Unit 4, Concept 1
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/34
Last updated 2:58 PM on 12/17/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
What are nucleic acids?
This is a macromolecule that carries our genetic information (DNA). Has the blueprint/instructions for making proteins.
2
New cards
\*\*What are two types of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA are these two types
3
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid is what this stands for.
4
New cards
What does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic acid is what this stands for.
5
New cards
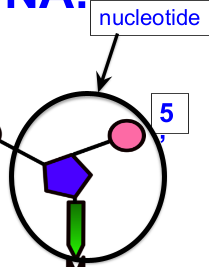
What are nucleotides?
These make up nucleic acids. They are monomers of DNA.
6
New cards
What 3 parts do nucleotides have?
These have sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base for their 3 parts.
7
New cards
What are examples of sugar?
Deoxyribose and Ribose are examples of this
8
New cards
What are nitrogen bases?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (DNA only), and Uracil (RNA only) are these.
9
New cards
What shape is DNA in?
This item’s shape is a double helix (a twisted ladder)
10
New cards
What two bonds bond things together in DNA?
Strong covalent bonds and weak hydrogen bonds are these two bonds.
11
New cards
What does Adenine and Cytosine bond with in DNA?
Thymine and Guanine bond with these in DNA.
12
New cards
What is it called when the nitrogen bases can only bond with certain others?
This is called the “complementary base pairing rules“.
13
New cards
What are Purines?
*(small word, big base*) These are big bases that have the nitrogen bases Adenine and Guanine.
14
New cards
What are Pyrimidines?
(big word, small base) These are big bases with Cytosine and Thymine.
15
New cards
What is the difference between Purines and Pyrimidines?
Purines are big bases with nitrogen bases Adenine and Guanine, while Pyrimidines are small bases with nitrogen bases Thymine and Cytosine.
16
New cards
What are Chargaff’s rules?
These rules state that A=T and C=G.
17
New cards
What do weak hydrogen bonds do?
These bonds hold the nitrogen pairs together
18
New cards
How many bonds do Adenine and Thymine share?
These two nitrogen bases share double bonds (2 bonds)
19
New cards
How many bonds do Cytosine and Guanine share?
These two bases share triple bonds (3 bonds).
20
New cards
What does antiparallel mean?
This term means the strands run in opposite (or antiparallel) directions.
21
New cards
How is DNA antiparallel?
DNA has two strands that run, and one starts with a phosphate and runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The other strand starts with deoxyribose (sugar) and runs in the 3’ to 5’ direction. Since these strands will always alternate and go in different directions, they are antiparallel.
22
New cards
What is the 5’ (5 prime) end?
This end is the phosphate end (“fa” sound - phosphate and five make the “fa” sound).
23
New cards
What is the 3’ (3 prime) end
This end is the sugar (deoxyribose) end.
24
New cards
Where are the weak hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule?
These bonds are found in the middle of the DNA molecule. These bond the nitrogen bases together.
25
New cards
Where are the strong covalent bonds in a DNA molecule?
These bonds are found on the outside of a DNA molecule. These bond the phosphates and sugars together (nucleotide).
26
New cards
Draw a nucleotide (What does it look like/have?)
A nucleotide has a phosphate bonded (covalently) with sugar (deoxyribose). That sugar is also being bonded to a nitrogen base, which is also bonding (hydrogen bond) with another nitrogen base.
\
*Tip: When we were having to cut out little pieces of DNA and put them together with the phosphates, sugars, and bases (Adenine, Thymine, etc.), those were nucleotides. When we put them all together in class, those all together made a DNA molecule, or nucleic acid.*
\
*Tip: When we were having to cut out little pieces of DNA and put them together with the phosphates, sugars, and bases (Adenine, Thymine, etc.), those were nucleotides. When we put them all together in class, those all together made a DNA molecule, or nucleic acid.*
27
New cards
What is the structure of a DNA molecule (in detail)?
For its structure, it has:
* Double Helix - sugar and phosphate form “sugar phosphate backbone", nitrogen bases bond in the middle.
* Nitrogen bases paired complementary with hydrogen bonds.
* It is antiparallel and runs in opposite directions (one strand runs in 5’ to 3’, the other runs in 3’ to 5’).
* Double Helix - sugar and phosphate form “sugar phosphate backbone", nitrogen bases bond in the middle.
* Nitrogen bases paired complementary with hydrogen bonds.
* It is antiparallel and runs in opposite directions (one strand runs in 5’ to 3’, the other runs in 3’ to 5’).
28
New cards
What’s the difference between a strand of DNA, genes, and a chromosome?
Genes are pieces/sections of DNA, chromosomes are long strands of DNA bunched up and coiled, and a strand is a long molecule with nucleotides/nitrogen bases.
29
New cards
Summarize the process of DNA Replication.
During DNA Replication, DNA is unzipped by Polymerase. Enzymes help find the complementary bases (basically match them up) according to the rules - A=T, C=G. Two identical DNA molecules are made, one “new” strand and one “old” strand.
30
New cards
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication?
* The leading strand needs 1 RNA primer but the lagging needs many.
* The leading strand is made continuously but the lagging strand is discontinuously.
* The lagging strand creates Okazaki fragments and the leading doesn’t.
* The leading strand is made continuously but the lagging strand is discontinuously.
* The lagging strand creates Okazaki fragments and the leading doesn’t.
31
New cards
Explain the function of each enzyme in the process of DNA Replication
* The enzyme Helicase unzips DNA into 2 strands.
* Enzyme DNA Polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the template strands.
* Enzyme primase makes short RNA primers.
* DNA ligase seals DNA gaps, connects DNA pieces by making bonds.
* Enzyme DNA Polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the template strands.
* Enzyme primase makes short RNA primers.
* DNA ligase seals DNA gaps, connects DNA pieces by making bonds.
32
New cards
What is RNA primer?
This is the RNA that initiates DNA synthesis.
33
New cards
What are Okazaki fragments?
These fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides that are made and later linked by DNA ligase to make the lagging strand.
34
New cards
What is the Semi-Conservative Model?
In this model, DNA’s 2 strands unwind and each help create a new, complementary strand.
35
New cards
What is Semi-Conservative Replication?
This is where DNA’s old (original) strands unzip and help create new strands that complement them. There one **new** strand and one **old** one, which is the original.