PPCP FINAL
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the five steps in the practice of Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM)?
1. Convert information needs into answerable questions.
2. Track down the best evidence.
3. Critically appraise the evidence for validity and usefulness.
4. Implement the results in clinical practice.
5. Evaluate performance
What are primary sources of biomedical information?
Original research studies and clinical trials conducted by the authors themselves
What are secondary sources of biomedical information?
Searchable databases like PubMed or Cochrane Library that provide access to primary and tertiary resources
What are tertiary sources of biomedical information?
Summarized information, such as textbooks, clinical guidelines, and review articles
What does PICO stand for in formulating a clinical question?
P: Patient or Problem
I: Intervention
C: Comparison
O: Outcome
(Good fill in the blank Q option)
How would you use the PICO framework to address a patient case?
Clearly define each element of PICO based on the clinical scenario to create an answerable question
What factors should be considered when critically appraising clinical evidence?
Validity: Is the study well-designed and free of bias?
Relevance: Does the evidence address the clinical question?
Applicability: Can the results be applied to the specific patient population?
What are common barriers to implementing EBM?
- Decision-making based on anecdote or tradition.
- Chasing trends without sufficient evidence.
- Limited resources or training.
What strategies can overcome these barriers?
- Encourage continuous education in EBM.
- Develop institutional support for evidence-based practices.
- Provide access to reliable databases and resources.
How can clinicians assess the effectiveness of applying EBM in practice?
- Review patient outcomes to ensure evidence-based decisions improved care.
- Identify areas where EBM application could be enhanced.
- Adjust practices based on reflections and updated evidence
What is the role of documentation in the Pharmacists' Patient Care Process (PPCP)?
Documentation ensures that critical steps like collect, assess, plan, implement, and follow-up are clearly recorded. It facilitates collaboration, communication, and optimization of medication use and healthcare quality
Why is documentation important in patient care activities?
It is important because it:
1. Meets professional and legal standards.
2. Establishes accountability.
3. Facilitates communication among healthcare providers.
4. Ensures continuity of care.
5. Provides evidence of clinical decision-making.
6. Justifies billing for cognitive services.
7. Tracks patient outcomes and healthcare progress.
What are common documentation formats used by pharmacists?
SOAP Notes: Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan.
FARM Notes: Findings, Assessment, Recommendations, Monitoring.
MTM/CMM Documentation: For medication therapy management.
Letters to Providers: Formal communication.
Patient Records and Medication Lists: Organized records of patient data
How does each step of the PPCP fit into SOAP notes?
Collect: Recorded in the Subjective and Objective sections.
Assess: Written in the Assessment section.
Plan, Implement, Follow-up: Documented in the Plan section
What are key "do's and don't's" in documentation?
Do’s:
Be clear, concise, and objective.
Use professional grammar and spelling.
Include pertinent information for understanding Assessment and Plan.
Don’t’s:
Avoid accusatory or judgmental language.
Do not include irrelevant details or omit critical information.
Avoid unapproved abbreviations or excessive jargon.
What are the main sections in the PPCP Documentation Template?
Subjective: Patient-reported information, including chief complaint, medical history, and social history.
Objective: Measurable or observed data, such as vital signs, lab results, and imaging studies.
Assessment: Identification and prioritization of Medication Therapy Problems (MTPs).
Plan: Detailed actions for addressing identified MTPs, including follow-up steps.
What is the purpose of the "Assess" component in the PPCP?
The "Assess" component identifies and prioritizes health and medication-related problems. It evaluates the appropriateness, effectiveness, safety, and adherence of the patient's therapy to achieve health goals
What does the "Assess" component involve?
It involves assessing:
- Health conditions and medication therapy problems.
- Risk factors, health status, literacy, and access to care.
- Immunization and preventive care needs.
How are disease or health problems assessed and prioritized?
- Assess active medical conditions (e.g., severity, control, goals).
- Evaluate medications for indication, effectiveness, safety, and adherence.
- Create and prioritize a Medication Therapy Problem (MTP) list based on clinical and patient goals.
What factors influence the prioritization of problems?
Clinical goals.
Patient goals.
Acuity and control levels.
Timeframe to achieve goals.
How should a Medication Therapy Problem (MTP) list be organized?
1. By health condition: Include MTPs under corresponding conditions (e.g., GERD with adherence issues listed under GERD).
2. By problem type: Categorize MTPs into indication, effectiveness, safety, and adherence
What is an example of an MTP?
- GERD: Uncontrolled symptoms due to untreated condition (Indication - needs additional therapy).
- Type 2 DM: Uncontrolled with A1C of 7.8%, requiring additional medication (Effectiveness - therapy enhancement).
Why are clinical calculations important in the PPCP?
Clinical calculations assist in evaluating patient data for accurate drug dosing, renal function assessment, and determining body metrics like BMI and BSA.
What are examples of clinical calculations in PPCP assessment?
BMI for weight classification, Cockcroft-Gault for renal function, and IBW for drug dosing.
What are common clinical calculations?
- BMI (Body Mass Index): Assess weight status.
- CrCl (Creatinine Clearance): Evaluate renal function for drug dosing.
- IBW (Ideal Body Weight): Determine doses for hydrophilic medications.
- AdjBW (Adjusted Body Weight): Used in obese patients.
- BSA (Body Surface Area): Used for chemotherapy and pediatric dosing.
How is BMI calculated?
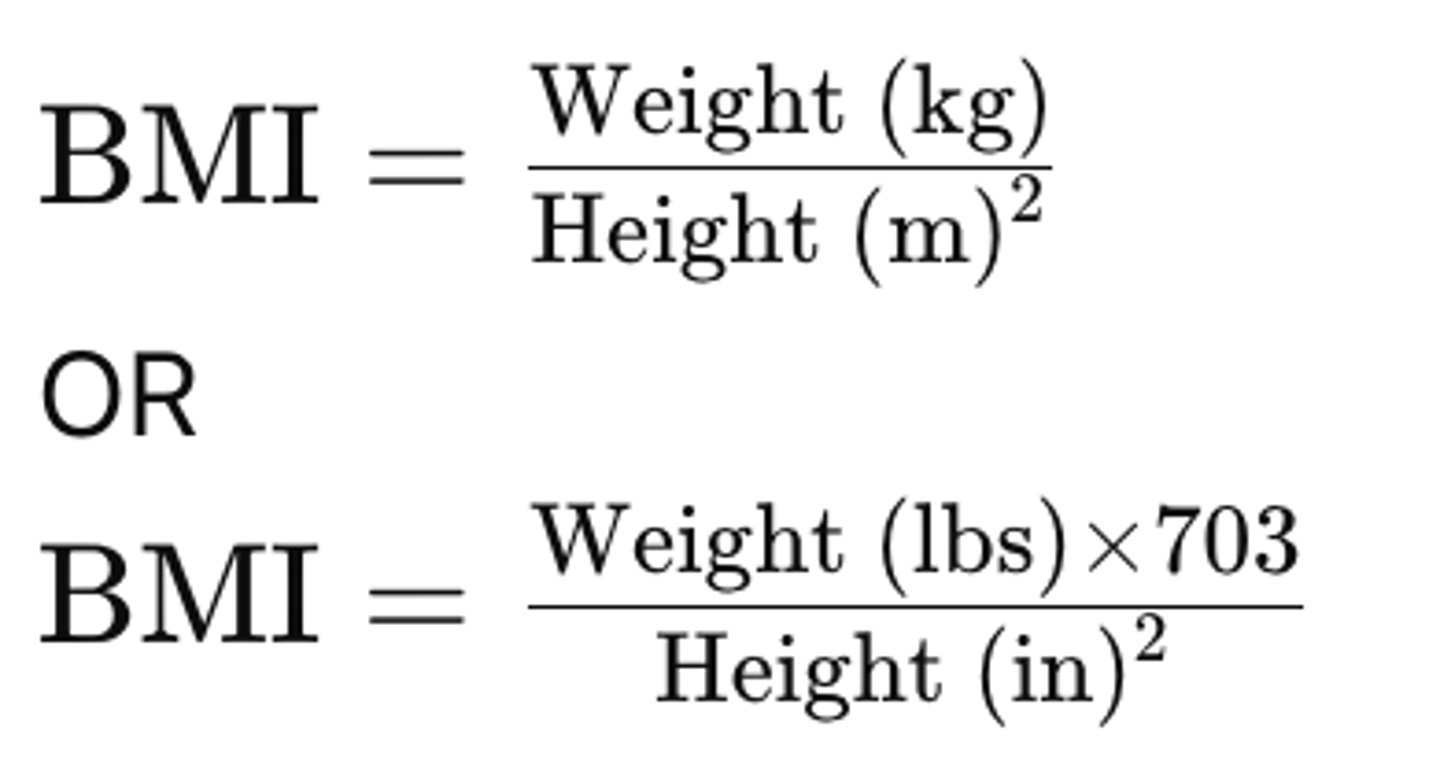
How is Creatinine Clearance (CrCl) calculated using Cockcroft-Gault?
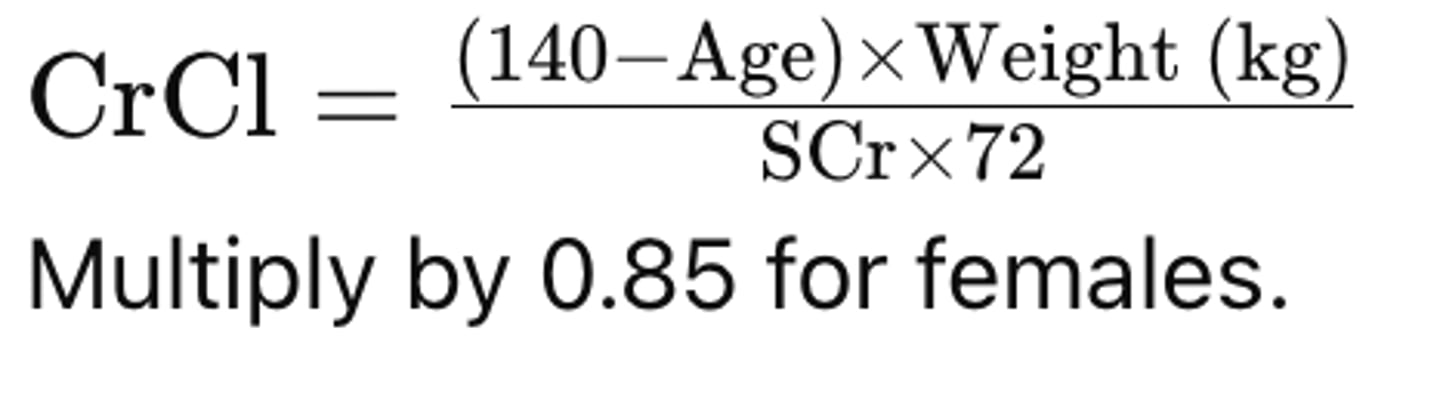
What is the formula for Ideal Body Weight (IBW)?
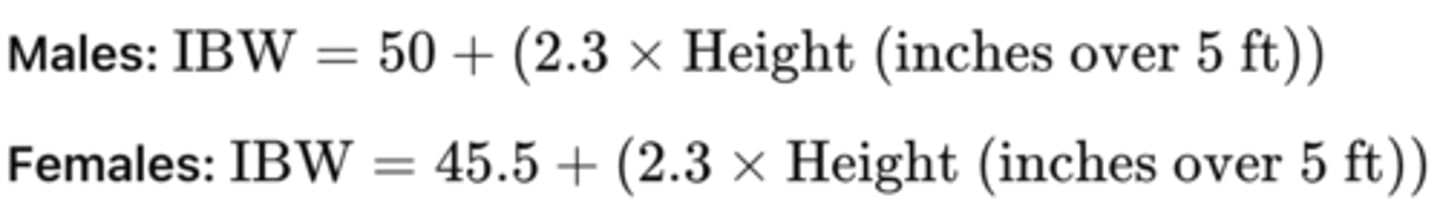
Adjusted Body Weight (AdjBW) formula?

What is the purpose of the Assess step in PPCP?
To identify and prioritize medication and health-related problems by evaluating collected information and clinical goals, optimizing patient therapy
What does the Assess step involve?
- Assessing active health conditions.
- Evaluating medications for indication, effectiveness, safety, and adherence (IESA).
- Creating and prioritizing a Medication Therapy Problem (MTP) list.