Chapter 11: Human Genetic Variation (and Chapter 15.2 Chromosomal Abnormalities)
]]Origins of DNA Sequence Variation]]
@@What types of sequence variation exist (single nucleotide to chromosomal level)?@@
- What is the difference between variant and mutation?
- same thing
- {{SNP Point mutations????????{{
- substitution
- deletion/ addition
- Copy number variation (CNV)
- polyploidy
- Aneuploidy
- Mixoploidy
- Recombination errors
- chromosome cross-over during mitosi
- Chromosomal
- Translocations
- Duplications
- Inversions
- Indels/Delins
@@What are the most common damages that occur to a DNA molecule as the result of endogenous sources, including chromosomal abnormalities (Ch. 15.2)?@@
- DNA replication errors:
- replication slippage → deletion or expansion ( especially during very repetitive strands
- causes Huntington disease ( accumulation of toxic debris) → CAG repeats → Q( glutamine accumulation)
- Base damage
- reactive oxygen species(ROS) proudes during normal metabolic processes can damage DNA base
- Strand breaks
- single strand breaks
- double-strand breaks
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Chemical damage
- hydrolytic most common damage to DNA → depurination the most common hydrolic damage of DNA
- reactive oxygen species(ROS)
- Methylation
@@What is aneuploidy and polyploidy (15.2)?@@
- Polyploidy → an extra set of chromosomes ( lethal/ not viable)
- aneuploidy → abnormal number of chromosomes ( a single chromosome is multiple or missing)
- example of aneuploidy where the people survive
- trisomy 21
- super male (XYY)
- chromosome 18
- mixoploidy → some cell have mutations that result in different number of chromosome sets → cause mosaicism (lethal)
@@What is a Robertsonian Translocation and how does it occur?@@
- Robertsonion Translocation (centric fusion)
- translocation in chromosomes but two parts of the chromosome that attach have two nearby centromeres. Both centromeres fuse together and don’t cause a problem during further mitosis → genetic information is not lost
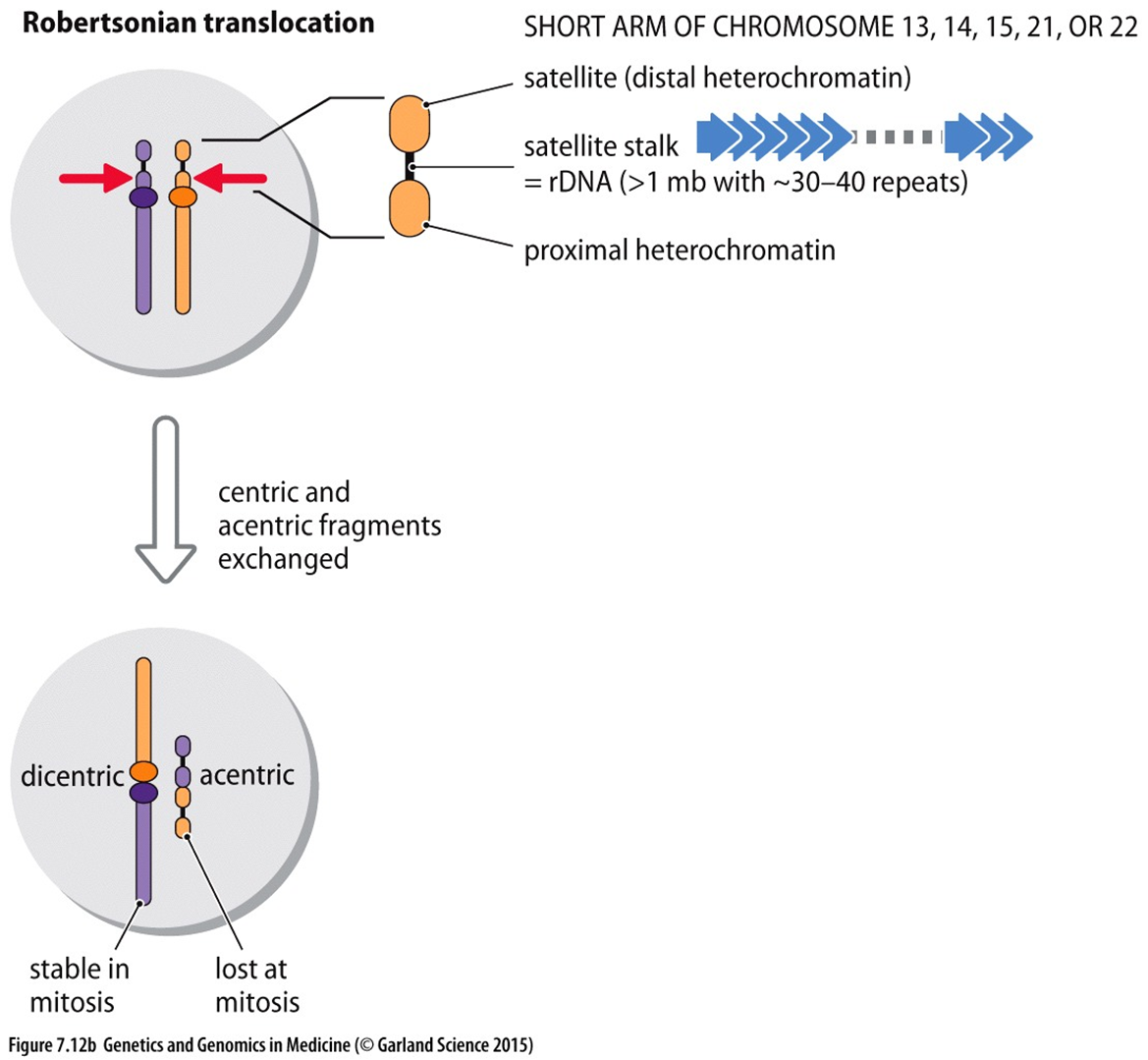
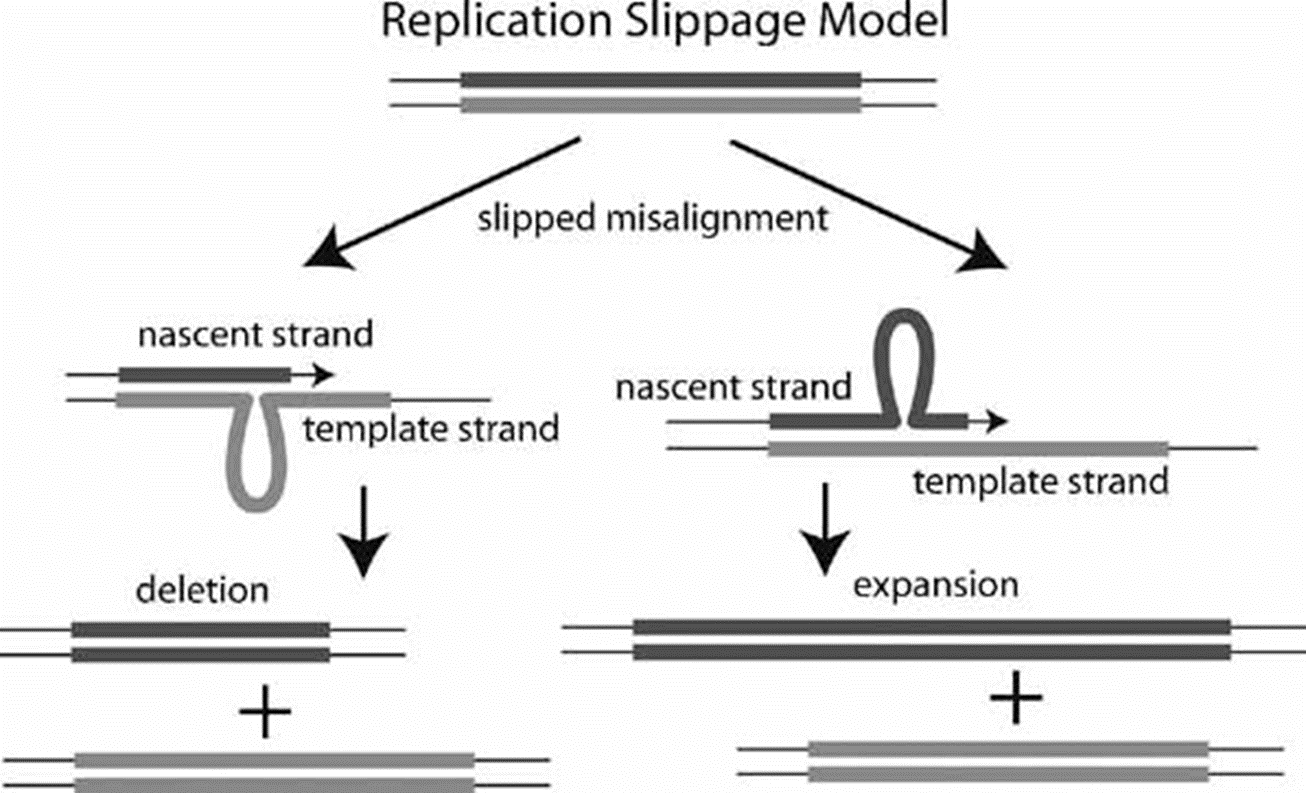
@@What is replication slippage and why are short repetitive sequences more vulnerable to this?@@
- occurs during DNA synthesis when the leading strand is misaligned with the leading strand template
- Polymerase can slip back wars or forward, causing an insertion or deletion
- all of this can cause egntic disorders and diseases
@@What genetic variations may result in Huntington Disease or Fragile X syndrome? Why?@@
- Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by an expansion of the CGG repeat in the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome. This results in reduced or absent production of the FMR1 protein, leading to a range of cognitive and behavioral problems. It is an X-linked dominant disorder, affecting males more severely than females because female shave another X and, therefore FMRI1 gene.
@@What are the most common exogenous sources of damage? What types of damage are created?@@
- Radiation
- UV
- Xrays
- chemicals
- cigarette smoke
- nitrate and nitrate preservatives
- benzoyl peroxide
- Infectious agents
- HPV
- Heliobacter pylor
@@What are the significance of CpG islands and why are they?@@
- Cp(phosphate)G island
- CGCGCGC
- found in promoters but not actively transcribed
- when the C get methylated( which it easily done C→T) then there is no transcription
[[Repair[[
==What are the primary mechanisms that cells use to repair DNA damages? How does DNA polymerase “proofread”?==
- if bases are mismatched, then they don’t fit together and the following bases are also wonky
- The polymerase also notices and pauses replication and uses exonuclease activity to remove the incorrect nucleotide.
==What are the general steps in Base Excision Repair (BER), Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER), Mismatch Repair (MMR), Homologous Recombination (HR) and Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ)?==
==What is translesion synthesis? When and why is it initiated?==
- only used in emergencies because there is no proof reading
==What are the primary diseases/outcomes seen in individuals with defective DNA repair mechanisms?==
- cancer
- apoptosis
%%The Scale of Human Genetic Variation%%
}}What are the varying scales of genetic variation? What is structural variation? How does balanced structural variation differ from unbalanced structural variation? What is aneuploidy?}}
balanced variation → all of the gentic martial is still there
- NO net loss or gain
- Translocations
- Inversions
- Point mutations
unbalanced → not all genetic material
- Change in copy number
- Abnormal chromosome segregation
- Point mutations
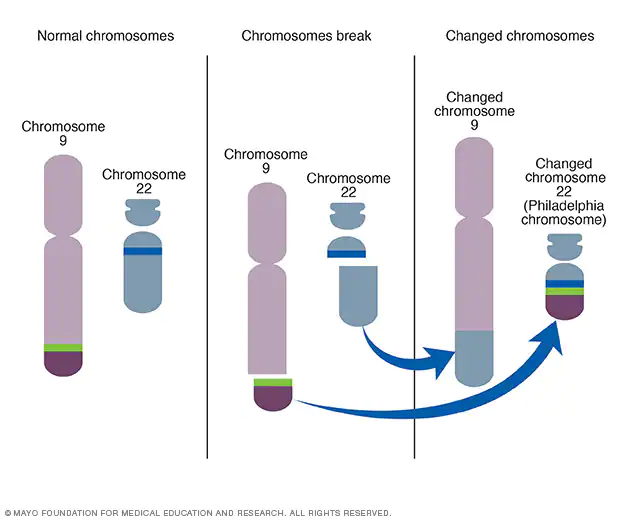
Example: Philadephia chromosome
- when chromosome 9 and chromosome 22 break and exchange portions
- causes Leukemia
}}What is satellite DNA? Why is replication slippage more common in arrays of tandem repeats?}}
Satellite DNA: highly repetitive noncoding region if the genome, located near the centromeres and telomeres region of chromosome
why is replication slippage more common?
- when the DNA polymerase enzymes slips from the DNA strand and adds or deletes on e or more repeats
- if slippage occurs pieces still fit together and polymerase is unable to detect if they made a mistake
}}Know the similarities and differences between Single Nucleotide Variation, Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP), “indels”, Copy Number Variants (CNV), Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTR).}}
| }}Type of Variation}} | }}%%Definition%%}} | }}%%Similarities%%}} | }}Differences}} |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNV | A single nucleotide change in the DNA sequence | Can occur anywhere in the genome; can be a germline or somatic mutation | Only involves a change in a single nucleotide base |
| SNP | A type of SNV that is present in at least 1% of the population | Can occur anywhere in the genome; can be a germline or somatic mutation | Must have a minor allele frequency of at least 1%; used as genetic markers in association studies |
| Indel | A small insertion or deletion of DNA sequence | Can occur anywhere in the genome; can be a germline or somatic mutation | Involves the addition or removal of one or more nucleotides |
| CNV | A large segment of DNA that is duplicated or deleted in the genome | Can occur anywhere in the genome; can be a germline or somatic mutation | Involves the gain or loss of a large segment of DNA; can be variable in size |
| VNTR | A region of DNA where a short sequence of nucleotides is repeated in tandem | Can occur anywhere in the genome; can be a germline or somatic mutation | Involves the gain or loss of a variable number of tandem repeats; can be used as genetic markers in forensics and population genetics |
Note: Germline mutations occur in the DNA of sperm or egg cells and are passed on to offspring, while somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and are not passed on to offspring.
}}What is population based genome sequencing? What is the 1000Genomes project. What is the T2T Consortium? What did they find?}}
- 1000Genome project: indicated in 2008 in 26 different population
- goal: search for de novo mutations
- found that African populations had the most variations in genome and Europe, east Asia and South Asia least variation
- → founders effect
- Telomere to telomere consortium: focused on identifying the first complete assembly of human genome with euchromatic and heterochromatic region8 coding and non-coding)
}}What percent of our genome is thought to be under functional constraint? Explain why this percentage is greater than the 1.2% (the genome that is encoding for proteins). Be able to explain multiple reasons why. Compare this idea of functional constraint to findings by the ENCODE Consortium.}}
- Functional constraint: parts of DNA genome is silenced through methylation and phosphorylation
- Most protein variation have a neutral effect and not necceraly cause a a dise( example blood groups)
- functional constrains 1.2% of DNA can´t change the protein because they are so important
- but more because of regulation
- promoter regions and enhancers
}}Be able to explain how post-zygotic mutations create individuals that are genetic mosaics. What is a chimera?}}
{{11.4 Functional Genetic Variation and Protein Polymorphism (some material covered in Lecture 2){{
Compare a selective sweep to balancing selection. What is a heterozygous advantage? What is loss of heterozygosity? Be able to describe each in relation to each other and positive or negative/purifying selection
What are examples of positive selection that have occurred in the human population? How and why did they occur?
What are examples of where genetic variation does indeed change the phenotype/protein(s) produced, but the effect is still neutral?
- %%blood group%%
Cytogenetics: How could a Philadelphia Chromosome be detected using FISH? (not in box 15.1)
- Cytogenetics: branch of genetics and biology concerned with chromosomal behavior
- FISH: a molecular cytogenetic technique that allows the localization of a specific DNA sequence or an entire chromosome in a cell
- for Philadelphia Chromosome: tag both chromosome with different fluorescence molecules and take multiple pictures of translocation
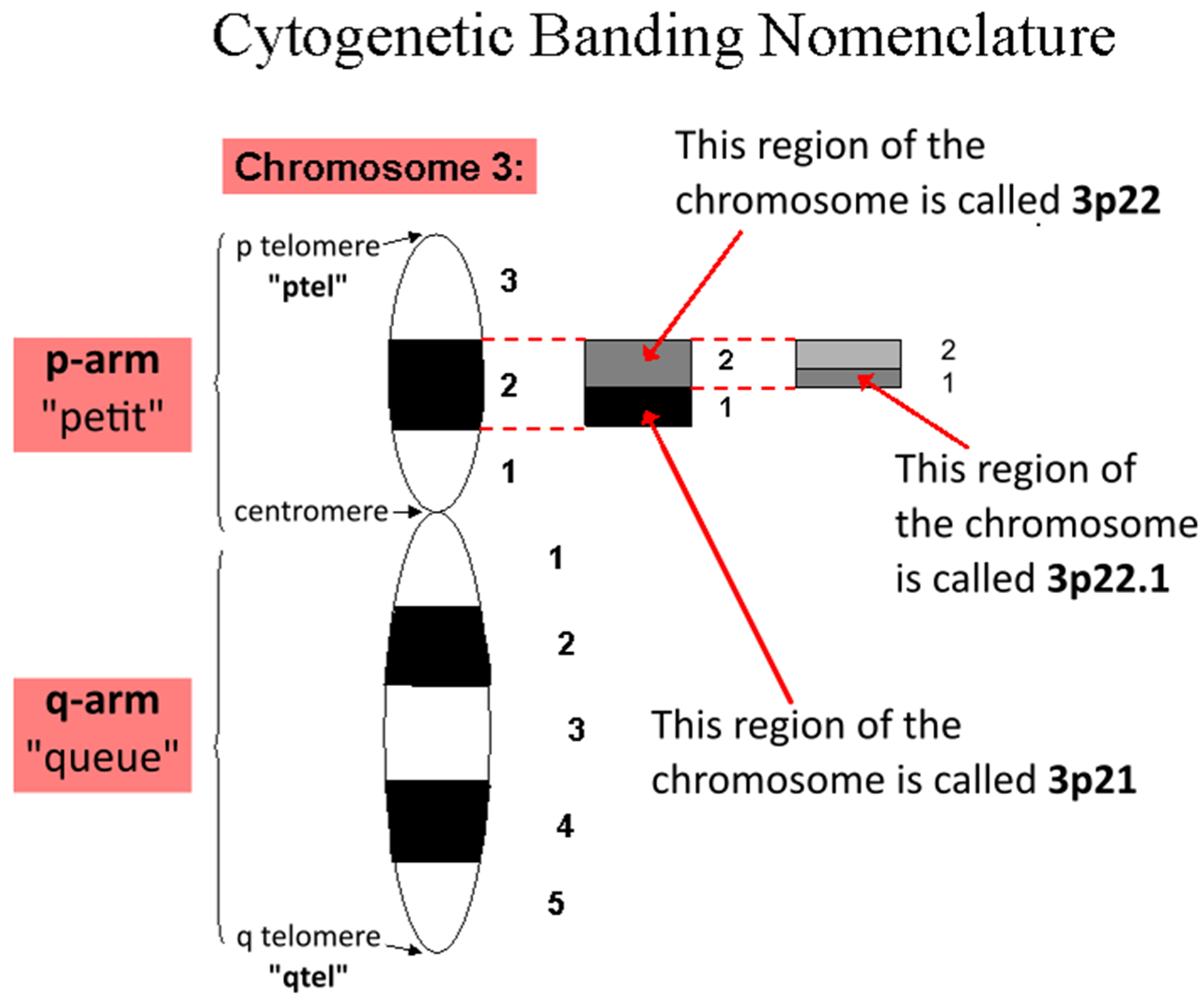
^^BOX 15.1 NOMENCLATURE OF CHROMOSOME BANDS^^
<<What is “G-banding”? In which stage of the cell cycle are chromosomes extracted and stained (mitotic or interphase)? Which parts of the chromosome stain darker and lighter?<<
- G-banding: A type of standing with Giemsa stain
- DNA from white blood cells during prometaphase ( as condenst)
- dark color= AT-rich → gene poor→ hetero chromatin
- light color= GC rich → gene-rich
<<What are the names of the two arms of a chromosome?<<
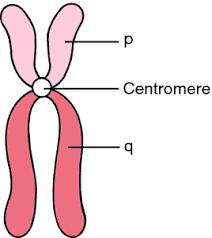
<<What does it mean to be Metacentric, Submetacentric, Acrocentric or for a chromosome to be acentric?<<
position of centromere
Metacentric (center)
Submetacentric (between middle and telomere)
Acrocentric (near telomere)
penetrance
anticpation
repication slippage
dynamic
18
- 5 open
- 1 hardy weinberg
- bonus