BIS 2B Properties of Life Midterm 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What are the properties of life?
Order and Organization
Energy Processing
Growth and Development
Evolutionary Adaptation
Regulation (Homeostasis)
Reproduction
Response to Stimuli
Of Every Girl Everywhere Rarely Risks Relationships
What is the smallest possible unit of life?
Cell
What is ecology?
Study of how organisms interact with each other, and with the environment in which they live
What is evolution?
Study of changes in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations
What is the biosphere?
All life lives within 10km within the surface of the earth
Why is the biosphere so compatible for life?
Water, Sunlight, Temperature
What is latitude
How north or south of the equator you are
each degree ~69 miles
What are the precipitation trends?
Rain near equator, dry 30 degrees north and south
What are hadley cells
patterns of atmospheric ciruclation with air rising near the equator (rain) and descending as dry air at 30degrees north and south
equator hot → warm moist air rises → cooler atmosphere condenses cloud → rain → cool dry air descends → desert
How does the earth’s tilt change affect temperature/season
when northern hemisphere tilted away → winter
northern hemisphere tilted towards → summer
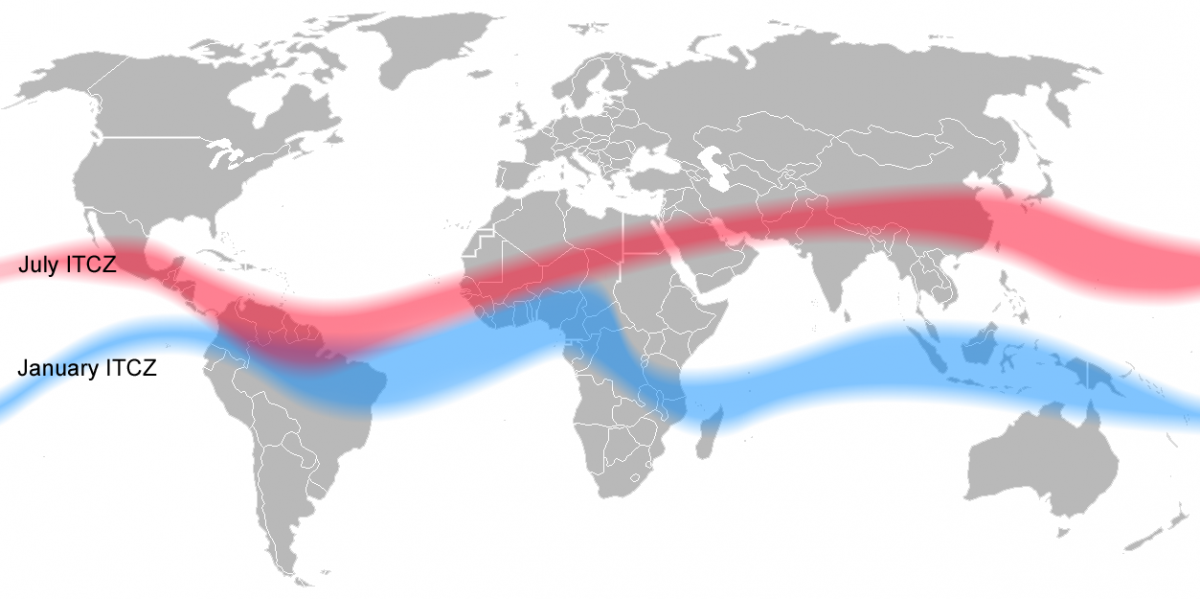
what is the intertropical convergence zone?
thermal equator:
band of clouds that shifts up and down throughout seasons
if above equator, june/july
if below, january
What does windward mean?
air rises, cools, and rains
side of mountain facing ocean
What does leeward mean?
dry air decends and warms
What is weather?
current, short-term atmospheric conditions
What is climate?
average atmospheric conditions/patterns/cycle over a longer period of time
How does visible light from the Sun interact with the Earth?
50% absorbed by the surface, 20% absorbed by the atmosphere, 30% reflected
How does infrared radiation from the Earth interact with the atmosphere/surface?
visible light/solar radiation → hitting Earth → Earth emits infrared radiation → atmosphere absorbs infrared radiation → radiates it back to Earth
What is the greenhouse effect?
Infrared radiation emitted by the Earth → getting absorbed by atmospheric gas → radiating back to earth
Why did CFCs decrease over time, also why was it bad?
World governments came together to ban the substance
CFCs depleted the ozone layer
What is the cryosphere?
all the frozen water on earth’s surface
How does thermal expansion contribute to sea level rise?
Warmer things are bigger
Ocean absorption vs Atmospheric Absorption
Ocean acts like a thermal sink, can absorb more heat but temperature raises less
What is ocean acidification?
ocean absorbing CO2 → creates carbonic acid → fewer carbonate ions → reduced coral health
What is the value of biodiversity?
market value, ecosystem services (bee pollination, wetlands, erosion control), tourism/recreation, life satisfaction, sceince/research, cultural/intrinsic value
What is genetic or trait diversity
different genes or traits within the same species
What is species diversity?
different species occupying same habitat at same time
What is diversity index composed of?
Species richness and species evenness
What does principle of allocation mean?
the limited amount of energy each organism can use for all life processes
• Obtaining food
• Escaping predators/pathogens
• Reproduction
• Growth and metabolic functions
Energy allocated to one function cannot be used for another function
What is C3 photosynthesis?
Most common pathway, 85% of plants use
All mesophyll cells take up CO2 and build sugar
Light reaction and carbon fixation occur at same time
Problems with C3 Photosynthesis
Water escapes from stomata that are open to allow CO2 to enter
C3 Plants perform carbon fixation during the daytime so water loss is unavoidable
Photorespiration occurs if they close stomata
oxygen binds onto rubisco, depletes carbon rather than fixing it
Wastes ATP
What is C4 Photosynthesis
Occurs in 3% of plants
Uses PEP-C and Rubisco
Carbon fixation and sugar building are separated
- CO2 + PEP-C → C4 → Moves C4 into different location → C4 + Rubisco → Glucose
Able to concentrate CO2 in area near Rubisco to reduce photorespiration waste
Problems with C4 Photosynthesis
Requires 2 extra ATP per sugar molecule
What is CAM Photosynthesis?
Occurs in 7% of Plants
CO2 and Sugar-building are separate in time
Open stomata at night, store CO2 as acid in vacuole
Close stomata during day, convert acid back to CO2 to build sugar
Night: CO2 + PEP-C → Malate (acid)
Day: Malate + Rubisco → Glucose
Very water efficient, less photorespiration than c3
good for plants with few competition and low water
Problems with CAM Photosynthesis
Requires 2 extra ATP per sugar molecule
slows growth due to temporal restriction
What is the relationship between nitrogen legumes and rhizobium?
(mutualistic relationship) rhizobium bacteria live in the roots of legumes that help fix nitrogen (converts nitrogen gas into ammonia)
allows legumes to thrive in soils with limited availble nitrogen
bacteria creates fertilizer for the legume
What is the relationship between plants and mycorrhizal fungi?
Mutualistic relationship, allows plants roots to stretch further to access additional water/nutrients (phosphorous)
Fungal cells penetrate/wrap around root
Fungi get sugars from plant
80-90% of plants have this
What is Liebig’s law of the minimum?
Plant growth is determined by the amount of the resource that is most scarce compared to what the plant needs
autotrophs vs heterotrophs
autotrophs must grow
heterotrophs must move (time management)
What determines foraging decisions?
Guiding principles: optimize rate of benefits through time
trade-off between handling time and calorie amount
E1/H1 and E2/H2
E1 and E2 are the energy values of large prey and small prey
H1 and H2 are the handing times of large prey and small prey
What are fundamental niches?
The abiotic conditions in which a species can survive and reproduce (ex. temperature, precipitation, soil type)
What are realized niches?
The biotic conditions that determines where the species occurs (interactions with other species)
What are some responses to abiotic stress?
Acclimation
physiological changes in response to experienced conditions
Adaptation
Heritable evolutionary changes in populations over generations driven by natural selection
What is the Root:Shoot ratio?
More sun → More Shoots
More water → More roots
Root/Shoot
Why does temperature matter?
Affects:
rates of reactions
shapes of proteins
membrane properties
Endotherms vs Ectotherms
Endotherm: constant body temperature, metabolism decreases with temperature
Ectotherm: body temperature equilibrates with room temperature, metabolism increases with temperature
How do ectotherms reduce temperature stress?
Behavioral strategies such as burrowing and basking
How do plants thermally regulate?
Water travels up the xylem and evaporates through open stomata
Orient their leaves vertically
Highly reflective leaves
Leaves are far away from ground to reduce radiation
Open wide structure for more wind
Describe the stress and risk of predation biotic favotr
P(predator eating prey) = P(detection) x P(capture) x P(Consumption)
Detection: Prey camouflage
drawbacks: less productive/optimized, restricted to location
Capture: Prey travel in large schools (Fish)
Consumption: Prey are hard to eat
Physical: porcupine/thorns
Chemical: Poison/Toxicity
What are the growth-defense trade offs?
More tannin = less growth
What is the life history strategy?
The way organisms allocate resources to growth, reproduction, and survival based on genetic and environmental factors
What is the life history/allocation of resources in young organisms?
Mostly growth, some maintenance, low storage
What is the life history/allocation of resources in old organisms?
Mostly reproduction, some maintenance, some storage, low growth
What does semelparous mean?
Organisms that reproduce once and then die
What doe iteroparous mean?
Organisms that reproduce many times throughout their lifespan
R strategist behaviors
Survivorship
short life span
density independent mortality
type 3 curve
Reproductive strategy
reproduce once
large number of offspring
large allocation of resources to reproduction
Population growth
exponential growth followed by periodic/seasonal decline
k strategist behaviors
Survivorship
long life span
density dependent mortality
type 1 or 2
Reproductive strategy
reproduce more than once
greater allocation of resources to growth rather than reproduction
fewer offspring
population growth
slow rising
stabilizes at/near carrying capacity
What is fecundity?
average amount of offspring a group will produce during that age class
What is the net reproductive
rate?
the mean number of offspring produced per individual across their lifetime
sum of lxmx
What is generation time?
G = sum of xlxmx / sum of lxmx
What is the formula for r?
ln(R0)/G