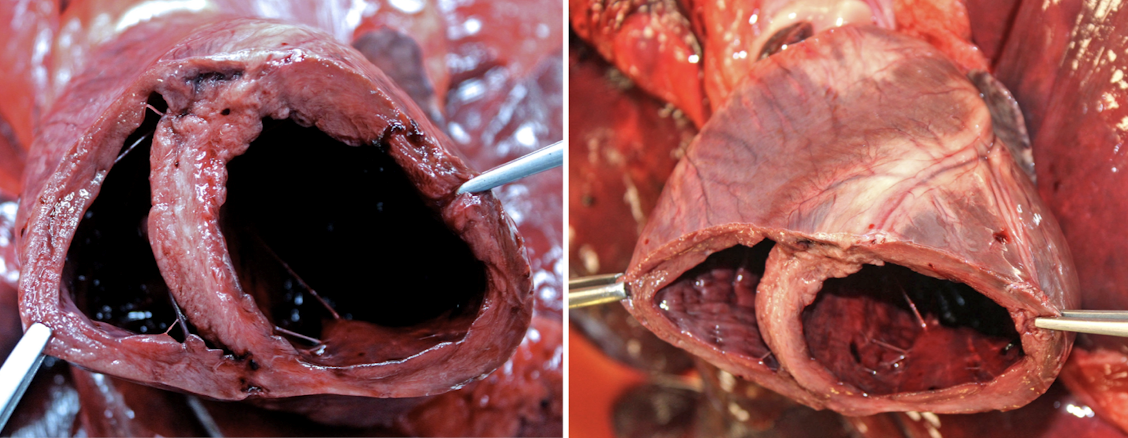
How is diet linked to dilated cardiomyopathy?
Diet-associated DCM has been linked to:
Taurine deficiency (especially in cats)
Certain dog breeds with altered taurine metabolism
Diets high in legumes, low protein, or unusual ingredients
Supplementation can partially or fully reverse disease in some cases
What are the key features of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)?
Primarily affects Boxer dogs
Causes sudden death due to arrhythmias → send in heart tissue especially R side
Gross lesions may be minimal or show RV dilation
Histology shows fibrofatty replacement of right ventricular myocardium
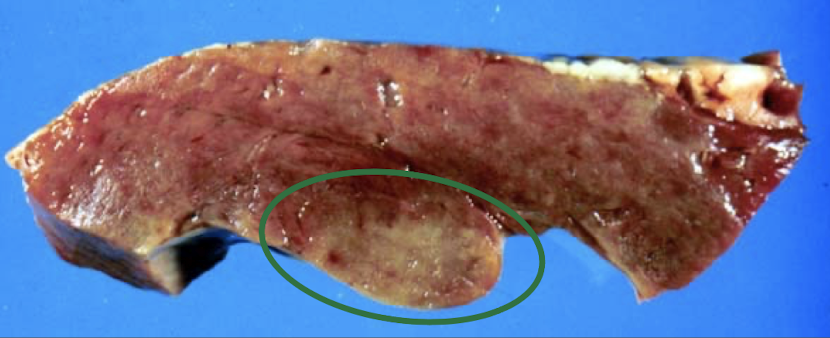
What are the major causes of myocardial necrosis?
Ischemia
Exertional injury, less likely in the heart, more SkM
Nutritional deficienc
Toxic injury (e.g. monensin)
Distinguished from myocarditis via histopathology → cannot distinguish grossly
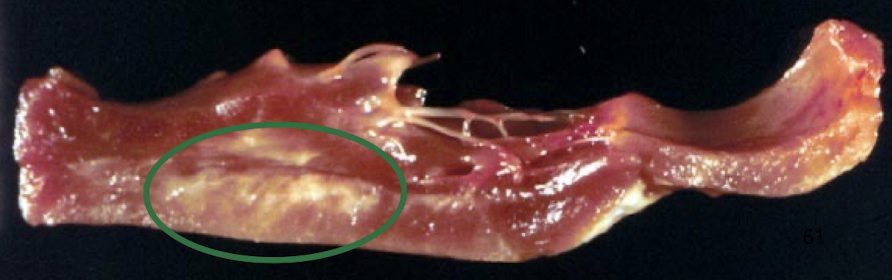
What causes white muscle disease and which tissues are affected?
White muscle disease is caused by vitamin E and selenium deficiency, leading to:
Oxidative damage to cell membranes
Necrosis of skeletal and/or cardiac muscle
± Mineralization of affected fibers
What causes atypical myopathy in horses?
Ingestion of box elder (Manitoba maple) toxins causes:
Severe rhabdomyolysis
Cardiac and skeletal muscle necrosis
Often fatal acute disease
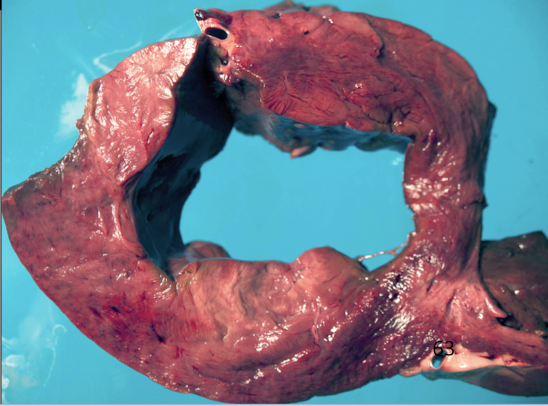
What infectious agents cause myocarditis?
Viral: parvovirus, distemper, BVDV
Protozoal: Toxoplasma, Neospora
Bacterial: Histophilus somni, Clostridium chauvoei
Immune-mediated: rheumatic fever (humans)
How does Histophilus somni cause myocardial injury?
Always effects papillary muscle of the L ventricle
Through:
Bacteremia
Vasculitis
Infarction of myocardium
Resulting in severe myocardial dysfunction.
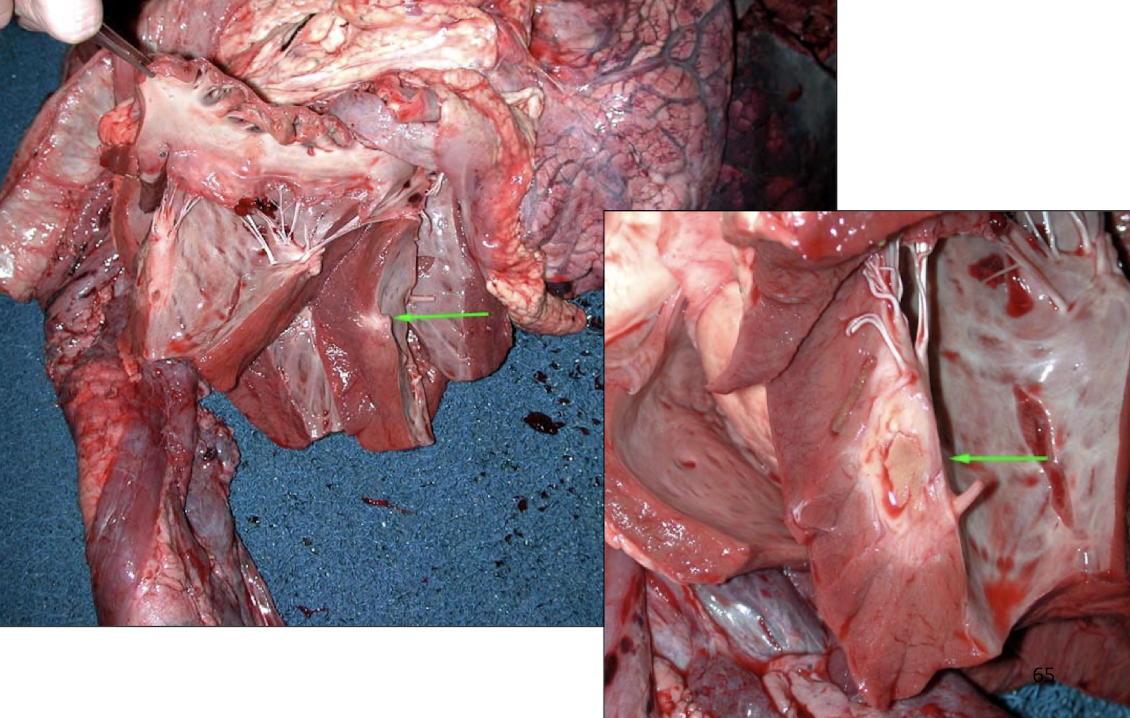
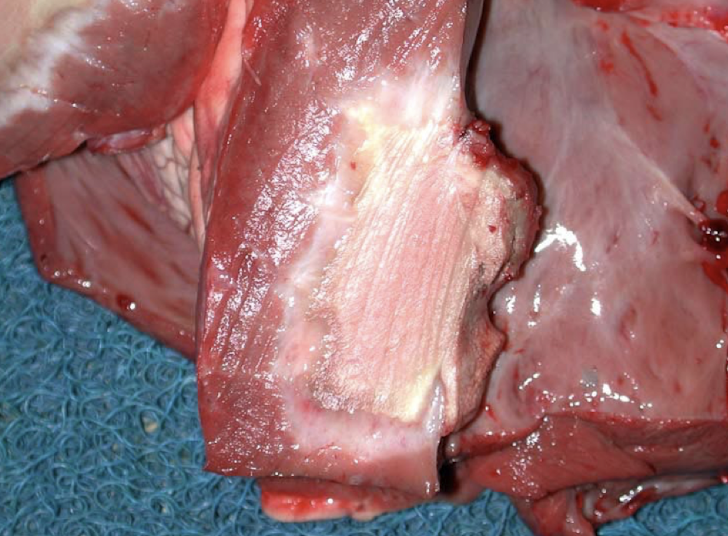
What are the major categories of myocardial disease?
Response to increased demand (hypertrophy)
Cardiomyopathies (HCM, DCM, RCM, ARVC)
Myocardial necrosis
Specific diseases (white muscle disease, monensin toxicity, Histophilus somni)
Where does heart worm go?
Pulmonary artery
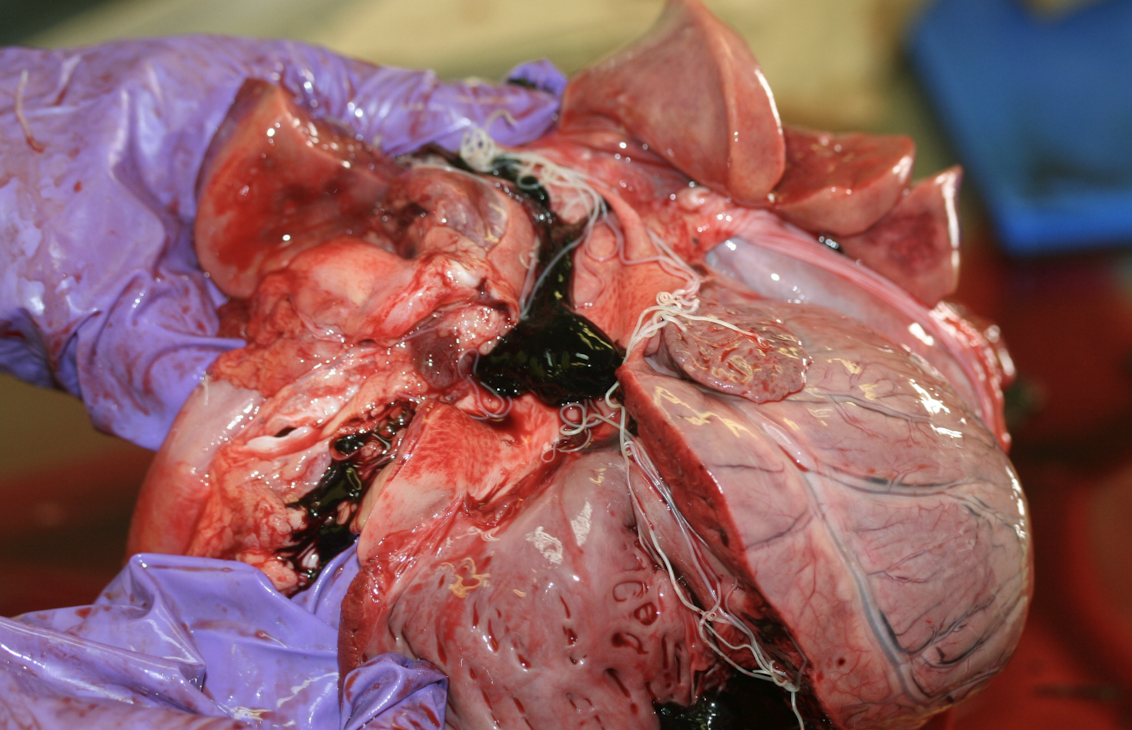
What structures and disease processes define pericardial pathology?
Pericardial diseases involve the pericardial sac and affect cardiac filling rather than myocardial contraction. Major processes include:
Abnormal fat metabolism
Fluid accumulation
Hemorrhage
Inflammation
These diseases primarily impair diastolic filling.
What is gelatinous transformation (serous atrophy) of fat, and why does it occur?
Serous atrophy of fat is caused by severe negative energy balance, leading to:
Mobilization of fat stores
Replacement of adipocytes with gelatinous, translucent material
Commonly affects epicardial fat, bone marrow, and perirenal fat
It indicates chronic disease or starvation, not primary heart disease
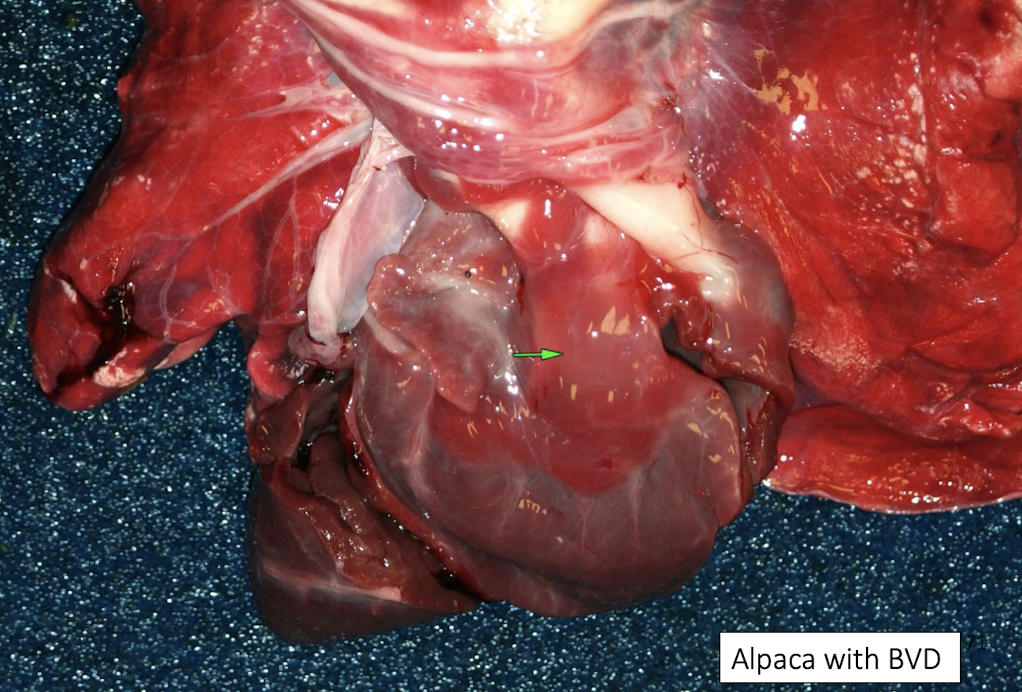
What is hydropericardium and what causes it?
Hydropericardium is accumulation of non-inflammatory fluid in the pericardial sac, caused by:
Hypoproteinemia
Congestive heart failure
Generalized edema states
It reduces cardiac filling but is usually secondary, not a primary cardiac disease
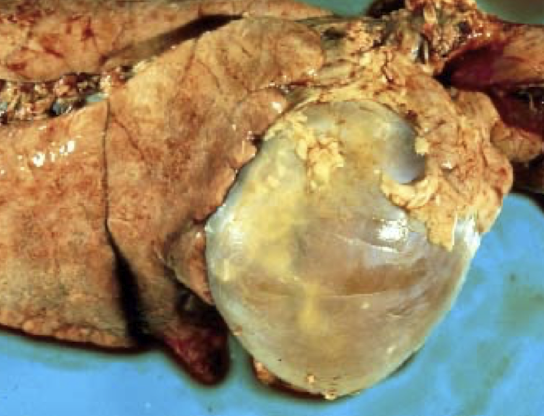
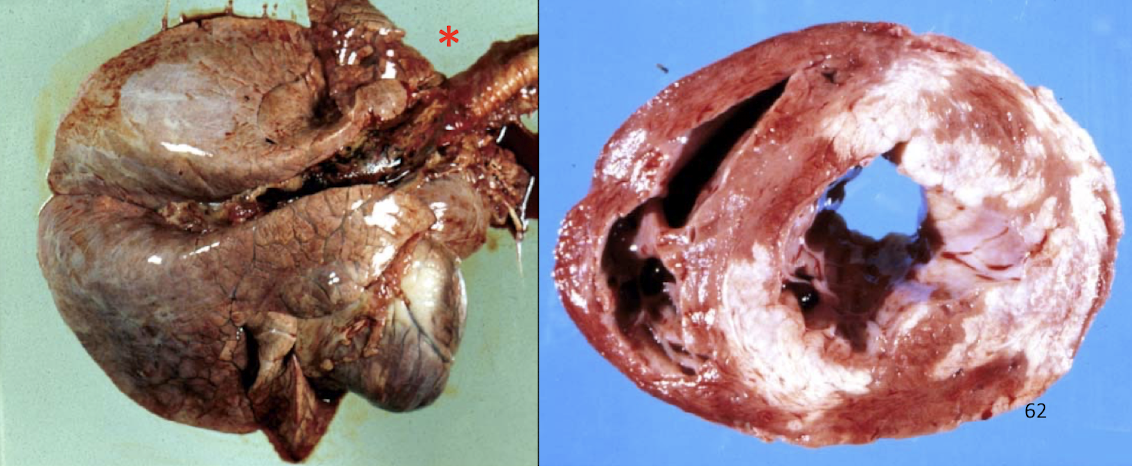
What is hemopericardium and why is it clinically significant?
Hemopericardium is blood accumulation in the pericardial sac, which can rapidly cause:
Cardiac tamponade
Reduced venous return
Acute circulatory collapse
Severity depends on rate of bleeding, not volume alone
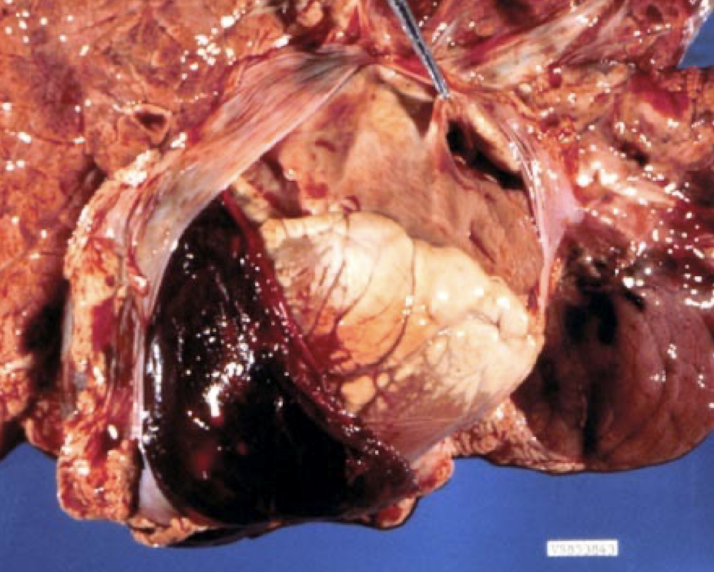
What are the most likely causes of hemopericardium in different animals?
Newborn calf: trauma, coagulopathy
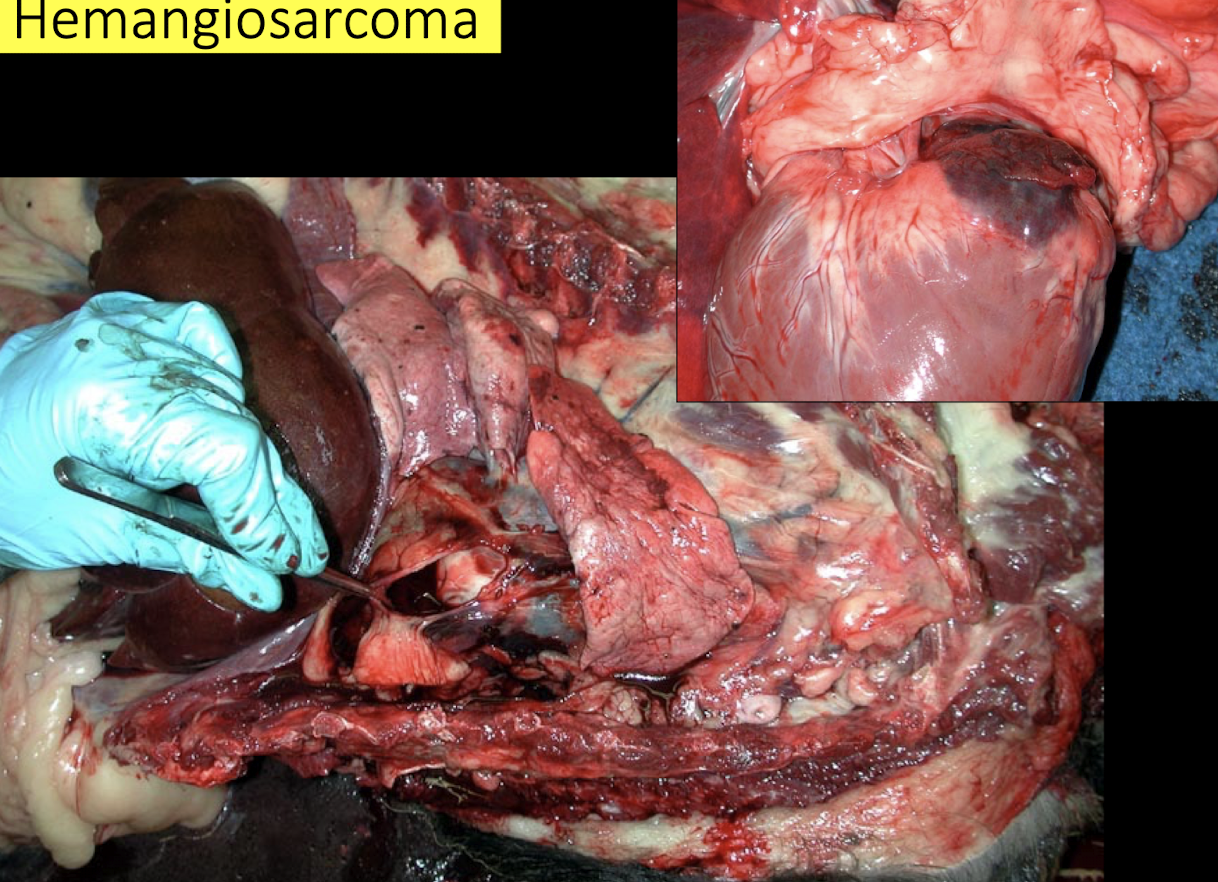
Older dog: hemangiosarcoma (right auricle)
Young adult dog: idiopathic (benign) pericardial effusion
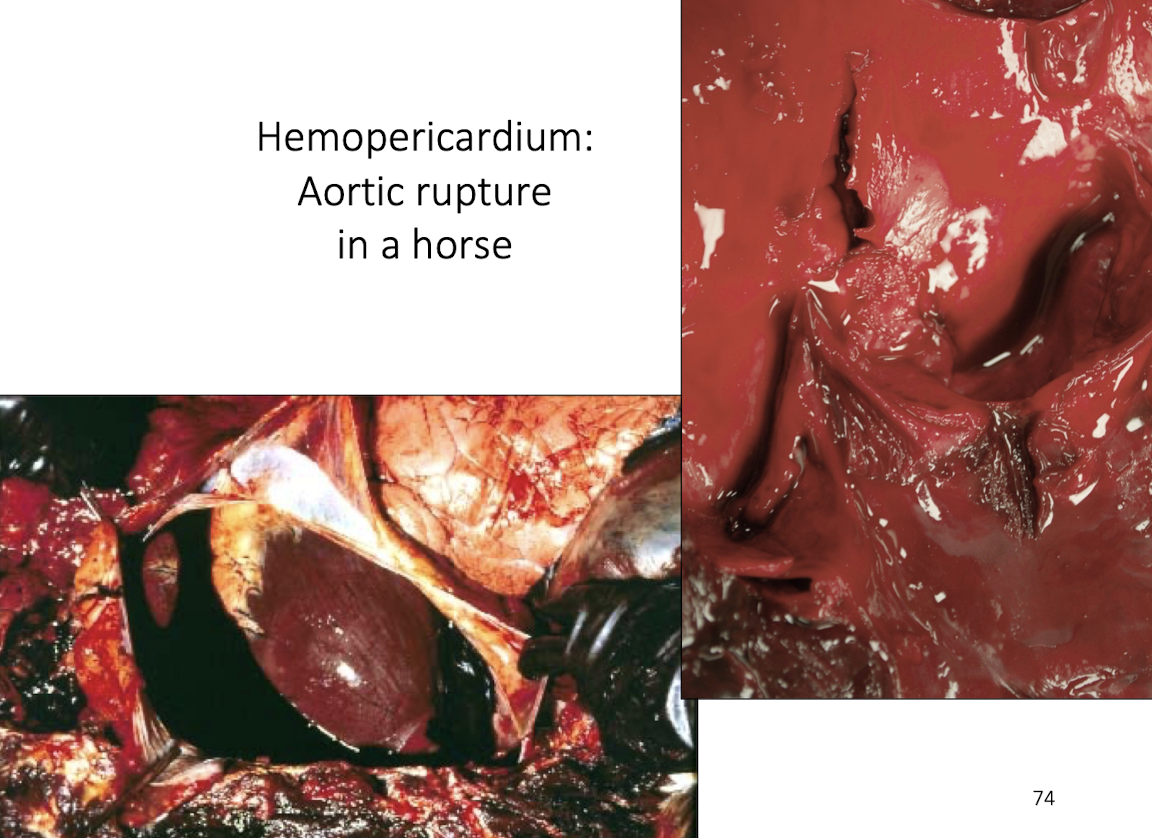
Horse: aortic rupture
How does aortic rupture lead to cardiac tamponade?
Rupture of the aorta causes rapid blood accumulation within the pericardial sac, resulting in:
Acute increase in intrapericardial pressure
Compression of the heart
Inability of ventricles to fill during diastole
Sudden death
What are the three routes by which infection reaches the pericardium?
Hematogenous spread
Extension from adjacent structures (lungs, myocardium)
Direct penetration (foreign bodies)
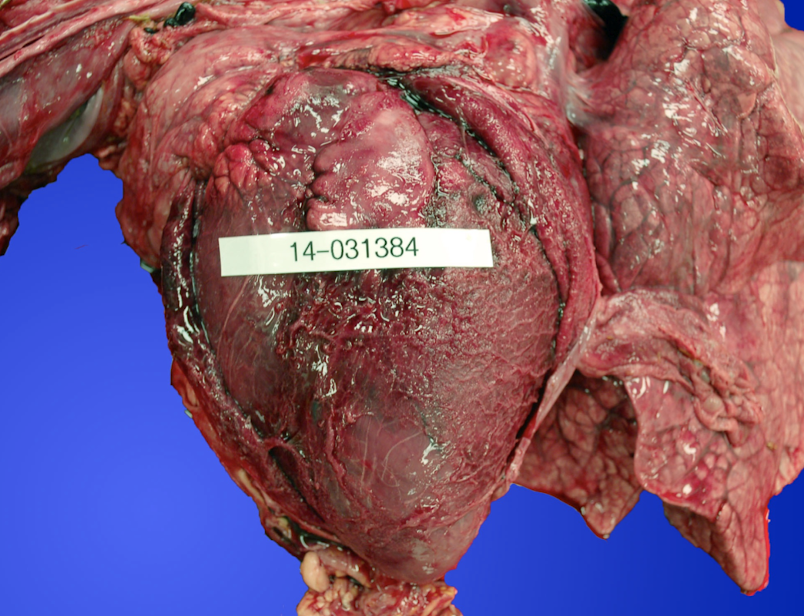
What are common bacterial causes of pericarditis by species?
Neonates: E. coli
Pigs: Streptococcus suis, Glaesserella parasuis
Cattle: hardware disease, Clostridium chauvoei
How do you determine the route of infection in pericarditis cases?
By evaluating:
Lesion distribution
Presence of foreign bodies
Concurrent systemic infection
Adjacent organ involvement
This determines whether spread was hematogenous, local extension, or penetrating
How does hardware disease cause pericarditis?
A sharp metallic foreign body penetrates the reticulum, diaphragm, and pericardium, causing:
Bacterial contamination
Severe inflammation
Often fibrinopurulent pericarditis
What lesion pattern is typical of hardware ds
Thick fibrin layers
Purulent exudate
Adhesions between pericardium and epicardium
Progressive restriction of cardiac filling
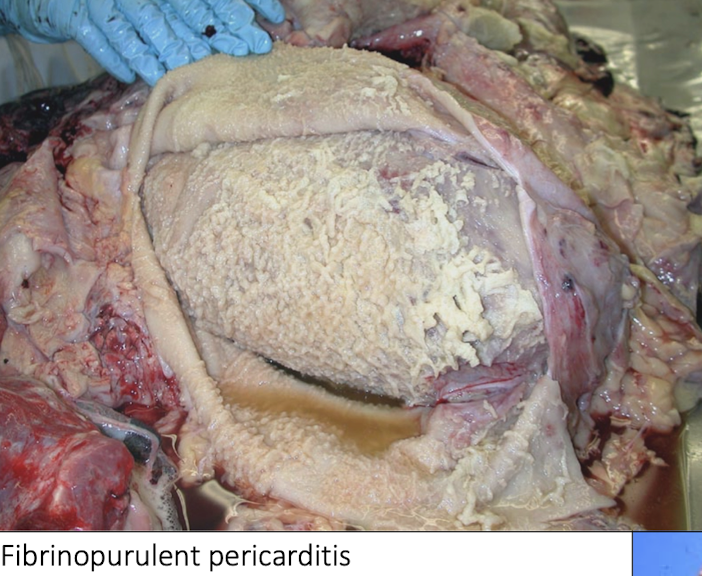
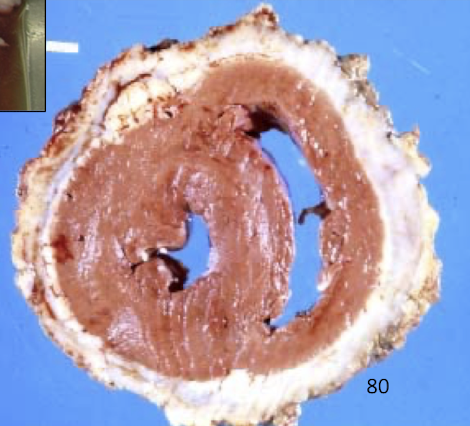
Why is fibrinopurulent pericarditis termed “constrictive”?
Because fibrin and fibrosis:
Physically restrict cardiac expansion
Prevent normal diastolic filling
Cause signs of right-sided heart failure
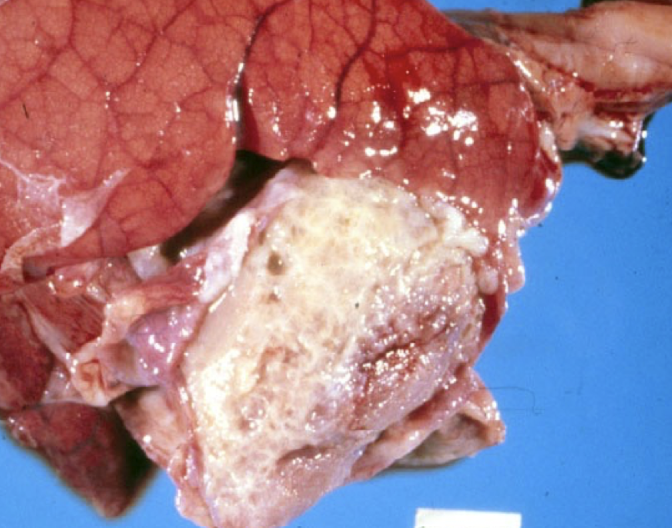
Which pathogens commonly cause fibrinous pericarditis in pigs?
Streptococcus suis
Glaesserella parasuis
Mycoplasma hyorhinis
These typically spread hematogenously
What are the major causes of vasculitis and vascular necrosis?
Immune complex deposition (Type III hypersensitivity)
Infectious agents
Physical injury (burns, frostbite)
Hypertension
Uremia
What are the major vascular pathologies introduced?
Vasculitis → targets wall of vessel
Aortic mineralization
Arteriosclerosis & atherosclerosis
Thrombosis and embolism
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Which infectious agents commonly damage blood vessels?
Bacteria: Erysipelothrix, Histophilus somni, Rickettsia rickettsii (RMSF)
Viruses: EVA, FIP, BVD, MCF, PCV
Fungi: Aspergillus
Parasites: Strongylus vulgaris
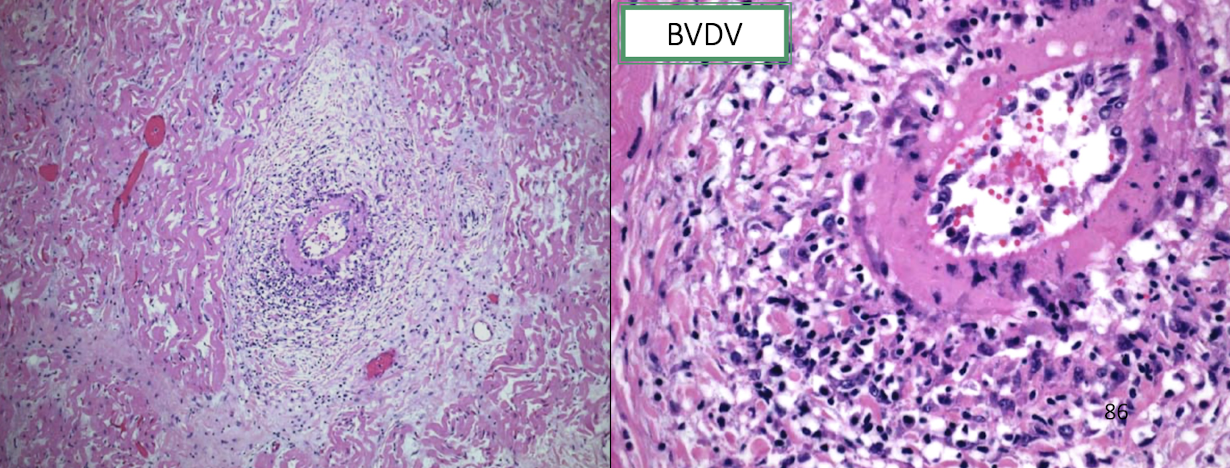
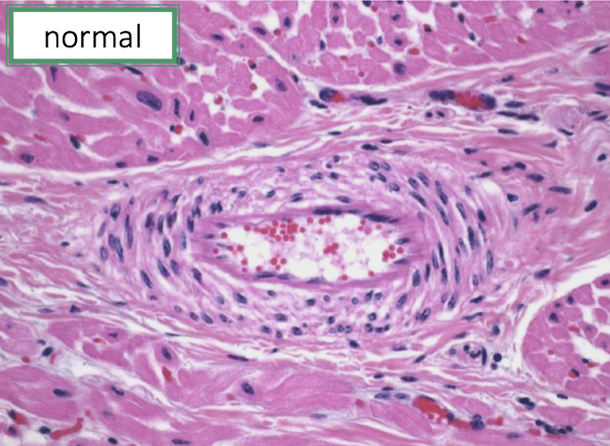
How does acute BVD cause vasculitis?
Through:
Endothelial injury
Immune-mediated inflammation
Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls
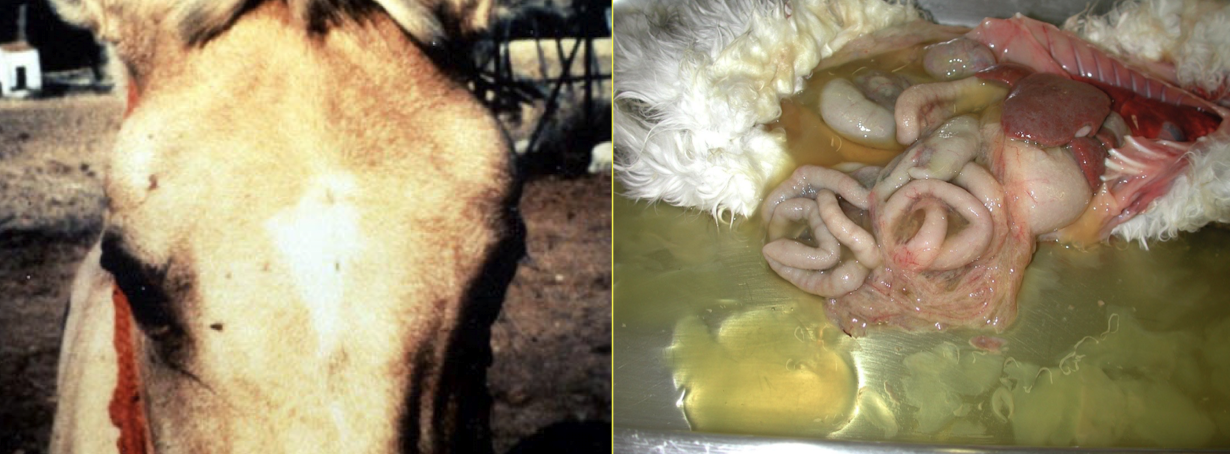
What is the primary vascular consequence of vascular injury: FIP and African horse sickness?
Edema
Increased vascular permeability
Leakage of protein-rich fluid
Severe edema and effusions
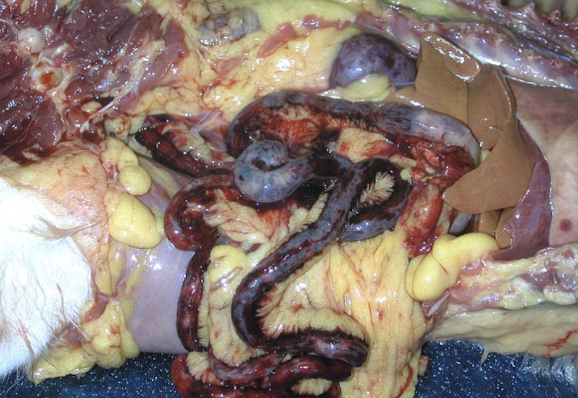
Ecchymotic hemorrhages (DIC)
Peripheral infarcts (sepsis)
How does disseminated intravascular coagulation cause hemorrhage?
DIC causes:
Widespread microthrombosis
Consumption of clotting factors
Secondary uncontrolled hemorrhage
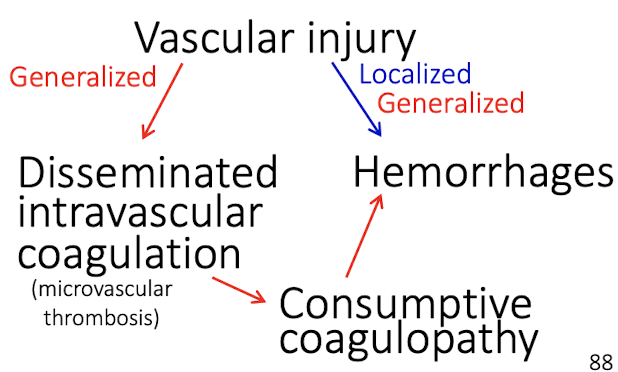
What are the major outcomes of blood vessel injury?
Thrombosis → ischemia, infarction
Increased permeability → edema, hemorrhage, protein rich exudates, Fibrinoid necrosis
DIC → consumptive coagulopathy, hemorrhages
What is the difference between metastatic and dystrophic vascular mineralization?
Metastatic: due to systemic mineral imbalance (vitamin D toxicity, Johne’s)
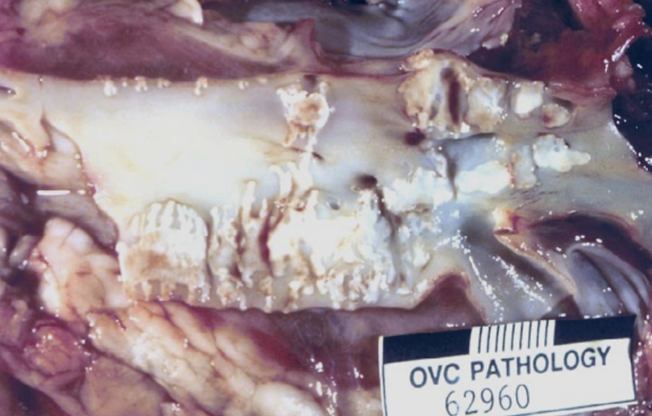
Dystrophic: occurs at sites of prior vascular injury
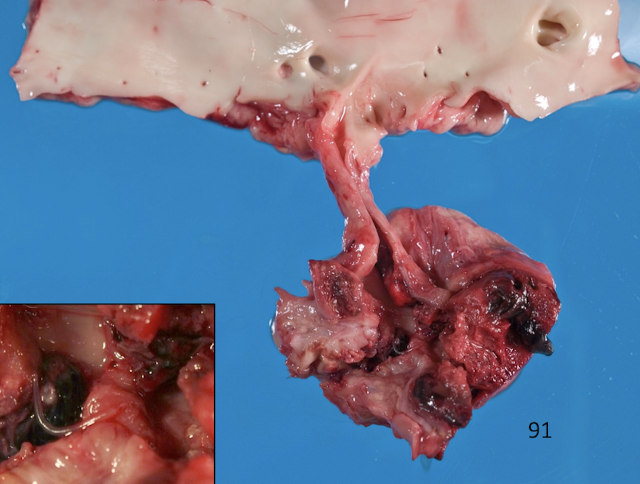
What defines hemangiosarcoma and why is it dangerous?
Hemangiosarcoma is a malignant endothelial tumor, commonly affecting:
Right auricle
Spleen
Skin
It causes:
Hemopericardium
Cardiac tamponade
Sudden death