The Leaf
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
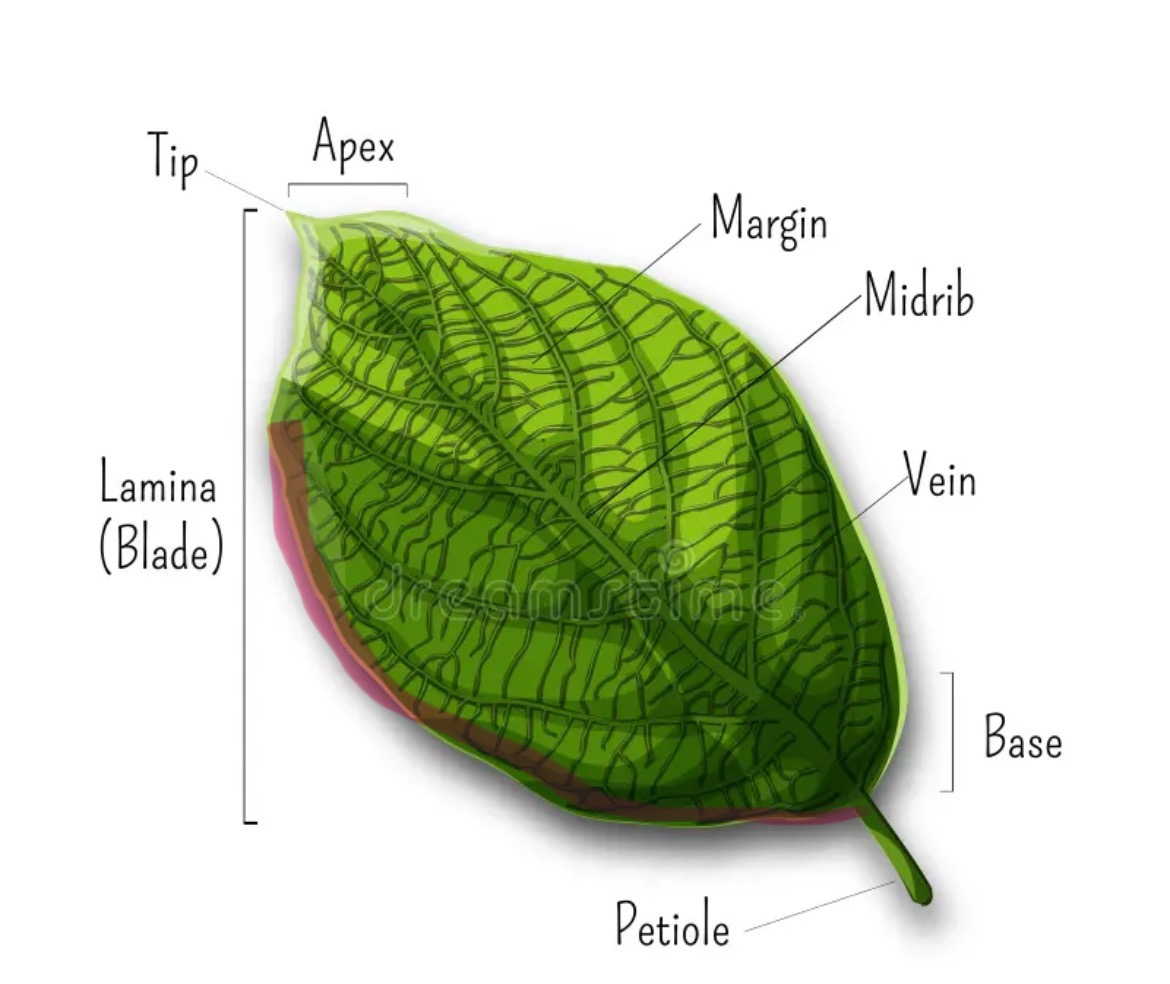
Lamina
The leaf blade which is usually broad and flat to increase the surface area for maximum sunlight absorption
Why is the thin shape of the lamina important for photosynthesis?
It allows sunlight to penetrate the layers of the leaf and provides a shorter diffusion distance for carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and the oxygen to exit
What does the network of veins along the lamina contain?
Vascular Bundles which consist of xyl vessels and phloem tubes
What is the function of the xylem vessels?
To transport water from the roots to the leaves
What is the function of the phloem tubes?
To transport the plant’s food (glucose) to other parts of the plant
What is the main vein in a leaf and where does it run
The midrib is continuous with the petiole and runs through the center of the leaf.
What is the main vein’s function?
To support the leaf
Petiole
The leaf stalk
What is the function of the petiole
Attaches the leaf to the plant and produces support for the leaf. It keeps the leaves at 90° angles for full exposure to sunlight
Why are most leaves green?
They contain chlorophyll
What is chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells
What is the function of chlorophyll?
To trap sunlight energy and convert it to chemical energy to be used in photosynthesis
What are leaf margins?
The edges of leaves
How can leaf margins vary?
They can be smooth or serrated and become narrow at the tip (apex) opposite the petiole
Cuticle
A waxy covering on the upper and lower surface
Epidermal cells
The outermost cells of a leaf that contain no chloroplasts
Stoma
A pore on the underside of the leaf through which carbon dioxide enters and oxygen exits
What happens when stomata are open
Water will escape the leaf resulting in dehydration
Stomata are usually found on which surface?
Lower surface
Guard Cells
A pair of sausage-shaped cells found on either side of the stomata.
Mesophyll cells
Specialized cells that contain chloroplasts . Consists of palisade cells and spongy cells.
Palisade cells
Contain more chloroplasts as they are the main site of photosynthesis
What do Air spaces allow?
Between the spongy cells, allow for diffusion of gases in and out of the leaf
What is the function of the Vein
Provides support for the leaf. It transports both water and minerals (via xylem) from the roots to the leaves and transports manufactured food, glucose, (via phloem) from the leaves to all parts of the plant.
What is the function if the Waxy Cuticle
prevents water loss