trying to tip the untippable!
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
w1-11 + 13 now:)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
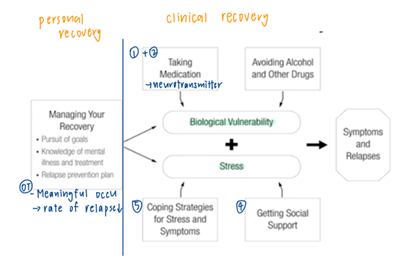
explain the interaction between biological vulnerability, stress level and individual’s response in the stress vulnerability model
biological determines the threshold. when stress level stays below the threshold, individuals react in a elastic homeostatic way; when the stress level exceeds this threshold, individuals experience psychopathological episode. when the stress level drops back to below the threshold, the episode ends and the individual returns to pre-episode state.
vulnerability-stress-protective factors model of mental illness
goal
types of protective factors
components of clinical progress and outcomes
goal: build up protective factors and shift the balance from disability towards recovery
types of protective factors: personal attributes & environmental factors
clinical progress and outcomes: symptoms & relapses, social functioning, cognitive impairment, QoL
medium for remediation and overcoming of disabilities in psychological rehab + aim + examples
skills training
remediate disabilities in social, family, and vocational functioning + learn to react with stressful env
e.g. social skills/ pre-vocational/ relaxation skills/ life skills/ emotional regulation training
environmental support
reduce potential stressors + compensate for disabilities
e.g. family support program, ICCMW, transitional housing, peer support, supported employment
societal rehab initiatives
change the system the the MI patient has to function in + promote occupational justice (reduce stigma)
e.g. equal opportunities in employment
define personal journey
rediscovery of self in the process of learning to live with an illness
4 focuses of recovery
journey, meaning, striving to achieve, transformation
characteristics of recovery
unique and individual
non-linear
gradual
recovery without cure
without professional intervention
CHIME framework + examples
connectedness (relationships/ community/ social support)
hope and optimism (belief in recovery/ aspirations/ positive thinking/ motivation)
identity (+ve self-identity/ overcoming stigma)
meaning (meaningful goals/ life/ roles/ meaning in mental health experience)
empowerment (sense of control/ taking personal responsibility/ focusing on strengths)
framework of recovery
stages of recovery (change model)
process (CHIME)
characteristics of journey
explain the stages of recovery + OT role
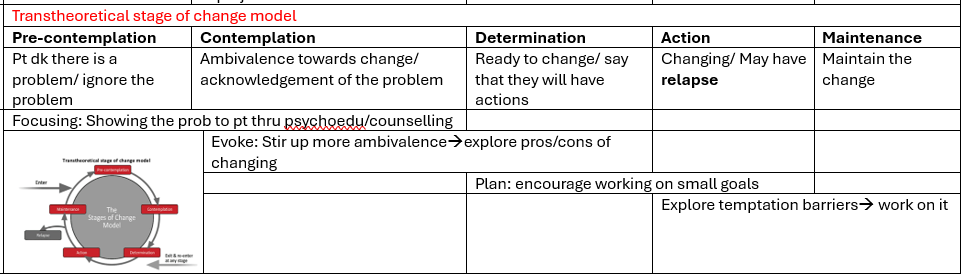
transtheoretical stages of change model
OR
moratorium (confusion/ withdrawal)
awareness (hope)
preparation (evaluate strengths and weaknesses)
rebuilding (positive identity/ goals/ empowerment)
growth (resilience)
domains of recovery
clinical
personal (hope/ resilience/ personal goals/ identity)
social (social participation/ roles/ inclusion/ contribution)
functional (skills/ adjustment/ adaptations)
types of strengths
talents & skills
personal attributes (e.g. good memory)
interests/ aspirations
environmental strengths
strength Ax
current strengths → aspirations and goals → past resources (used before)
how identification of strengths supports mental health recovery?
i just guess
identify strengths → promotes commitment and motivation + focus on the +ve aspects in life → hope and optimism (CHIME)
strength Ax → identify meaningful goals and aspirations → meaning (CHIME)
identify strengths → utilize them to achieve goals → regain sense of empowerment (CHIME)
empowerment + strength-based = ROP
purpose of OT Ax and evaluation
therapist
answer specific (referral) questions
continuous documentation progress
set ST and LT recovery goals
patient
motivation on rehab
domains of OT to be assessed + examples of components of each domains + example of Ax)
pattern of occupation - occupational questionnaire (routine)/ role checklist (role)
Motivation of occupation - Interest checklist (interest)
communication and interaction skills - ACIS (e.g. non-verbal/ conversational skills)
motor (energy/ coordination) and processing (knowledge/ problem solving) skills - AMPS
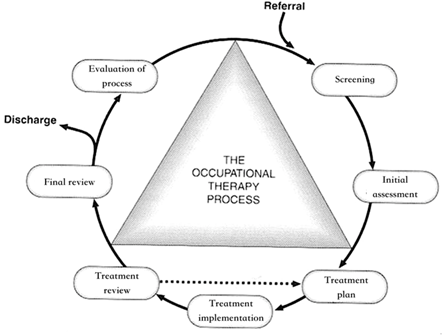
OT process
group process (Cole’s 7 steps group)
introduction
activity
sharing
processing
generalizing
application
summary
group roles (good/ bad)
task roles (8) (good)
coordinator/ elaborator/ orienter (CEO)
procedural technician
info seeker/ giver
opinion seeker/ giver
initiator-contributor
recorder
building and maintenance roles (good) (4)
harmonizer
compromiser
gatekeeper (ensure everyone participates)
follower
individual roles (6)
play boy/girl
blocker
aggressor
recognition seeker
self confessor
dominator
group leaders responsibilities + qualities
motivate the group (encourage participation/ enthusiasm) - confidence
set limit/ rules (limit inappropriate behaviours) - authority
establish therapeutic communication (build trust and rapport/ understand feelings) - attentiveness/ empathy
purpose of OT group intervention
social context for training
mutual support
social learning (observational)
connect with others → new roles (social recovery)
resources consideration
(target all types of recovery + any timing in recovery process)
definition of social skills
interacting with others in social situations appropriately and effectively
appropriate: x violate social expectations/ values/ norms
effectively: achieved the intention of the social interaction
components of social skills
conversational
verbal (e.g. tone/ choice of wordings/ continuation of dialogue)
non-verbal (e.g. facial expressions/ gestures)
assertiveness
between submissive and aggressive
express moods
say no
ask for help from others
structure of group SST
explanation
demonstration
role play (behavioural rehearsal, repetition, modeling)
immediate concrete, encouraging and corrective feedback (+ve reinforcement, shaping)
HW to promote generalization
social learning theory: 4 factors affecting social learning (did not appear in ppt but appeared in PP)
attention
retention
reproduction
motivation
approaches of SST
shaping and +ve reinforcement (token/ social reinforcement)
errorless learning
immediate cues and prompts to minimize errors → do not need to unlearn mistakes and no frustration
esp for schiz patients with low procedural/ implicit learning capacity
requires detailed analysis of the behavioural task to be learned and precision teaching techniques
breakdown task into behavioural components → sequential teaching, start with easiest and smallest behavioural component → successfully display desired behaviour for at least 10 times → move on to next
demonstrate (role model) → prompts and reinforcement → desired response → repetition and fading
relationship between social skills and MI
biological vulnerability of depression and schizophrenia
poor social skills causes depression and depression leads to poor social skills
poor social skills → unable to express their needs/ themselves → more likely to develop schiz
definition of social cognition & components
mental process that underlies social interaction, including perception, interpretation and response towards others’ dispositions, behaviours and intentions
social cognition deficit: emotion and social perception/ theory-of-mind
social cognitive bias: jumping to conclusion/ attributional style (internal vs external/ global vs specific/ temporary vs permanent)
significance of social cognition in functioning
better explain variance in functional outcome than neurocognition
mediator between neurocognition and functioning
structure/ process of SCIT
recognizing emotions and understanding social cognition
addressing social cognitive bias and thinking
integration/ application
how does SCIT improve functioning & what are the ways to improve effectiveness of SCIT
it causes neuroplastic changes in social brain
effectiveness
target wider range of social cognition domains instead of just one
combine it with cognitive remediation (CR)
significance of life skills training in MI
schiz patients tend to have functional deficits in life skills
structure of life skills training for ADL/ IADL
introduction
video tape + QnA review
identify resources used + ways to obtain them
suggest alternative resources + evaluate pros and cons
role-play to re-enact the scenario in video tape
rehearse the skills in real-life with limited support from trainer
independently use the skills in everyday life
effectiveness of life skills training
meal prep and cooking → improve cognitive fx and independence
grocery shopping → improve IADL skills + EF
concepts of IMR (5-2-9)
5 strategies
psychoeducation for MI & Tx
behavioural tailoring for medication adherence → optimal mental state
relapse prevention plan (identify warning signs + empowerment)
social skills training → more social support
coping skills training
2 models
state of change
stress & vulnerability model
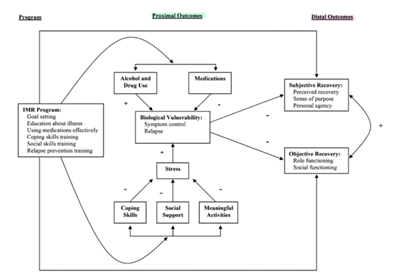
9 curriculum
practical facts about MI
building social support
getting needs met in mental health system
coping with stress
coping with problems and symtoms
Tx strategies and stress-vulnerability model
reducing relapse
managing medication
recovery strategies (set goals/ awareness of recovery)
(HLS/ substance use)
process/ structure of IMR
informal socializing
review prev session
review HW
FU on goals
set agenda
teach new stuff and practice
HW
summary
(target the whole process of recovery)
nature of attention
selective and limited → constantly filter unnecessary info to avoid overload (x multitask but switch tasks)
tend to wander → unhappiness → default mode of network → rumination
window of tolerance theory
in your window of tolerance ~ below the threshold of stress-vulnerability mode
above threshold → hypo/ hyperarousal
definition of body-mind intervention
therapeutic approach focusing on harnessing the power of mind
interaction between brain, mind, body, behaviours → use the mind to promote physical funcitoning and health
definition of mindfulness
awareness that emerges from intentionally paying attention to things as they are non-judgmentally in the present
types of body-mind intervention + examples
physical (e.g. progressive muscle relaxation/ acupuncture/ diaphragmatic breathing)
psychological (e.g. meditation/ mindfulness/ music therapy)
combined (e.g. dance therapy, yoga, qigong, baduanjin, taichi)
types of mindfulness
non-secular (religious)
secular
mindfulness based program (MBP) - e.g. MBSR program/ MBCT
axioms of mindfulness in MBP
attention (to present moment + internal & external experiences)
intention (e.g. improving well-being)
action (integrate into daily activities)
attitude (compassion/ kindness/ curiosity)
definitions + examples of formal and informal mindfulness practice
formal: specific time + regular basis + devoted solely for cultivating mindfulness
breathing practice
anchoring practice
mindful stretching practice
mindful walking practice
body scan practice
sitting practice
informal: integrate into daily activities + mindfulness attitudes
sitting
walking
running
eating
washing hands
bathing, etc
neuropsychology (parts of brain/ nerve/ system) of mindfulness
parasympathetic system + vagus nerve (CN X)
attention control (sustained attention)
activation: ACC, dlPFC
emotional regulation
activation: dlPFC, vlPFC, insula
deactivation: amygdala
self awareness (noticing and decentering from rumination)
activation: PFC
deactivate: PCC
function of vagus nerve
control bp, slow HR
regulate resp. rate
stimulate digestion (stomach/ intestines motility and secretion)
swallowing, gag reflex etc.
psychological mechanism and effects of mindfulness
enables us to skillfully react to life experiences
create space between stimuli and reaction
shift from driven-doing mode (constantly comparing progress to your own goals while nth can be done) → rumination) to being mode (accept + allow)
+ve effects of MBP
MBCT: QoL, reduce depression Sx, relapse recurrence
MBSR: QoL, anxiety, reduce stress
difference between adverse reaction and side effects
adverse reaction: unwanted events caused by treatment
side effects: unwanted events caused by effective treatment
source of adverse effects of MBP
program, participant, teacher/ clinician factors
define stigma
negative/ discriminative attitudes
happens when society degrades/ loses respect for someone w/ discrediting attributes → marginalization
components of stigma + define
stereotype - making inference/ categorizing info according to people’s assignment to a particular group (for quick adaptive response/ simplification of social info) (+ve/ -ve)
prejudice - negative affective attitudes towards a particular stereotyped group
discrimination - enacted prejudice as a negative reaction towards a particular group
types of stigma + impacts
institutional
systemic stigma → unintentional/ intentional limitations of opportunities for PIR
public
public + media: media representation/ public discrimination → decreased help-seeking behaviour/ low awareness and discussion of mental health
courtesy: stigma towards people in relation to PIR → alienation/ burden/ conceal relationship/ distress
professional: medical/ social service providers → distress of PIR/ adverse experience
self
low self esteem and self efficacy
social isolation/ ostracism
poor QoL
models of stigma
stage model (awareness → agreement → apply/ self-concurrence → harm (low self efficacy/ self esteem)
model of personal response (stigma → group identification → perception of legitimacy → contingency of self worth → righteous anger & empowerment/ low self esteem and efficacy/ indifference)
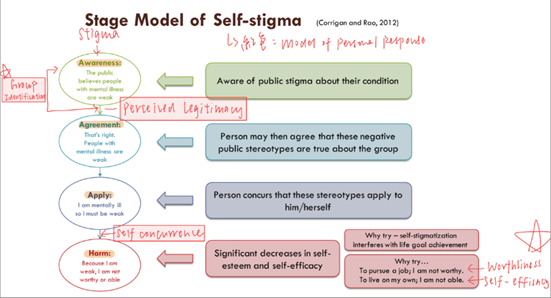
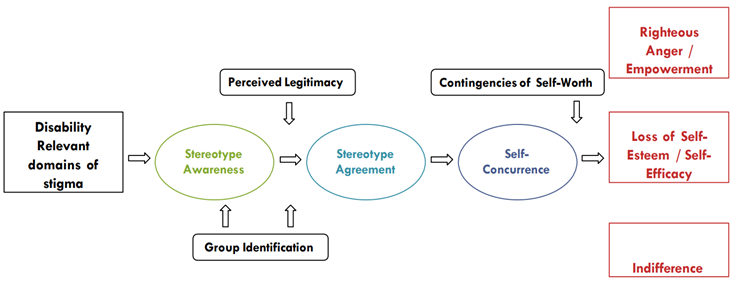
consequences of stigma
direct: avoidance of anticipated stigma → refused to seek psy help
indirect: reduced insight in the benefits of Tx and focus on -ve aspects of tx → non-compliance
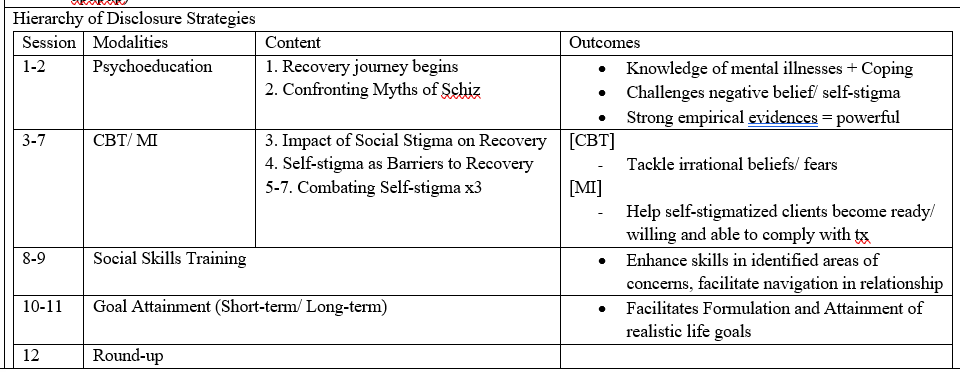
intervention to combat stigma + details
personal empowerment
encourage people they can achieve
disclosure
stages: social avoidance → secrecy → selected disclosure → indiscriminant disclosure → broadcasting (be proud and educate people)
promote empowerment + reduce self-stigma/ worry and concerns of secrecy
hierarchy
psychoeducation about MI/ challenge -ve beiefs and self stigma
CBT (change dysfunctional beliefs/ stigma) or MI (encourage Tx compliance)
SST (navigation of relationship)
goals (formulate and guide them to attain)
round-up
define SMI
mental, behavioural or emotional disorder that causes serious functional impairment substantially interfering with or limiting life activities
symptoms of schizophrenia
+ve
hallucinations - sensory experience w/o external input (mostly auditory)
delusion - misinterpretation of reality (mostly delusions of grandeur and persecutions)
-ve
apathy/ avolition - asociality/ anhedonia/ avolition (due to lack of anticipatory pleasure
diminished expression (blunted affect/ alogia)
cognitive
social cognition (social and emotional perception/ theory of mind/ attributional styles)
neurocognition (processing speed/ attention/ EF/ prospective memory/ verbal learning/ visual memory/ WM)
concept of anticipatory pleasure
→ avolition
inability to anticipate pleasure in achieving or pursuing goals
reward processing disturbances: reward prediction/ learning deficit, inaccurate/ maladaptive internal value representation (e.g. sense of achievement/ social recognition)
major phases of symptoms development of schiz
prodromal: deteriorating functioning, last for few days to years
active: fluctuating, active and prominent psychotic symptoms
residual: psychotic symptoms subsides and less active; -ve and cog Sx remains stable and still exist, +ve Sx remission
Mx of schizophrenia
pharmacological: antipsychotics (x response well → clozapine as last resort; attack WBC)
psychosocial: individual CBT/ family intervention
employment: supported employment
education: pre-vocational training/ educational activities
routinely record daytime activities in their care plan + occupational outcomes
major groups of mood disorder
depression only
unipolar depression
dysthymic depression (milder)
mania + depression
bipolar I: manic + depression
bipolar II: hypomania + depression
cyclothymia
Sx of manic and hypomanic episodes
mood Sx
elevated, expansive or irritable mood
Cog Sx
distractibility
sense of grandiosity
racing thoughts
behavioural sx
pressure speech
decreased need for sleep
talkativeness
psychomotor agitation
excessive involvement in pleasurable yet foolish activities
neurobiological predispositions of bipolar disorder
dysregulation of norepinephrine and dopamine systems in the brain
Mx of BD
pharmacological: antipsychotics/ mood stabilizers
psychological: CBT/ interpersonal therapy/ behavioural couples therapy
EBP OT interventions for SMI
CR
CBT
supported employment (w/ SST & CR)
supported education
occupational based interventions
focus: valued life roles and occupations
definition of NEAR
neuropsychiatric educational approach to cognitive remediation
highly individualized learning
group based Tx of cognitive remediation
promote intrinsic motivation through
personalized: tasks suit their cognitive needs + interest
contextualized tasks: related to real-life + practical → more motivated
learner control: control pace and choose activities → engaging
structure of NEAR
group size: 6-8 people
at least 2 sessions per week (1-1.5 hrs each)
¾ cognitive activities; ¼ bridging group
computer- assisted cognitive training (~3 activities)
bridging group
naming cognitive skills: discuss the cognitive skills used in daily activities → metacognitive knowledge and awareness
metacognitive group: discuss CR software and the cognitive problems that it addresses → enhance metacognition regulation
metacognition type and level (Cella et al)
knowledge 1: knows cognitive operation is necessary for doing everyday tasks
knowledge 2: knows the cognitive skills needed for the tasks
knowledge 3: know the impact/ diff associated with the cognitive deficit/ operation
regulation 1: x adjust/ compensate for cognitive deficits
regulation 2: can anticipate demand + limited planning and adaptations
regulation 3: can adapt with planning regularly + adjust according to feedback

how to increase effectiveness of NEAR
w/ psychiatric rehab
w/ practice and drills + strategy coaching
types of intervention in CR
strategy (skills e.g. chunking)/ remediation (change ext factors)/ aids (add external facilitator)
Ax for SMI + function (brief)
CFNA (chinese functional needs Ax)
self-care
community living skills
→ community independence
CWPP (chinese work personality profile)
work functioning/ job suitability
C-LASER
work readiness
setting that are suitable for applying NEAR and what can NEAR improve
any setting (out/ in patient/ supportive housing facilities)
improve attention, processing speed, immediate learning and memory, delayed verbal memory
*x improve physical fitness/ medical adherence
theoretical background and bases of family intervention
relapse rate is lower if lived in resident setting than those with family
based in systemic approach (context & environment matter)
dynamic relationship b/t symptoms and the interpersonal context in which the symptoms occur
family = system, made of complex relationship b/t members and the world outside → causes symptoms (i.e. structure/ belief/ pattern of family = perpetuating factors)
Sx reduced change in family and increases the predictability → homeostasis (e.g. PIR becomes the shared project that allows the family to escape from old problems)
explain the concept of EE
expressed emotion
measures the family env
high EE (criticism/ hostility/ emotional over-involvement) → high relapse rate of schiz/ mood disorder)
low EE (low levels of emotion/ empathy/ calm and respectful/ positive
hooley’s controllability model
family beliefs about PIR ability to control Sx and behaviours → emotional responses → controlling actions
underlying belief (Pt should control their Sx/ problem)
attributional staff (assign responsibility to patient)
utility belief (use criticism/ EOI as means to reduce Sx even if they are ineffective → -ve affective and behavioural responses → high EE)
criticism/ hostility = think patient should take responsibility to control her illness
EOI = think Pt do not have the ability to control Sx/ problem
types of interaction pattern of high EE
pursuer distancer
conflict avoidance
high conflict
over/ under functioning
→ high EE leads to problem maintaining functional interaction pattern among family members
impacts of high/ low EE
high relapse rate for SMI
intensify delusions
criticizing remarks increases -ve Sx
EOI increases +ve Sx
warmth/ +ve improves overall social functioning
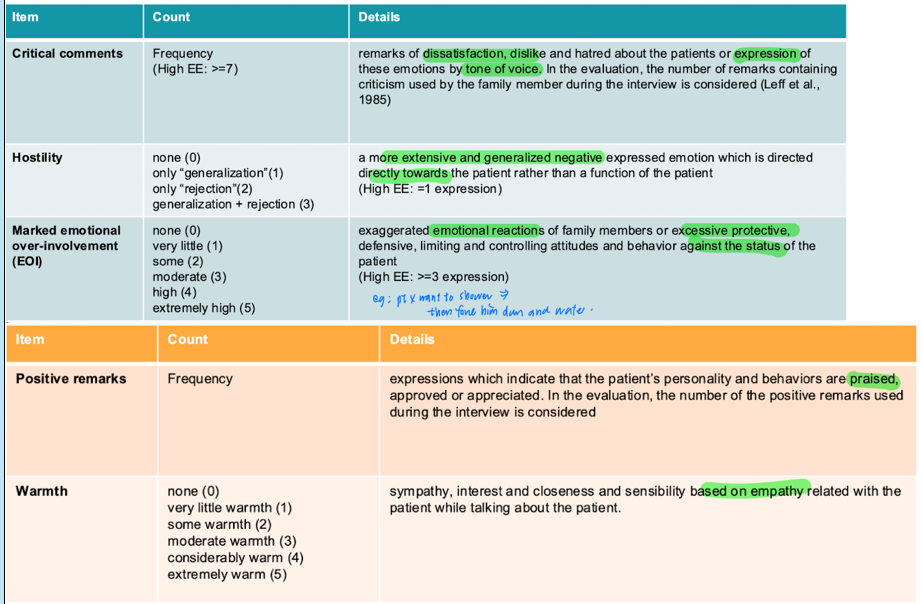
camberwell family interview schedule
gold standard measure of EE
interview key relatives w/o pt
items
criticism (dislike/ hatred/ dissatisfaction about the patient expressed by tone of voice; high EE: >=7 )
hostility (general + extensive expressed emotional towards the patient rather than their function; high EE: >=1)
EOI (exaggerated emotional reaction/ excessive protective, defensive, limiting, controlling attitudes and behaviour against the status of the patient; high EE: >=3)
positive remarks
warmth (expressed empathy)
FMSS/ RAI
five-minute speech sample
high EE
CRIT (-ve initial statement/ -ve relationship rating/ >=1 criticism)
EOI (self-sacrificing/ overprotectiveness, emotional displays, >=2 ratings of excessive detail about the past, expressions of love for pt, excessive praise of pt)
relative assessment interview
bg info
chronicity of illness
irritability
financial/ chores
interests and social activities of relatives
current prob + Sx
impacts of poor insight into MI
poor medication adherence
impaired vocational functioning → should consider interventions of improving insights (e.g. psychoedu) when prescribing vocational rehab
x correlates with social skills
approaches of intervention to improve insights
clinical insight: educate pt of MI (e.g. psychoedu)
cognitive insights: improve understanding of experience by targeting thinking style (e.g. CBT/ metacognitive therapy)
behavioural changes: engage more in Tx (e.g. MI)
interventions for insight Mx
behavioural changes
MERIT metacognitive reflection and insight therapy (stimulate 4 elements of metacog: self-reflectivity/ understanding other’s mind/ decentration/ mastery)
key family recovery stages
recognition of problem
clearer recognition/ confirmation, hoping for cure
accept the chronicity of illness
accept MI, reclaim own life
basis/ goal of family psychoeducation
based on stress-vulnerability model
partnering w/ PIR and family to support recovery
create optimal env for recovery
help family develop skills and knowledge to assist recovery + avoid past eteological dysfx
assumptions of family psychoeducation
misunderstandings of MI → conflicts and unrealistic expectations
relatives as env protective factor
emphasize on family strength
purposes + elements of FPE
purpose
provide knowledge about illness
reduce overinvolvement → improve independence of PIR
increase tolerance of problems and reduce criticism
improve PIR’s skills/ performance/ coping
tackling problems arising from MI
answering questions
exchanging info
coping strategies
defusing emotions and engender optimism for future
elements
natural course of MI
possible etiology
Diagnosis and prognosis
treatment options expected outcomes
SSx
side effects and effects of Tx
relapse prevention
structure of FPE
orientation & engagement x3
knowledge abt MI (w/ pt) x6
building strength and therapeutic family roles (w/o pt) x7
termination x2
mainly: illness related info + behavioral problem solving skills (stress coping & problem solving)
FPE: prescribe to whom + when + effects
to all family in close contact with PIR (psychosis/ schiz)
betwee 3m to 1 year period
at least 10 planned session
group (multiple fam)/ individual (single fam) - consider preference of family
effects
reduction of relapse/ rehospitalization/ hospital days/ improve family understanding and well being
no change in belief for the sytem
reduced distress and burden in relatives
gain knowledge
neuroendocrine factor for depression
high secretion of cortisol
thyroid hormone → better antidepressants effect for women
hormones make people more responsive to antidepressants
name the biochemical systems involved in major depression
HPA
HPT
episodes vs disorder
episode
anytime
abnormally happy/ sad
functional performance as indicator
disorder
pattern of illness
dx based in episodes
types of manic episode and the major difference
manic
more severe
last for at least one week
impaired functioning
hypomanic
at least 4 days
milder
no impairment in daily functioning
mixed
manic + major depressive episode last for at least one week
functional impairment
types of depressive disorder
MDD, single episode
MDD, recurrent episode
at least 2 major depressive episode at last 2 months apart
persistent depressive disorder (dysthymic disorder)
milder
at least 2 years (adults); others: at last one yr
x Sx free for more than 2 months
common intervention strategies + theories for depression
+ve psychology
focus on well-being, resilience and recovery instead of the disease itself
bio/ personal/ relational/ institutional/ cultural/ global dimensions of life
3 paths to happiness
pleasant life: optimal experience of +ve feelings; normal healthy life)
good life: optimally engaging in primary activities → sense of accomplishment
meaningful life: belonging and contributing to larger groups
flow theory
flow = state of intense absorption in work/ activities that one finds pleasurable
just right challenge (use most of our ability) → sense of accomplishment
aims to create more flow opportunities
PERMA theory of wellbeing
positive emotions (happiness = genetic set range + factors under voluntary control + life circumstances)
engagement (flow)
meaning (contribute + belong)
accomplishment
5 ways of wellbeing (lifestyle redesign)
be active
keep learning
take notice
connect
give
meds for anxiety
anxiolytics
antidepressants
OT intervention for anxiety
counselling
CBT
panic/ avoidance/ safety behaviour/ anticipatory anxiety cycles
knowledge (fear cycles/ misinterpretations & catastrophization)
skills (challenge irrational fears/ beliefs)
exposure
behavioural approach
exposure
desensitization
sensory modulation
sensory over responsive → sensory defensiveness/ hyposensitivity
sensory defensiveness → anxiety/ depression/ maladjustment
through tactile/ proprioceptive/ deep pressure activities to reduce anxiety level
sensory diet: balance of arousal and tolerance + interest and needs of individuals
can resolve childhood abuse issues
periods with highest suicidal risks + what to ask
start
later remission period (fear for relapse/ got better → able to plan for suicide)
ask if there is fomulated plan/ means for suicide
diff lev of suicidal risk
ideation
plan
attempt
OT interventions to suicide
relaxation training
progressive muscle relaxation
breathing exercise
SST + assertiveness
expressive activities
journal writing
arts and crafts
education lifestyle alternations
time management
cognitive/ functional behavioral training
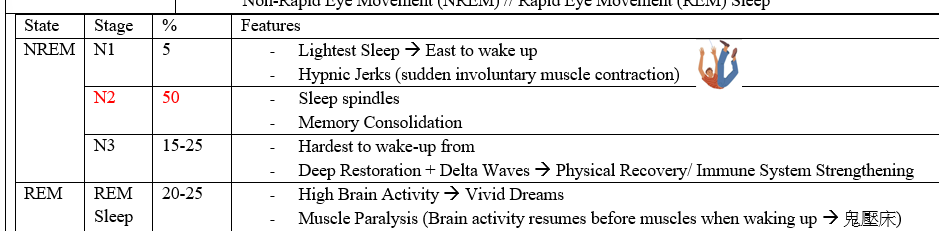
stages of sleep
4-5 sleep cycles (90-120min each)
2 physiological stages: REM/ NREM