Anatomy and Physiology Semester A final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/320
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:20 PM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
321 Terms
1
New cards
tomy
to cut
2
New cards
ana
apart
3
New cards
two types of anatomy
gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy
4
New cards
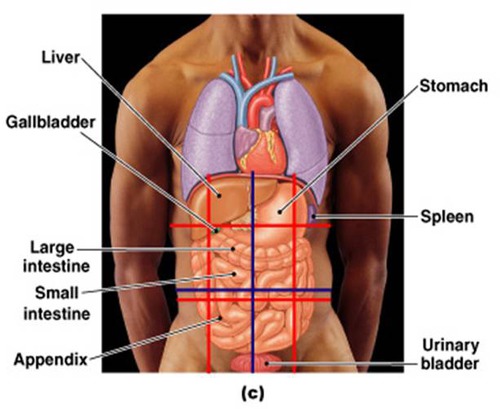
Gross Anatomy
large structures, easily observable
5
New cards
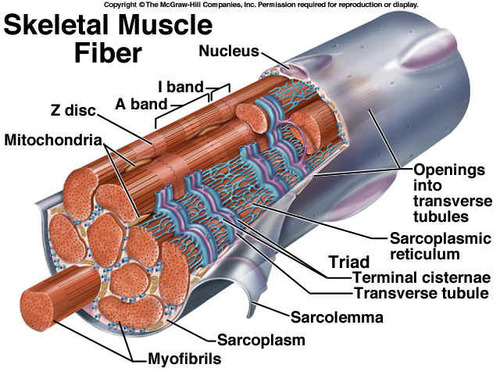
Microscopic Anatomy
structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
6
New cards
Physiology
the study of how the body and its parts work or function
7
New cards
Anatomists__________ structure
observe
8
New cards
physiologists....
experiment
9
New cards
6 levels of structural organization (in order from smallest to greatest)
atoms/chemicals, cells, tissues , organs, organ system, and organism
10
New cards
number of organ systems in the body
11
11
New cards
integumentary system
the external covering of the body, or the skin
12
New cards
integumentary system Functions
protection, water retention, thermoregulation, vitamin D synthesis, cutaneous sensation, nonverbal communication
13
New cards
skeletal system
bones, artilages, ligaments and joints
14
New cards
Function of skeletal system
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell production(hematopoiesis)
15
New cards
Muscular system function
Contract or shorten to move skeleton
Maintains posture
Produces heat
Maintains posture
Produces heat
16
New cards
Nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors
17
New cards
nervous system functions
Speedy control system that responds to external stimuli (Light
Sound
Temperature changes
Pain
Pressure) assesses information and responds by activating appropriate effector
Sound
Temperature changes
Pain
Pressure) assesses information and responds by activating appropriate effector
18
New cards
endocrine system
series of glands that slowly control body by producing and releasing hormones for growth, metabolism, and reproduction
19
New cards
glands of the endocrine system
Pituitary,
Thyroid,
Parathyroid,
Adrenal,
Thymus,
Pancreas,
Pineal ,
Ovaries (females),
Testes (males)
Thyroid,
Parathyroid,
Adrenal,
Thymus,
Pancreas,
Pineal ,
Ovaries (females),
Testes (males)
20
New cards
cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessels
21
New cards
Cardiovacular System Function
Work together to transport materials in blood
(Nutrients, Hormones, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, and Waste
(Nutrients, Hormones, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, and Waste
22
New cards
lymphatic system
Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, and tonsils
23
New cards
function of lymphatic system
Returns fluid leaked from blood back to blood vessels, and Lymph nodes (and others) help cleanse blood and store cells involved in immunity
24
New cards
respiratory system
Lungs, nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi
25
New cards
function of respiratory system
supplies the body with oxygen and disposes of carbon dioxide
26
New cards
digestive system
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, and rectum
27
New cards
function of digestive system
break down and absorbs nutrients from food; removes waste; maintains water balance
28
New cards
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
29
New cards
function of urinary system
elimination of excess water, salts, and waste products; control of pH
30
New cards
Reproductive system
Male: testes, penis, accessory glands, and ducts
Females: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
Females: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
31
New cards
Fuction of Reproductive System
to produce offspring
32
New cards
healthy body must
maintain boundaries, move, respond, digest, excretion, reproduce, and grow
33
New cards
human body must have these five items to maintain the ight functions for living
nutrients, O2, water, core body temp, and standard atmospheric pressure
34
New cards
anatomical position
body standing erect, feet parallel, arms hanging at sides, and palms facing forward
35
New cards
Anterior
front of the body
36
New cards
Posterior
back
37
New cards
superior
toward the head
38
New cards
inferior
away from head; below
39
New cards
Medial
toward or at midline
40
New cards
lateral
away from midline
41
New cards
intermediate
between a more medial and more lateral structure
42
New cards
proximal
close to origin of body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
43
New cards
distal
farther from origin of a body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
44
New cards
Superficial (external)
toward or at body surface
45
New cards
deep (internal)
away from body surface
46
New cards
Supine
lying face up
47
New cards
Prone
lying face down
48
New cards
midsagittal plane
left and right
49
New cards
frontal
anterior & posterior
50
New cards
transverse
top & bottom
51
New cards
Oblique
diagonal
52
New cards
body cavities
Dorsal side (posterior)
Ventral side (anterior)
Ventral side (anterior)
53
New cards
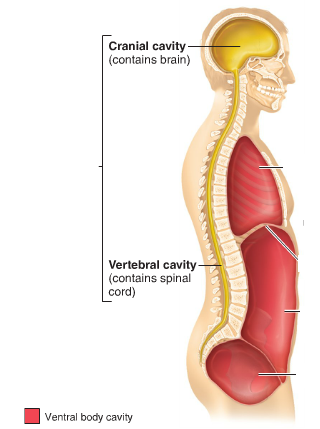
dorsal cavity
54
New cards
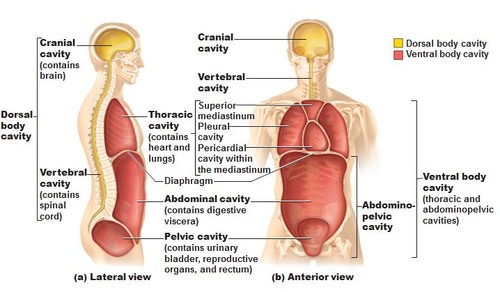
ventral cavity
55
New cards
What are the nine regions of the abdomen?
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right inguinal, hypogastric, left inguinal
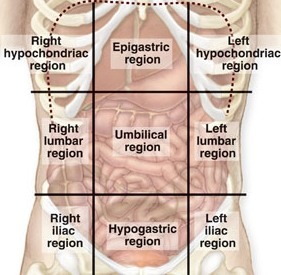
56
New cards
homeostatsis
a state of physiological equilibrium or stability
57
New cards
Homeostatic imbalance is the ...what does this cause?
body is not functioning smoothly.. results in disease, distress, or even death
58
New cards
Chain reaction set of by homeostatic imbalance to restore equilibrium
Stimulus
(Produces change in variable)
Detection
(Change detected by receptor)
Input
(Information sent from receptor to control center)
Output
(Control center decides what action/response should be taken)
Response
(Action/response feeds back to influence magnitude of stimulus and returns variable to homeostasis)
(Produces change in variable)
Detection
(Change detected by receptor)
Input
(Information sent from receptor to control center)
Output
(Control center decides what action/response should be taken)
Response
(Action/response feeds back to influence magnitude of stimulus and returns variable to homeostasis)
59
New cards
Components of a Homeostatic Control Mechanism
receptor(afferent pathway), control center, effector
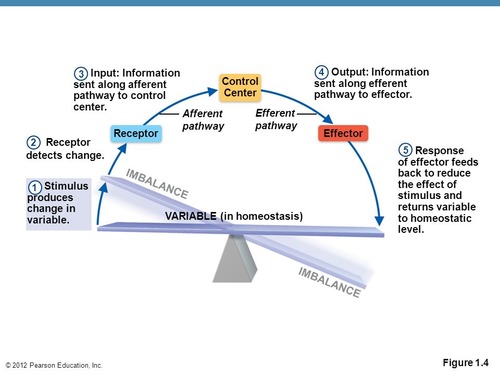
60
New cards
negative feedback
stimulus not welcomed; back to normal
61
New cards
positive feedback
stimulus desired; wants more; keep new change
62
New cards
almost all control mechanisms are ...
negative
63
New cards
Hypothalamus
located in brain, regulates body temperature
64
New cards
4 control mechanisms that are positive feedback
blood clotting, childbirth, breastfeeding, and protein digestion
65
New cards
What make sit more difficult to keep homeostasis?
aging
66
New cards
Characteristics of blood
fluid tissue(8% body weight), connective tissue made of formed elements (living and non-living plasma, Sticky, metallic (due to Fe), salty, opaque fluid, pH 7.35-7.45, 38°
67
New cards
bright red blood
- rich in oxygen and hemoglobin
68
New cards
dark red blood
oxygen poor
69
New cards
breakdown of blood
Plasma (55%) Hematocrit(45%), and Buffy coat (
70
New cards
Plasma
Liquid part of blood (90% water, salts(electrolytes), proteins, nutrients, wastes, gases, hormones)
71
New cards
Acidosis
too acidic
72
New cards
Alkalosis
too basic
73
New cards
regulates ph of blood
respiratory system and excretory system
74
New cards
red blood cells
erythrocytes
75
New cards
Neutrophils(WBC)
Granulocyte , Multi-lobed nucleus (usually 3), 40-70% of WBC (3,000-7,000/mm3), Active phagocytes - foreign invader EATERS, and in short-term infection, numbers increase rapidly to fight off invaders
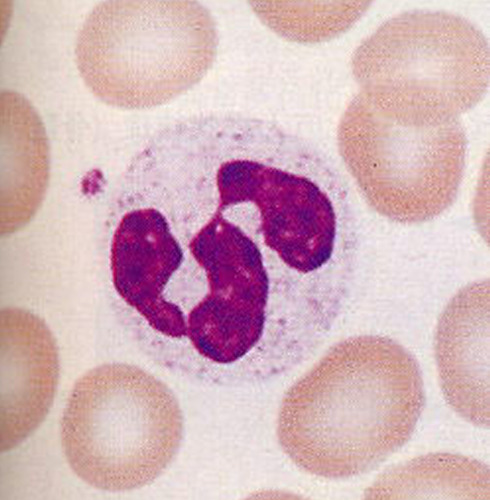
76
New cards
Immature RBCs are called
reticulocytes
77
New cards
Characteristics of RBCs
most abundant, no nucleus, few organelles, hemoglobin caries 4 O2,(men have more than women)
78
New cards
White blood cells
leukocytes
79
New cards
Characteristics of WBCs
complete cells, diapedesis(Able to slip in & out of blood vessels to tissues & back), and chemotaxis(Locate tissue damage through chemical signals & move via ameboid motion)
80
New cards
Leukocytosis
>11,000 (sign of infection)
81
New cards
leukopenia (Rx drugs, anticancer agents)
82
New cards
Granulocytes
("the phils")
Contain granules
Contain granules
83
New cards
Agranulocytes
("the cytes")
No granules
No granules
84
New cards
Eosinophils
Granulocyte
Bi-lobed nucleus
1 - 4% of WBC (100 - 400/mm3)
Kills parasitic worms (tapeworms, flatworms, pinworms)
Increase in number during allergy attacks
May phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes thereby inactivating inflammatory chemicals
Bi-lobed nucleus
1 - 4% of WBC (100 - 400/mm3)
Kills parasitic worms (tapeworms, flatworms, pinworms)
Increase in number during allergy attacks
May phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes thereby inactivating inflammatory chemicals
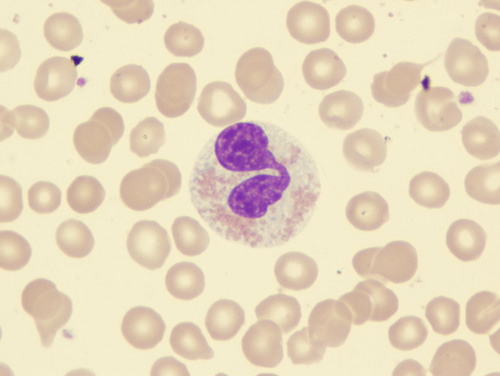
85
New cards
Basophils
Granulocyte, U or S shaped, 0-1% of WBCS, contain chemical histamine(initiates inflammatory response),makes blood vessel dilate and attracts other WBCS
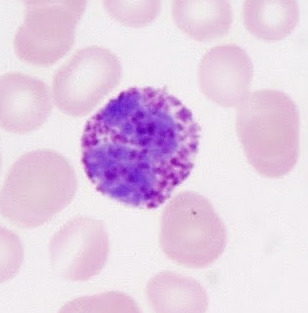
86
New cards
Lymphocytes
agranulocyte, large round nucleus, 20 - 45% of WBCs (1,500 - 3,000/mm3), aggregate around lymphatic tissues(lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen)
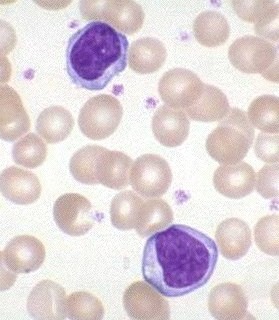
87
New cards
3 types of lymphocytes
B(Bone) cells produce antibodies, T (Thymus) cells activates more B cells, and NK(Natural KIller) cells recognize abnormal cells (tumors and virus-infected) to kill
88
New cards
Monocyte
Agranulocyte, 4 - 8% of WBCs (100 - 700/mm3), largest, irregular shaped cell fragments, activated by macrophages (large phagocytes) for long-term infections (tuberculosis)
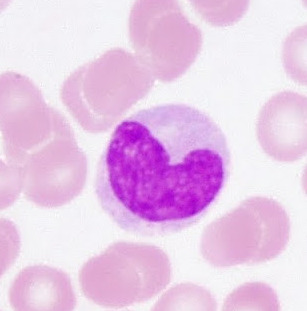
89
New cards
Platelets
thrombocytes, fragments of megakaryocytes, 250,000 - 500,000/mm3, necessary for normal blood clotting
90
New cards
Hemostasis
process of stopping blood flow, 3 major phases:
1. platelet plug formation
2. vascular spasms
3. coagulation (blood clotting), takes 3 - 6 min
1. platelet plug formation
2. vascular spasms
3. coagulation (blood clotting), takes 3 - 6 min
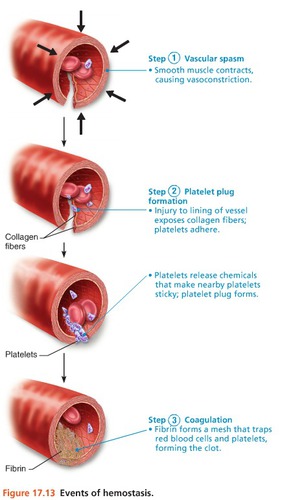
91
New cards
1. platelet plug formation
underlying collagen fibers are exposed - platelets stick to them , release chemical signals to attract more platelets (positive feedback),
called a platelet plug/white thrombus
called a platelet plug/white thrombus
92
New cards
2. vascular spasms
anchored platelets release serotonin, cause blood vessel to spasm , at injury, decreases blood loss until complete clotting can occur
93
New cards
3. coagulation
injured tissues releasing Tissue factor interacts with PH3, Vitamin K, Ca, etc.,
Prothrombin activator converts prothrombin to thrombin, joining fibrinogen into fibrin, after 1 hour clot retracts squeezing serum to pull riptures edes of clod vessel, clot breaks down
Prothrombin activator converts prothrombin to thrombin, joining fibrinogen into fibrin, after 1 hour clot retracts squeezing serum to pull riptures edes of clod vessel, clot breaks down
94
New cards
Hematopoiesis
occurs in red blood marrow
starts with cell (hemocytoblast)
two pathways : lymphoid(lymphocytes) and myeloid
starts with cell (hemocytoblast)
two pathways : lymphoid(lymphocytes) and myeloid
95
New cards
Sites of hematopoiesis for adults
skull, pelvis,ribs, sternum, end of epiphyses of femur and humerus
96
New cards
life span of RBCs
100-120 days after they become rigid and fragment, eliminated by phagocytes in spleen, liver, and other tissues
97
New cards
hormone controlling rate of erythrocyte production
erythropoietin
98
New cards
Erythropoeitin is a hormone produced by the kidneys in response to low levels of:
O2
99
New cards
Rate of platelet production controlled by hormone
thrombopoietin
100
New cards
leukocyte & platelet formation controlled by multiple hormones -
colony stimulating factors (CSFs) and interleukins
Enhances ability of mature leukocytes to perform
Enhances ability of mature leukocytes to perform