Biology - B1 You and your genes
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Last updated 12:43 PM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Prokaryotic
Small simple cells including bacteria
2
New cards
Eukaryotic
Complex cells including animal and plant cells
3
New cards
Nucleus
A subcellular structure which contains DNA arranged into chromosomes
4
New cards
Cytoplasm
A gel-like substance within cells where all the reactions happen. Also contains enzymes.
5
New cards
Partially permeable cell membrane
Holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out.
6
New cards
Mitochondria
Contains enzymes needed to control aerobic respiration within the cell
7
New cards
Ribosomes
A subcellular structure that is involved with protein synthesis
8
New cards
Cell wall
Supports the cell and is made of cellulose. Only found in plant cells
9
New cards
Vacuole
A subcellular structure that contains cell sap. Only found in plant cells.
10
New cards
Chloroplasts
A subcellular structure where photosynthesis occurs. Contain chlorophyll.
11
New cards
Plasmids
Subcellular structures that are small loops of extra DNA which typically carry traits such as drug resistance. Only in Prokaryotic cells.
12
New cards
Light microscope
These pass light through a specimen to magnify and identify the specimen’s features (usually subcellular structures).
13
New cards
Stage
Where the specimen is placed on a light microscope.
14
New cards
Objective lens
The part that magnifies the specimen on a light microscope.
15
New cards
Coarse adjustment knob
Moves the stage quickly to gain focus on a light microscope.
16
New cards
Fine adjustment knob
Slowly moves the stage to gain focus on a light microscope.
17
New cards
Genome
The entire genetic material of an organism
18
New cards
Chromosome
A long molecule of DNA coiled up. Usually in pairs. Humans have 23 pairs.
19
New cards
DNA
A polymer made up of nucleotides in a double helix.
20
New cards
Gene
A short length of DNA that codes for specific amino acids to make a specific protein.
21
New cards
Alleles
Genetic variants or different versions of a gene created when DNA mutates
22
New cards
Genotype
The combinations of alleles the organisms have
23
New cards
Phenotype
The characteristics that an organisms presents with. It’s effected by the genotype and the organism’s environment.
24
New cards
Nucleotide
The monomer that makes up DNA. Made up of a base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Only the base varies.
25
New cards
Base of nucleotides
There are four different ones: Adenine(A), Thymine(T), Cytosine(C) and Guanine(G)
26
New cards
Complementary base pairing
Adenine always pairs with Thymine and Cytosine always pairs with Guanine.
27
New cards
Amino Acids
Coded for by triplets (three nucleotide bases) to make specific proteins.
28
New cards
mRNA
Like DNA but single stranded and uses Uracil instead on Thymine. Responsible for protein synthesis.
29
New cards
Protein Synthesis
The DNA in the nucleus 'unzips' and mRNA is created as complementary to the DNA strand. The mRNA then moves out of the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome. The Ribosome then sequences the correct amino acids based on the mRNA and codes for the protein.
30
New cards
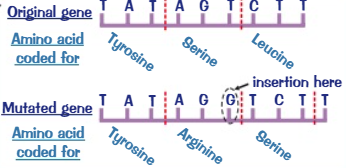
Insertion
A type of DNA mutation where a new base is inserted and changes the way that triplets are read
31
New cards
Deletion
A type of DNA where a base is removed from the sequence and changes the way triplets are read.
32
New cards
Substitution
A type of DNA mutation where a random base is changed to another. It doesn’t always effect the amino acids because they can be coded for by more than one triplet.
33
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
caused by the deletion of three bases, this disorder produces a protein that doesn’t control the movement of salt of water out of cells like it should causing excess mucus production.
34
New cards
Mutation
When a base sequence is changed in someway. It usually has no or little effect on coding DNA and the organisms phenotype. It can cause non-coding DNA to wrongly control the expression of a protein and therefore effect the phenotype.
35
New cards
Gametes
Reproductive cells which only have one copy of each gene. This means that when the male and female cell combine, the offspring has a pair of each gene (2 alleles).
36
New cards
Dominant Allele
A trait that is present in offspring even if heterozygous (i.e. Bb)
37
New cards
Recessive allele
A trait that is only present if homozygous (i.e. bb)
38
New cards
Homozygous
Two alleles that are the same like BB or bb
39
New cards
Heterozygous
Two alleles that are different like Bb
40
New cards
Punnet square
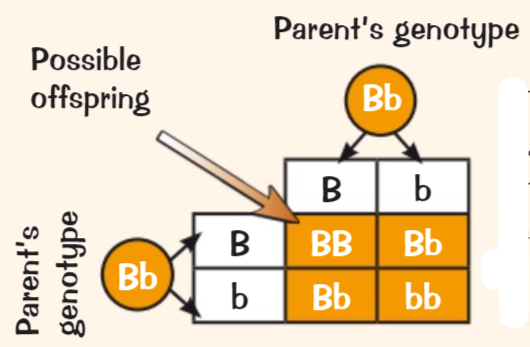
41
New cards
Sex chromosomes
Men have XY chromosomes and women have XX chromosomes
42
New cards
Family tree
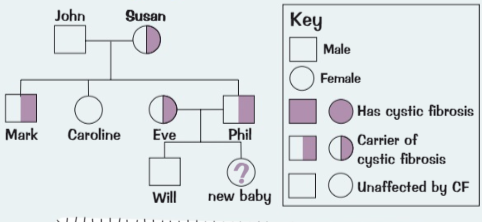
43
New cards
Mendel
An Austrian monk who studied the transfer of characteristics from a parent to it’s offspring in pea plants. The base of modern genetics
44
New cards
Genetic testing
This can find certain genetic variants in children so that treatment can start early or if a person were to have a variant that caused a treatment to have no effect this would allow the doctor to find an alternative early in the treatment process.
45
New cards
drawbacks to knowing genetic information
Employers may discriminate if they know that you’re more likely to get a disease. Unnecessary stress or health paranoia if you know that you’re susceptible to a disease.
46
New cards
Parent testing
This can allow doctors to find if a parent is even just a carrier of a disease to help with family planning
47
New cards
Embryo testing
Similar to IVF, eggs can be extracted and fertilized then tested and those without the disease can then be implanted.
48
New cards
Foetus testing
Testing some DNA from the Amniotic fluid can determine if the child has a genetic disease but this has a chance of miscarriage.
49
New cards
Cons of embryonic/foetus testing
It is not 100% perfect and it could cause accidental termination of a pregnancy.
50
New cards
Genetic engineering
The transfer of a desired gene from one genome to another genome.
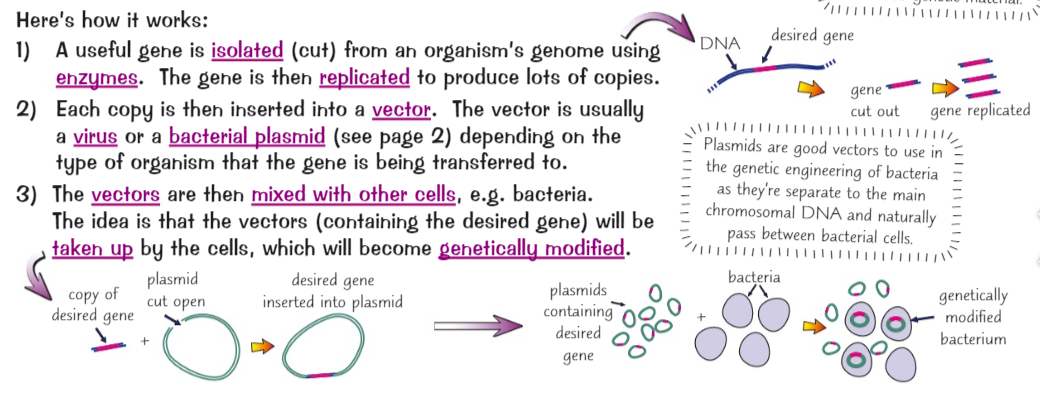
51
New cards
Genetic engineering in agriculture and medicine
Genetic engineering can be used in place of herbicides to create a weed resistant plant( runs the risk of creating a super weed in the process) or to make medicine such as insulin by adding useful genes toa cow or sheep then extracting the useful proteins through it’s risk (could cause the animal to become ill or diseased).