Axial Skeleton, Vertebrae, Ribs, Sternum, Hyoid Bone
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
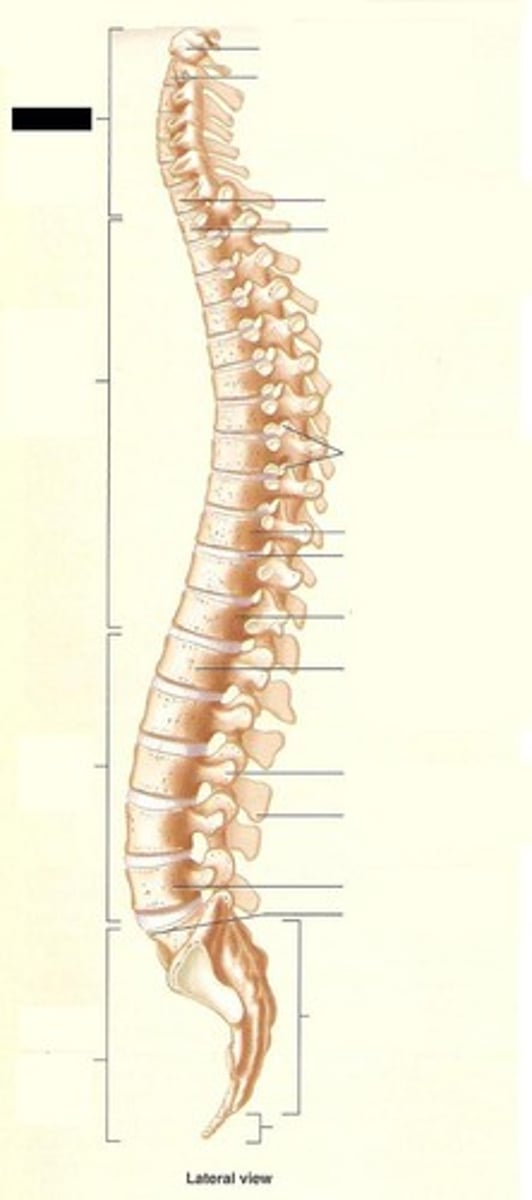
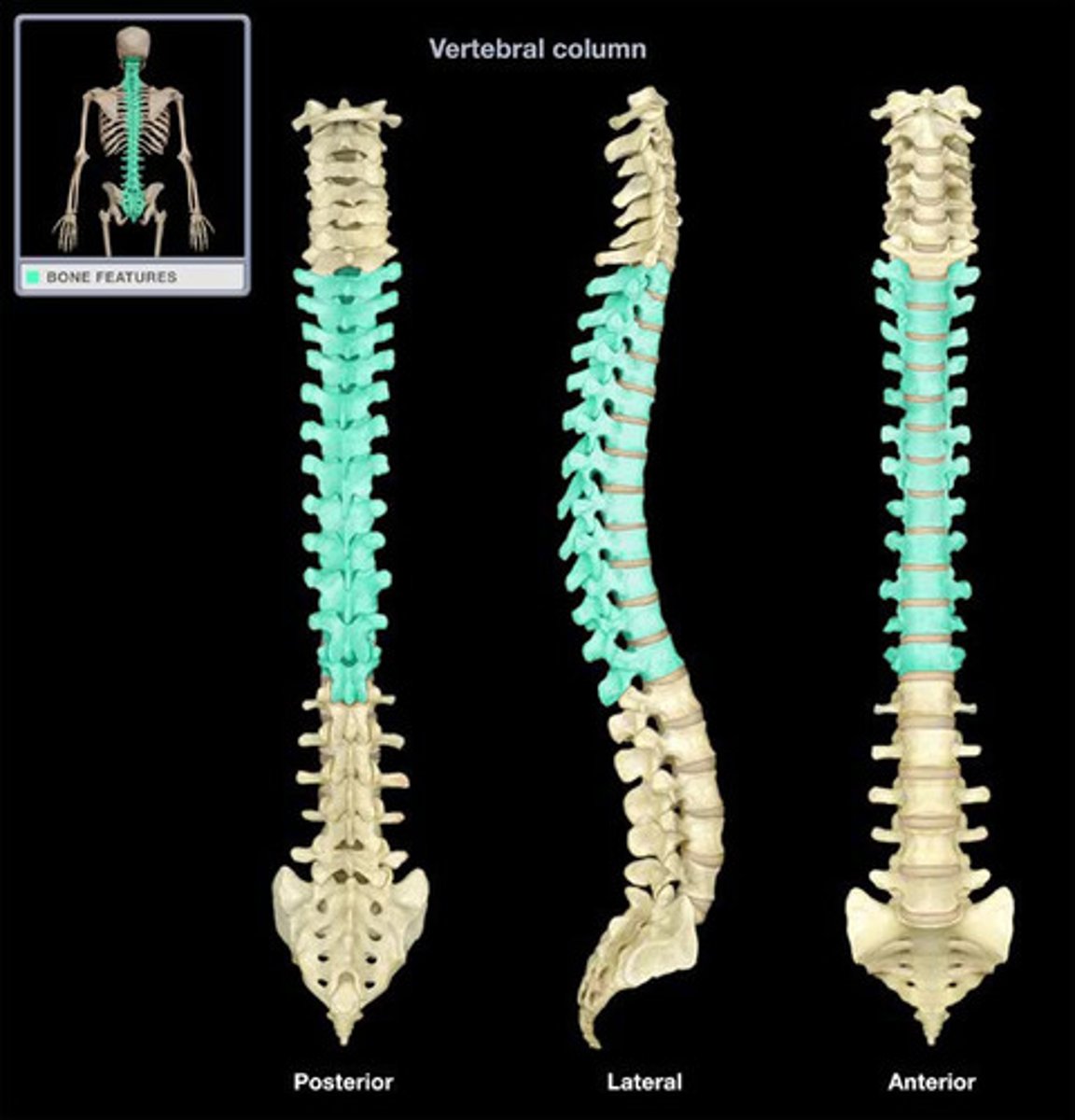
Vertebral column
the spine, formed of a number of individual bones called vertebrae and two composite bones (sacrum and coccyx)
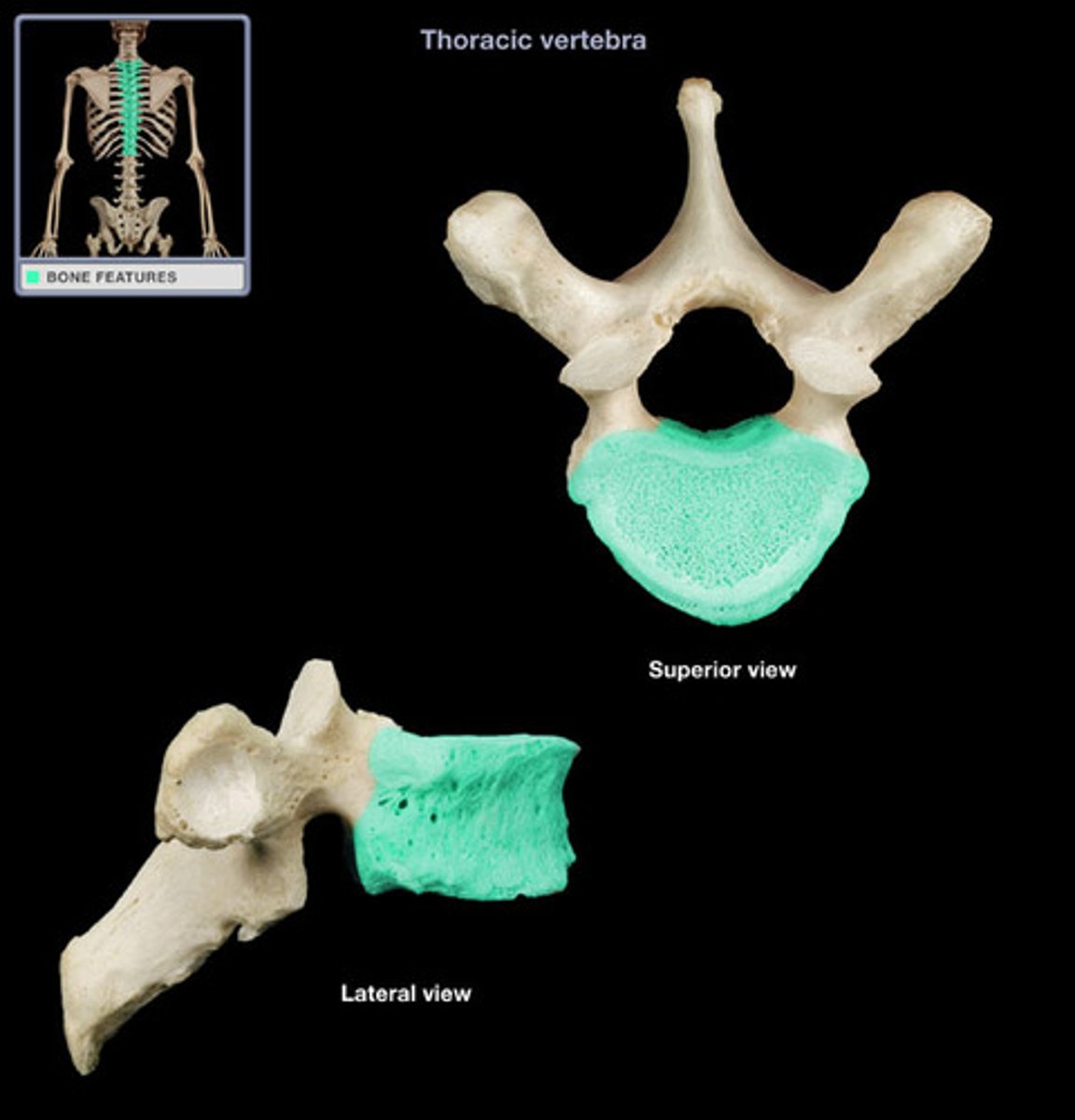
Body of Vertebra
big circular part, is weight bearing
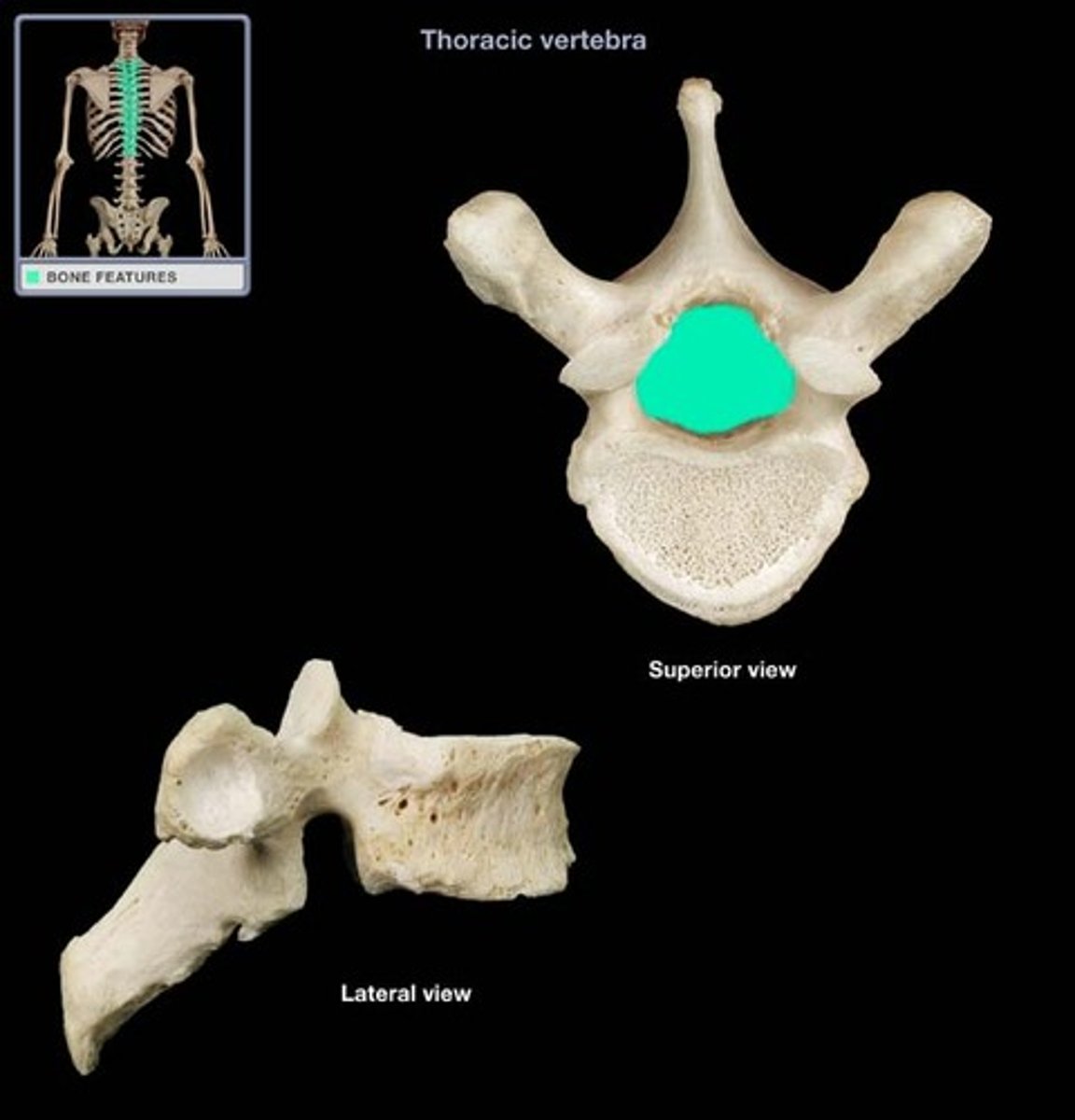
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
pedicle of vertebra
attached to and extends posteriorly on either side of the body
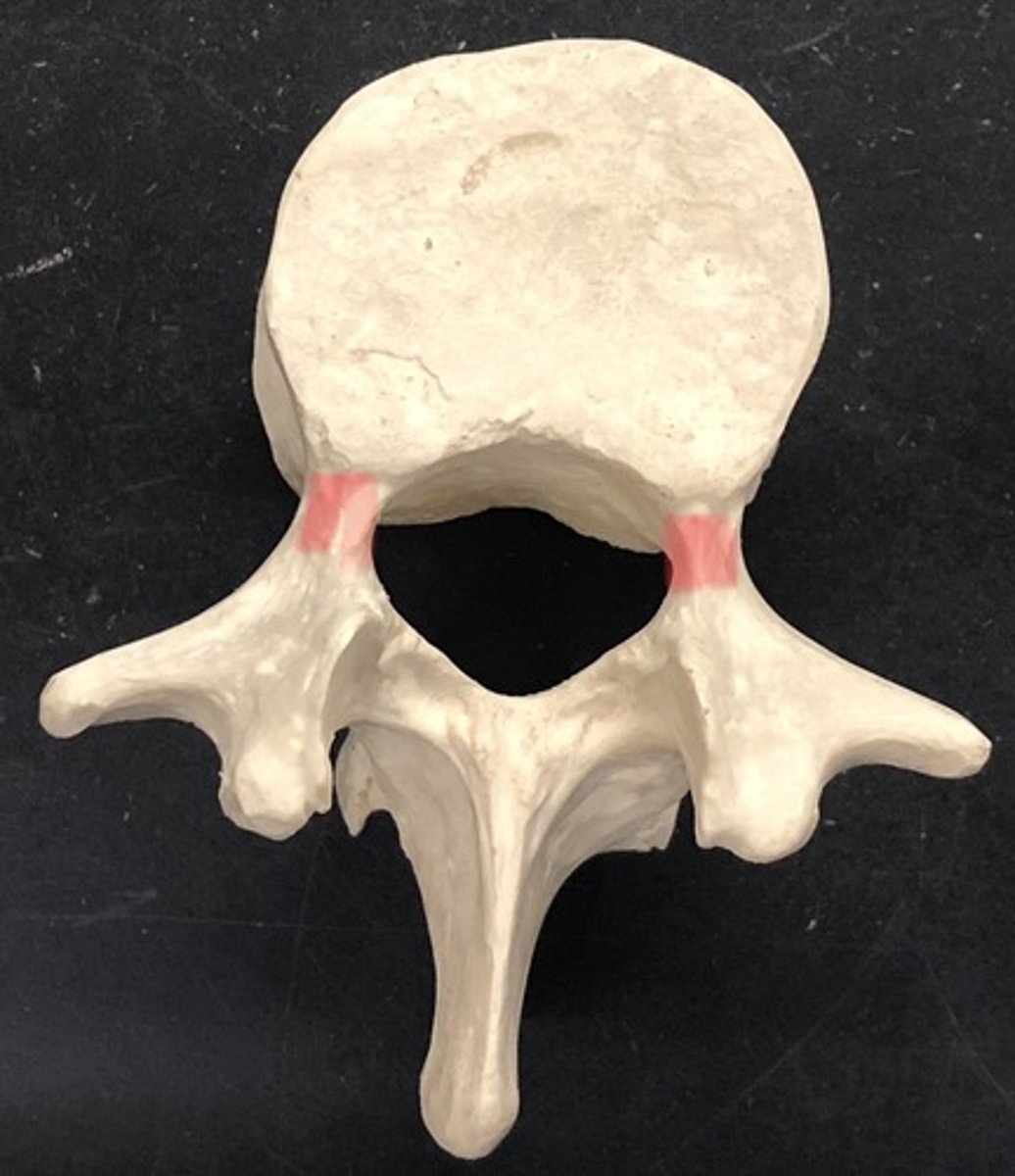
Lamina of vertebra
supporting bone between the spikes of the vertebra
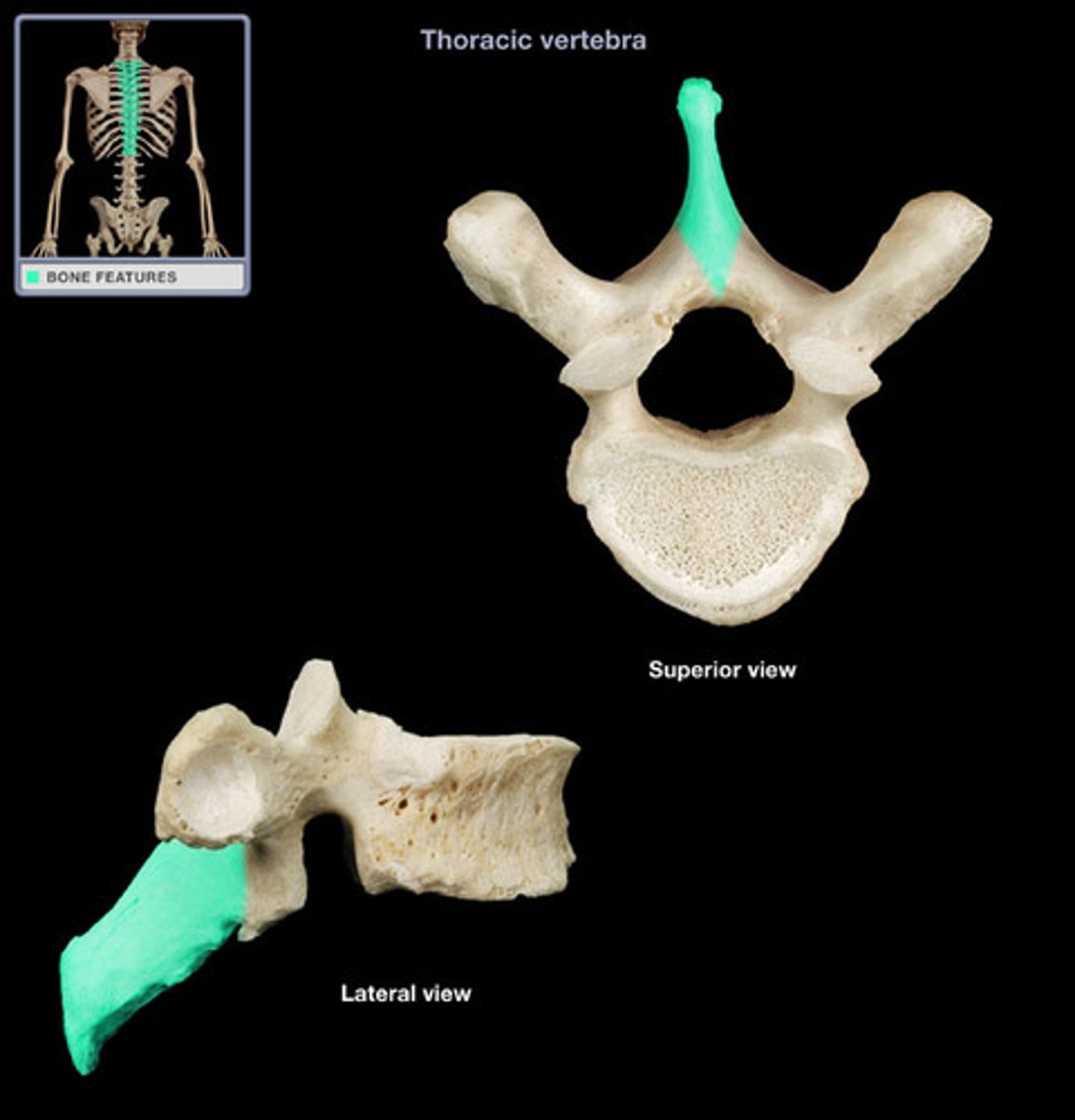
spinous process
Posterior projection of a vertebra...usually points down
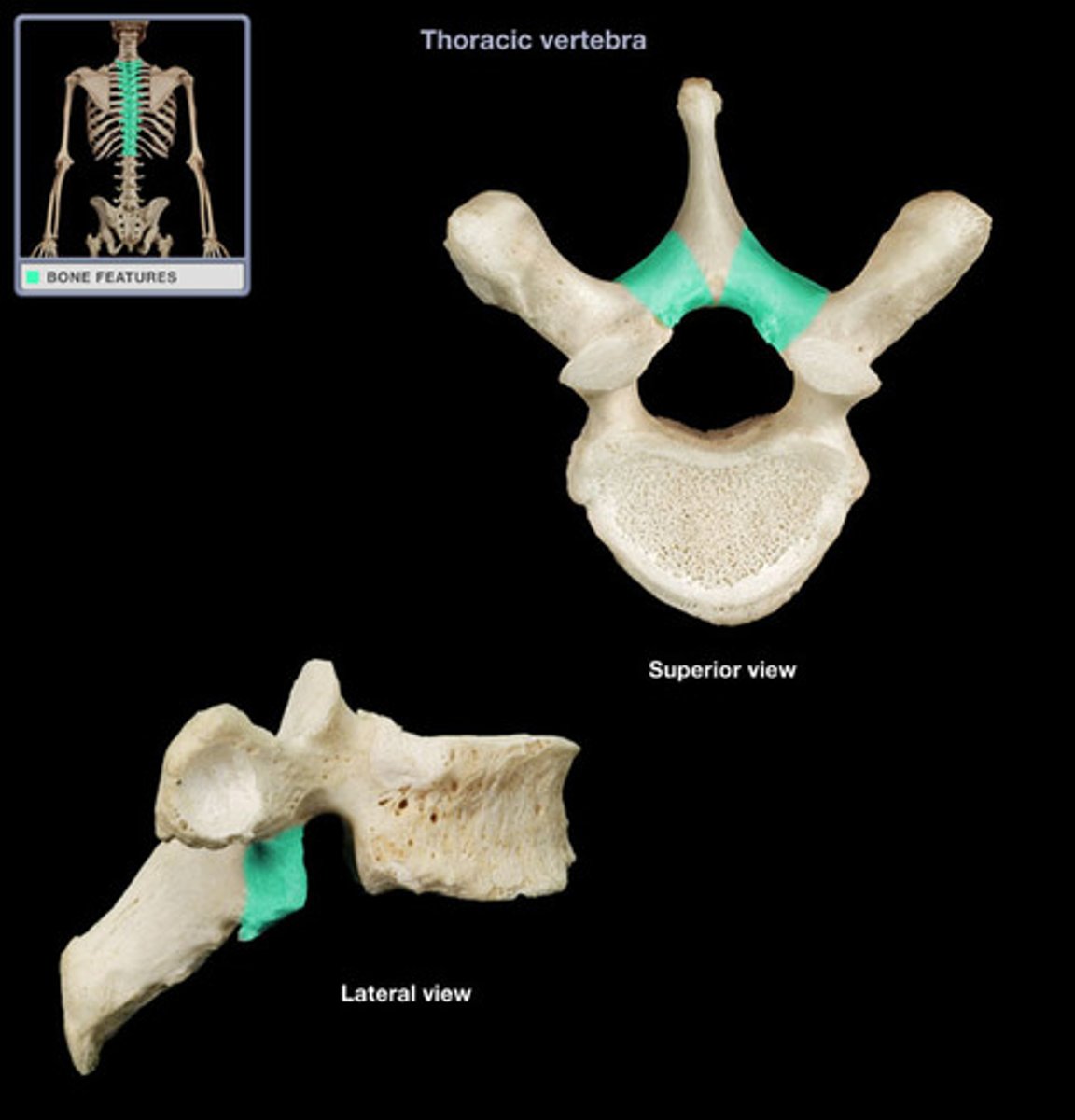
Transverse process of vertebra
forms joint with ribs in thoracic region, site for muscle attachment in lumbar region
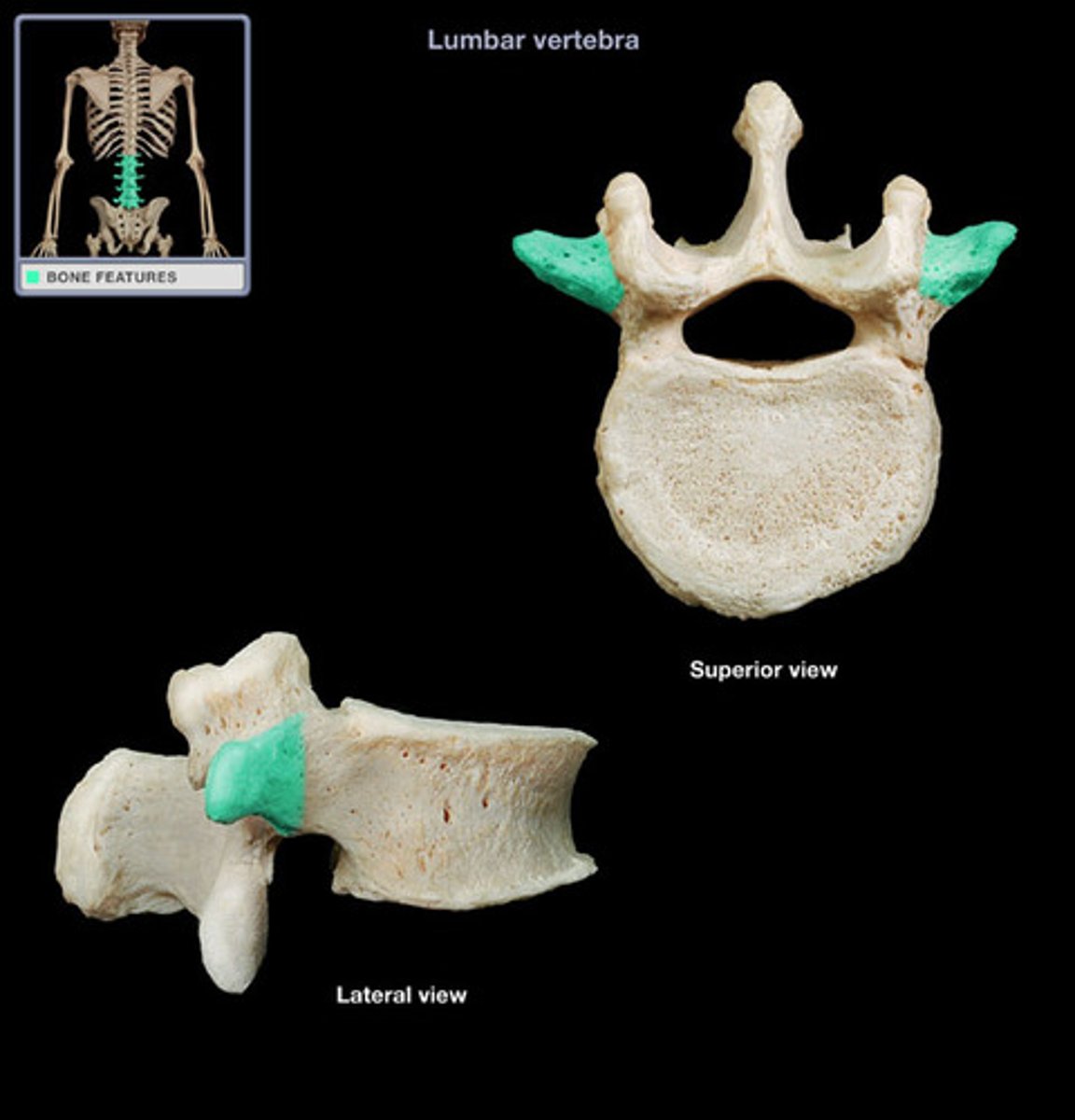
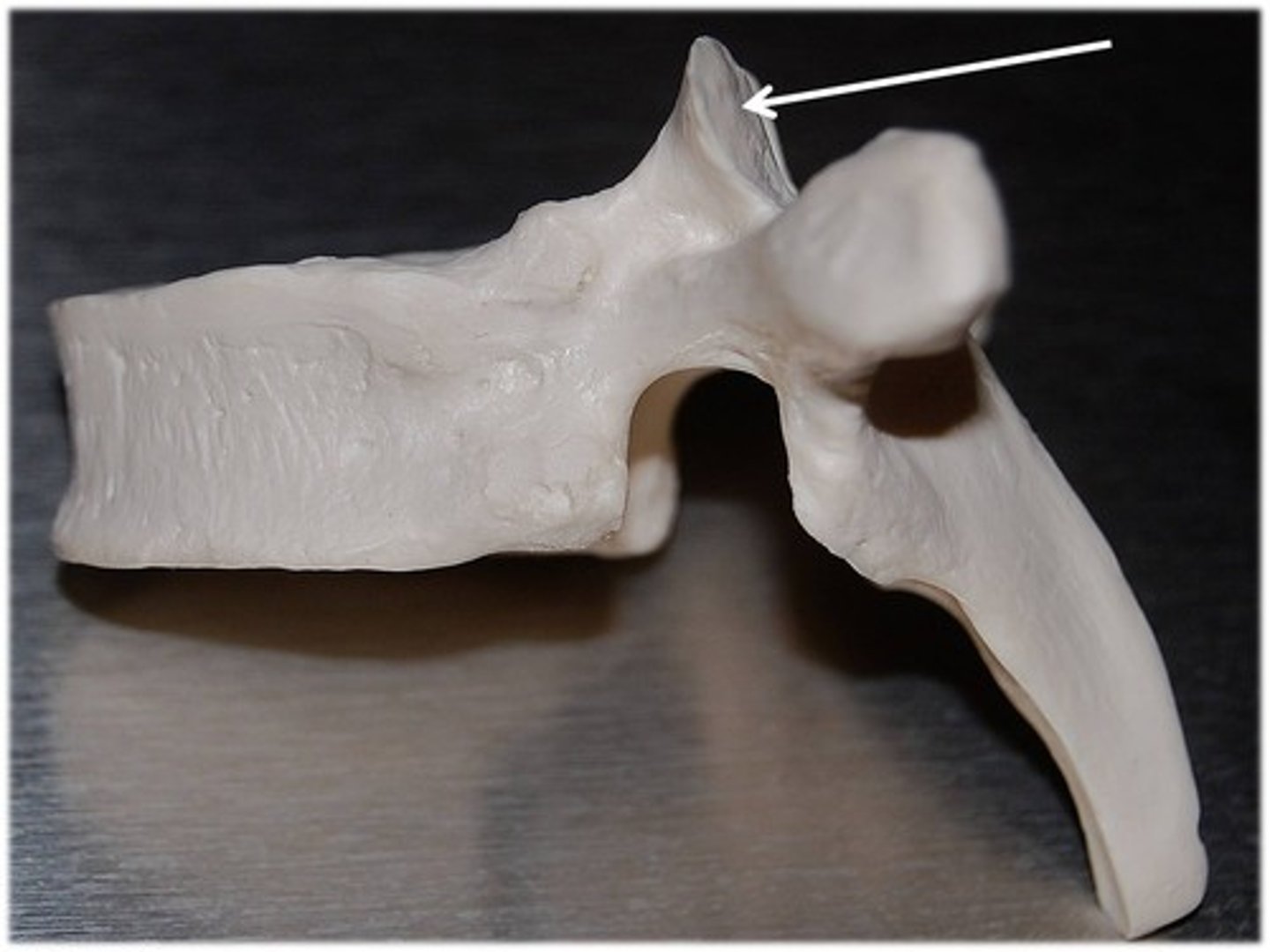
superior articular process
bony process that extends upward from the vertebral arch of a vertebra that articulates with the superior articular process of the next upper vertebra
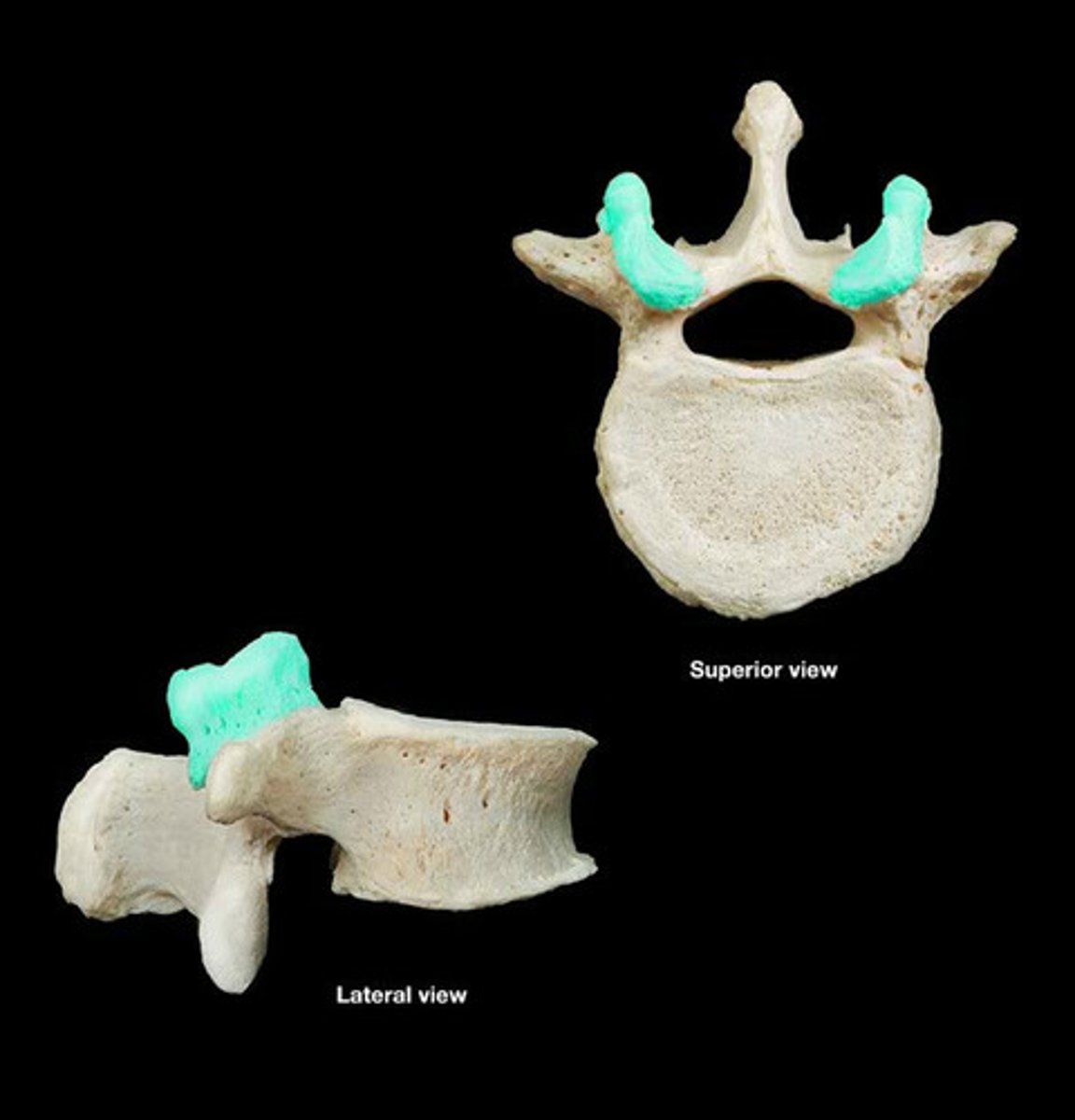
inferior articular process
bony process that extends downward from the vertebral arch of a vertebra that articulates with the superior articular process of the next lower vertebra
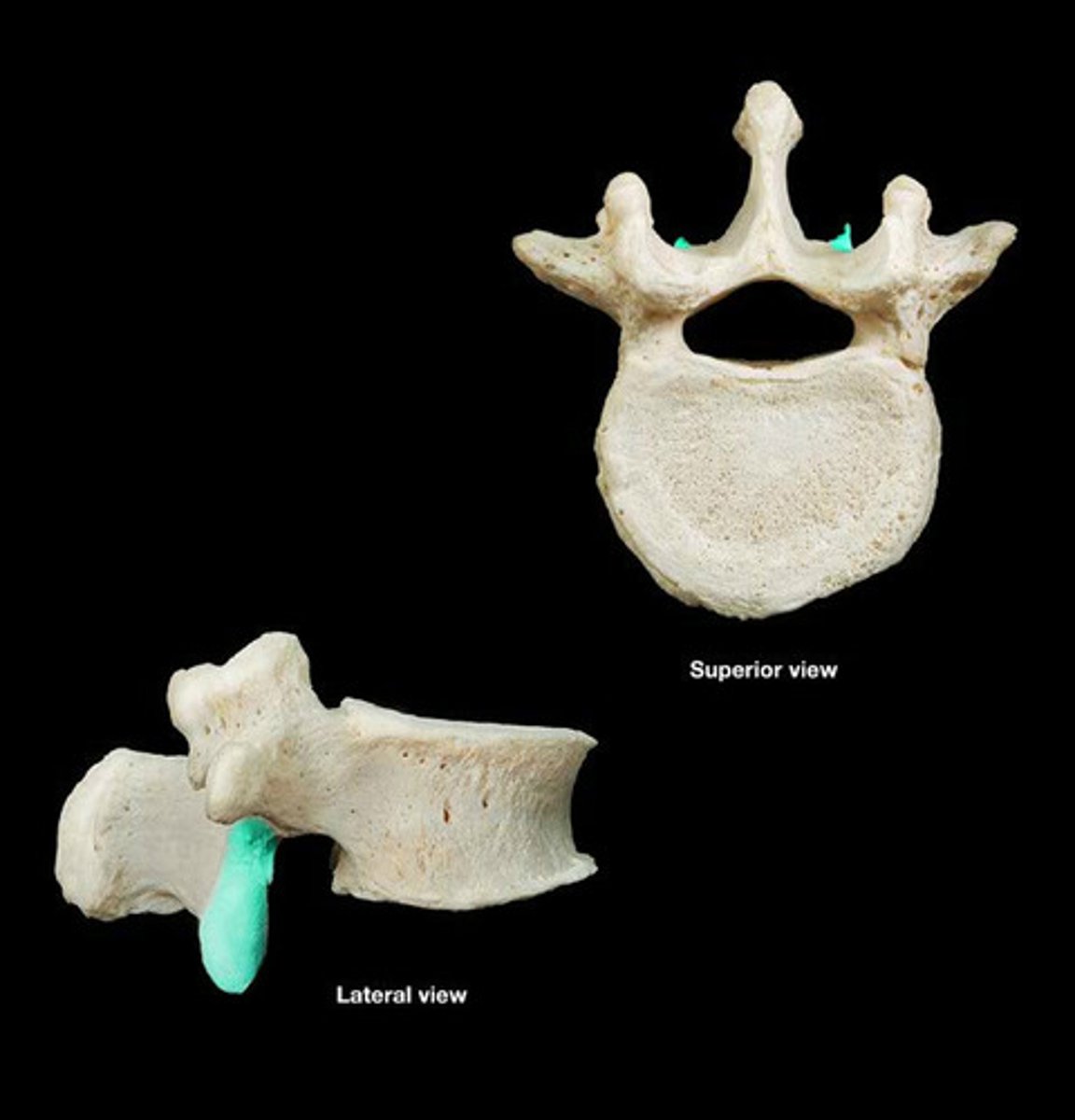
superior articular facet
the part of the superior articular process that articulates with the superior bone to it
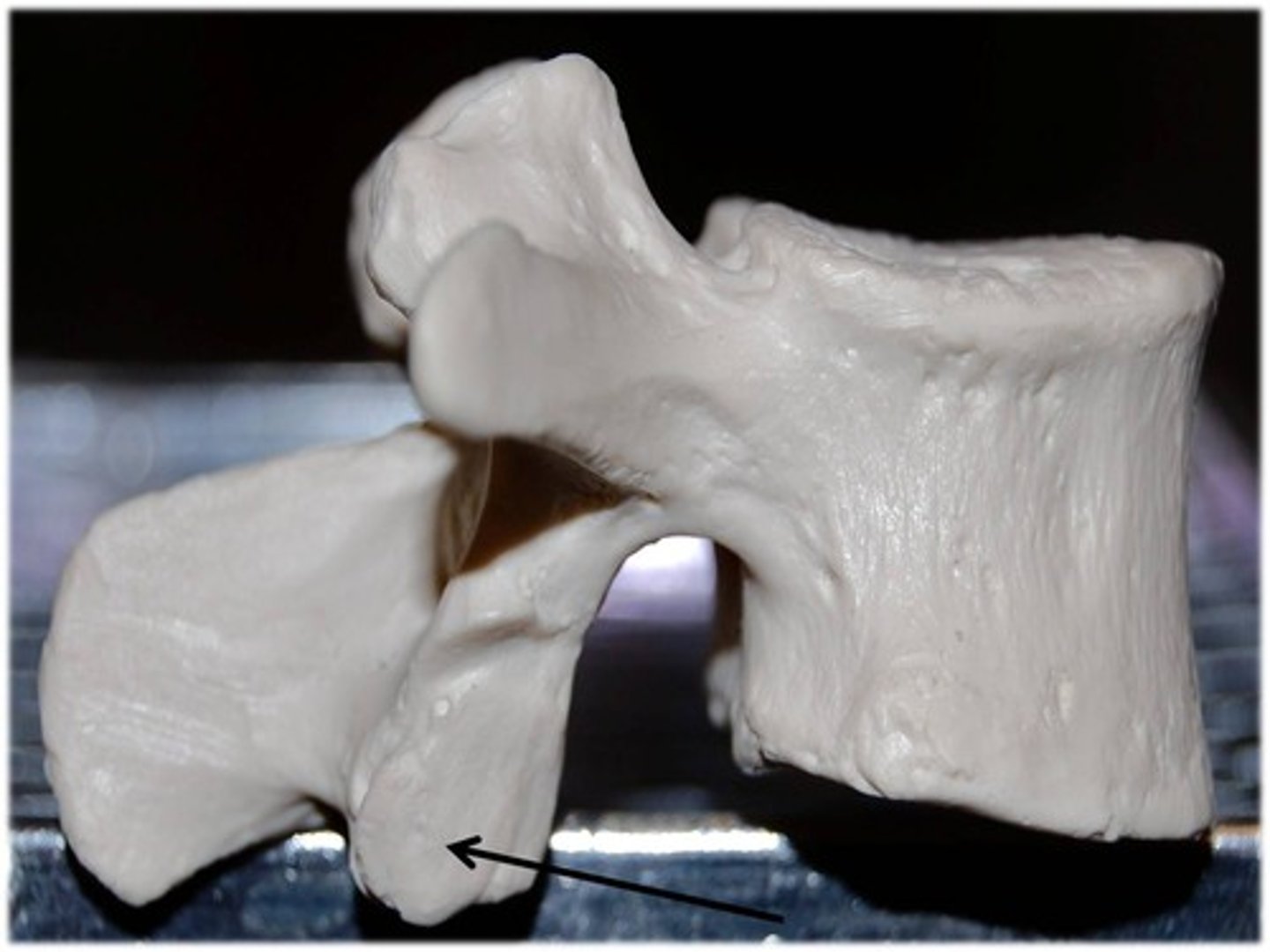
inferior articular process
the part of the inferior articular process that articulates with the inferior bone to it
Intervertebral disks
23 total, disks in the spine
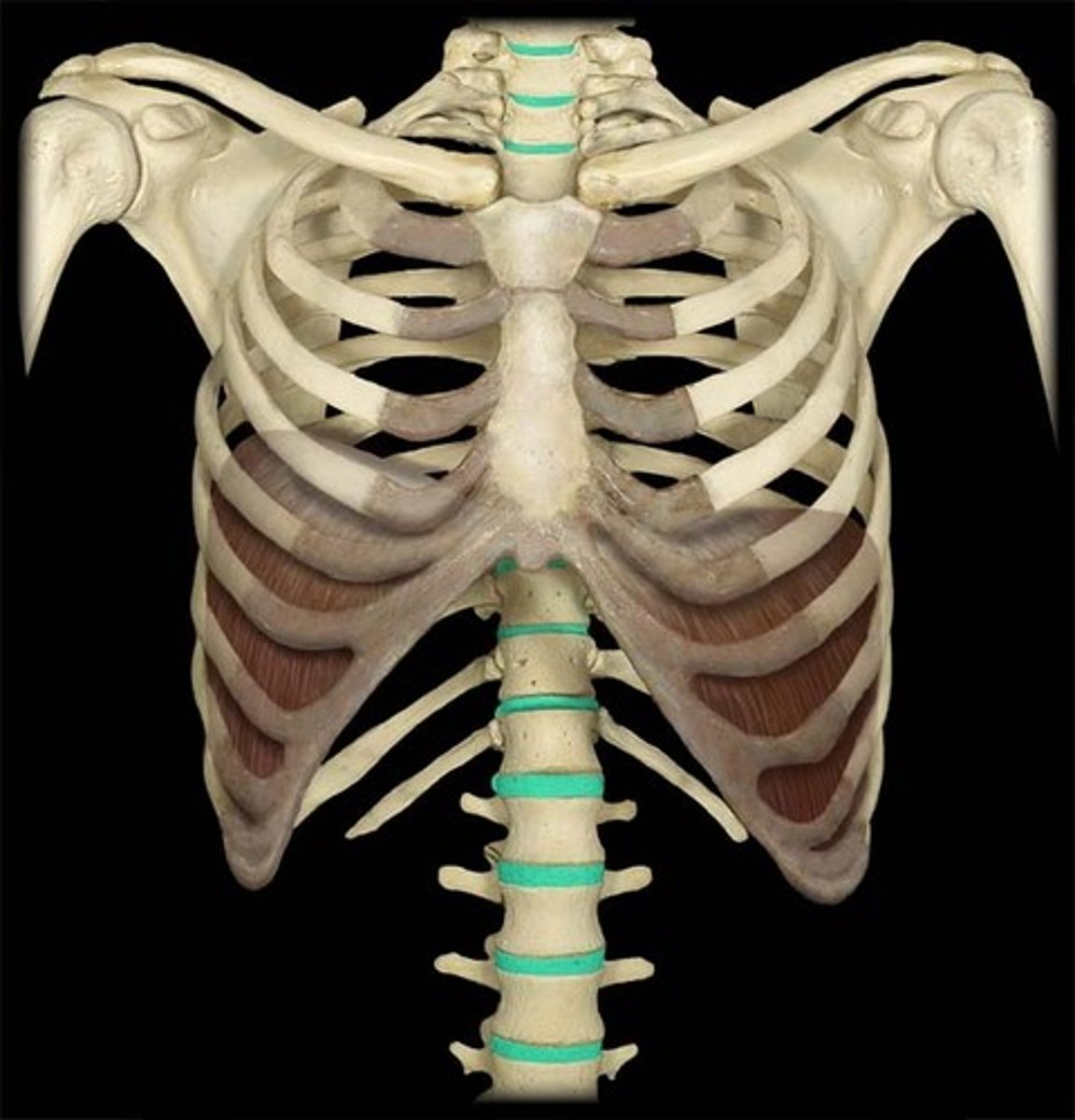
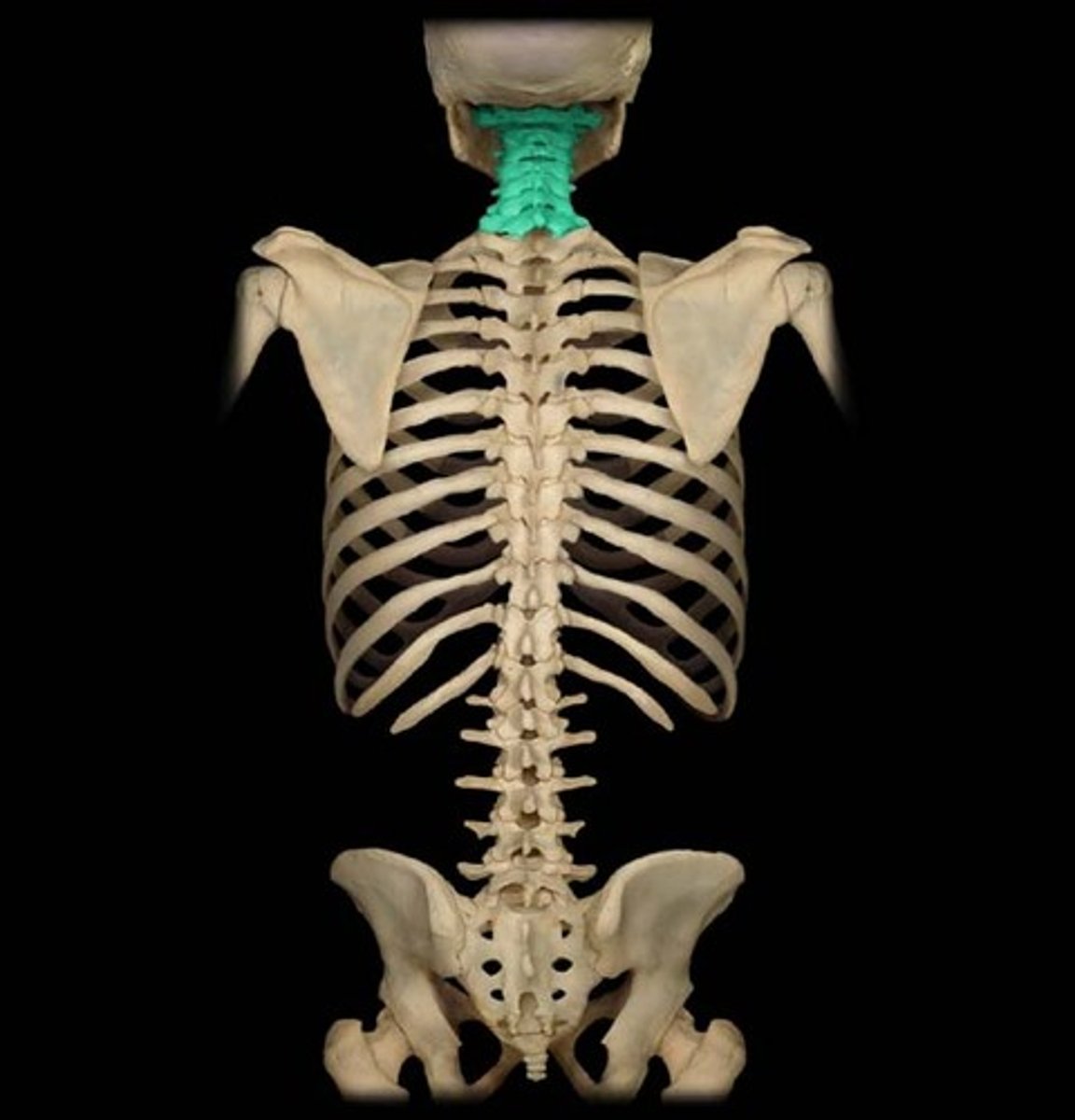
cervical vertebrae
C1-C7, have transverse foreamen, has arteries
transverse foramen
holds arteries in cervical vertebra
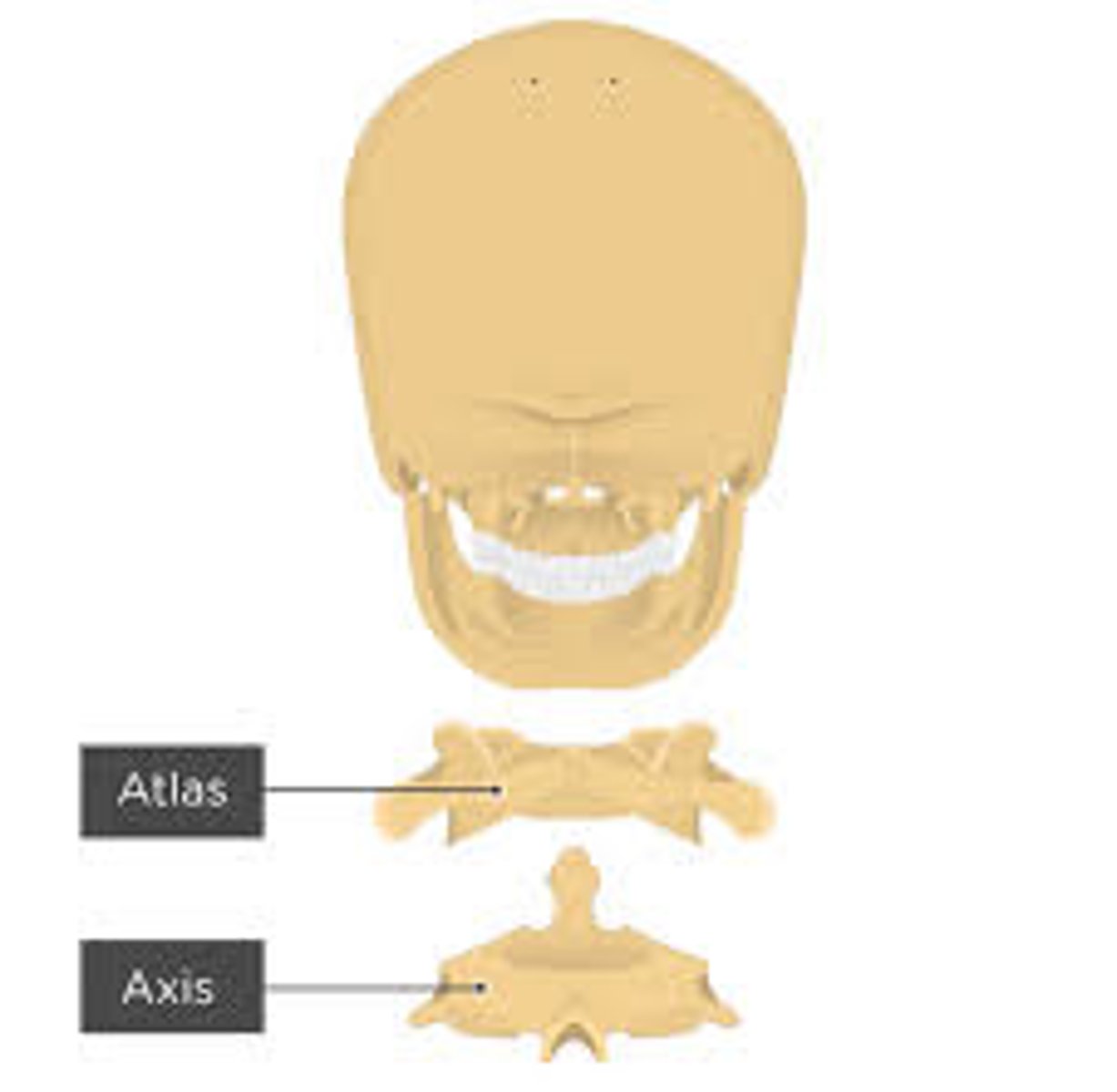
Atlas
C1, the first vertebra, fits into C2
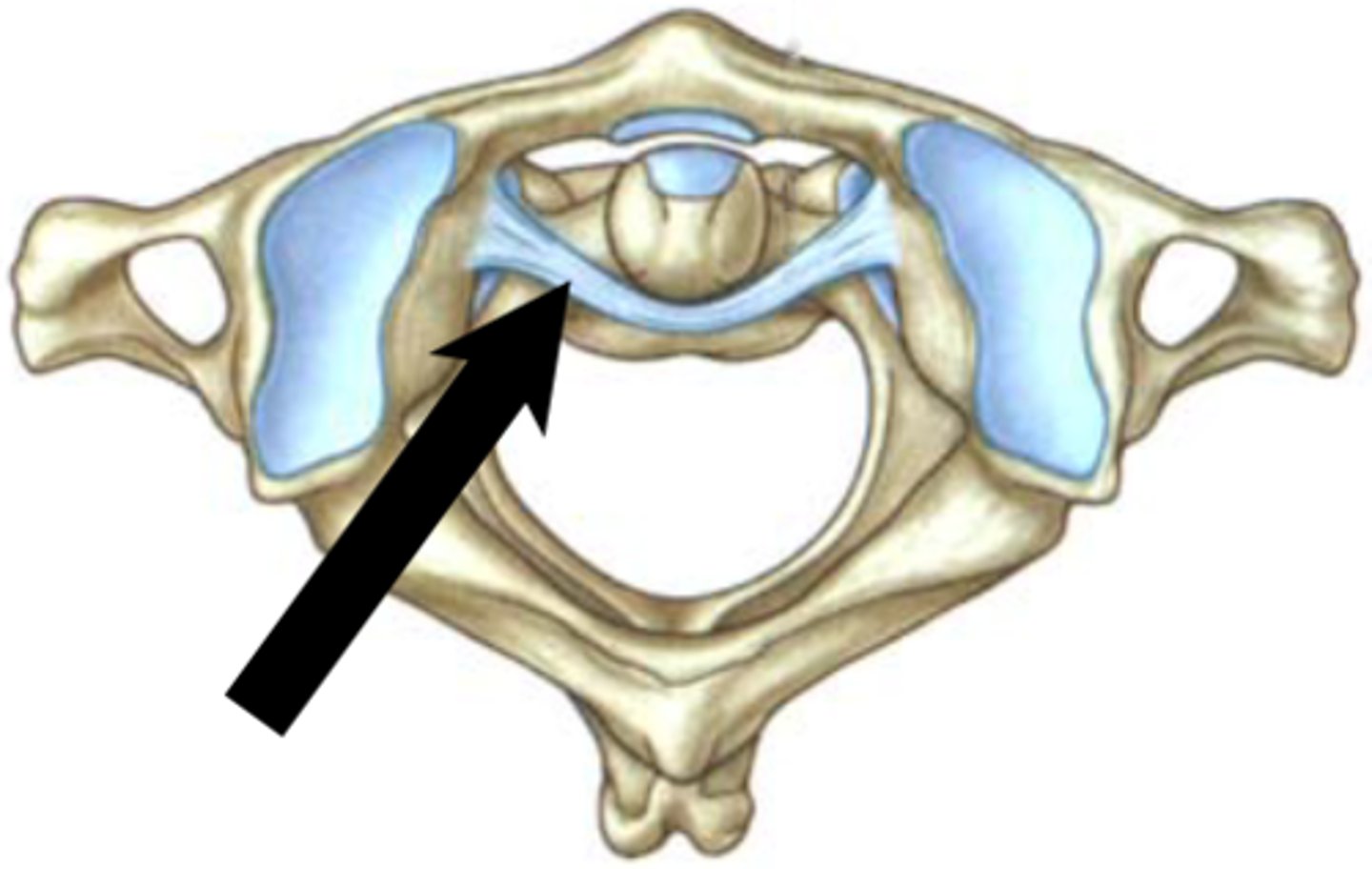
transverse ligament
This ligament attaches to the lateral masses of C1 to hold the dens in place
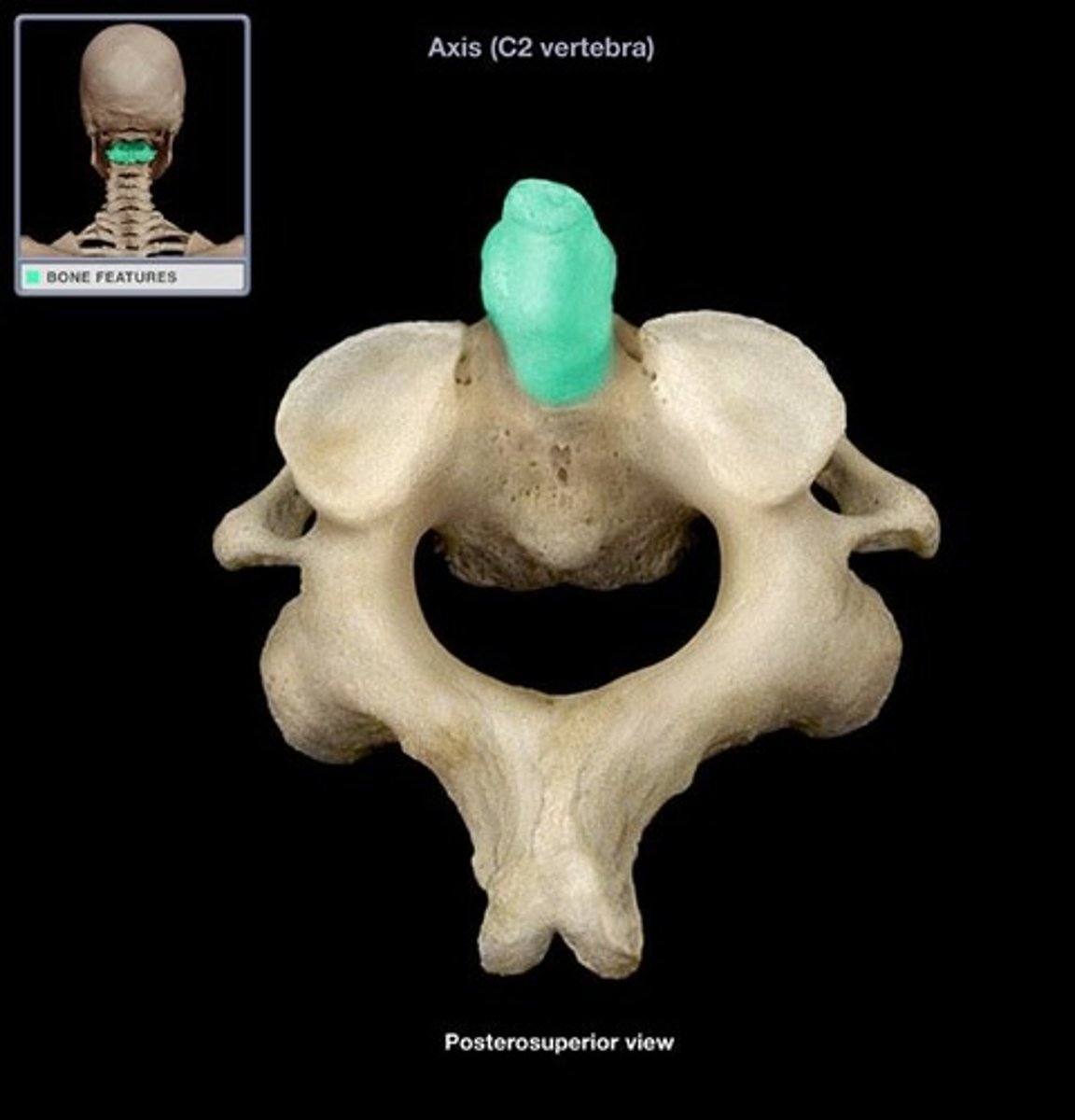
Axis C2
has bump where C1 fits into (shake head)
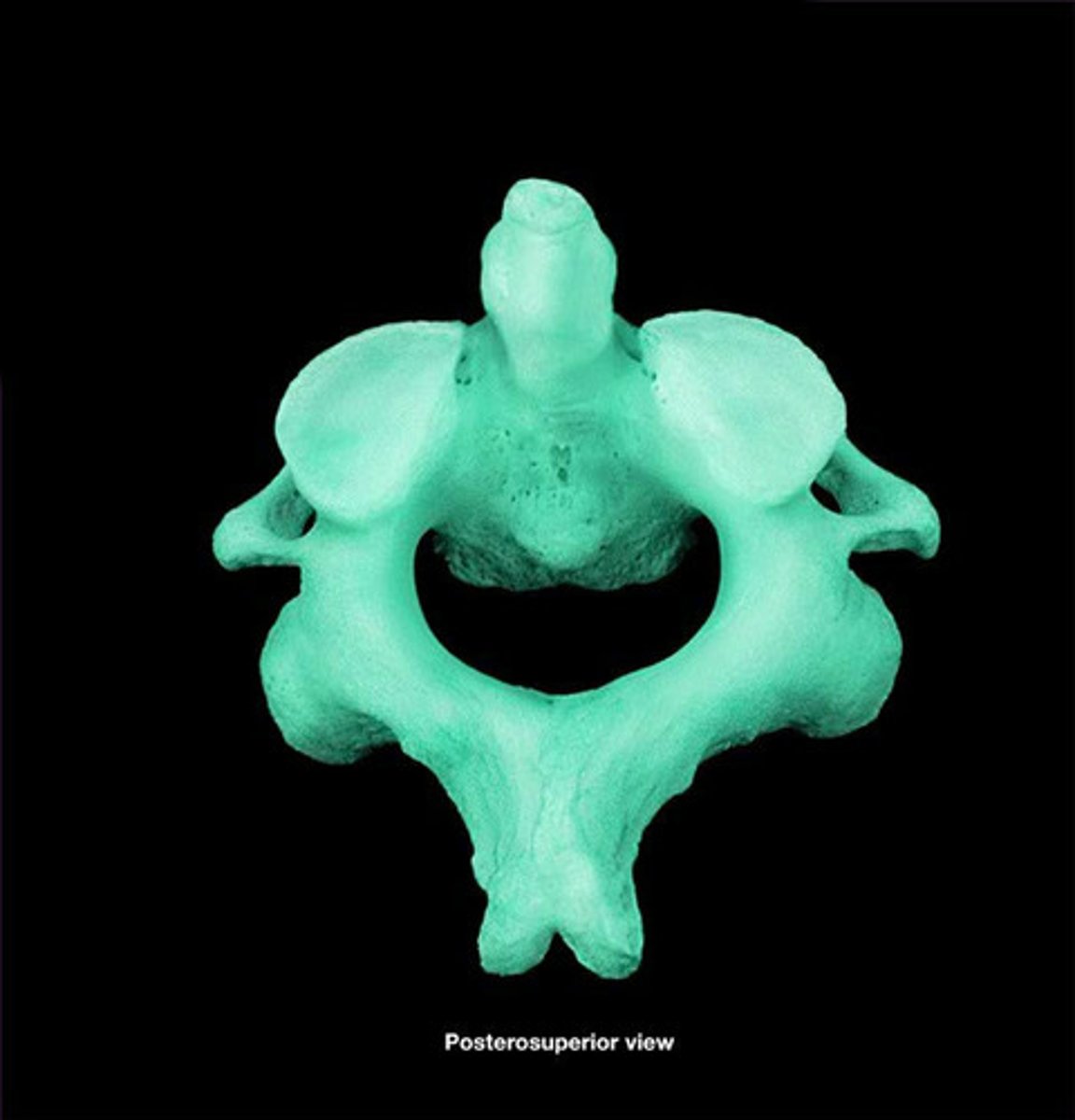
Dens (odontoid process)
a bony projection that extends upward from the vertebral body where C1 rotates on
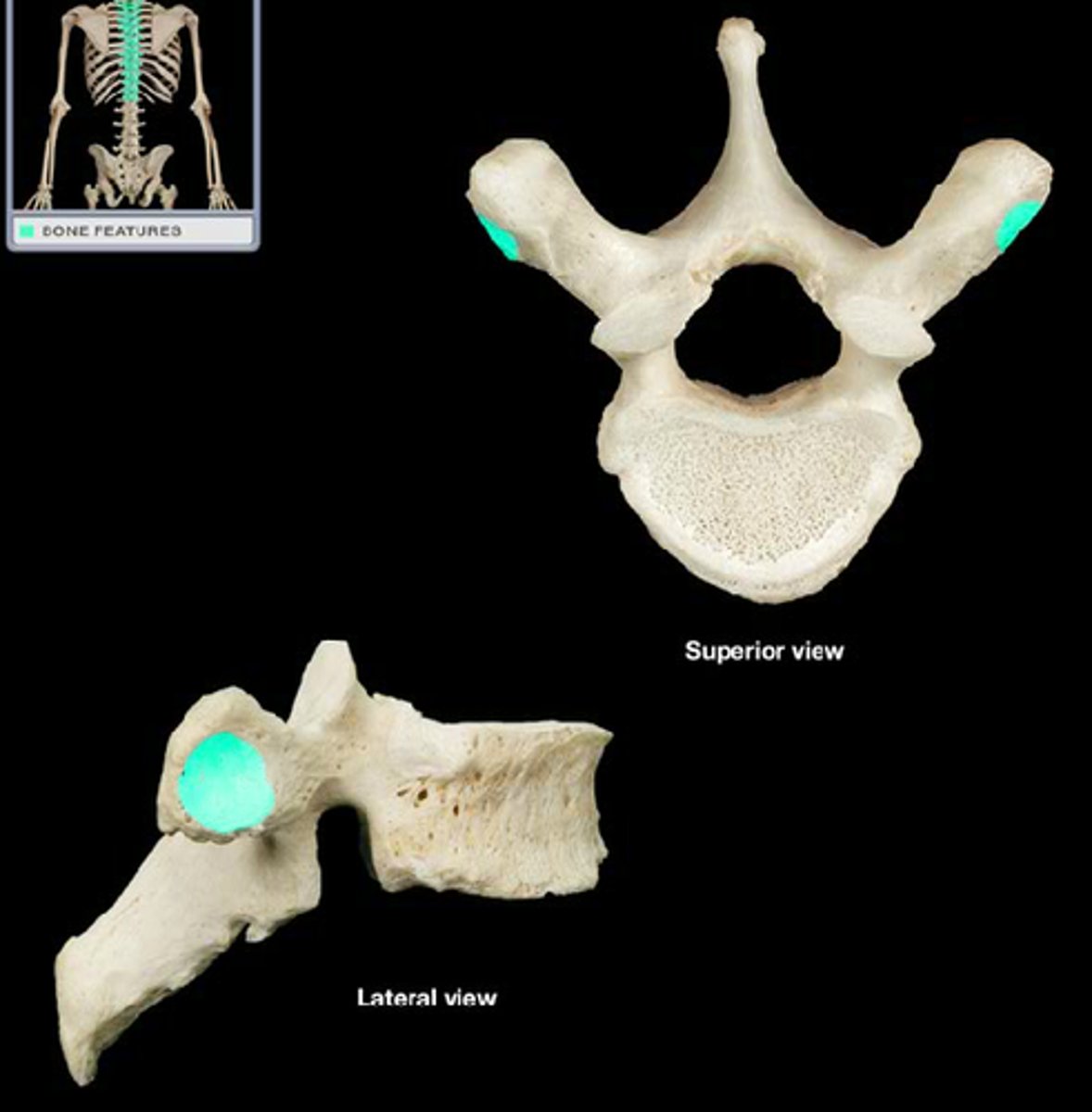
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12)
second set of 12 vertebrae; they articulate with the 12 pairs of ribs to form the outward curve of the spine
costal facets of thoracic vertebrae
where head of rib connects
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5)
third set of five larger vertebrae, which forms the inward curve of the spine, lack facets and foreamer
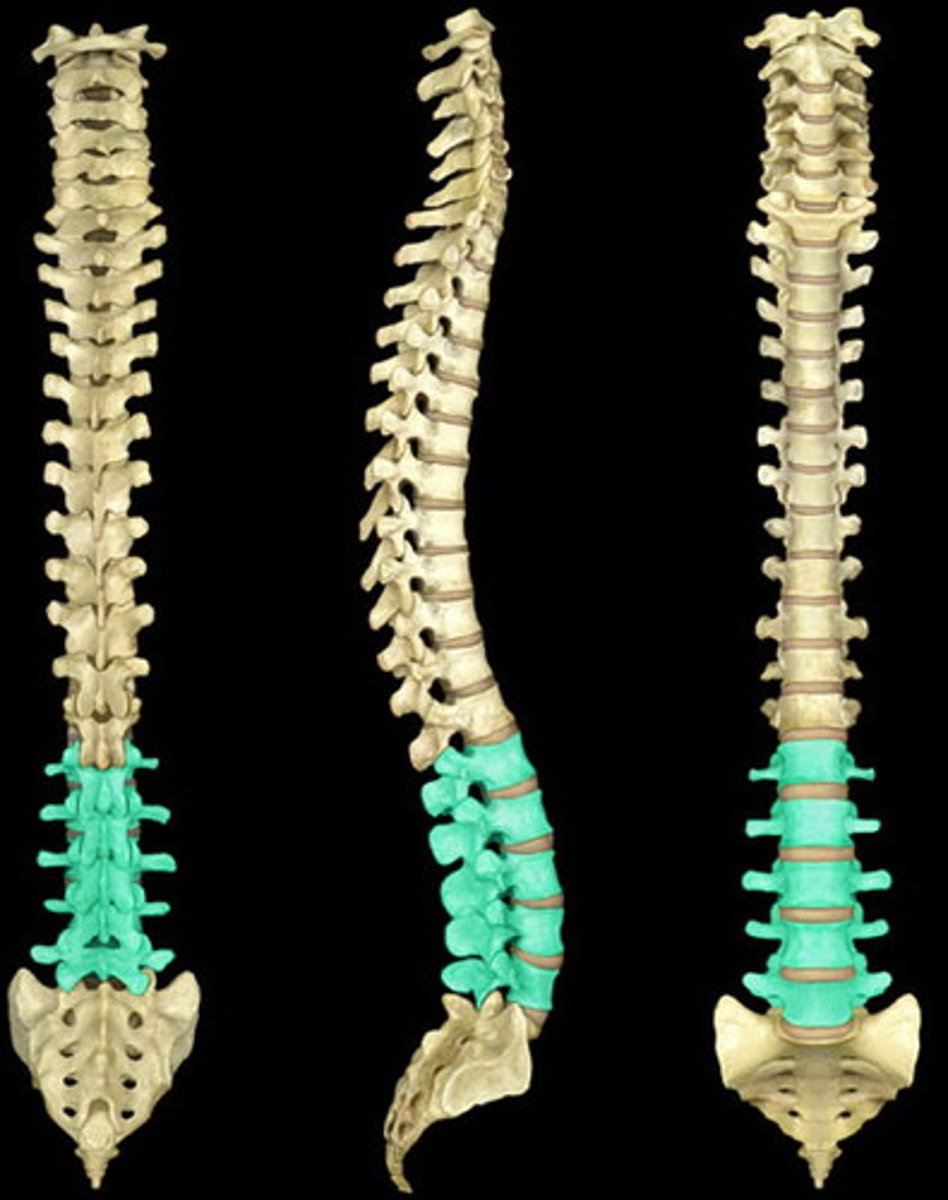
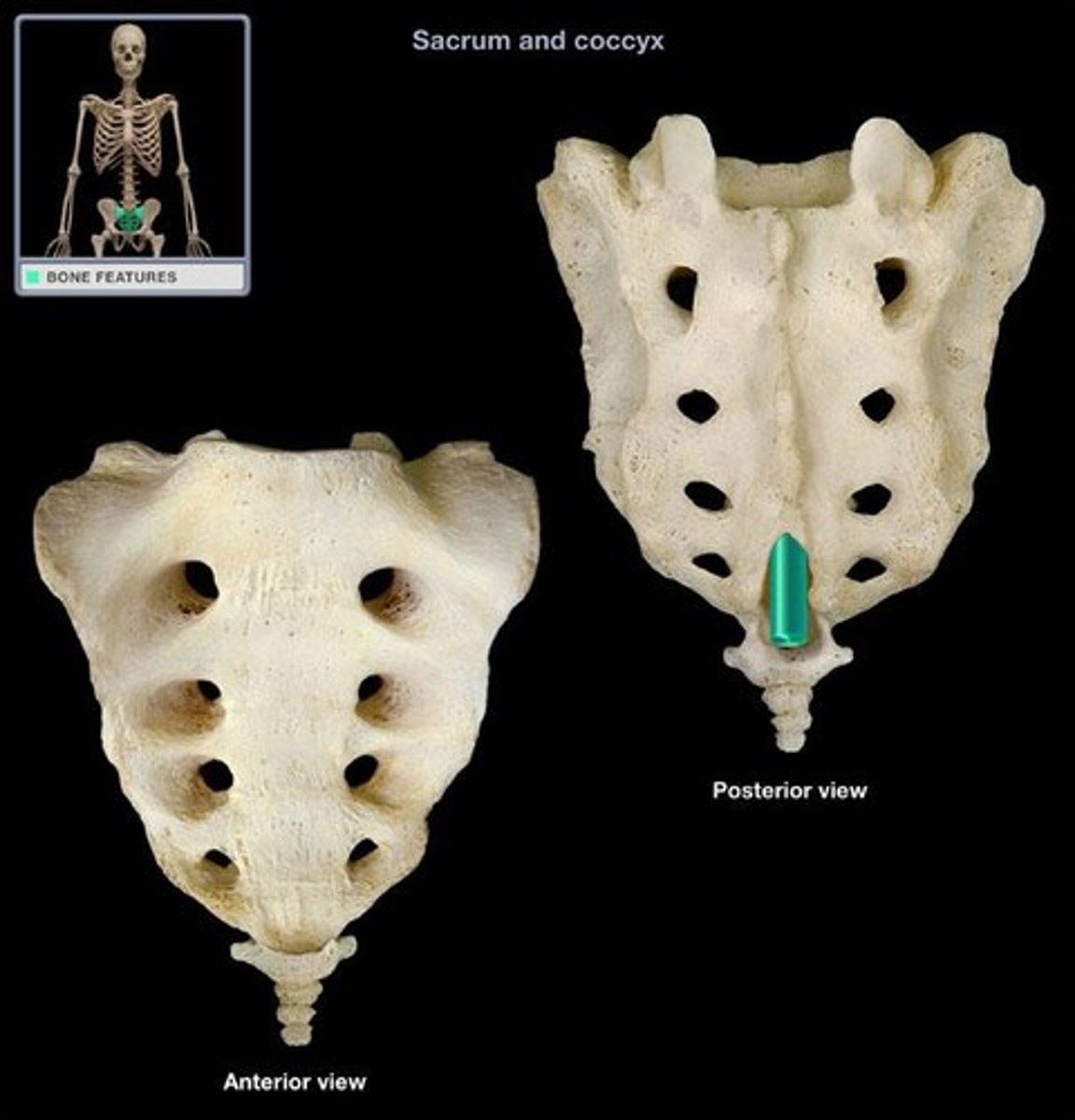
Sacrum (S1-S5)
Shapes the posterior wall of pelvis
Formed from 5 fused vertebrae
Superior surface articulates with L5
Inferiorly articulates with coccyx
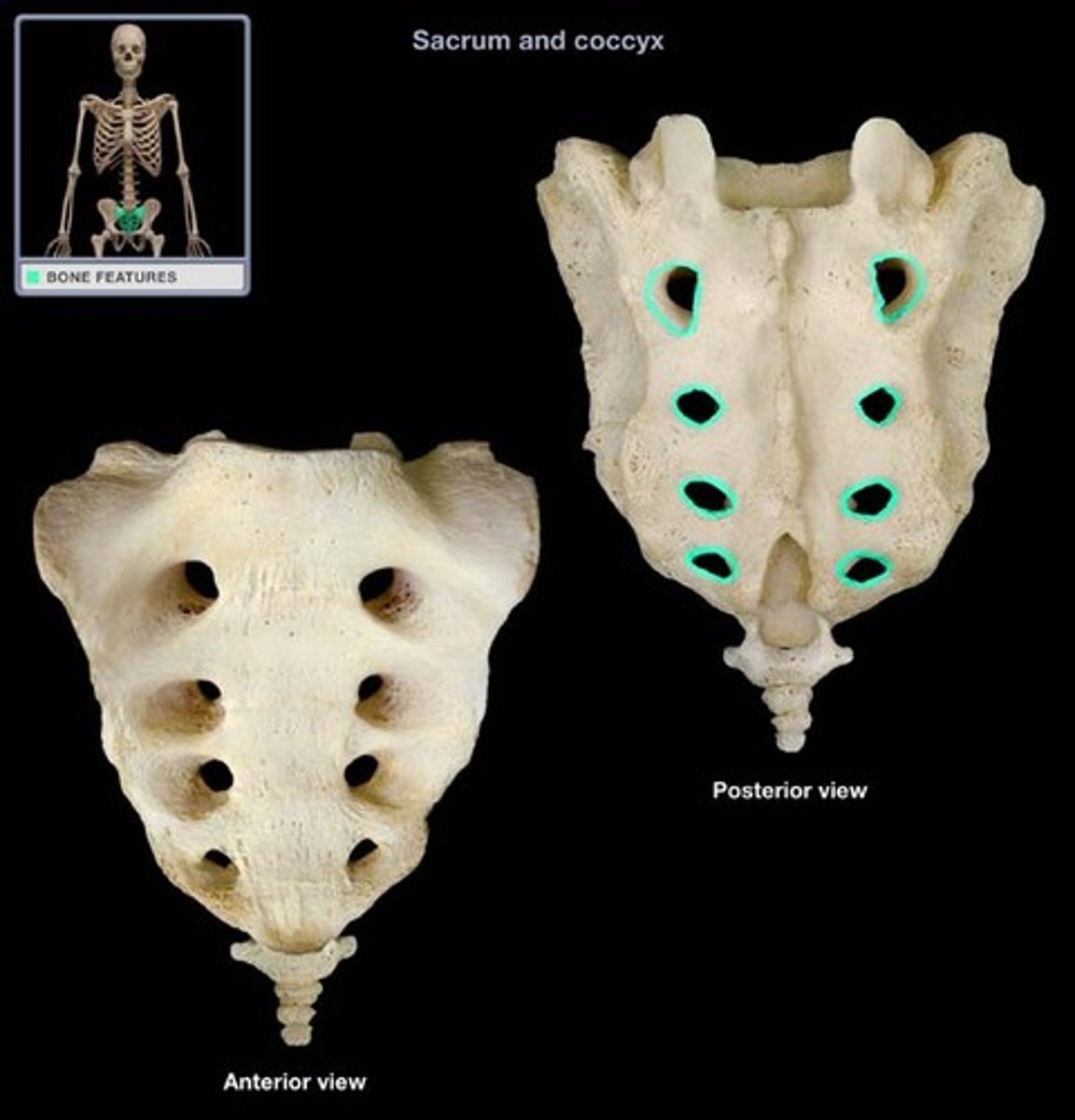
anterior sacral foramina
holes on the front of the sacrum
Posterior sacral foramina
holes on back of sacrum
sacral canal
continuation of vertebral canal
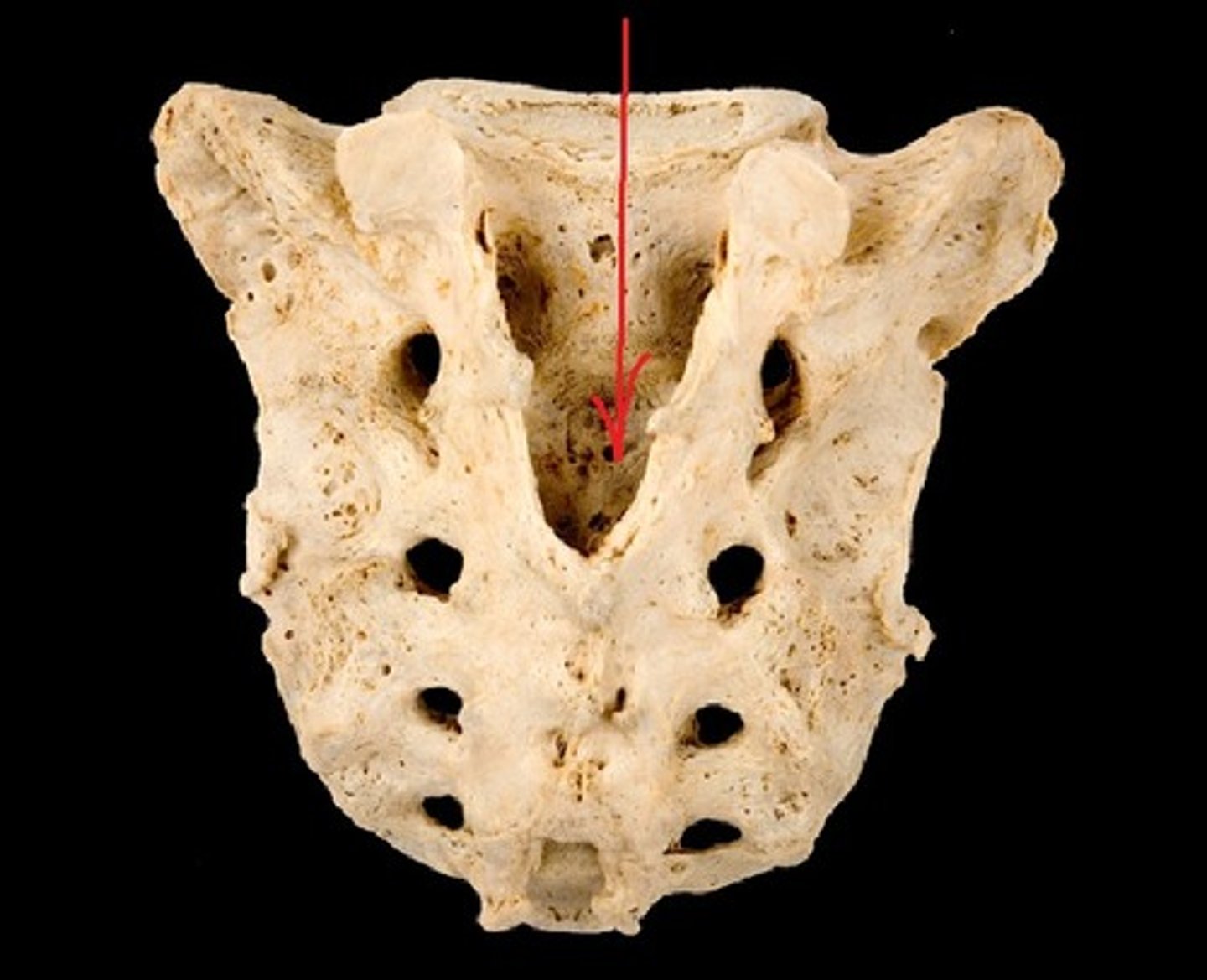
sacral hiatus
inferior opening of the sacral canal
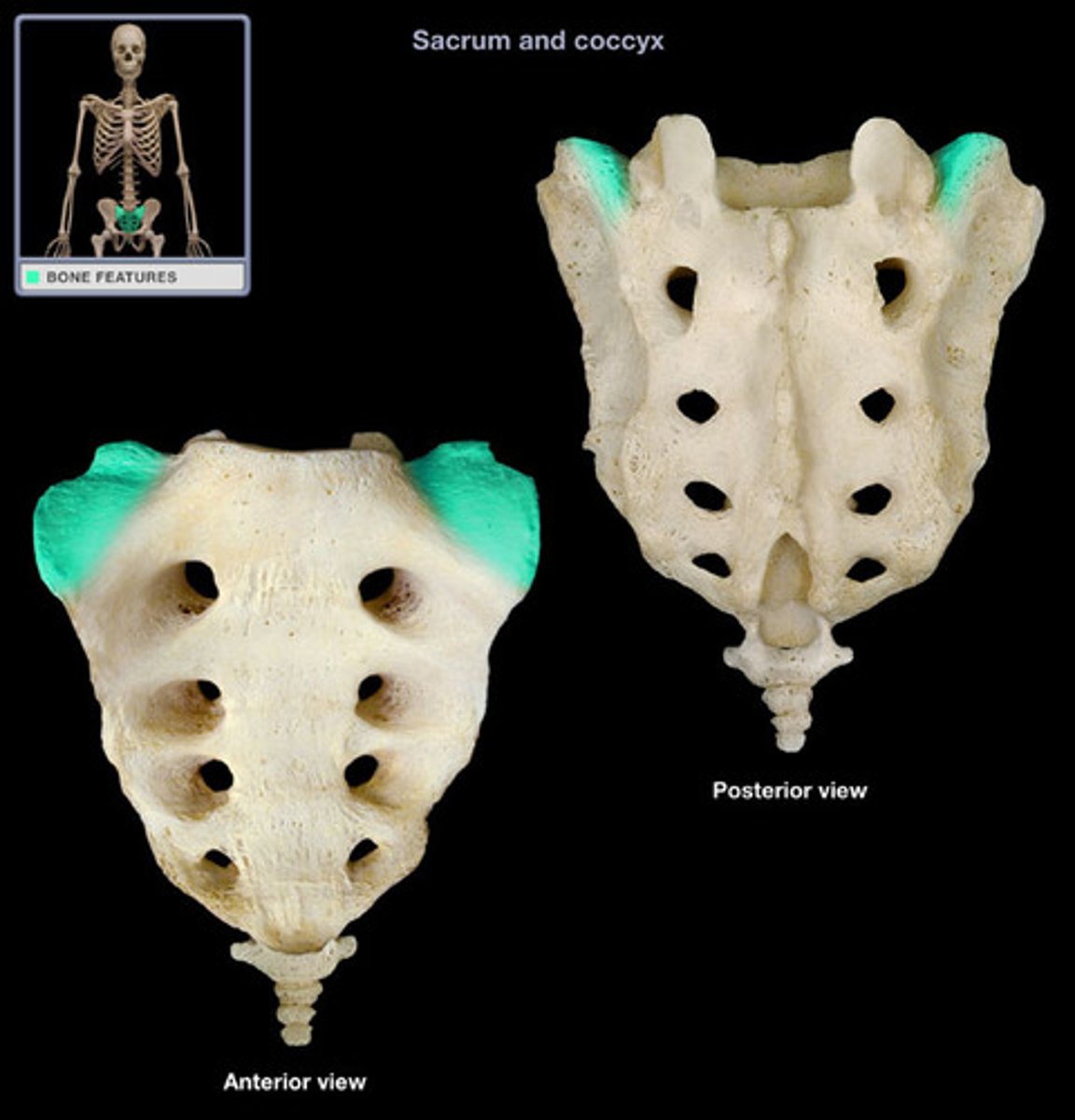
ala of sacrum
The wing-like projections on either side of the sacrum.
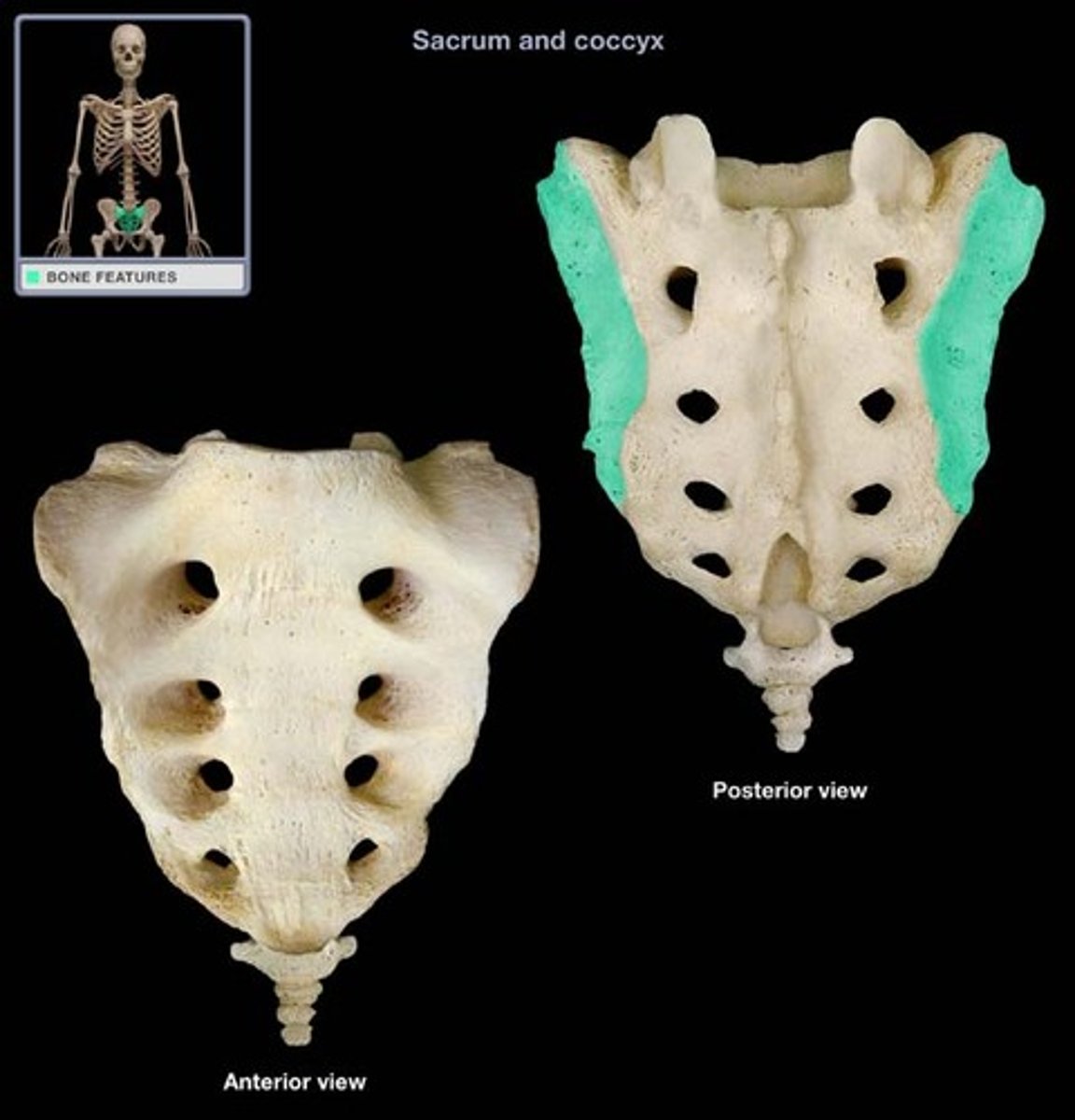
auricular surface
where pelvic bone articulates with sacrum
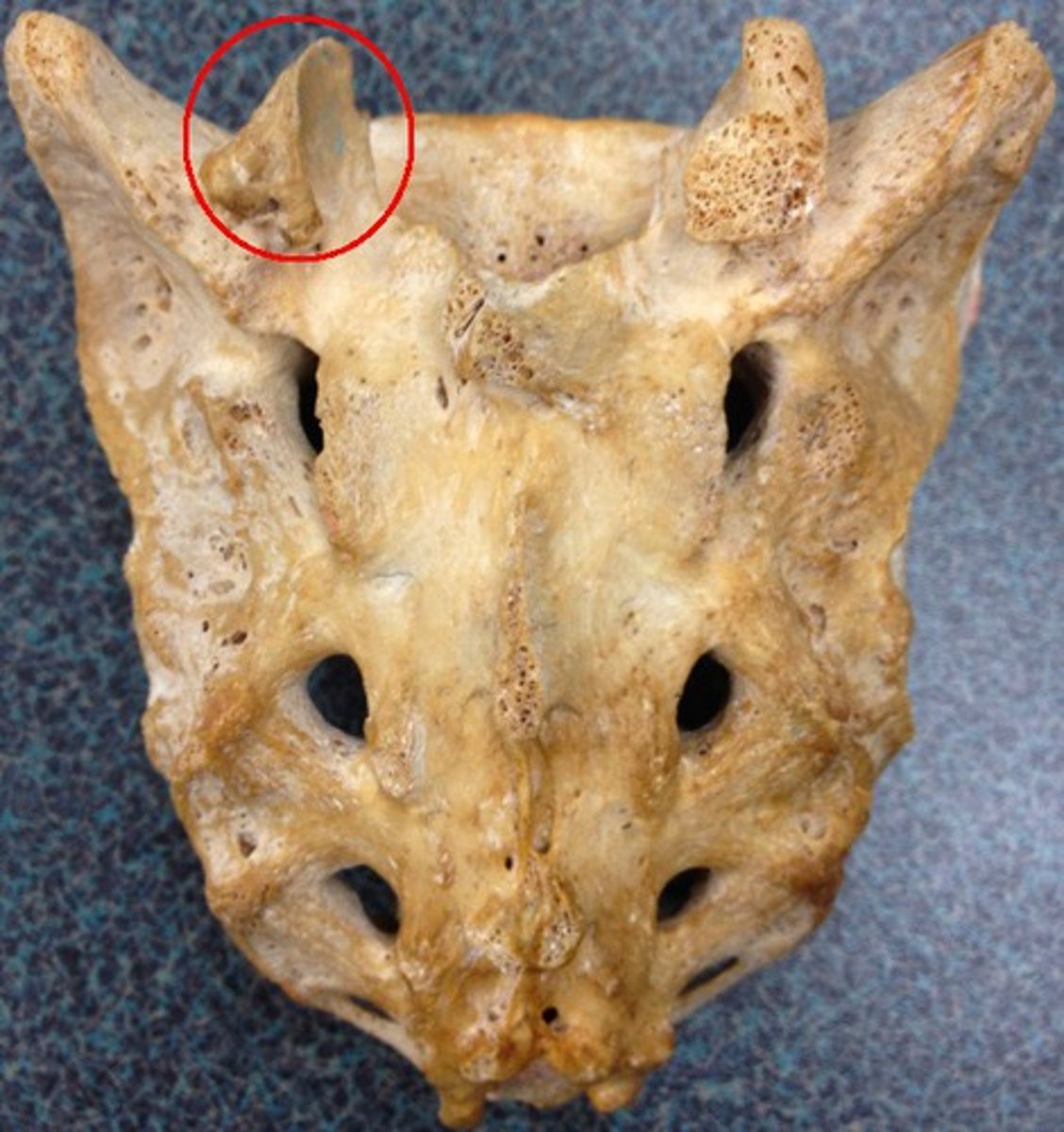
superior articular process of sacrum
paired processes that extend upward from the sacrum to articulate (join) with the inferior articular processes from the L5 vertebra
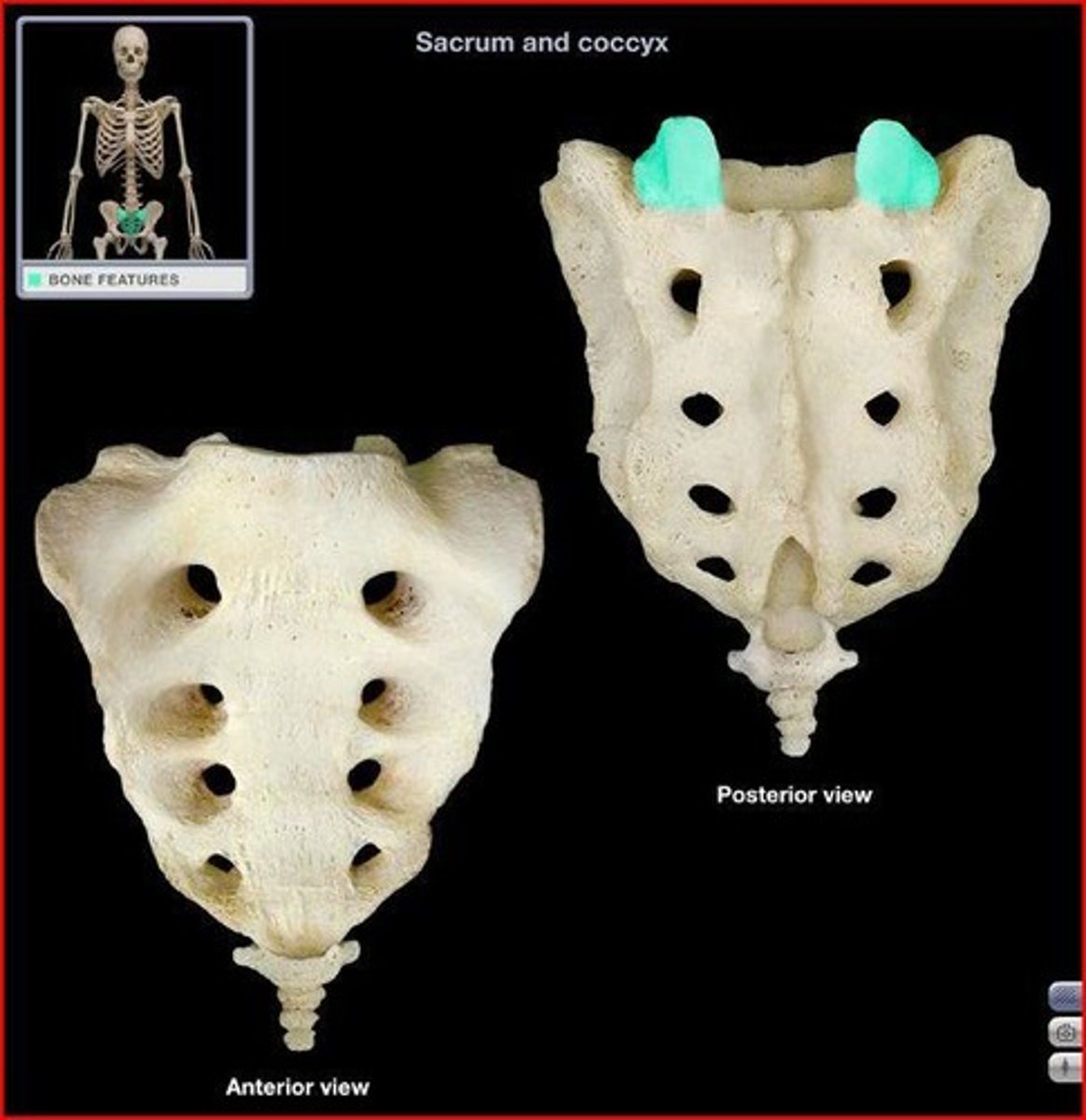
superior articular facet of sacrum
where smooth surface is on process
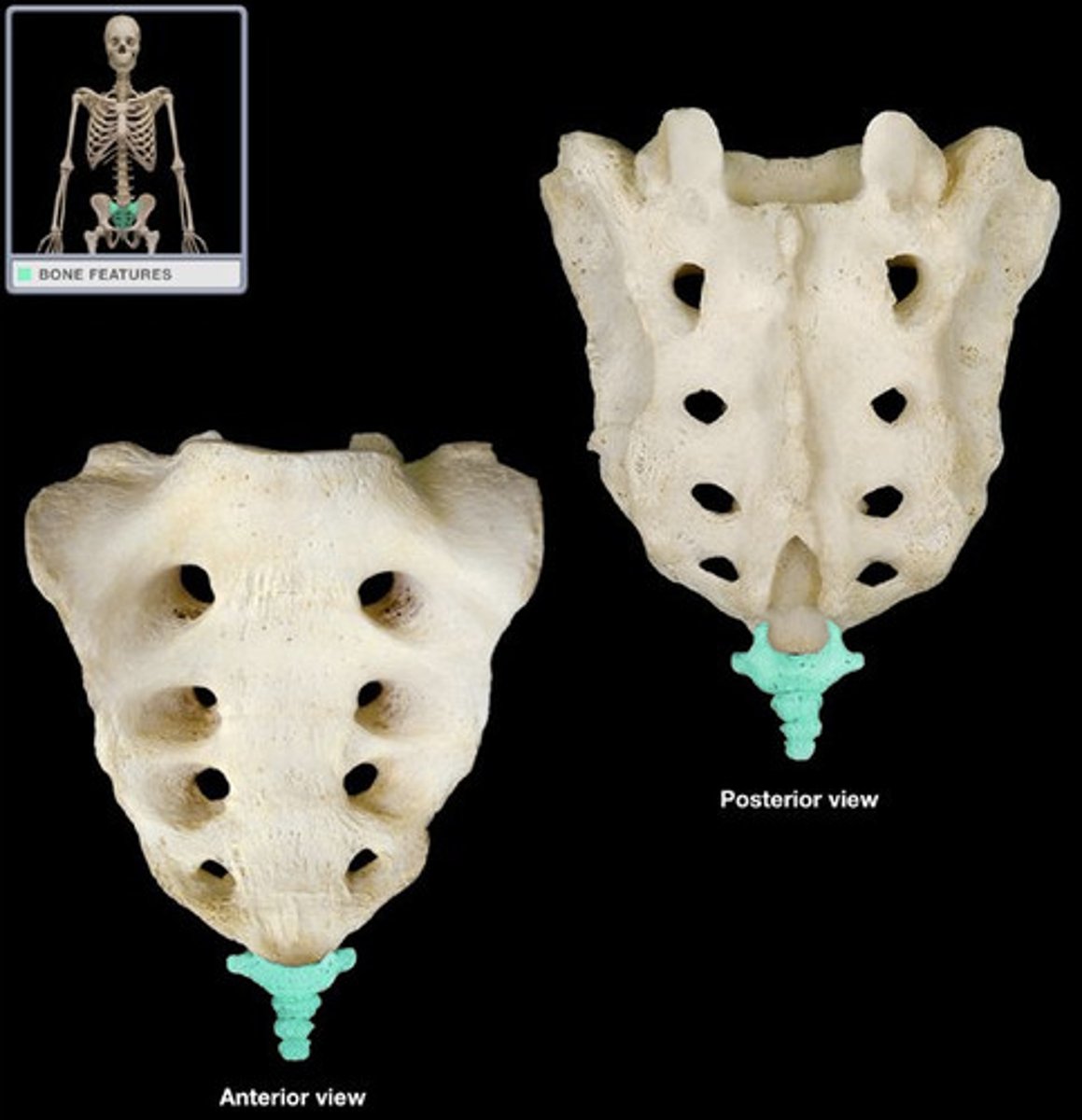
Coccyx
Tailbone
Sternum
Breastbone
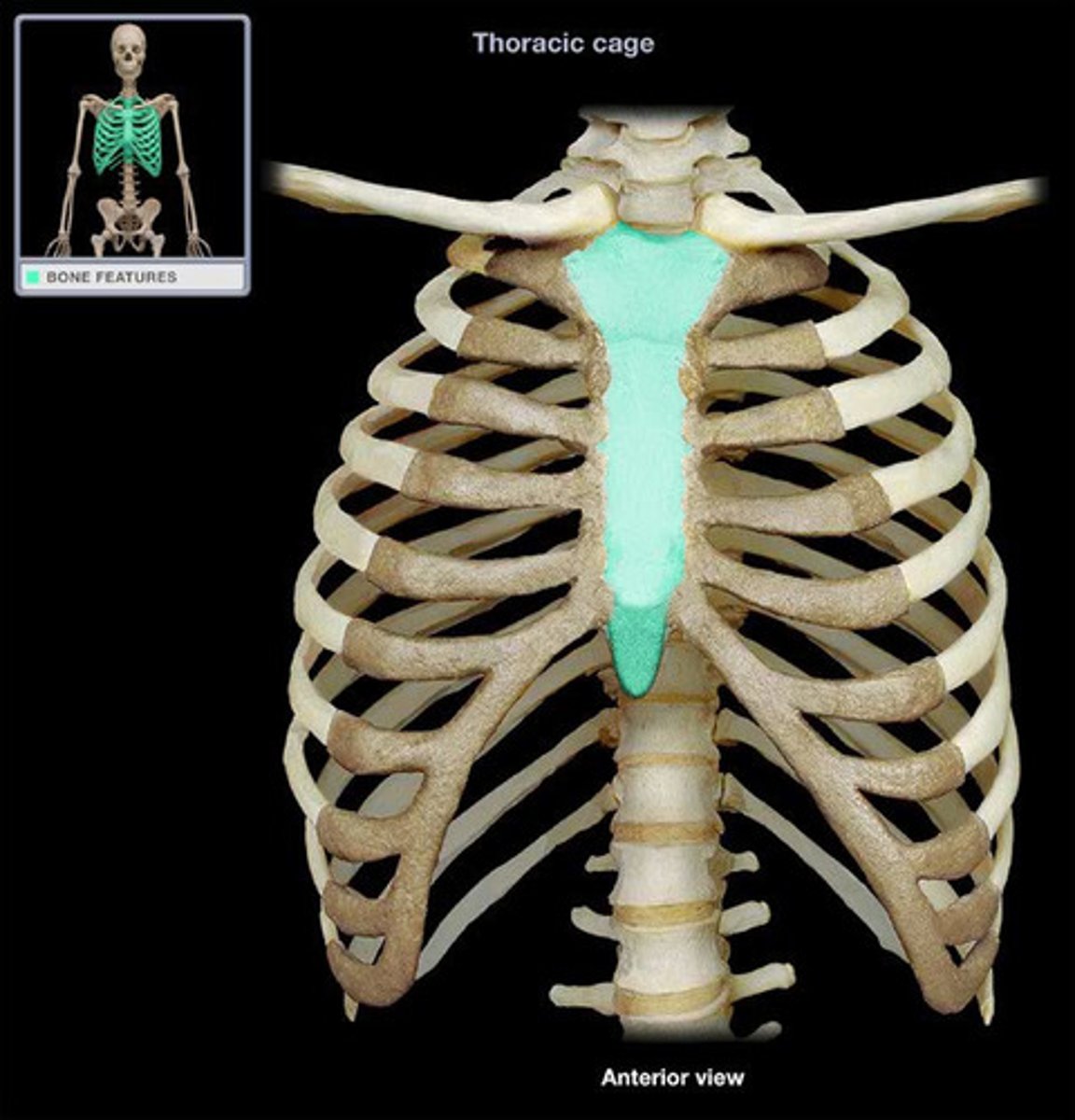
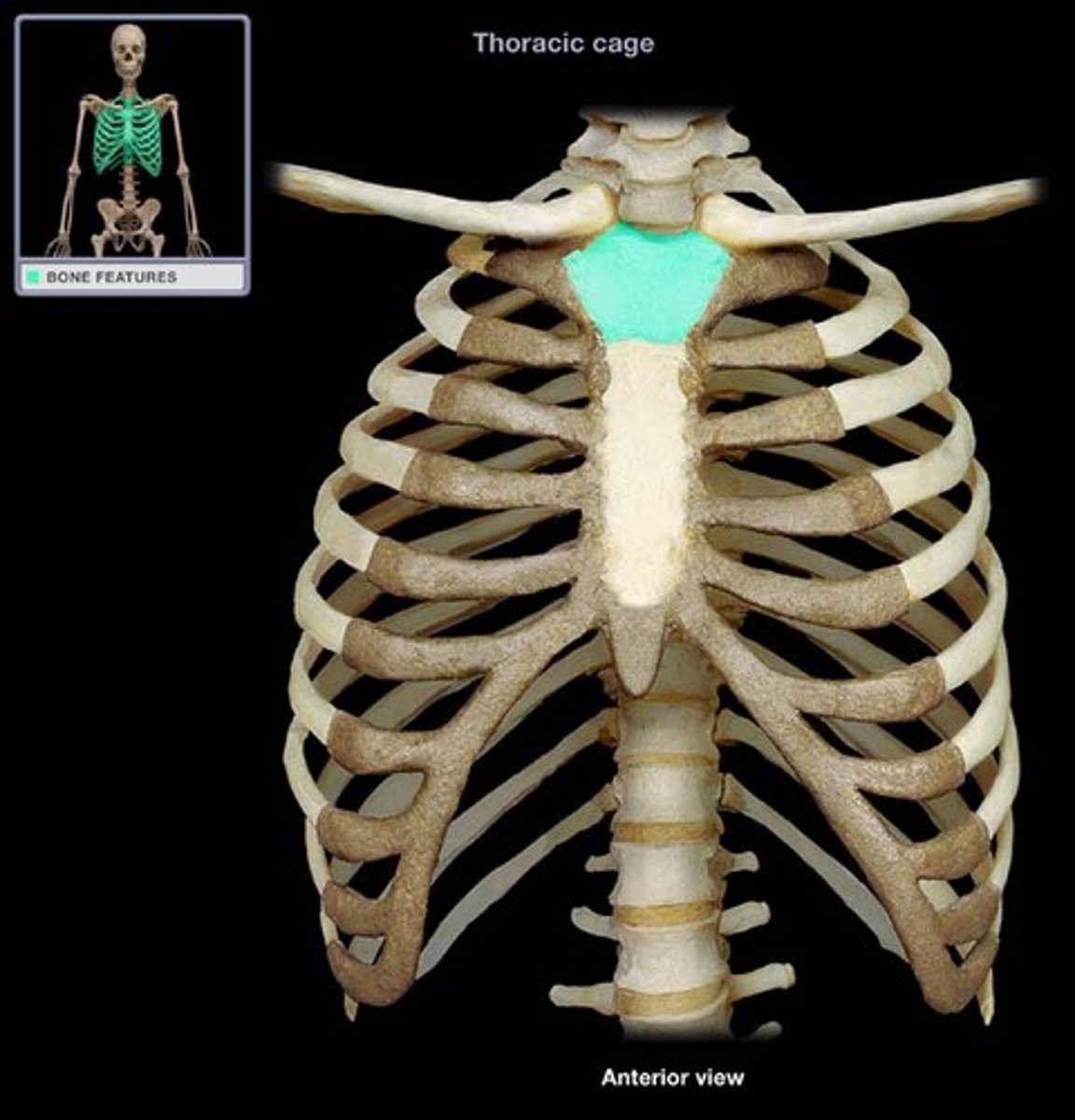
manubrium
upper portion of the sternum
clavicular notch
where sternum connects to clavicles

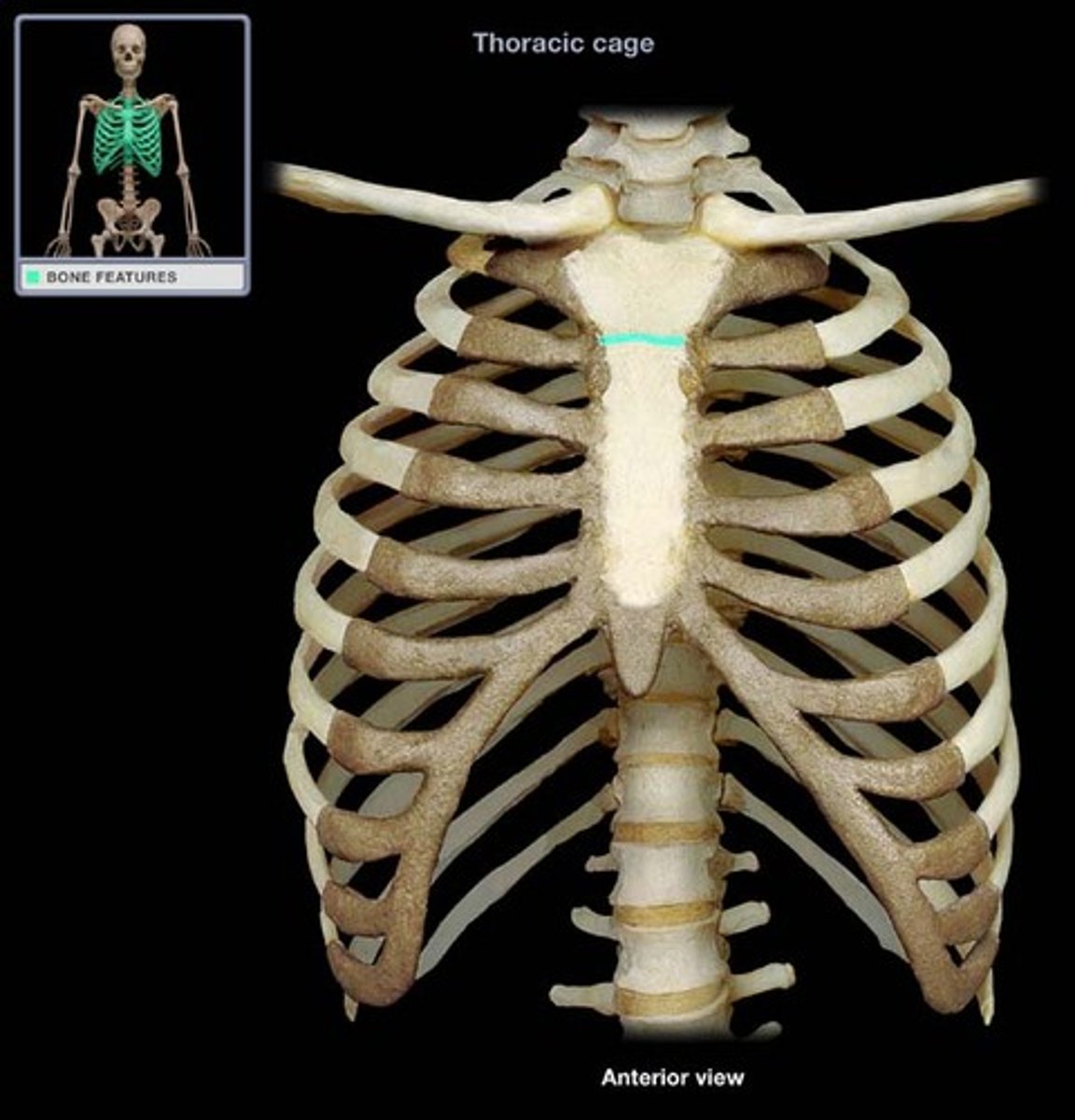
sternal angle
horizontal ridge across front of sternum where manubrium and body meet
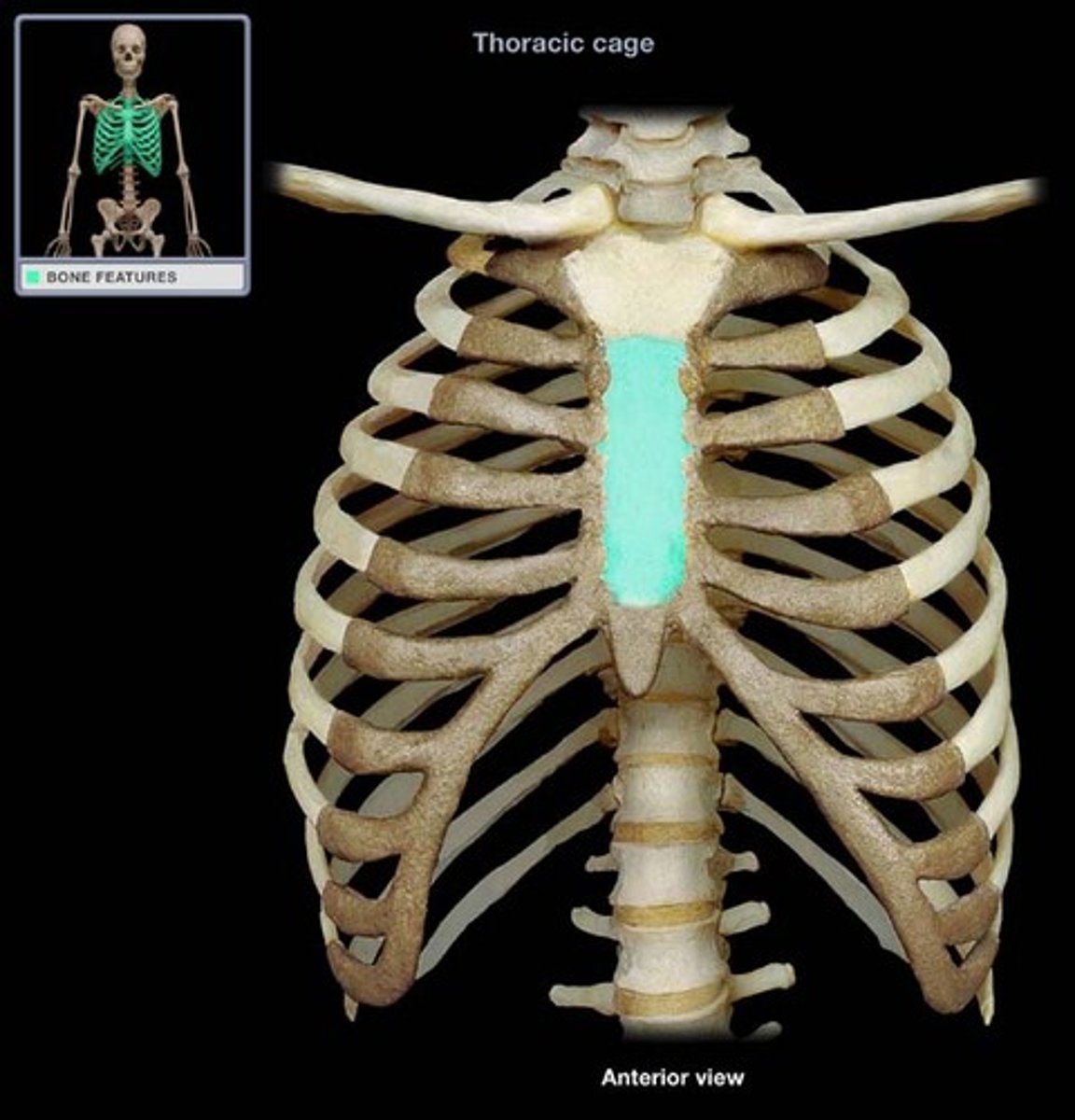
body of sternum
large middle portion of the sternum
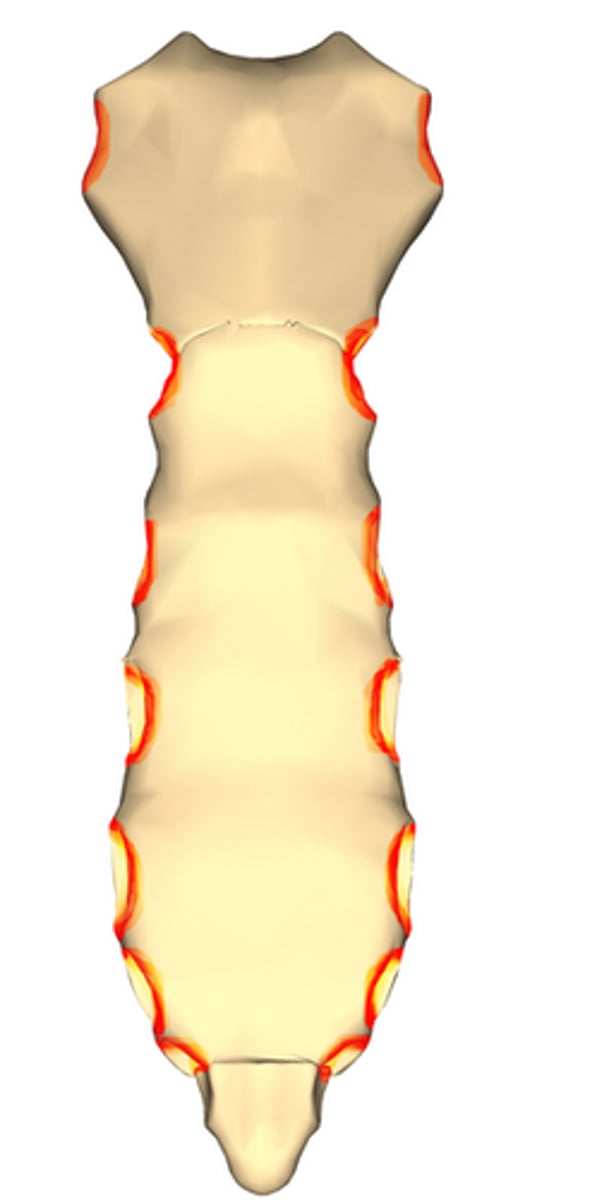
costal notches of sternum
indentations on sternum where costal cartilages from the ribs articulate
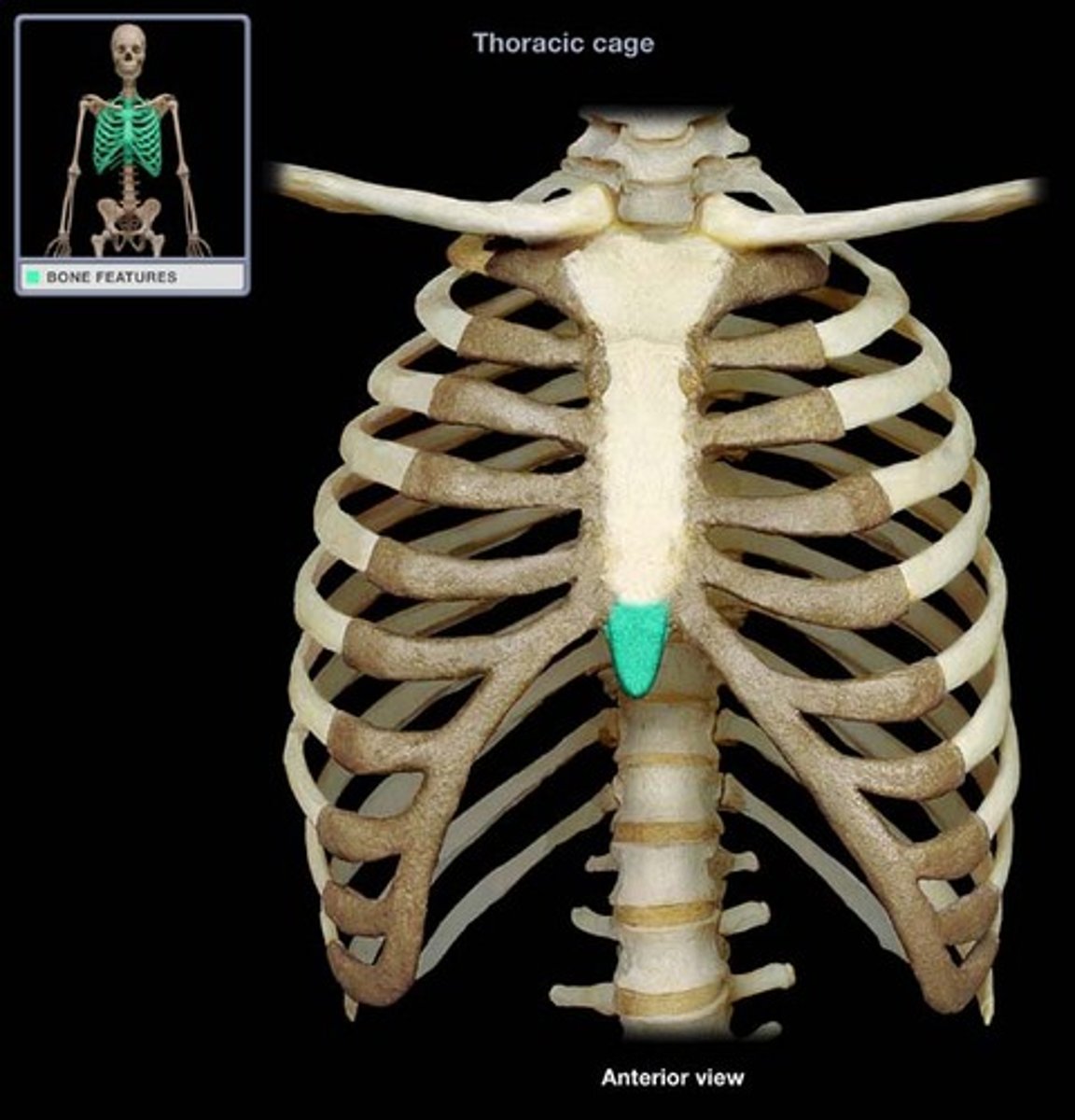
xiphoid process
lower, narrow portion of the sternum
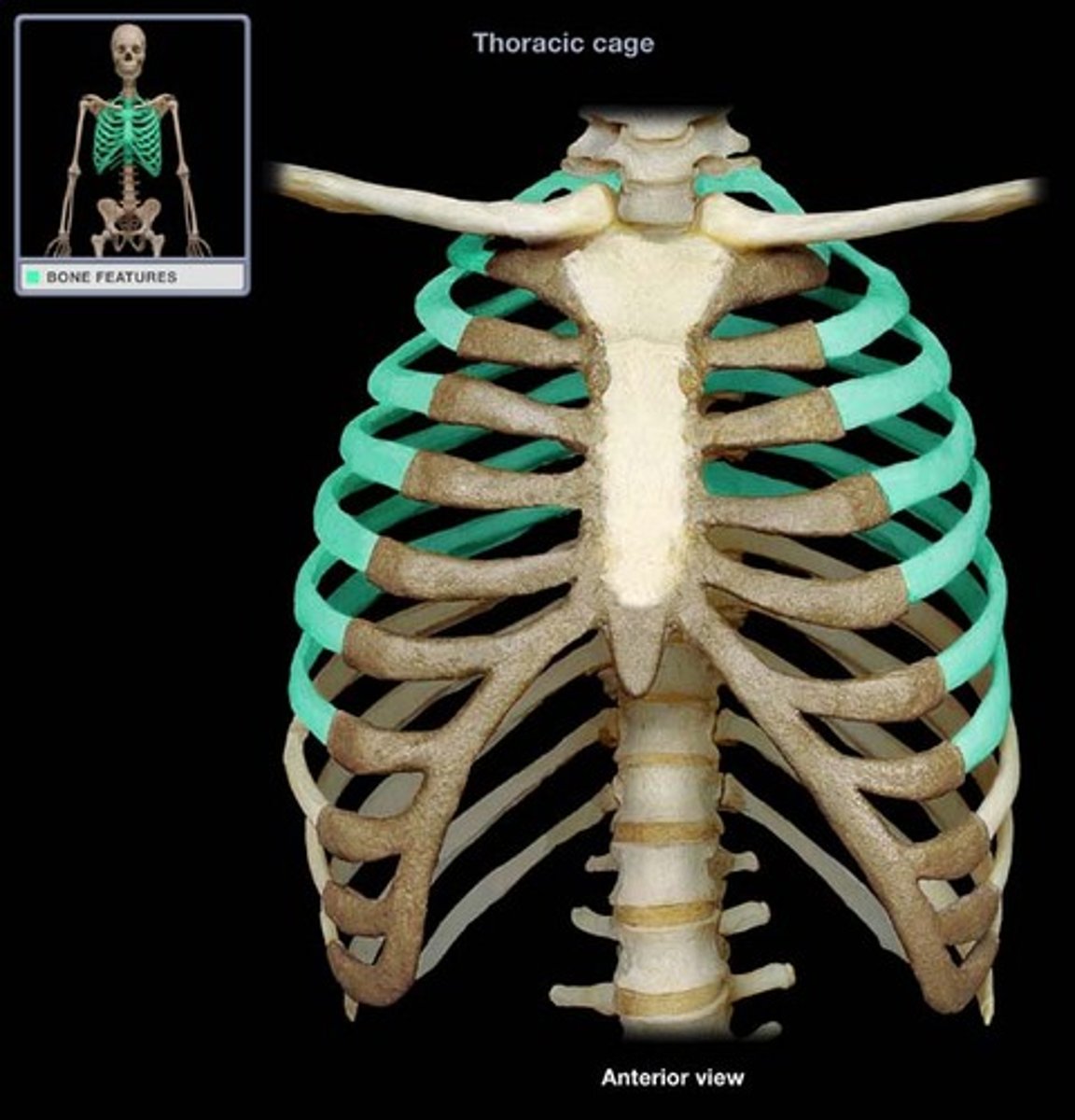
True ribs (1-7)
Cartilage leads to sternum
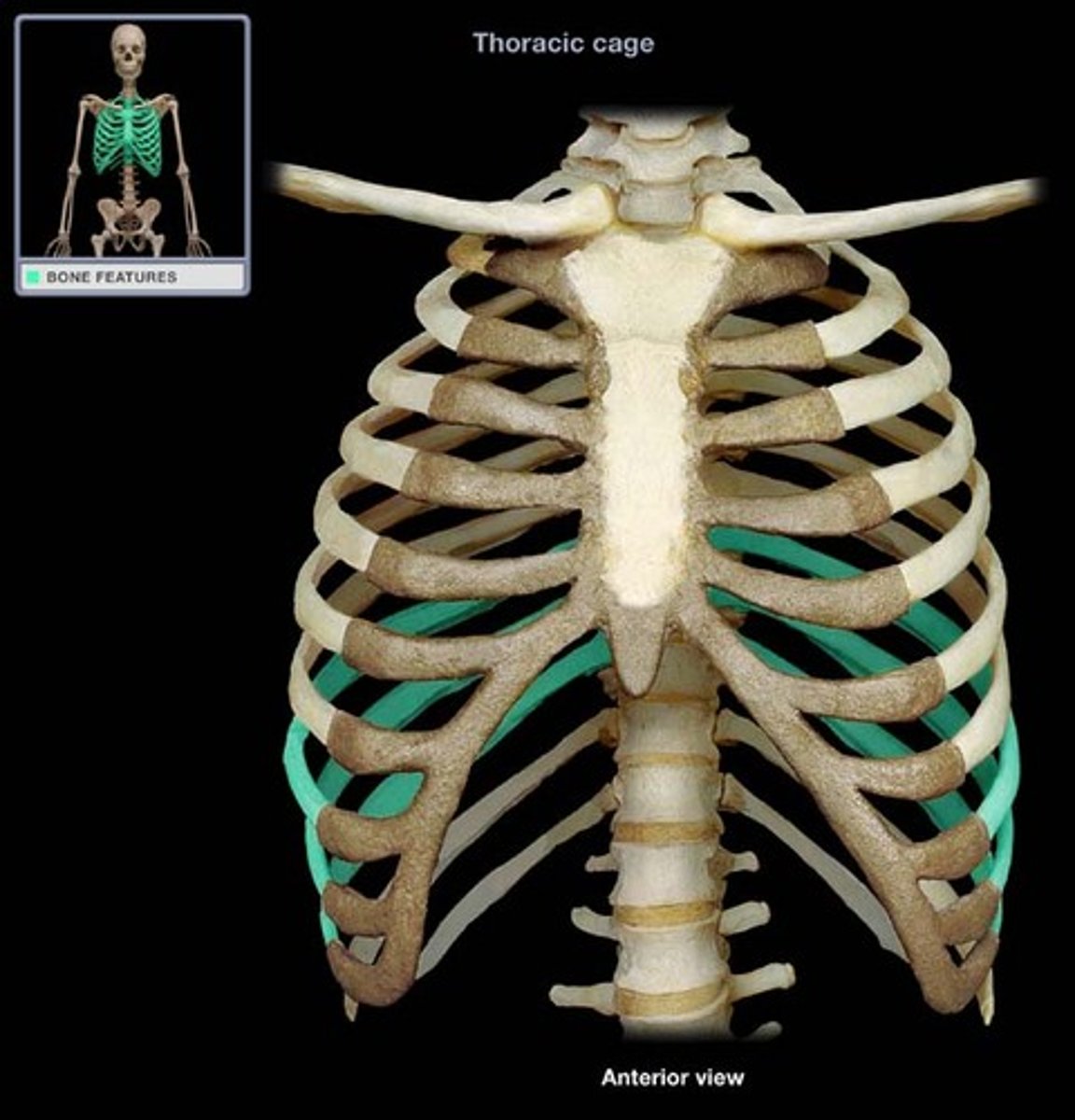
false ribs (8-12)
ribs that do not have a direct attachment to the sternum
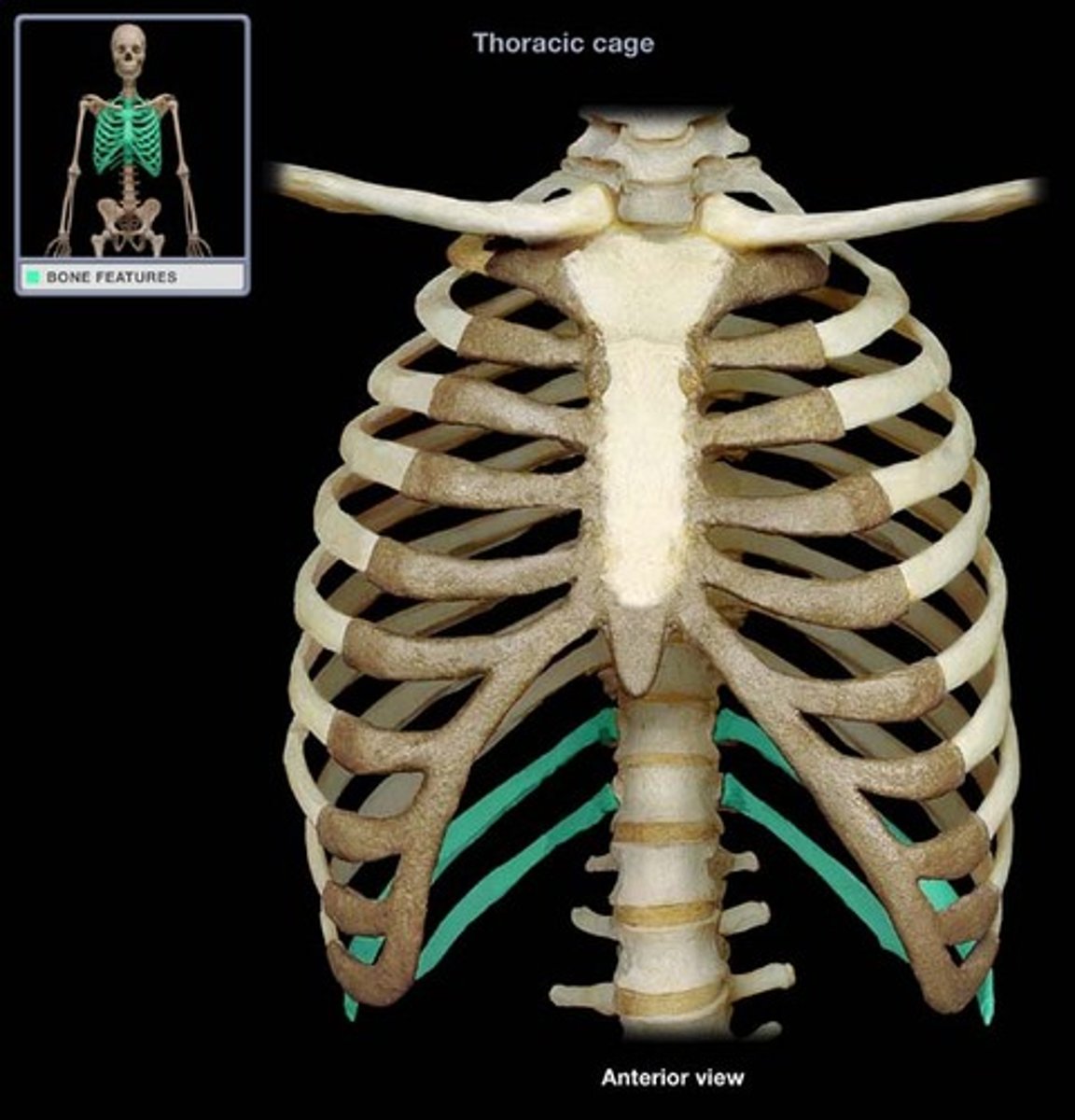
floating ribs
last two pairs of ribs; do not attach to sternum
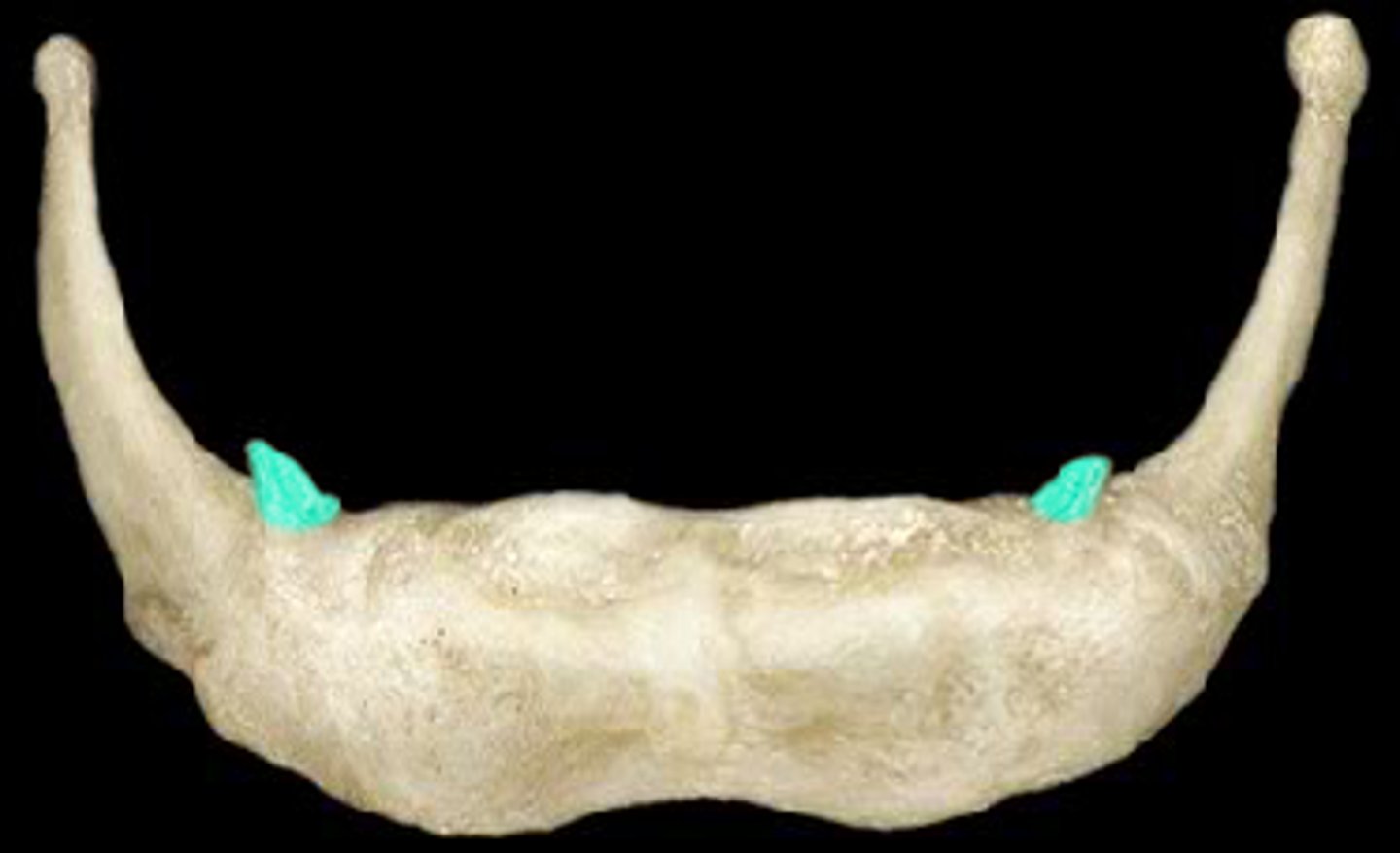
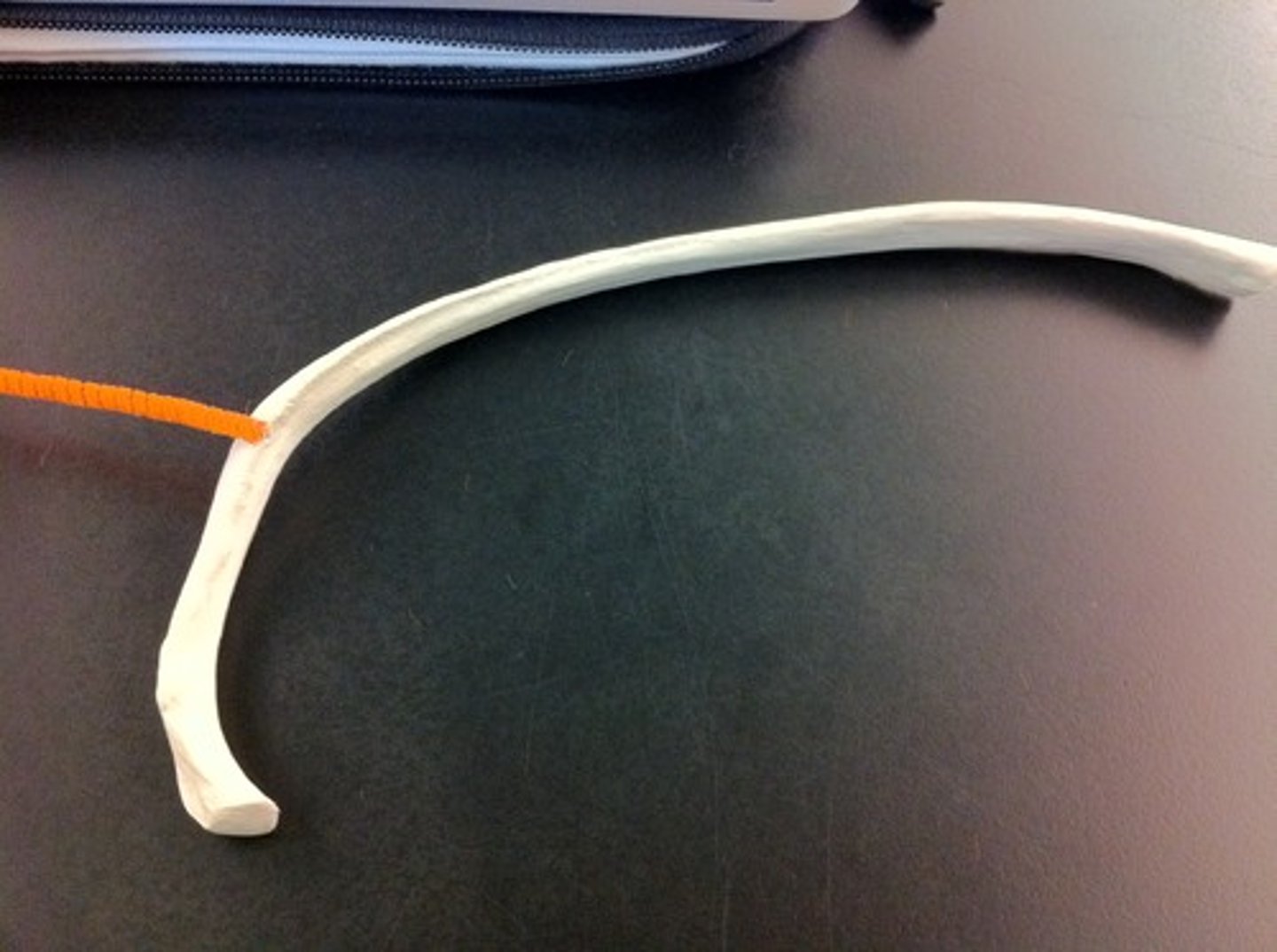
head of rib
Articulates with the costal facet of a thoracic vertebral body
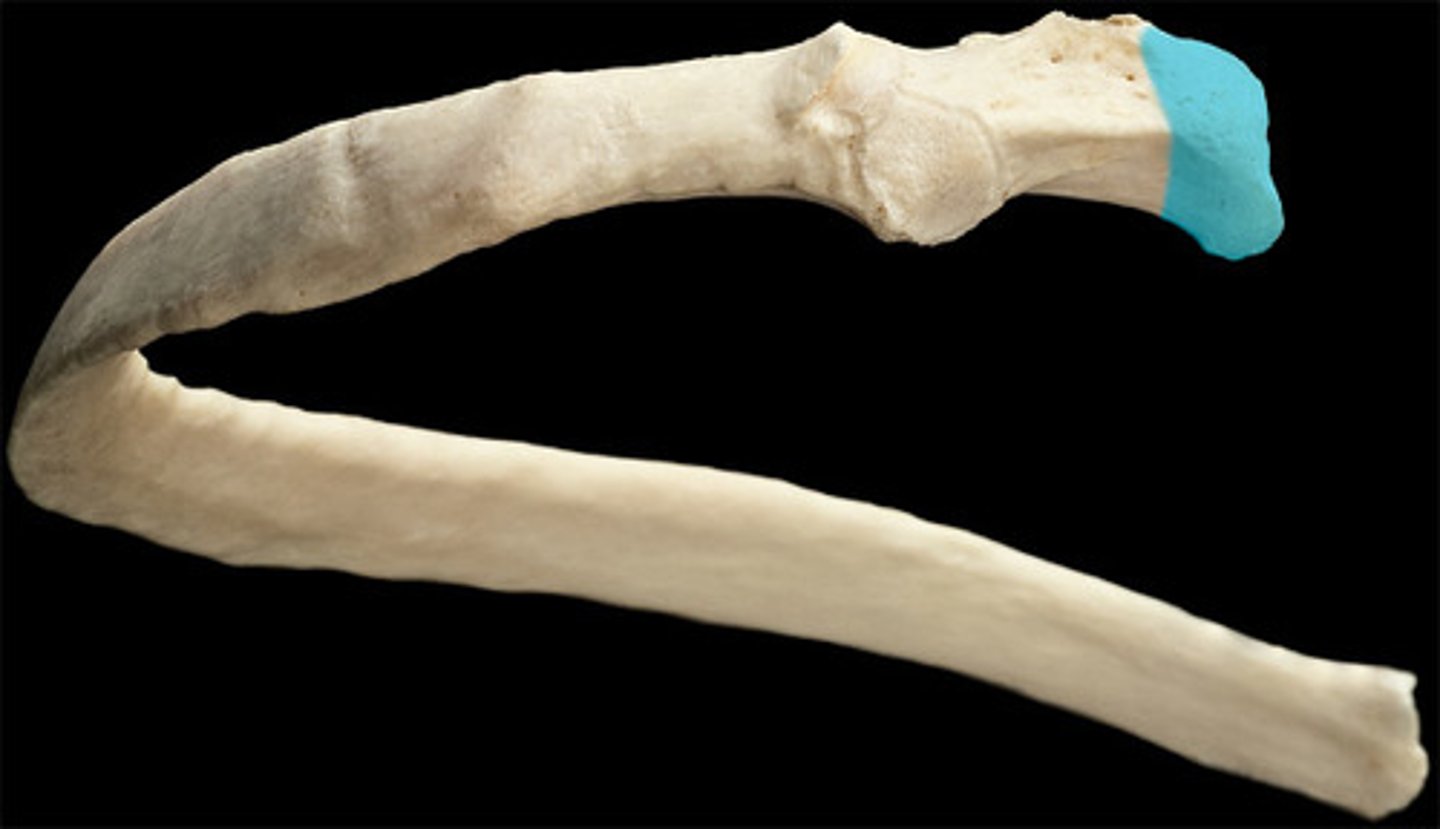
superior articular facet of rib
articulates with inferior costal demifacet of the thoracic vertebral body one numeric segment superior
inferior articulating facet of rib
articular surface at bottom of rib
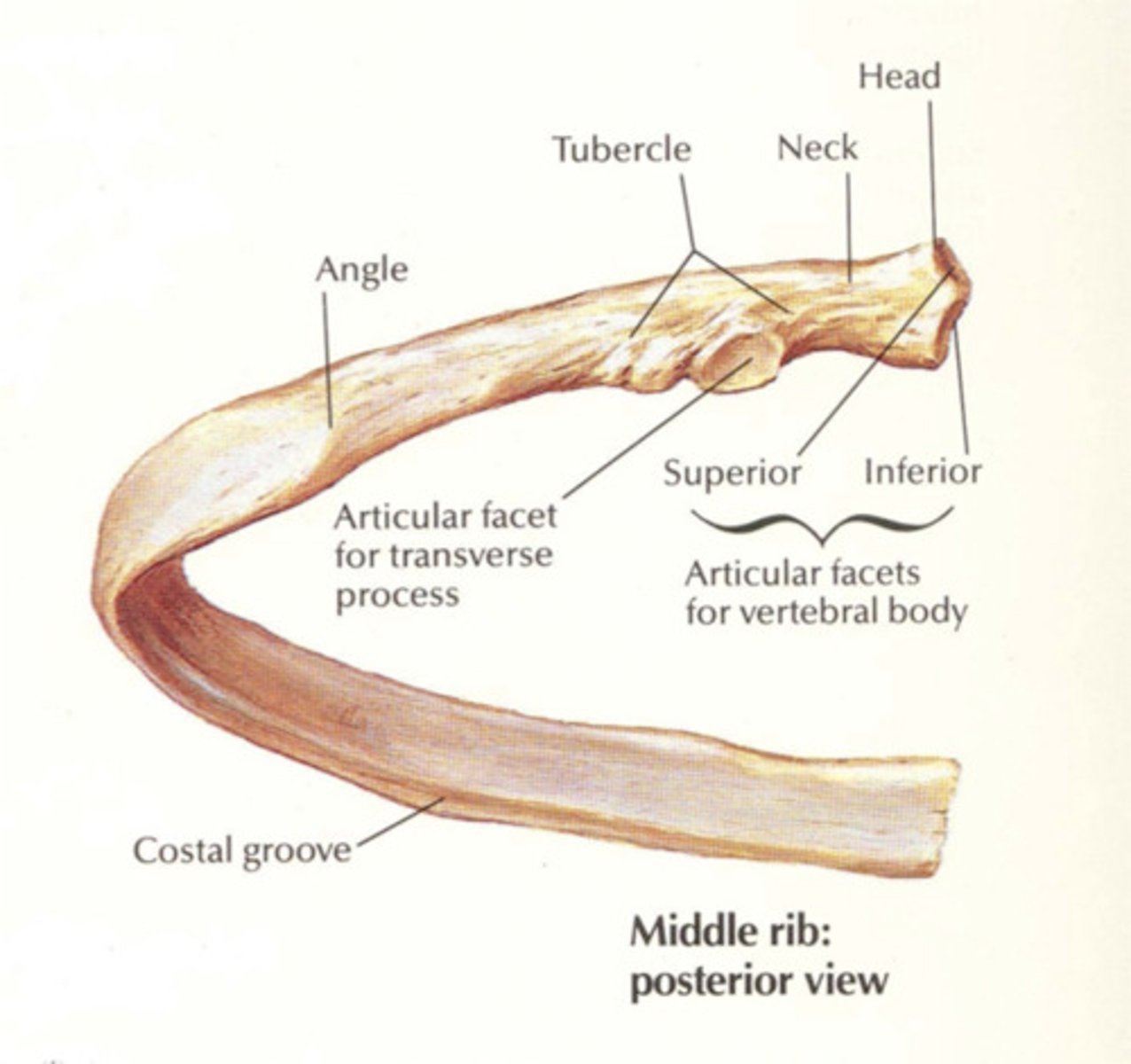
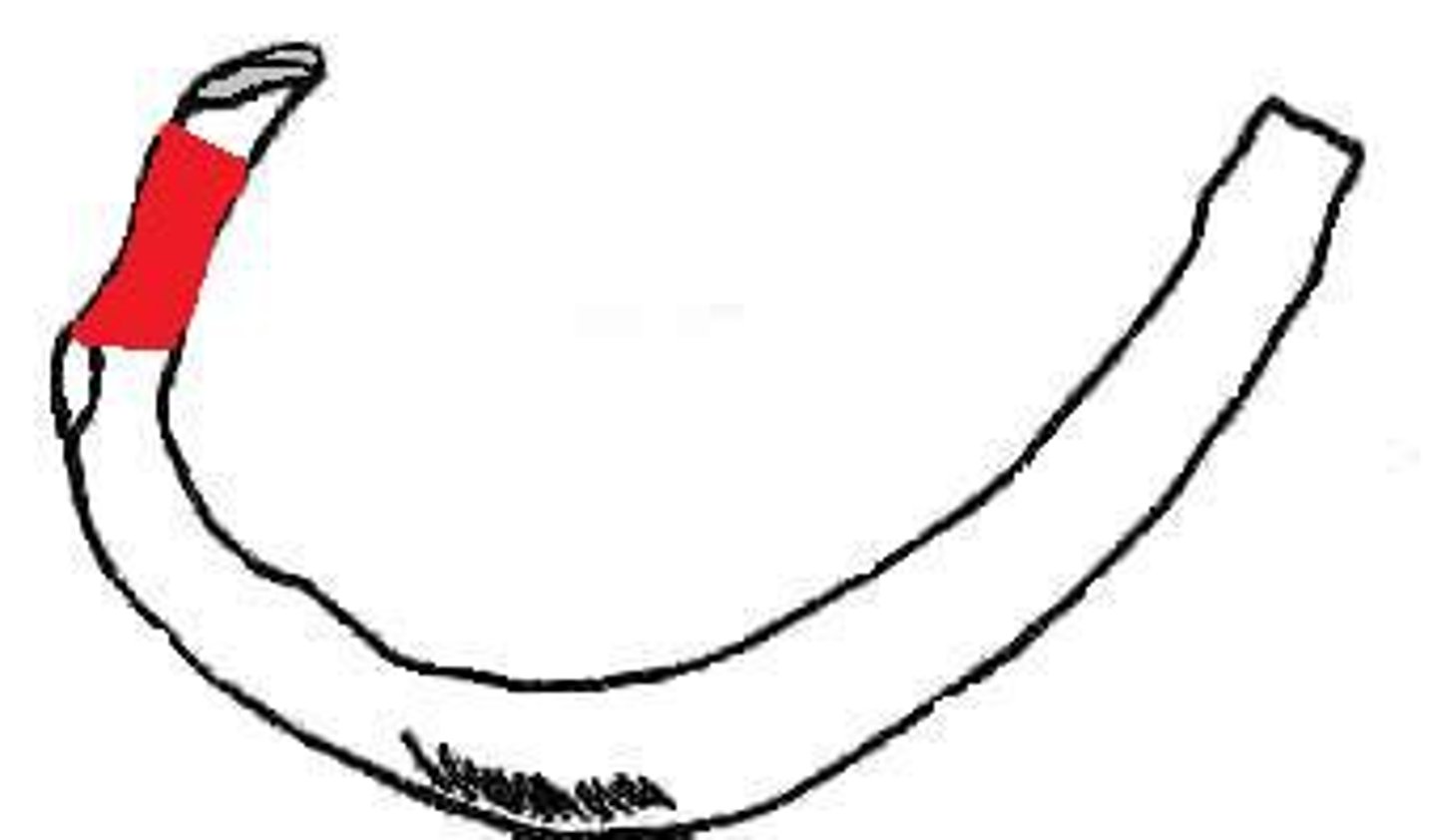
neck of rib
between head and tubercle
tubercle of rib
bump on head (lower) points down
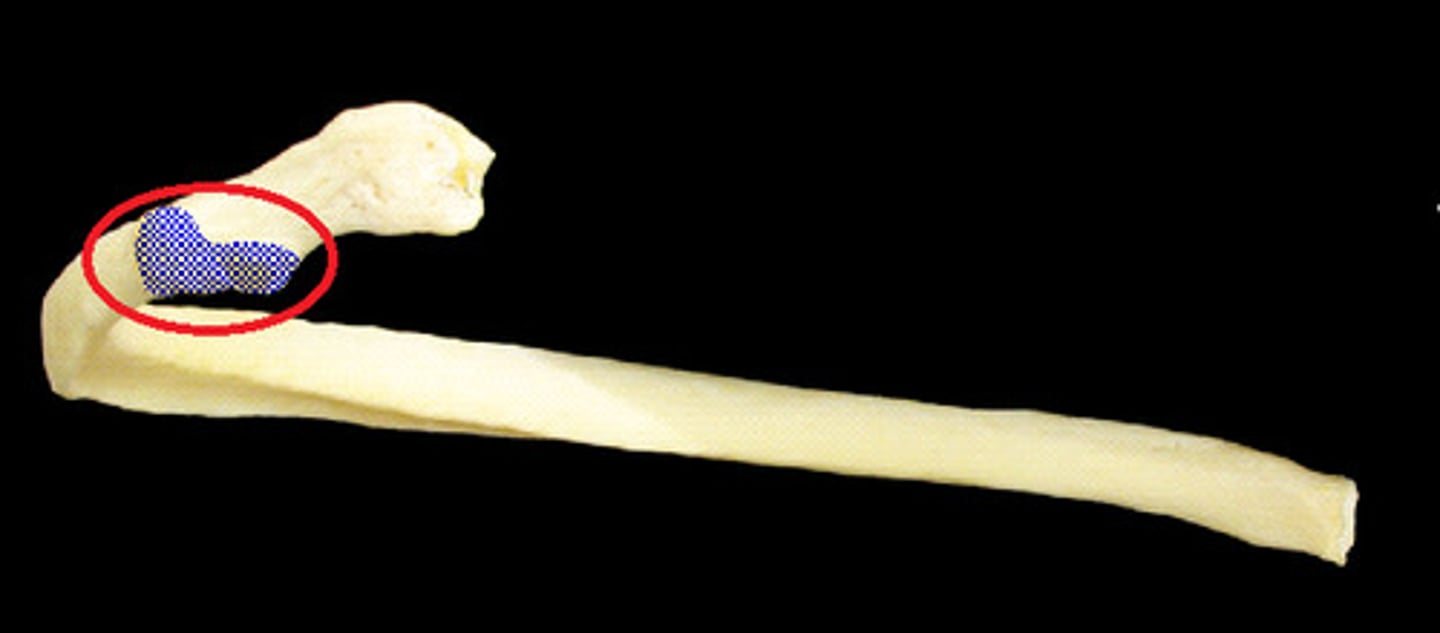

Angle of rib
where rib bends

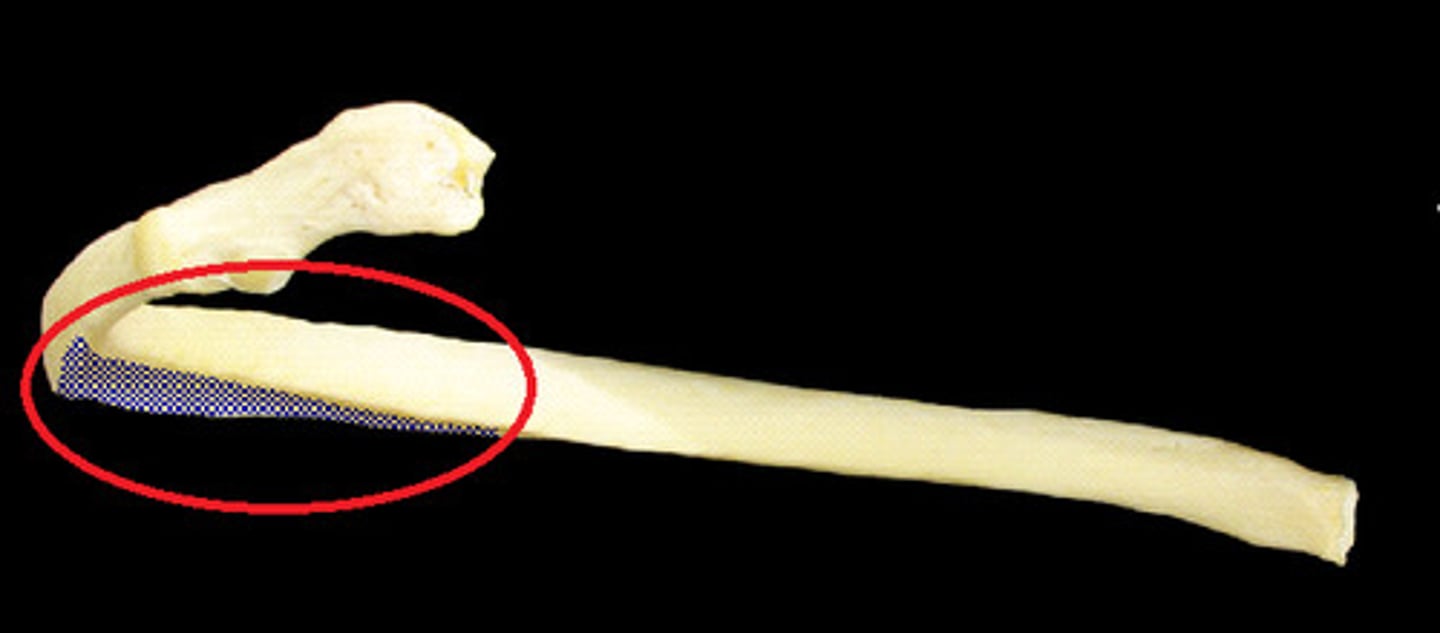
Costal groove of rib
groove on the inferior side of the rib shaft
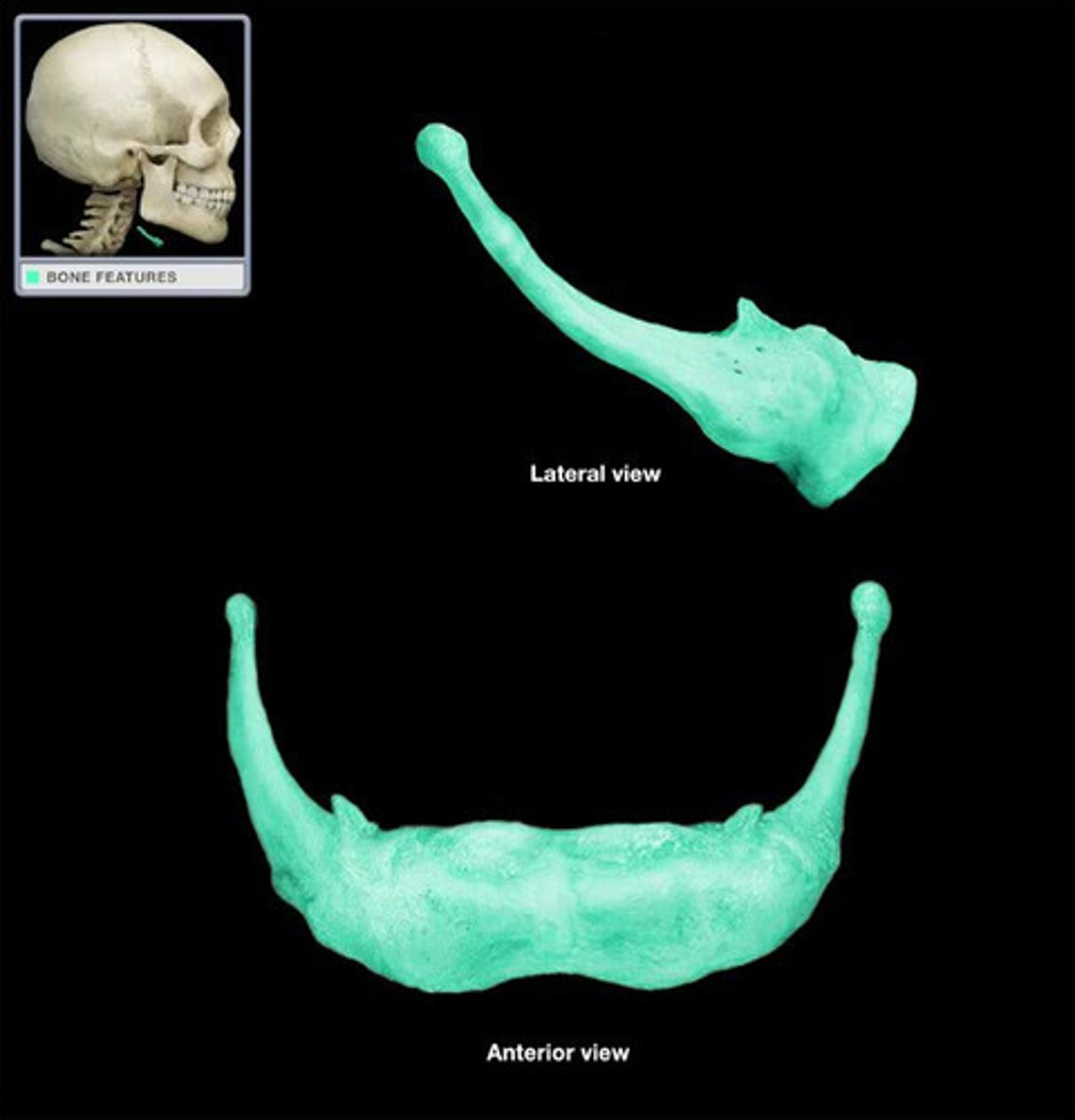
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
body of hyoid bone
middle of bone
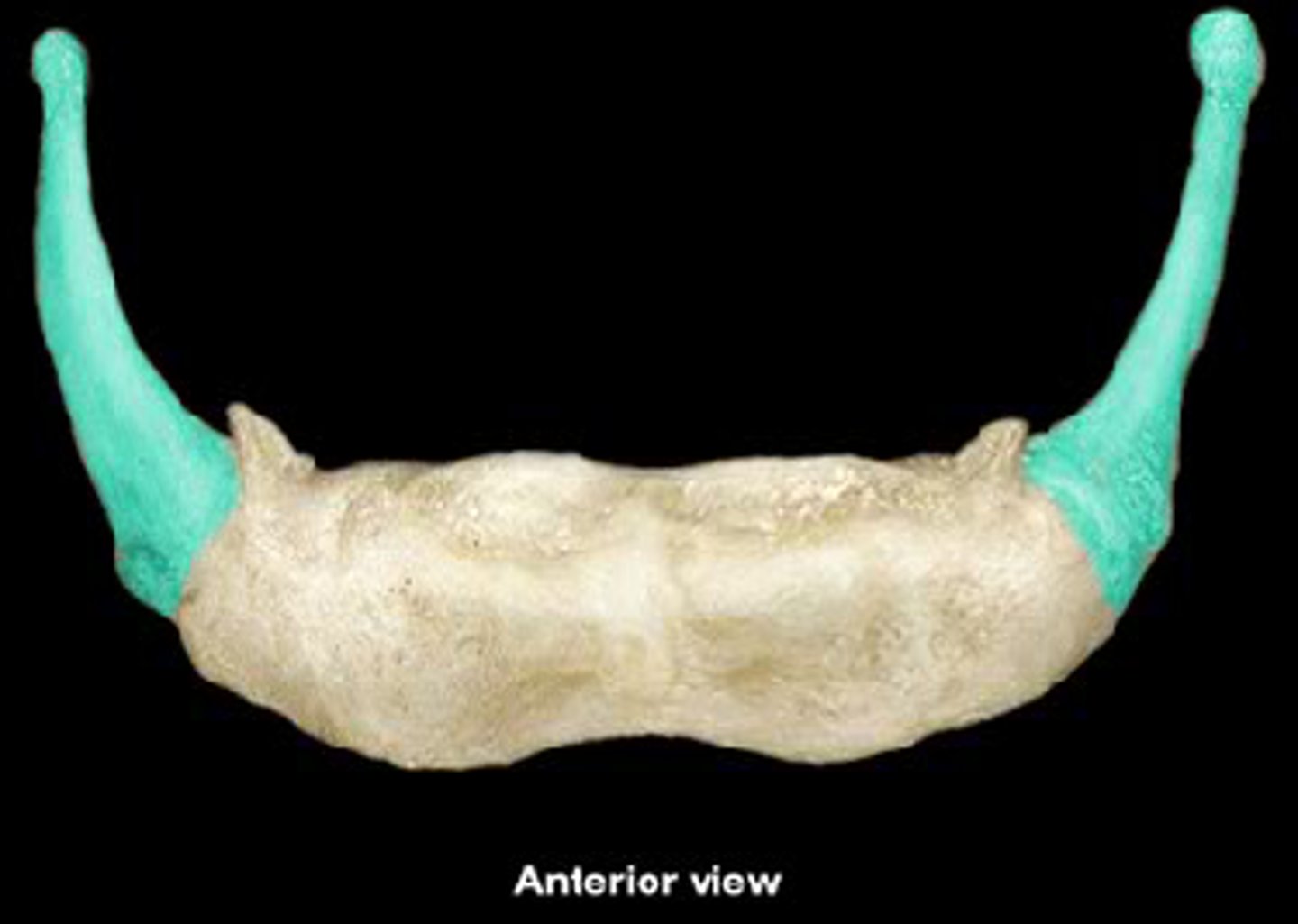
greater cornu/horns of hyoid bone
long projections on back
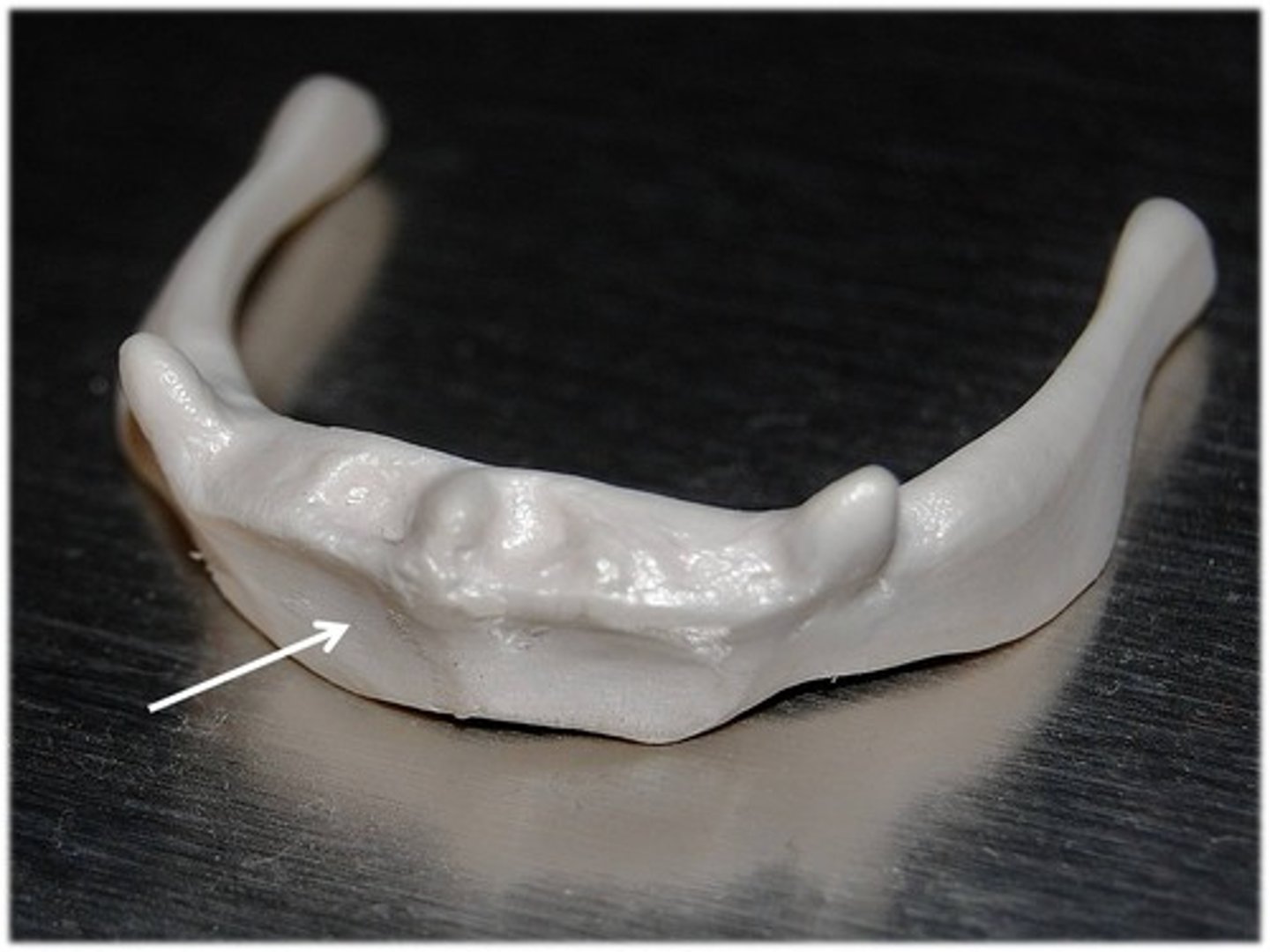
lesser cornu/horns of hyoid bone
teeth like projections