Nervous System and Brain: Neurons, Glia, and Cranial Nerves
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is the trigger zone?
The trigger zone is the area of a neuron where action potentials are initiated, typically located at the axon hillock.
What are the different types of neurons?
The main types of neurons include multipolar neurons (many processes), bipolar neurons (two processes), and unipolar neurons (one process).
What is axonal transport?
Axonal transport is the process by which materials are moved along the axon of a neuron, which can be anterograde (away from the cell body) or retrograde (toward the cell body).
What are the six types of glial cells?
The six types of glial cells are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, Schwann cells, and satellite cells.
What are the differences between Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes?
Schwann cells myelinate axons in the peripheral nervous system, while oligodendrocytes myelinate axons in the central nervous system.
What are nodes of Ranvier and internodes?
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath of an axon, while internodes are the segments of the axon that are covered by myelin.
How do unmyelinated vs. myelinated nerve fibers differ?
Myelinated nerve fibers (large diameter) conduct impulses faster due to saltatory conduction, while unmyelinated fibers (small diameter) conduct impulses more slowly.
What is a regeneration tube?
A regeneration tube is a structure formed by Schwann cells that guides the regrowth of a damaged axon.
What is denervation atrophy?
Denervation atrophy is the wasting away of muscle tissue due to loss of nerve supply.
What are local potentials?
Local potentials are small changes in membrane potential that occur in response to stimuli, which can lead to action potentials if they reach a threshold.
What is hyperpolarization?
Hyperpolarization is an increase in the membrane potential of a cell, making it more negative and less likely to fire an action potential.
What are the two types of refractory periods?
The two types of refractory periods are the absolute refractory period (no action potential can occur) and the relative refractory period (a stronger than usual stimulus is needed to elicit an action potential).
What is saltatory conduction?
Saltatory conduction is the process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to another along a myelinated axon, increasing the speed of conduction.
What are pre- and post-synaptic neurons?
Pre-synaptic neurons release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, while post-synaptic neurons receive these neurotransmitters.
What are the four major categories of neurotransmitters?
The four major categories of neurotransmitters are amino acids, peptides, monoamines, and gases.
What are the embryonic derivations of the CNS?
The central nervous system (CNS) develops from three primary brain vesicles: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
What is the general structural arrangement of the cerebral hemispheres?
The cerebral hemispheres consist of gray matter (outer layer), white matter (inner layer), the cortex (surface layer), and the corpus callosum (connects the two hemispheres).
What do rostral and caudal refer to?
Rostral refers to the front or head end of the body, while caudal refers to the back or tail end.
What are the layers of the meninges?
The meninges consist of three layers: dura mater (outer), arachnoid mater (middle), and pia mater (inner).
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is the inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, often caused by infection.
How many ventricles are in the brain?
There are four ventricles in the brain: two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle.
What are the three functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
The three functions of CSF are to cushion the brain, provide buoyancy, and remove waste products.
What is the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain barrier is a selective permeability barrier that protects the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass.
What is the order of the brainstem from rostral to caudal?
The order of the brainstem from rostral to caudal is the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
How many cranial nerves are there?
There are twelve cranial nerves, each with specific functions related to sensory, motor, or mixed activities.
What are the three layers of the meninges?
The three layers of the meninges are the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
What is spina bifida?
Spina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal column does not close completely, potentially leading to nerve damage and physical disabilities.
What are ascending and descending tracts?
Ascending tracts carry sensory information to the brain, while descending tracts carry motor commands from the brain to the body.
What are fascicles, tracts, endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium?
Fascicles are bundles of nerve fibers; tracts are pathways of nerve fibers in the CNS; endoneurium is the connective tissue surrounding individual nerve fibers; perineurium surrounds fascicles; and epineurium surrounds the entire nerve.
How many spinal nerves are there?
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in the human body.
What is poliomyelitis?
Poliomyelitis is a viral disease that can cause paralysis by attacking the motor neurons in the spinal cord.
What is ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
What are the layers in a nerve?
The layers in a nerve include the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium.
What are the different types of nerve fibers?
Nerve fibers can be classified as sensory, somatic, visceral, and autonomic based on their function.
What are the terms posterior root, anterior root, posterior root ganglion, rootlets, anterior/posterior ramus?
The posterior root carries sensory information to the spinal cord, the anterior root carries motor information away, the posterior root ganglion contains sensory neuron cell bodies, rootlets are small branches of roots, and anterior/posterior ramus are branches of spinal nerves that innervate different body regions.
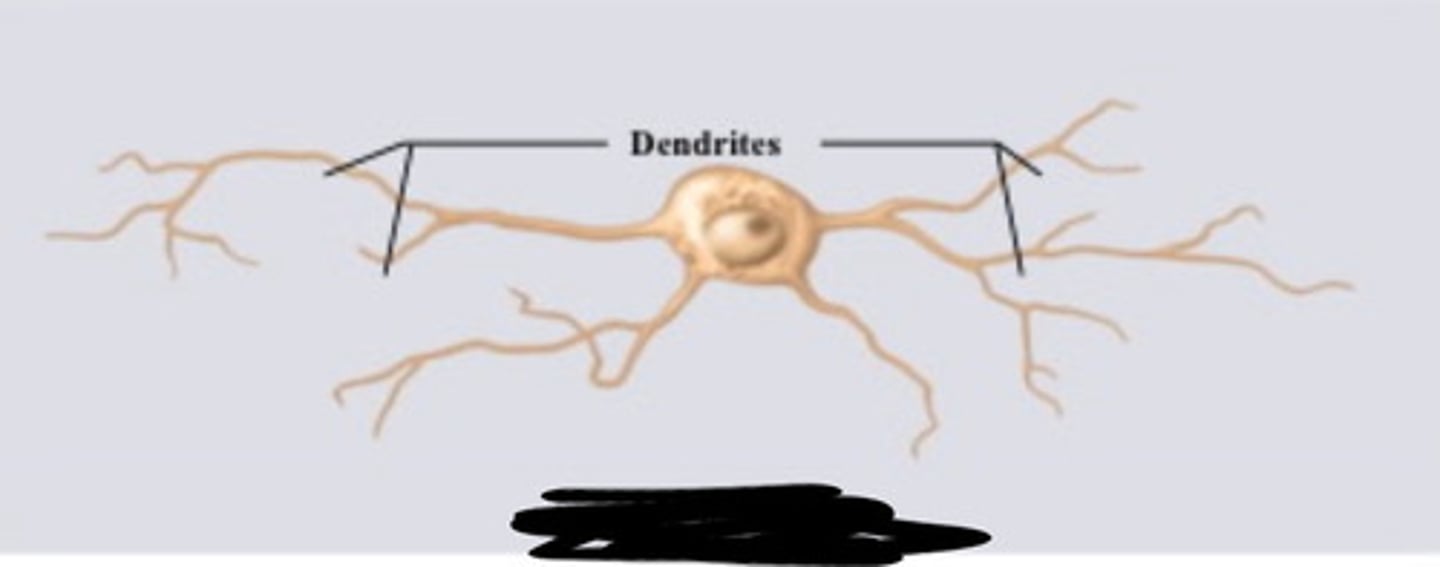
anaxonic neuron
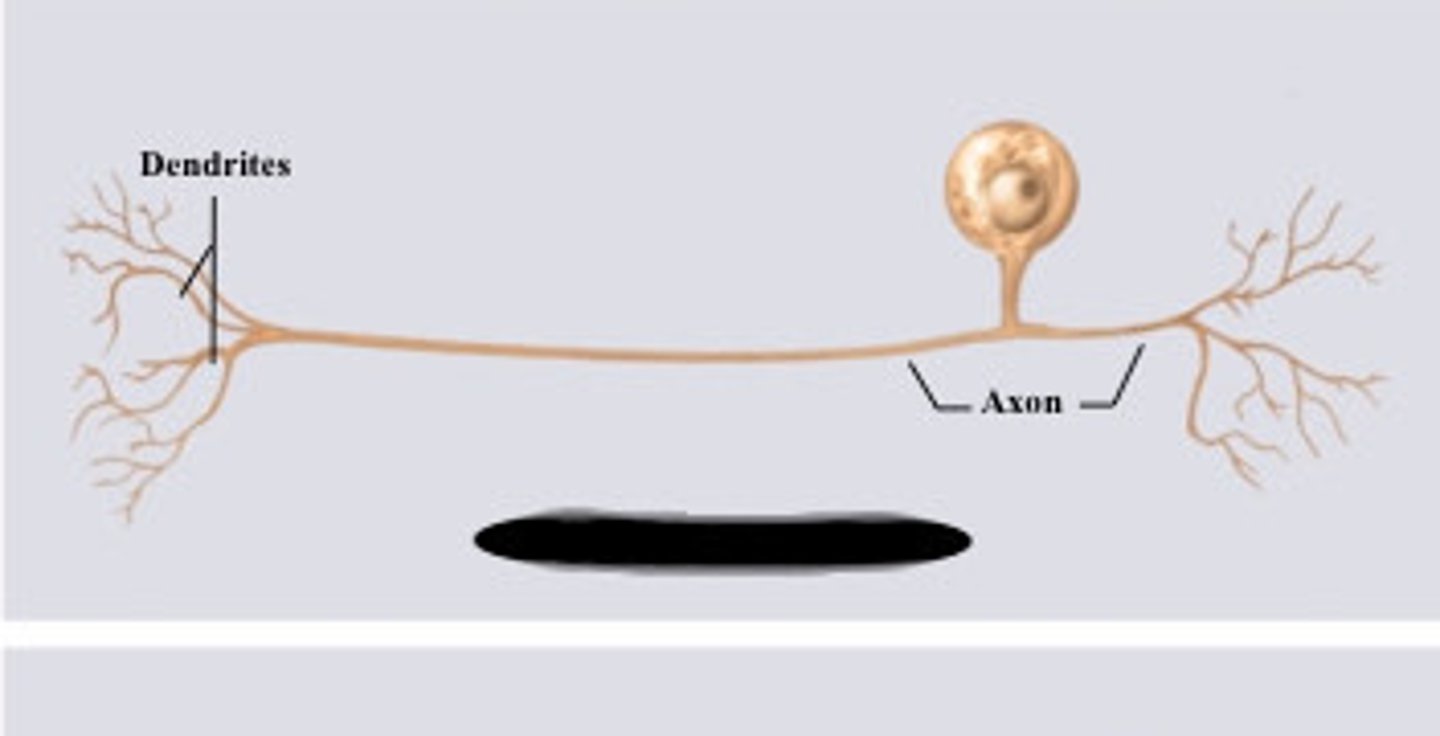
unipolar neuron
bipolar neuron
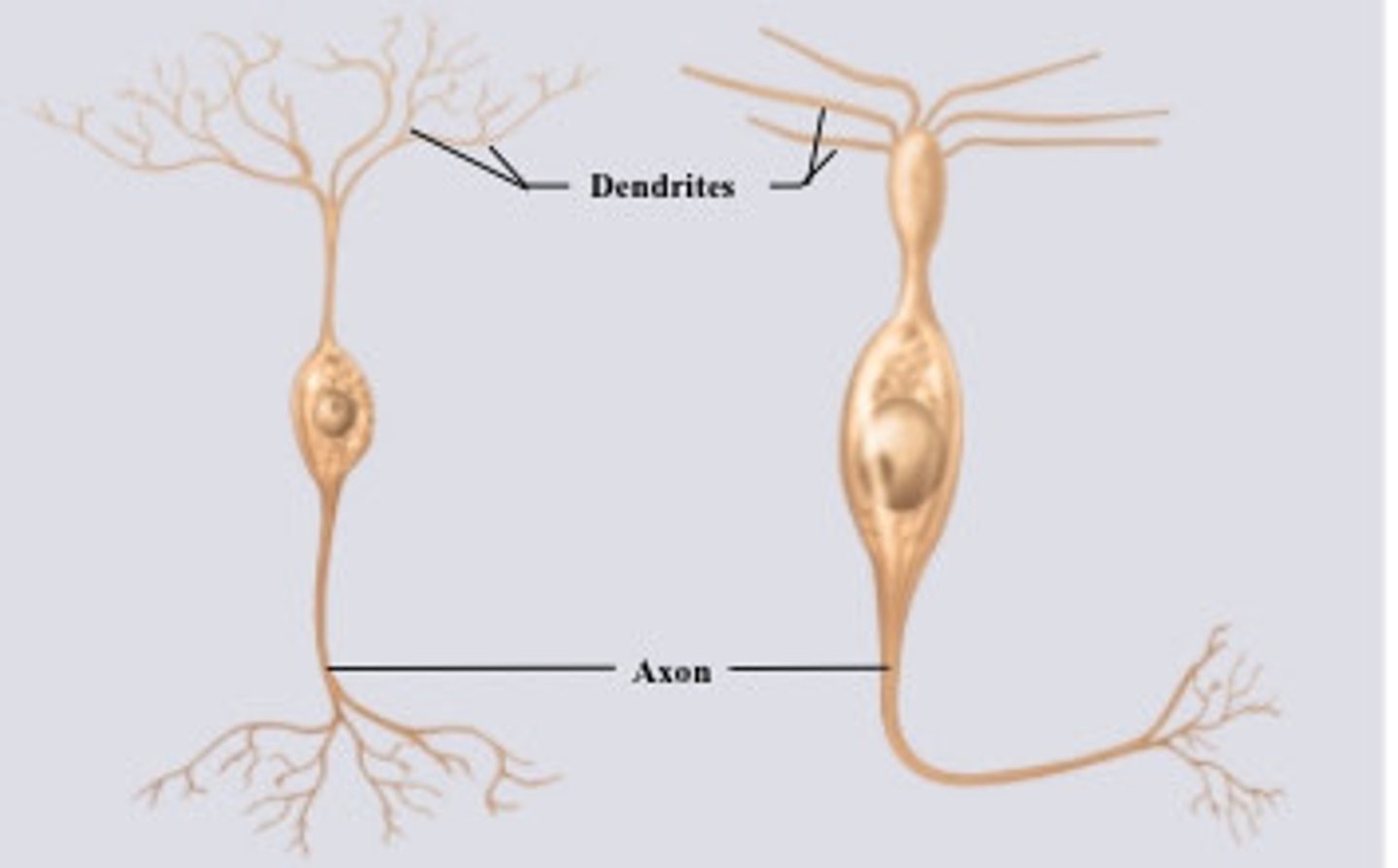
multipolar neuron
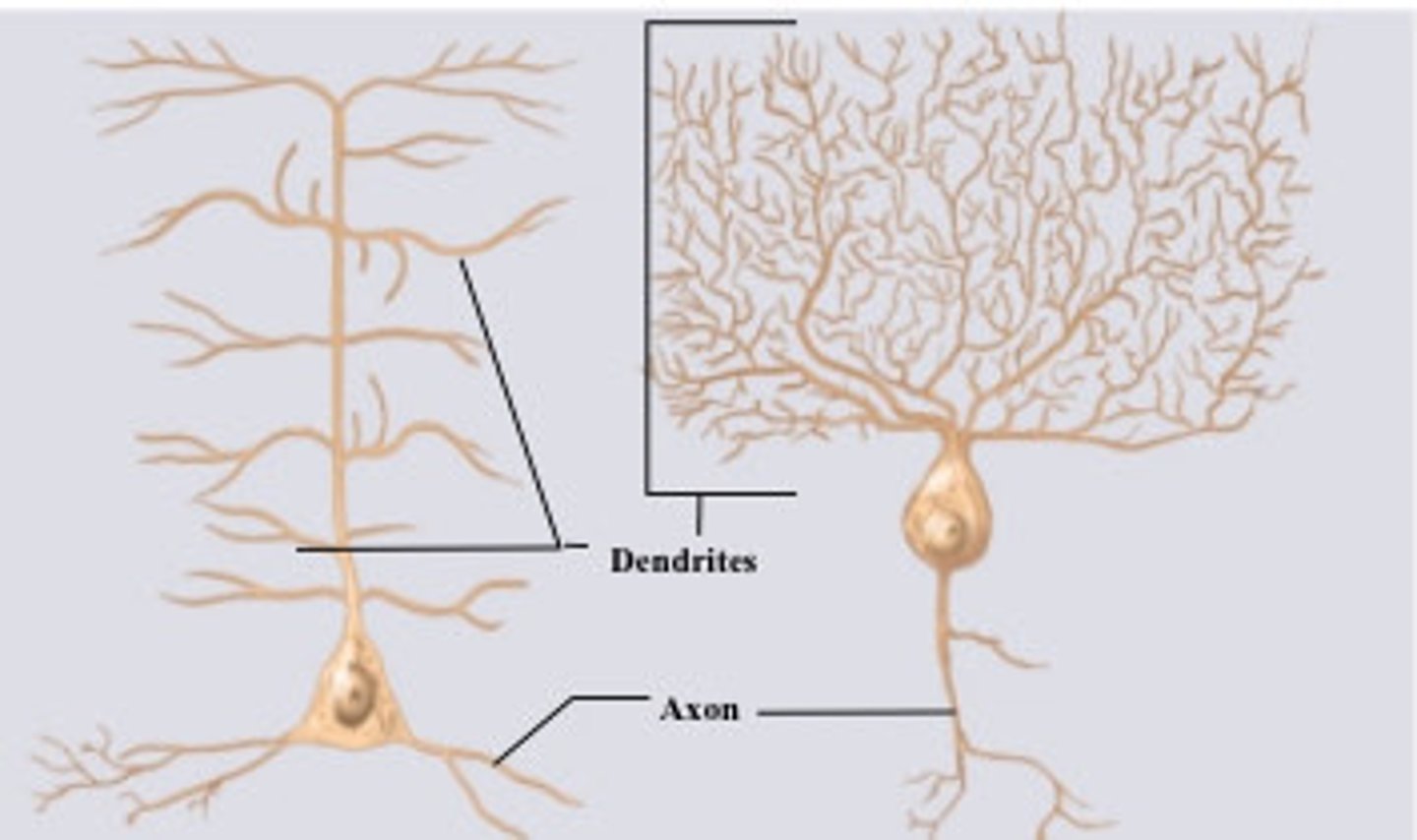
when does absolute refractory period occur?
immediately after an action potential when it is impossible for a neuron or muscle cell to be stimulated again, regardless of the stimulus's strength. It happens during the depolarization and repolarization phases when voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated, preventing further sodium influx and the generation of a new action potential.
when does relative refractory period occur?
after the absolute refractory period, during the repolarization and hyperpolarization phases of an action potential
Where can 2 lateral ventricles be found
cerebral hemispheres
where can the third ventricle be found
midline (forebrain)
where can the fourth ventricle be found
hindbrain
what is the blood-csf barrier
The blood-CSF barrier is defined as a blood-brain interface located at the choroid plexus epithelium that regulates exchanges between the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), inhibiting the free migration of molecules while allowing for transport and signaling functions.
what are the 12 cranial nerves and what are their numbers
Olfactory (1), Optic (2), Oculomotor (3), Trochlear (4), Trigeminal (5), Abducens (6), Facial (7), Vestibulocochlear (8), Glossopharyngeal (9), Vagus (10), Accessory (11), and Hypoglossal (12)
what is the olfactory function?
Smell
what is the optic function?
vision
what is the Oculomotor function?
Eye movement, pupil adjustment, eyelid movement.
what is the Trochlear function?
Eye movement (superior oblique muscle).
what is the Trigeminal function?
Facial sensation, chewing muscles.
what is the Abducens function
Eye movement (lateral rectus muscle).
facial function
Facial expressions, taste, salivary/tear glands.
Vestibulocochlear function
Hearing and balance.
Glossopharyngeal function
Taste, swallowing, salivary glands.
Vagus function
Swallowing, voice, heart rate, digestion.
Accessory function
Shoulder and neck movement (trapezius, sternocleidomastoid).
Hypoglossal function
Tongue movement for speech and swallowing.
what cranial nerves are sensory
CN I (Olfactory): Smell.
CN II (Optic): Vision.
CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear): Hearing & balance
what cranial nerves are motor
CN III (Oculomotor): Eye movement, pupil/lens.
CN IV (Trochlear): Eye movement.
CN VI (Abducens): Eye movement (side-to-side).
CN XI (Accessory): Neck/shoulder muscles.
CN XII (Hypoglossal): Tongue movement.
what cranial nerves are mixed
CN V (Trigeminal): Face sensation & chewing.
CN VII (Facial): Taste & facial expressions.
CN IX (Glossopharyngeal): Taste, swallowing, salivation.
CN X (Vagus): Taste, swallowing, voice, parasympathetic.
Where does an "epidural" take place and when is it given?
An epidural takes place in the epidural space in the lower back, near the spinal cord, using a catheter to deliver pain medication, and is given during childbirth (labor/C-sections), surgery (before/after), or for chronic pain management, often when pain relief is needed for hours or days.
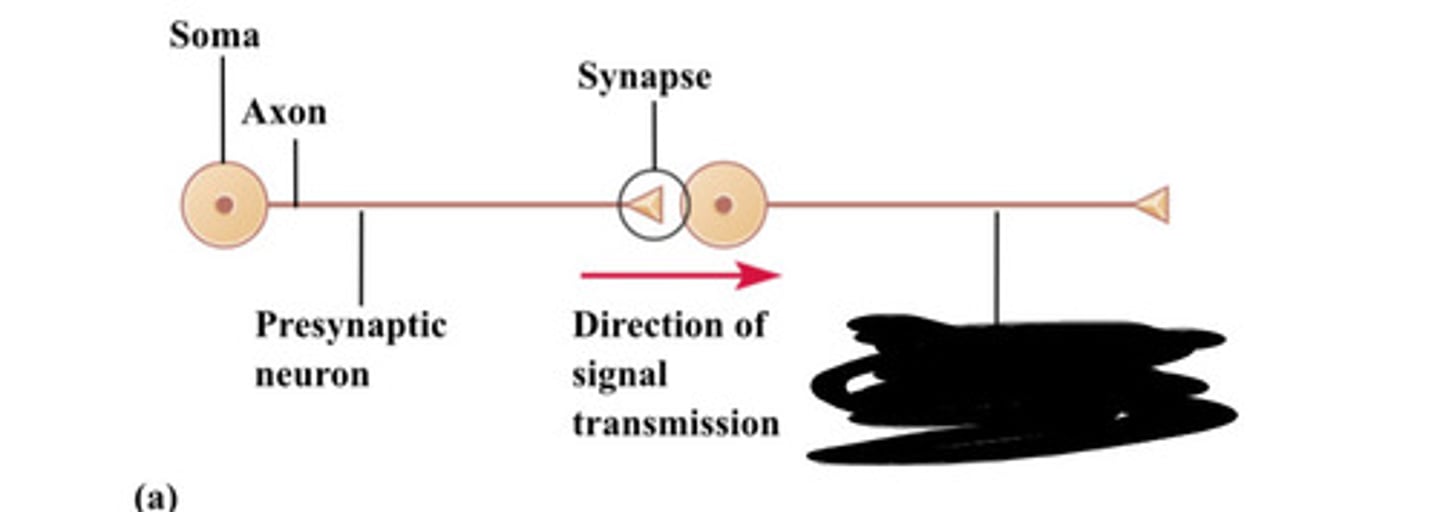
Axon
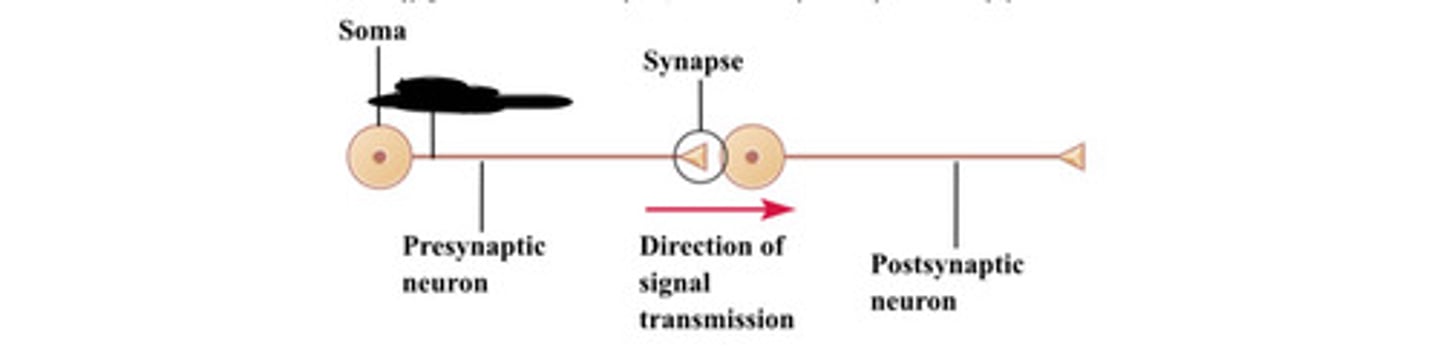
Soma
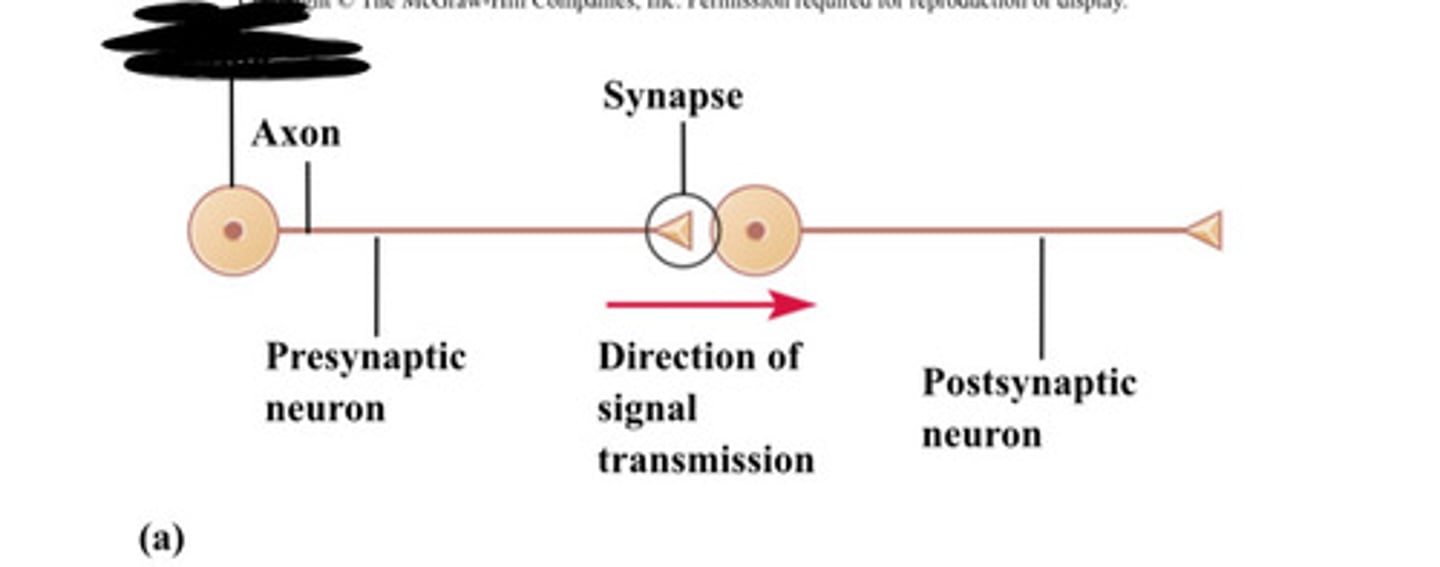
Synapse
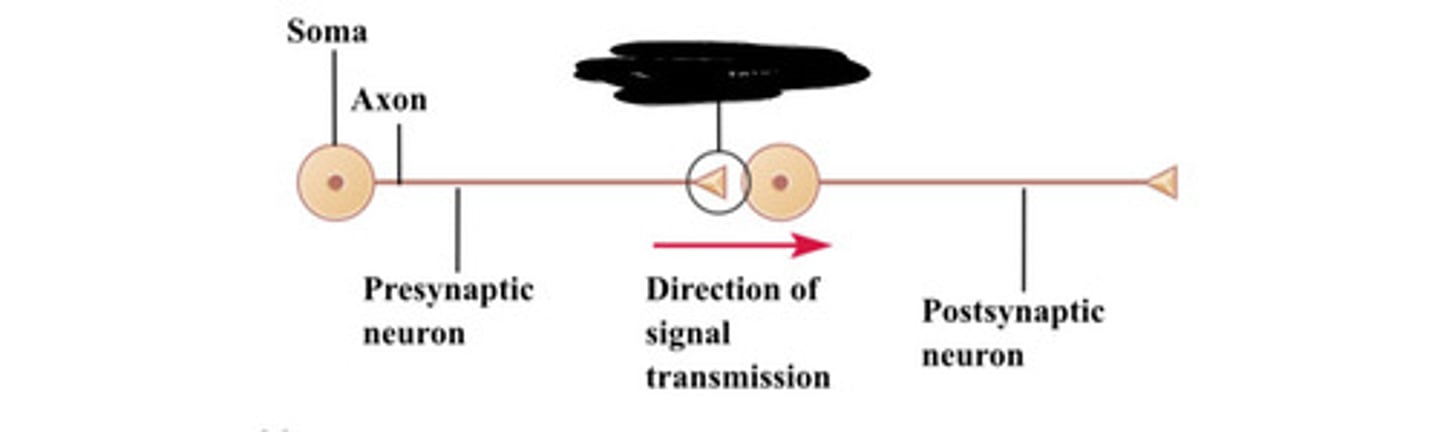
Presynaptic neuron
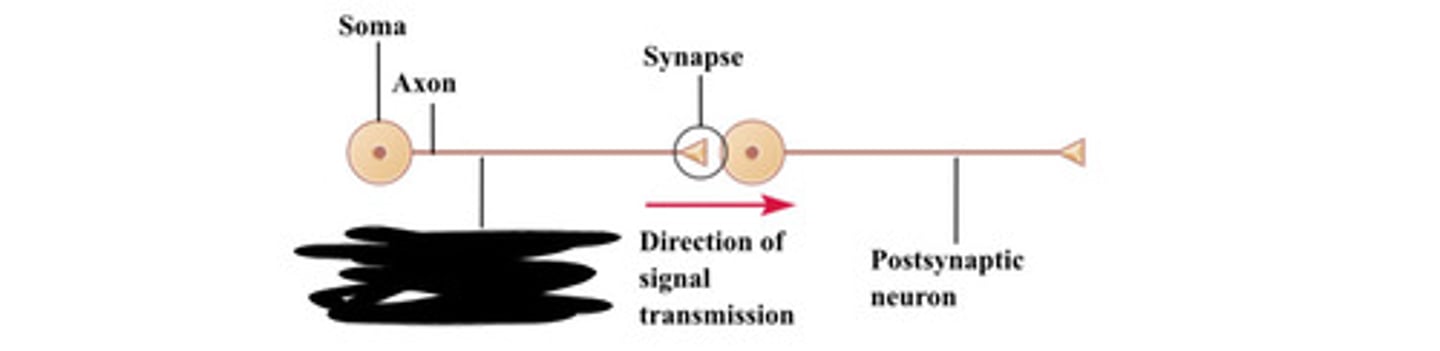
Direction of signal transmission
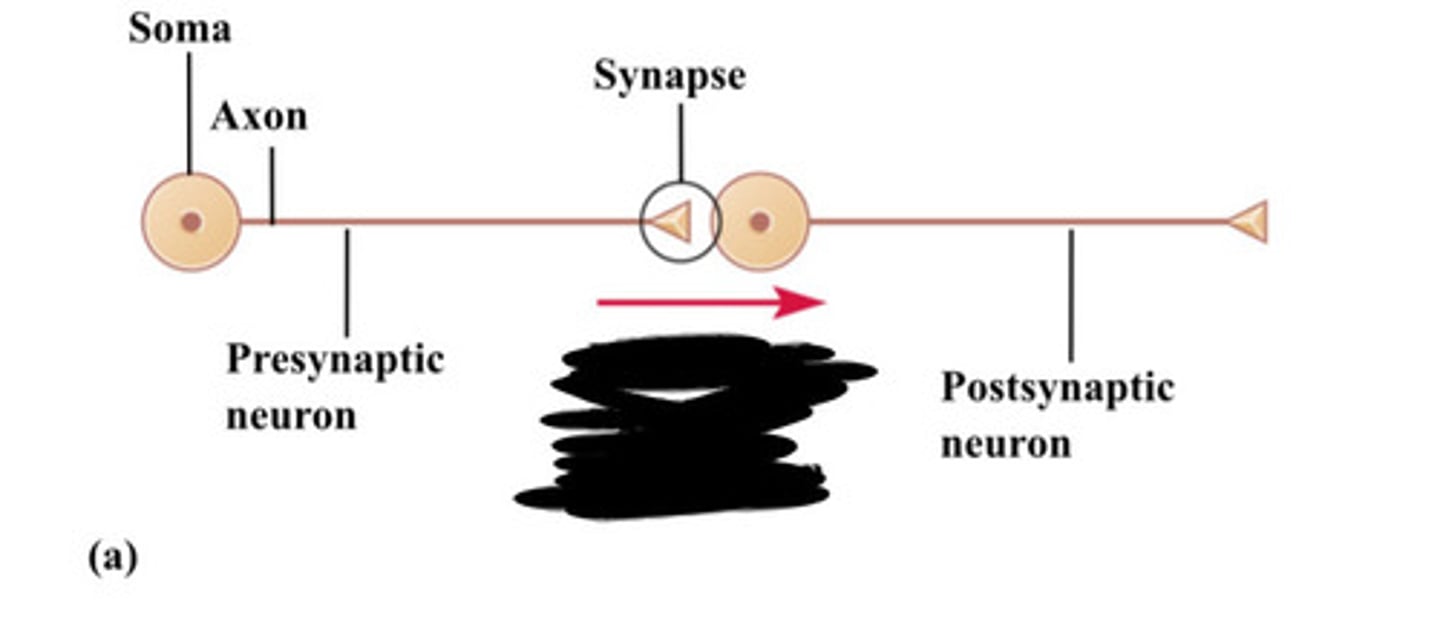
Postsynaptic neuron