1.2 Types of organizations
Introduction
Public sector comprises organizations accountable to and controlled by central or local government (the state).
Private sector comprises businesses owned and controlled by individuals or groups of individuals.
Private sector and public sector organizations
Mixed economy: economic resources are owned and controlled by both private and public sectors.
Free-market economy: economic resources are owned largely by the private sector with very little state intervention.
Command economy: economic resources are owned, planned and controlled by the state.
Distinctions between the sectors
Public sector organizations provide essential goods and services for individual citizens and organizations.
Private sector organizations are owned and operated by individuals or groups of people. These organizations are usually operated for a profit, but not all are.
- For example, charities are non-profit-making organizations in the private sector; they are not owned and controlled by the government or state.
Privatization: sale of public sector organizations to the private sector.
Public sector enterprises
- Public corporation: business enterprise owned and controlled by the state also known as nationalized industry or public sector enterprise.
For-profit organizations
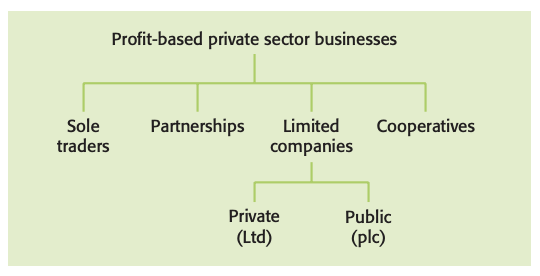
Sole trader: business in which one person provides the permanent finance and, in return, has full control of the business and is able to keep all of the profits.
Partnership: business formed by two or more people to carry on a business together, with shared capital investment and, usually, shared responsibilities.
Limited company
- Limited liability: the only liability or potential loss a shareholder has if the company fails is the amount invested in the company, not the total wealth of the shareholder.
- Share: certificate confirming part ownership of a company and entitling the shareholder to dividends and certain shareholder rights.
- Shareholders: individuals or institutions that buy/own shares in a limited company.
- Private limited company (Ltd): small to medium-sized business that is owned by shareholders who are often members of the same family; this company cannot sell shares to the general public.
- Public limited company (pic): limited company, often a large business, with the legal right to sell shares to the general public; its share price is quoted on the national stock exchange.
For-profit social enterprises
Social enterprise: business with mainly social objectives that reinvests most of its profits into benefiting society rather than maximizing returns to owners.
- Triple bottom line:
- Economic - to make a profit or surplus to reinvest back into the business and provide some return to the owners.
- Social - to provide jobs or support for local, often disadvantaged, communities.
- Environmental - to protect the environment and to manage the business in an environmentally sustainable way.
Cooperative: group of people acting together to meet the common needs and aspirations of its members, sharing ownership and making decisions democratically.
Microfinance: provision of very small loans by specialist finance businesses, usually not traditional commercial banks.
Public-private partnership (PPP)
Public-private partnership (PPP): involvement of the private sector, in the form of management expertise and/or financial investment, in public sector projects aimed at benefiting the public.
- Types:
- Government-funded
- Private sector-funded
- Government-directed but with private sector finance and management
Private finance initiative (PFI): investment by private sector organizations in public sector projects.
Non-profit social enterprises
Non-profit organization: any organization that has aims other than making and distributing profit and which is usually governed by a voluntary board.
Non-governmental organization (NGO): legally constituted body with no participation or representation of any government which has a specific aim and purpose, e.g. supporting disadvantaged groups in developing countries or advocating the protection of human rights.
Charities: organization set up to raise money to help people in need or to support causes that require funding.