5. Notes Receivable
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a promissory note?
A written promise to pay a specified amount, usually with interest, either on demand or at a stated future date.
What types of transactions are promisorry notes used for?
Used in many transactions, including paying for products and services and lending and borrowing money.
When would sellers sometimes ask for a note from a customer?
Sellers sometimes ask for a note to replace an accounts receivable when a customer requests more time to pay a past-due account.
When do sellers prefer notes?
When the credit period is long and when the receivable is for a large amount. If a lawsuit is needed to collect from a customer, a note is the customer's written promise to pay the debt, its amount, and its terms.
What is the principle of a note?
The amount the maker (signs note and promises to pay) of the note promises to pay the payee.
Who is the maker of the note?
The one who signed the note and promises to pay
Who is the payee of the note?
The person/company to whom the note is payable.
To the maker of the note what is the note?
A liability called a note payable.
To the payee of the note what is the note?
The note is an asset called a note receivable.
What is interest?
The charge for using the money until its due date. To the borrower it is an expense and to the lender it is revenue.
Review figure 9.11 under Notes Receivable.
What is the maturity date of a note?
The day the note (principle and interest) must be repaid.
What is the period of a note?
The time frame from the note’s (contract) date to its maturity date. Many notes mature in less than a full year, and the period they cover is often expressed in days.
How would we calculate when a 90 day note matures if it is dated July 10. Assume July goes to the 31st, August has 31 days, September has 30 days.
Days in July = 31. The date of the note is the 10 so we do 31 - 10. There is 21 days remaining in July so we add that. There are 31 days in August so we add that. There are 30 days in september so we add that. This totals to 82. The note is for 90 days so there are 8 days left. Therefore the maturity date is October 8.
How do we count days when computing the maturity date?
Omit the day a note is issued but count the due date. i.e. The note is issued on July 10 but July 11 - 31 is 21 days.
When does a note mature when months are used instead of days?
The note is payable in the month of its maturity on the same day of the month as its original date. A nine-month note dated July 10, for example, is payable on April 10. The same rule applies when years are used.
Review
Interest is the cost of borrowing money for the borrower and the profit from lending money for the lender. Unless otherwise stated, the rate of interest on a note is the rate charged for the use of principle of one year (annual rate).
What is the formula for computing interest on a note?
Principle of the note x Annual interest rate x Time expressed in fraction of the year (for example if 20 days then 20/360) = Interest.
To simplify interest computations, a year is commonly treated as having how many days?
360 days (called the banker’s rule and widely used in business transactions).
What is the interest if we have a 90 day note for $1,000 with a 12% interest rate?
1,000 x .12 x (90/360) = 1,000 x .12 x .25 = $30.
To which account are notes receivable usually recorded?
Notes receivable are usually recorded in a single Notes Receivable account to simplify record-keeping.
What is the entry to record receipt of a note where the amount is $1,000?
debit Notes Receivable $1,000, credit Sales for $1,000.
When might a seller collect part of a past-due balance in cash?
When a seller accepts a note from an overdue customer to grant a time extension on a past-due account receivable.
If a company agrees to accept $232 cash along with a $600, 60-day, 15% note from J. Cook to settle the $832 past-due account, what is the correct entry?
debit Cash $232, debit Notes Receivable $600, credit Accounts Receivable $832.
What is due on a note’s maturity date?
The principle and interest of the note.
What is the entry to record an honored note?
debit Cash for full amount, credit Notes Receivable for amount on note, credit Interest revenue for interest amount calculated.
Which statement is interest revenue reported on?
The income statement.
When is a note dishonored?
When a note’s maker does not pay at maturity.
Does dishonoring a note mean the maker no longer has to pay?
No, the payee still tries to collect.
What should the balance of the Notes Receivable account only include and what needs to be done if a note is dishonored?
It should only include notes that have not matured. When a note is dishonored, we remove the amount of this note from Notes Receivable and charge it to an account receivable from its maker.
If the maker dishonors the note at maturity and it was originally for $600 with $15 interest, what is the entry to record the dishonoring of the note?
debit Accounts Receivable - J. Cook for $615 (principle + interest), credit Interest revenue for $15, credit Notes Receivable for $600.
Charging a dishonored note to accounts receivable does two things, what are these two things?
First, it removes the note from the Notes Receivable account and records the dishonored note in the maker's account.
Second, if the maker of the dishonored note asks for credit in the future, their account will show the dishonored note.
If notes receivable are outstanding at period-end what needs to be recorded? (If we have a notes receivable but it does not mature until a future accounting period).
We need to record accrued interest.
Assume on December 16, TechCom accepts a $3,000, 60-day, 12% note from a customer. When TechCom's accounting period ends on December 31, $15 of interest has accrued on this note ($3,000 x 12% x 15/360). What is the adjusting entry to record this interest revenue for the 15 days in December?
debit Interest Receivable $15, credit Interest Revenue $15.
What statements do interest revenue and interest receivable go on?
Interest revenue is on the income statement, and interest receivable is on the balance sheet as a current asset.
Assume on December 16, TechCom accepts a $3,000, 60-day, 12% note from a customer. When the note is collected on February 14, what is the entry to record cash receipt?
debit Cash $3060 (principle + interest), credit Interest Revenue $45 (interest earned this period), credit Interest Receivable $15 (we have received the interest amount that was calculated for the last period), credit Notes receivable (amount without interest)
Review
Total interest on the 60-day note is $60 ($3,000 x .12 x 60/360). The $15 credit to Interest Receivable is the collection of interest accrued from the December 31 entry. The $45 interest revenue is from holding the note from January 1 to February 14. $15 + $45 = $60.
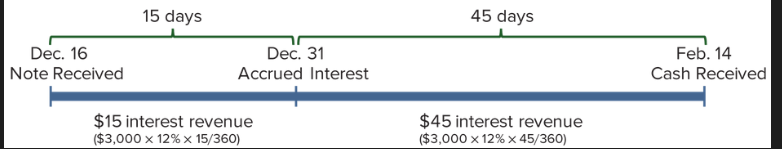
What is the adjusting entry to record interest revenue if the note does not mature until a future period and the current period is ending?
debit Interest Receivable for interest amount for number of days so far, credit Interest Revenue for same amount.
What is the adjusting entry to record cash receipt when the note that matures in the current period was created in the previous period?
debit Cash for principle + interest, credit Interest Revenue (this period’s interest amount), credit Interest Receivable (last period’s interest amount), credit Note Receivable (amount without interest)
Review Need-To-Know 9-5