Biol 241 - Locomotion
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What does understanding max metabolic rates allow us to make predictions on?
Reproduction, distribution, range, migration, other constraints on survival
What are physiological limitations on MRmax and MR sustained?
Metabolic (cellular) pools of ATP + phosphocreatine + PCr + ADP _> C + ATP
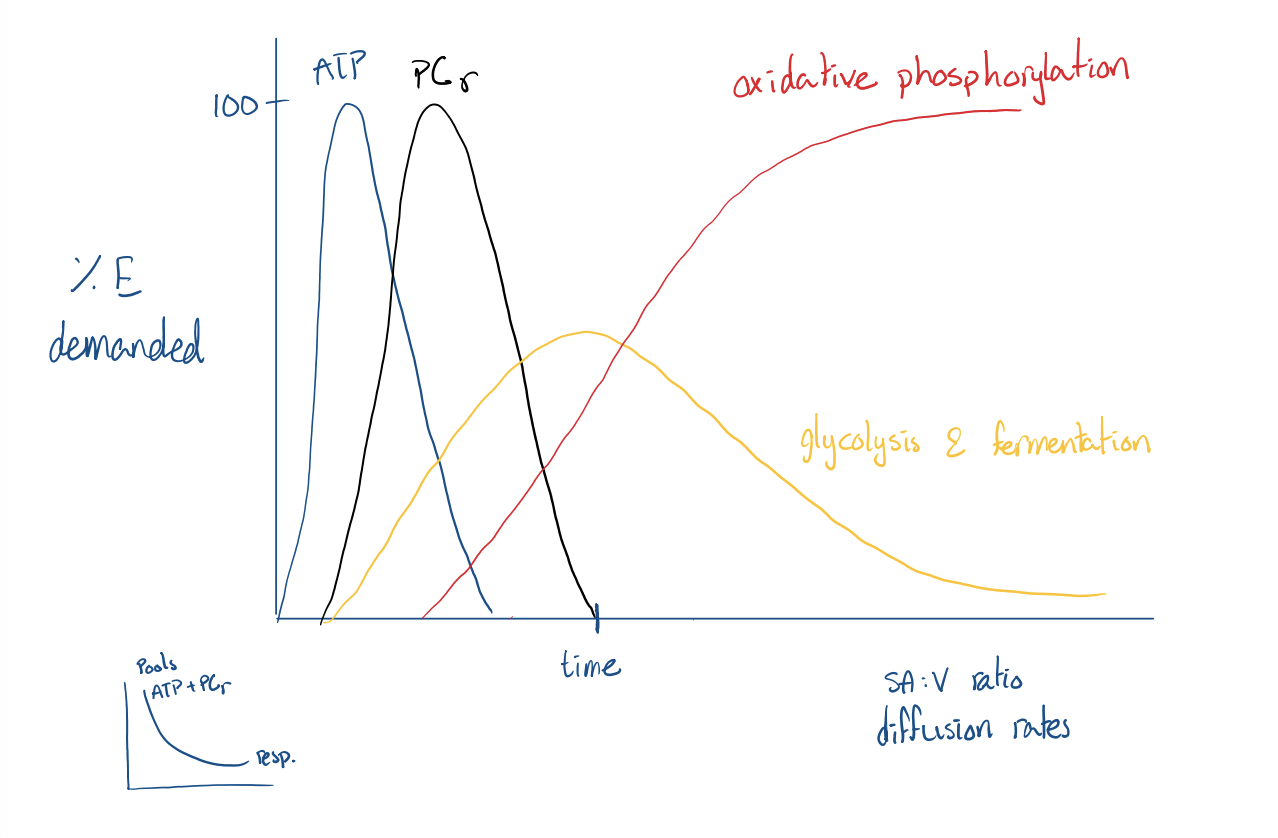
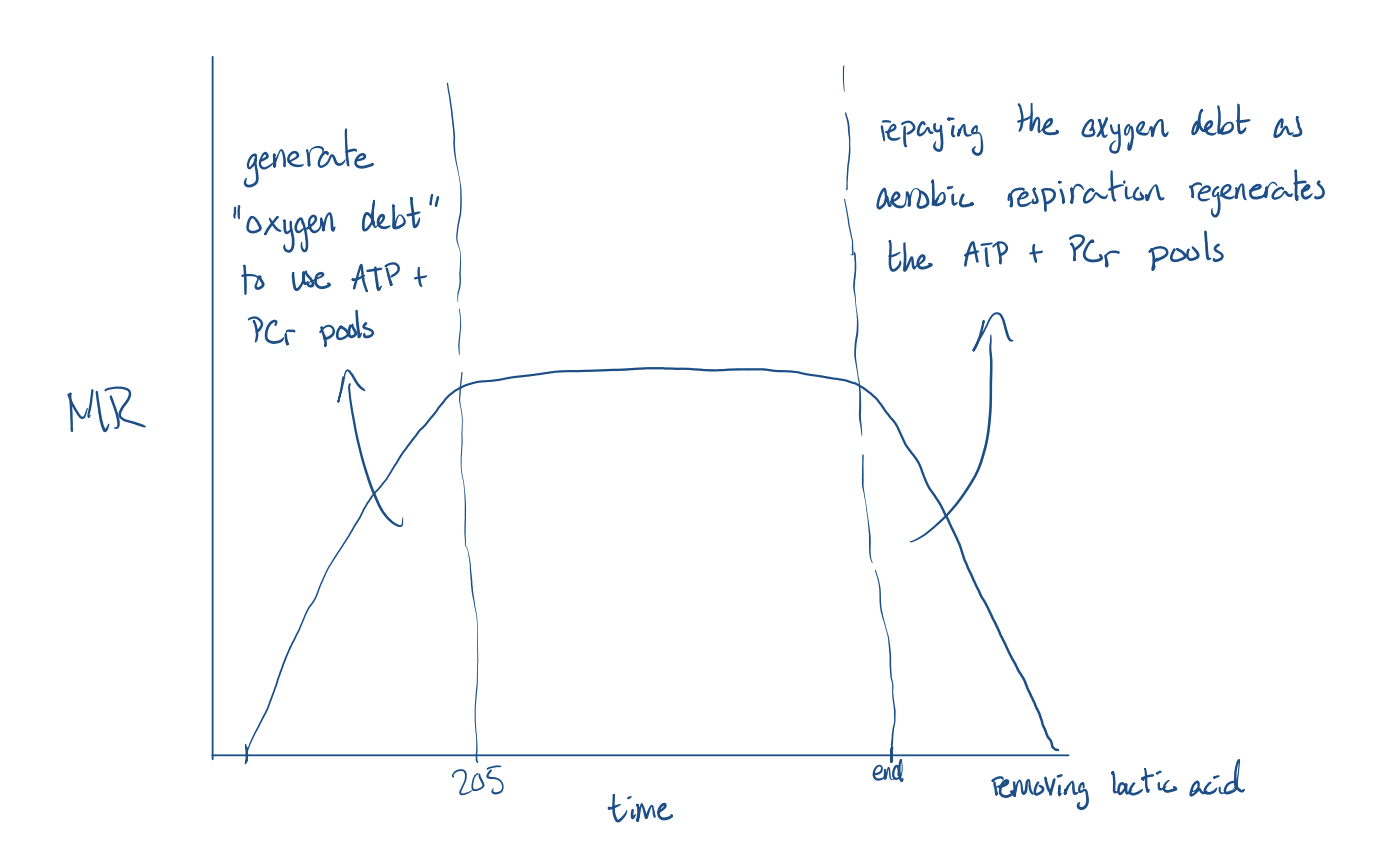
Recovery metabolism
Repaying oxygen debt as aerobic respiration regenerates the ATP + PCr pools
Muscles use ___ to contract, generating what?
ATP, force
The force generated by any muscle will increase as you increase… (2 things)
the number of muscle cells in a muscle
the length of the muscle
The force generated by any muscle will decrease with…
the speed of contraction
A muscle is a bundle of what?
muscle fibres (muscle cells)
During muscle growth, what occurs?
hundreds of myoplasts fuse to form a long, multi-nucleate cell
Muscle fibres are filled with bundles of what?
myofibrils: proteins that are as long as cell length
What do myofibrils consist of?
alternating thick and thin filaments
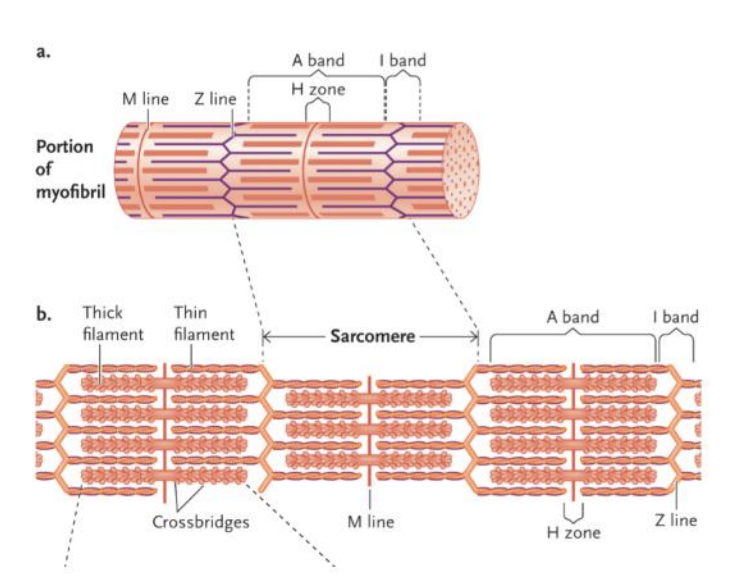
The myofibrils thick and thin filaments are arranged along the length of the myofibril in what?
repeating sarcomeres (the functional unit of muscle)
Myofibrils are what?
striated: marked with long, thin parallel streaks.
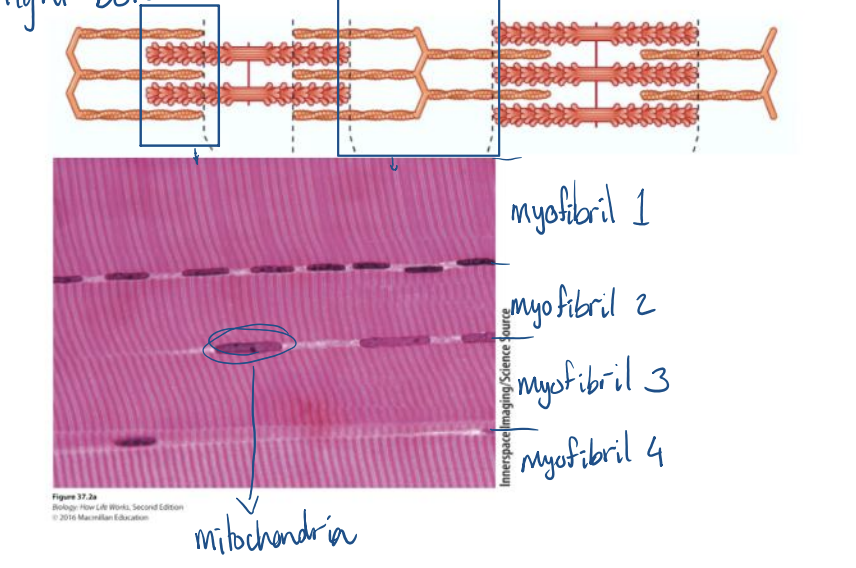
The muscle is denser where?
where the thick and thin filaments overlap = dark bonds
The muscle is less dense where?
where the filaments do not overlap = light bonds
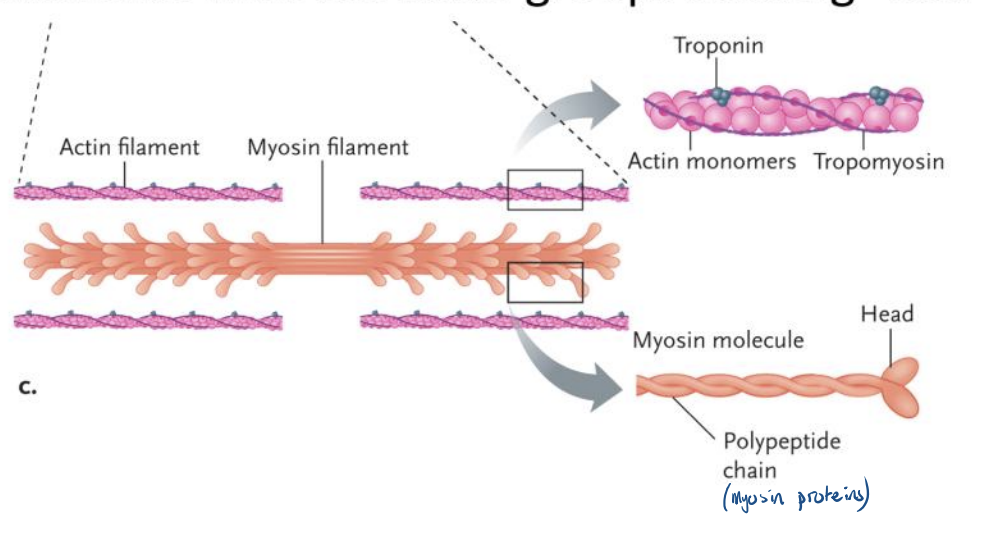
What are thin filaments?
two linear polymers of actin proteins wound around each other
What do tropomyosin proteins wrap around?
the thin filament
What proteins associate with tropomyosin along the length of the filament?
Troponin
What are thick filaments?
Bundles of myosin
each myosin protein is a dimer of what?
dimer of two polypeptide coiled around each other with a globular “head” at one end and a long helical “tail”
dozens of myosin homodimers are arranged into the thick filaments with the head groups sticking which way?
Out
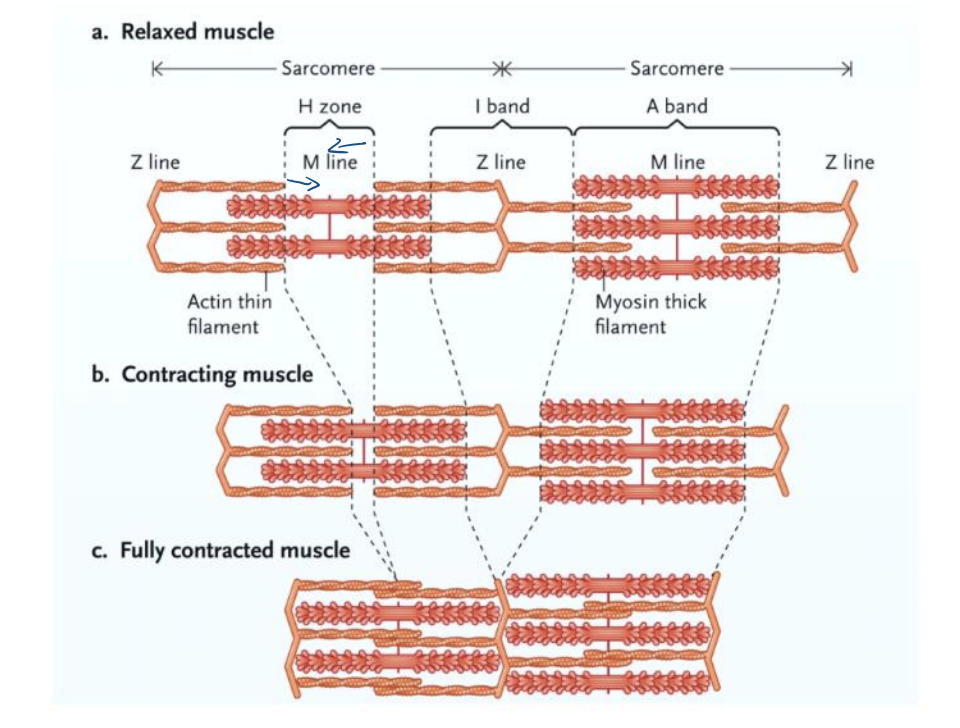
Sarcomeres have a ___ at each end
Z-line
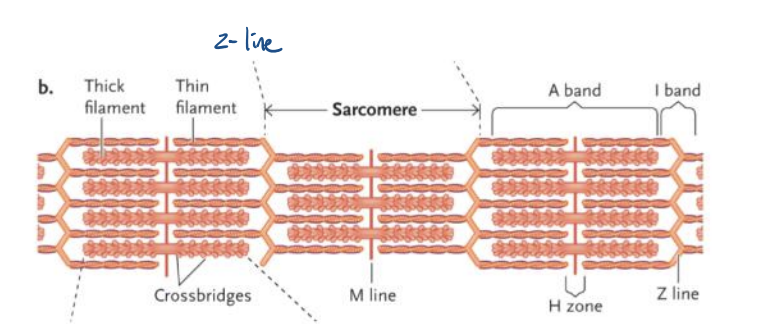
What extends out from each z-line towards the middle of the sarcomere?
actin (thin) filaments
Sarcomeres have a ___in the middle
M-line
what extends out from each M-line towards each end of the sarcomere?
Myosin (thick) filaments
What is a crossbridge?
the interaction between a actin proteins and a myosin head group
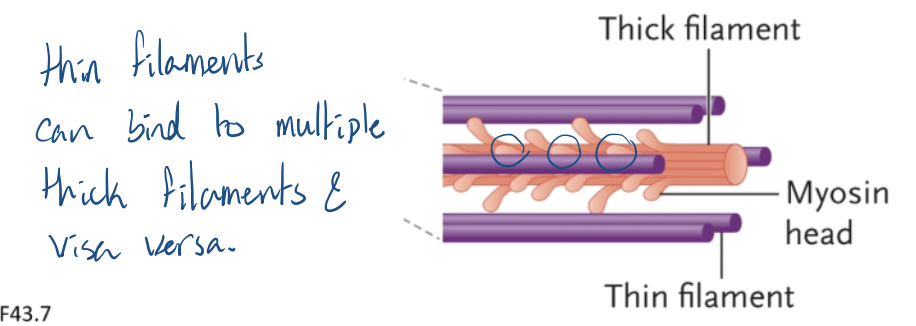
each actin protein has a….
myosin binding site and a ATP binding site
where multiple myosin (thick) and actin (thin) filaments overlap what can form?
multiple crossbridges
What increases with number of cross bridges and interaction between thick and thin filaments?
force
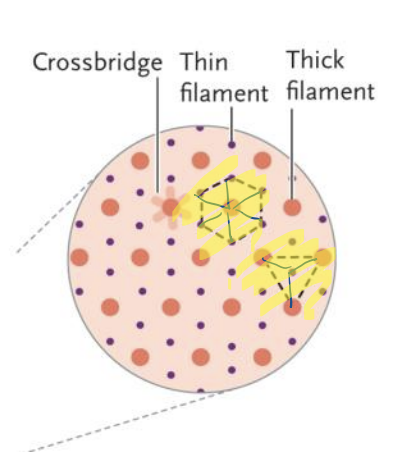
What is the sliding filament model?
muscles contract when the myosin filaments pull the opposing actin filaments toward each other
what is sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum that surrounds muscle myofibrils
when a signal is received from a motor neuron, what is the first step of activating muscle contraction?
calcium facilitates diffusion, proteins open
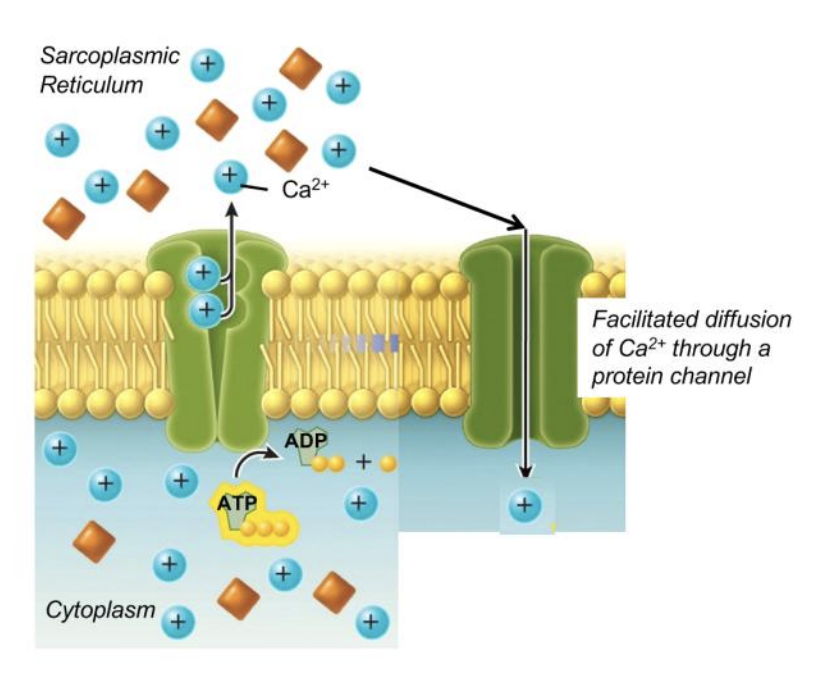
when a signal is received from a motor neuron, what is the second step of activating muscle contraction?
Ca 2+ diffuses down its [gradient] back into cytosol
![<p>Ca 2+ diffuses down its [gradient] back into cytosol</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a77094d6-77b6-49db-8b1c-44f0d3d2409c.png)
when Ca2+ enters the cytosol, what is the first step of excitation-contraction coupling?
Ca2+ binds the troponin on the thin filaments
when Ca2+ enters the cytosol, what is the second step of excitation-contraction coupling?
Ca2+ binding causes troponin to change shape which causes tropomyosin to shift
when Ca2+ enters the cytosol, what is the third step of excitation-contraction coupling?
tropomyosin covers myosin binding site when it moves, it exposes these binding sites allowing a cross-bridge to form
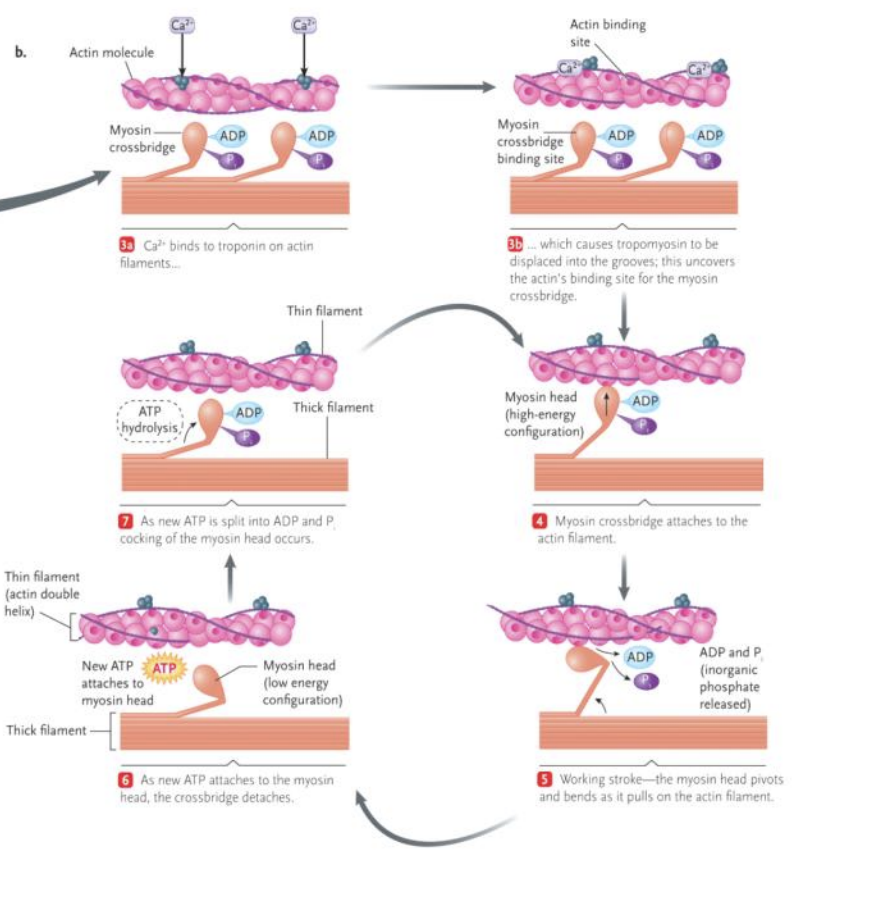
The crossbridge cycle - what occurs in the first step here?
ATP is used so the myosin pulls on actin filaments
each Z-line will move toward the M-line
Muscle contraction - what do myosin head groups repeat during muscle contraction?
each myosin head group repeats the cross-bridge cycle many times during muscle contraction
muscle contraction - what do myosin filaments work in unison to do?
each myosin filament (containing dozens of myosin molecules) work in unison to pull on six surrounding actin filaments at each end
muscle contaction - what occurs when the thousands of sarcomeres within each myofibril and muscle fiber shorten?
the muscle contracts
the force generated by muscles increases when ____
when the number of cross bridges formed in sarcomere increases
the force generated by any muscle will increase as you increase what?
increase the number of muscle cells in the tissue, more muscle cells = more sarcomere
and
increase the length of the muscle tissue, longer muscle cells = more sarcomeres
the force generated by any muscle will decrease with…
speed of contraction, rapid contraction decreases number of crossbridges
muscle relaxation - when the signal from the motor neuron stops, what is the first step?
the facilitated Ca2+channels in the SR close, Ca2+ can’t leave SR
SR = sarcoplasmic reticulum
muscle relaxation - when the signal from the motor neuron stops, what is the second step?
the Ca2+ -ATPase pumps Ca2+ from cytosol
muscle relaxation - when the signal from the motor neuron stops, what is the third step?
Troponin releases Ca2+, causing tropomyosin to change back into its original shape and block the myosin binding sites
muscle relaxation - when the signal from the motor neuron stops, what is the fourth step?
unable to bind myosin, the actin filaments slide back, lengthening the sarcomeres
Forces acting on a runner
gravity, thrust, muscle action, only a bit of drag
what is mass-specific metabolic rate?
energy (volume of oxygen) required to move 1 unit mass of an organism
What is cost of transport?
the energy required to move 1 unit mass of an organism 1 unit distance
what are the forces acting on a swimmer?
thrust, buoyancy, drag
what are viscous forces?
skin friction drag
what are inertial forces?
pressure drag
what are the forces acting on a flier?
gravity, thrust, lift, drag
wings generate lift + thrust to counter gravity and drag