Mitochondria
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms

What does this appear to be
LHON: Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
What is LHON: Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
Bilateral, painless, subacute visual failure that develops during young adult life
Are males/females more likely to get LHON
Males are approximately four times more likely to be affected than females
How does LHOn present
Entirely asymptomatic until onset in one eye
Similar symptoms appear in the other eye an average of eight weeks later
In about 25% of cases, visual loss is bilateral at onset
In a small percentage of cases, central vision gradually improves – but recovery is incomplete
For most central vision loss is profound and permanent
women with LHON may also have what as well when described as LHON plus
Some individuals with LHON, usually women, may also have a multiple sclerosis (MS)-like illness – termed ‘LHON-plus
What is the founder effect
A community within a community that share common genetics due to intermarriage
Approximately 95% of individuals with LHON have one of three point mutations of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Name these point mutations

Heteroplasmy
Coexistence of both normal (wild-type) and mutated mtDNA within the same cell/tissue.
The proportion of mutant mtDNA determines whether disease manifests (threshold effect).
Heteroplasmy in Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes occurs in what % of those with a pathogenic LHON causing mtDNA mutation
Heteroplasmy in Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes occurs in 10 - 15 % of those with a pathogenic LHON causing mtDNA mutation
Individuals with which pathogenic variant load of less than ___% in their leukocytes may be unaffected
Individuals with a m.11778G>A pathogenic variant load of less than 75% in their leukocytes may be unaffected
However in general heteroplasmy of <75% pathogenic variant load is rare – majority of LHON carriers are homoplasmic
How is LHON managed
Treatment is mainly supportive:
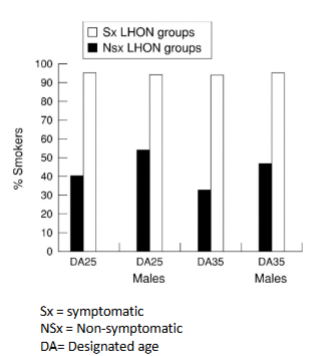
Avoid smoking! Smokers more likely to be symptomatic
Limit alcohol use
Avoid other environmental toxins
Diet
Proband
The affected individual through whom a family with a genetic disorder is first brought to medical attention.
Does LHON have gender- and age-dependent penetrance
Yes - 95th centile for age of onset = 50 years
Will the father of a LHON proband show any link to the condition
No. A male (affected or unaffected) with a primary LHON-causing mtDNA mutation cannot transmit the mutation to any of his offspring.
Will the mother of a LHON proband show any link to the condition
Mother of a proband usually has the mtDNA mutation and may or may not have symptoms.
A female (affected or unaffected) with a primary LHON-causing mtDNA mutation transmits the mutation to all of her offspring but to varying degrees (heteroplasmy)
Up to 40% of LHON cases are simplex. What does this mean
It occurs in a single individual in a family
Can you get a prenatal diagnosis for LHON
Not really.
The mtDNA mutational load in amniocytes and chorionic villi is unlikely to correspond to that of other fetal or adult tissues
The presence of the mtDNA mutation does not reliably predict the occurrence, age of onset, severity, or rate of disease progression
Approximately __% of males & approximately _% of females who harbor a primary LHON-causing mtDNA mutation become affected
Approximately 50% of males & approximately 10% of females who harbor a primary LHON-causing mtDNA mutation become affected
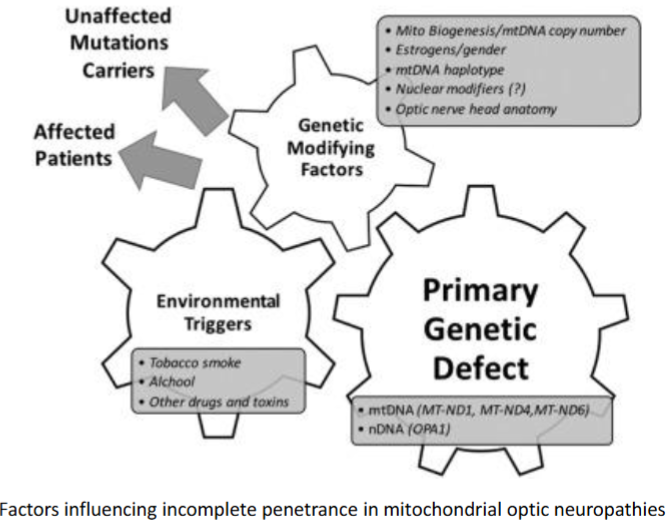
What factors play into carriers being affected or not
A compensatory mechanism of activated mitochondrial biogenesis and increased mtDNA copy number may explain why some carriers are unaffected
This is promoted by estrogens in females, which may partially explain the gender bias
Haplogroup
Describes individual branches – or closely related groups of branches – on the genetic family tree of all humans.
All members of a haplogroup can trace their ancestry back to a single individual.
Haplogroups arose through mutation and migration
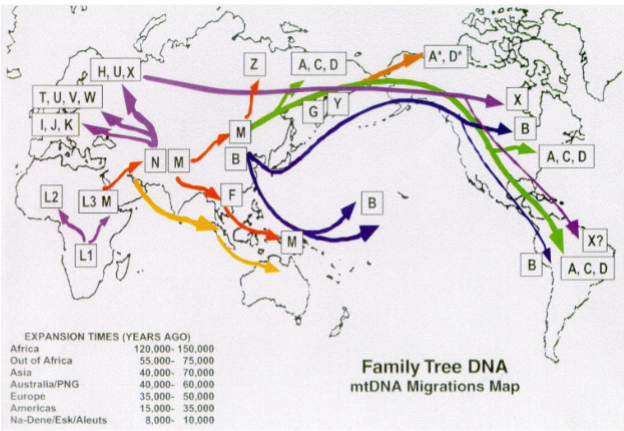
How do we trace haplogroups
mtDNA sequence polymorphism variations that have occurred over more than 150 000 years and correlate with the geographic origins of populations traced through the maternal lineages.
There is no meiosis - no crossing over → linear inheritance (matrilineal).
By aligning mtDNA sequences we can identify groups of individuals that appear to have a more/less recent common ancestor
MRCA
More recent common ancestor
MRCAs are marked with a what and subclades within haplogroups are marked with a what
MRCAs market with a letter
Subclades marked with a number
Most mtDNA codes for what
Significance?
Proteins
As most mtDNA codes for proteins, mitochondrial polymorphisms can influence energy metabolism and contribute to the expression of the overall clinical phenotype
A meta-analysis of 159 European LHON pedigrees indicated a:
Greater risk when what mutations arose on haplogroup J background
Greater risk when what mutation arose on haplogroup K background
Lower risk when what mutation arose on haplogroup H
Greater risk when the m.11778G>A and m.14484T>C mutations arose on haplogroup J background
Greater risk when the m.3460G>A mutation arose on haplogroup K background
Lower risk when the m.11778G>A mutation arose on haplogroup H
What race LHON pedigrees show no association between mtDNA haplogroups and the risk of visual loss
Southeast Asian
Parkinson Disease has been found to be higher among mtDNA haplogroup _, but lower for haplogroups _ and _
Parkinson Disease has been found to be higher among mtDNA haplogroup H, but lower for haplogroups J and K
Haplogroup _ associated with protection from sepsis
H
Haplogroups _, _ & _ are associated with increased longevity
I, J and T also associated with increased longevity
We can follow the maternal line through haplogroups. Is there a way of following the paternal line
Yes – the Y Chromosome (except for the pseudoautosomal region)
Y – Chromosomal Adam
Is paternal mtDNA ever passed to offspring
Only in very exceptional cases
What is Leigh Syndrome
A progressive neurometabolic disorder first described in 1951
Leigh Syndrome mortality %
Mortality 50% per year from diagnosis
Leigh Syndrome is caused by what
Mitochondrial dysfunction caused by a hereditary genetic defect
How is Leigh syndrome characterised
Characterized by MRI necrotizing lesions in the midbrain and brainstem
Bilateral symmetrical degeneration of the brain stem, cerebellum and basal ganglia
Typical onset in infancy or childhood, often after a viral infection (metabolic challenge), but may begin later
Estimated incidence of Leigh syndrome
at least 1 in 40,000 births
What is Leigh-like syndrome
Criteria for LS only partially met despite overall clinical picture indicative of LS
What is different with Leigh-like Syndrome compared to Leigh Syndrome
Often peripheral nervous system involvement, including polyneuropathy or myopathy
Often non neurologic abnormalities – dysmorphic features, cardiac, endocrine and GI
Respiratory impairment due to brainstem involvement usually absent
Mutations in how many genes have been identified with Leigh Syndrome
at least 75 genes
It is the mitochondrial disorder with broadest genetic (and clinical) heterogeneity
What mutations cause the Respiratory chain enzyme defects of complexes I, II, IV, and V associated with Leigh syndrome
The NARP mutation (mtDNA)
The MERRF mutation (mt DNA)
What in the citric acid cycle is affected by Leigh syndrome
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDHC) deficiency (citric acid cycle)
There are 4 different ways of inheriting Leigh syndrome - name them
• Matrilineal (mitochondrial) ~20%
• De novo mutation
• X-linked recessive
• Autosomal recessive
True/False Most inherited disorders of mitochondria are related to changes in nuclear DNA rather than mtDNA
True - most mitochondrial proteins are encoded on nuclear genome, synthesised in cytoplasm & transported to mitochondria.
These mutations are inherited according to the classic Mendelian rules, not mitochondrial (matrilineal) inheritance
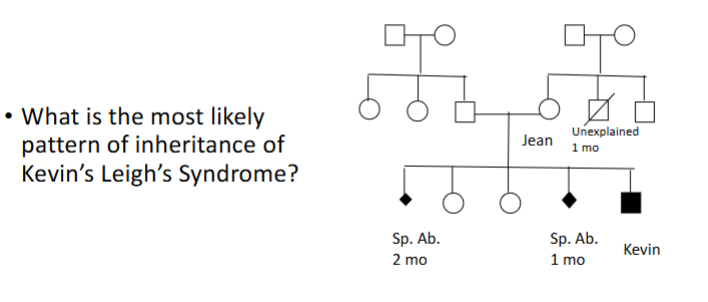
Autosomal recessive
X linked recessive
Matrilineal (mitochondrial)
De novo mutation in Kevin
X linked dominant
X linked recessive
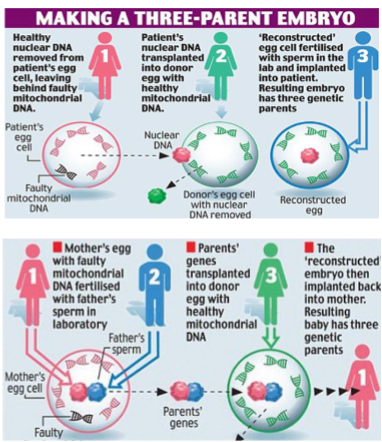
Is there a way to prevent passing on your hereditary mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial transplantation/donation
Can be done before or after fertilisation
3-parent embryo
Why is predicting phenotype from mtDNA genotype particularly difficult
heteroplasmy
If the mutation is on the nuclear genome, for e.g. 80% of Leigh Syndrome, then the inheritance pattern of the mitochondrial disease will usually be ________
Mendelian