Chapter 12 review quiz
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
A PA radiograph taken on a hypersthenic patient during an upper GI series reveals that the pylorus and duodenal bulb are superimposed. Which of the following modifications will best eliminate the superimposition between these structures
angle the CR 35 to 45 degrees cephalad
which of the following kV ranges should be used for an upper GI series using barium sulfate
110 to 125 kV
how much barium is typically given to a 3 to 10 year old during an upper GI series
6 to 12 ounces
protective aprons worn during fluoroscopy must process at least ____ mm lead equivalency (Pb/Eq)
0.5
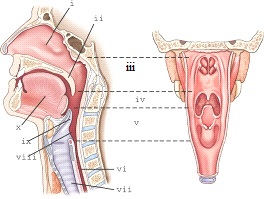
part v refers to the
laryngopharynx
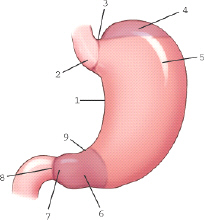
which part of the stomach is labeled 9
angular notch
“chole-” is a prefix for terms pertaining to the
bile
what structure indicates the junction between the duodenum and jejunum
suspensory muscle of the duodenum
most esophagograms begin with the patient
erect
what is the most common radiographic procedure performed to diagnose GERD
endoscopy
the act of swallowing is termed
deglutition
the act of swallowing is termed
deglutition
where is cholecystokinin produced
duodena mucosa
which of the following conditions involves dilated veins in the distal aspect of the esophagus, which in some cases can lead to internal bleeding
esophageal varices
a stomach with the duodenal bulb at the level of L1-L2 would be found in a ______ patient
sthenic
which of the following upper GI projections and/or positions will best fill the body and pylorus with barium
PA
which of the conditions is an example of GERD
esophageal reflux
when using computed radiography, inadequate kV or mAs will produce a _____ image
mottled
which aspect of the gastrointestinal tract is primarily responsible for the absorption of digestive end products along with water, vitamins, and minerals
small intestine
saliva contains certain enzymes to begin the digestion of
starch
what is the primary purpose of the membranous folds located within the cystic duct
prevents distention or collapse of the cystic duct
what type of solution is formed when barium is mixed with water
colloidal suspension
patient preparation for an adult upper GI series includes
NPO 8 hours before the procedure
radiographic examination of the biliary ducts only is termed
cholangiography
which aspect of the stomach is attached to the duodenum
pyloris
the liver performs more than 100 different functions
true
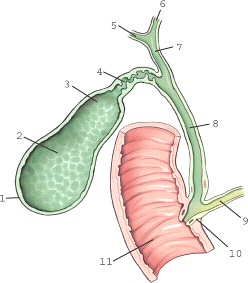
which biliary structure is labeled 4
cystic duct
which of the following positions is not normally considered to be part of the esophagogram basic routine
AP
what is the classification of barium sulfate as a contrast media
radiopaque
CR centering for an esophagogram should be to the vertebral level of
T5-6
why would a patient undergo valsalva maneuver during an esophagogram
to demonstrate possible esophageal reflux
which of the following statements is true about barium sulfate
it rarely produces an allergic reaction
the liver secretes approximately _____ mL of bile per day
800 to 1000
achalasia is generally defined as
motor disorder of the esophagus
only 5% of all ulcers lead to bowel perforation
true
what is an older term for the hepatopancreatic sphincter
sphincter of oddi
the esophagus is located ______ to the larynx
posterior
a patient comes to radiology with a history of a gastric ulcer. which of the following procedures would be most diagnostic to demonstrate this lesion
double-contrast upper GI series
A patient comes to radiology for an upper GI series. Her clinical history indicates that there may be a tumor posterior to the stomach. Which one of the following projections and/or positions will best demonstrate this condition
right lateral
sodium bicarbonate is often used as a negative contrast medium during an upper GI series
false
the opening between the stomach and esophagus is termed the
esophagogastric junction
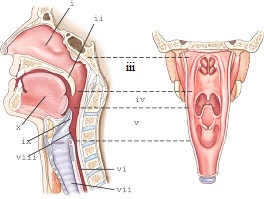
part ii refers to the
soft palate
the RAO position of the esophagus is preferred over the LAO because it
increase the visibility of the esophagus between the vertebrae and heart
what type of contrast media is ideal for demonstrating a diverticulum within the stomach
double-contrast barium/negative contrast agent
digital fluoroscopy has distinct advantages but produces a slightly higher patient dose as compared with conventional fluoroscopy
true
which of the following patient care concerns would prevent the use of an oral, water-soluble contrast medium
the patient is sensitive to iodine
research suggests that peptic ulcers may be caused by
bacteria
which of the following devices reduces scatter exposure during fluoroscopy from the fluoroscopy tube
bucky slot cover
which of the following is not one of the cardinal principles of radiation protection
intensity
gastritis is defined as inflammation of the
stomach
A radiograph taken during an upper GI series demonstrates poor visibility of the gastric mucosa. The following factors were used: 80 kV, 30 mAs, and 1/40-second exposure time. Barium sulfate was used during the procedure. Which of the following factors needs to be modified during the repeat exposure
increased kV (decrease mAs as needed)
which specific part of the pancreas is adjacent to the c-loop of the duodenum
head
a large outpouching of the proximal esophagus above the upper esophageal sphincter is termed
zenker diverticulum
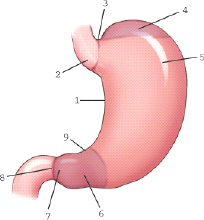
which part of the stomach is labeled 3
cardiac notch
which one of the following cardinal principles of radiation protection is most effective in reducing the dose to the technologist during fluoroscopy
distance
what is the term for the longitudinal mucosal folds found within the stomach
rugae
where is bile formed
liver
lipids (fats) are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol as they are digested and absorbed by the
small bowel only
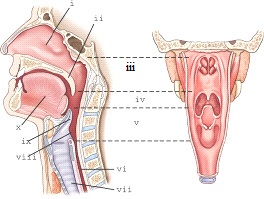
part iii refers to the
nasopharynx
the liver is divided into _____ major and minor lobes
4
the liver is located primarily in the _____ of the abdomen
RUQ
no cassettes are required for imaging with a digital fluoroscopy system
true
which of the following imaging modalities is an alternative to an esophagogram for detecting esophageal varices
sonography
which of the following imaging modalities is ideal for demonstrating signs of barrett esophagus
nuclear medicine
which of the following functions are performed by the gallbladder
all of the above
which term describes the outer, lateral border of the stomach
greater curvature
which of the following procedures will not demonstrate possible esophageal reflux
reverse trendelenburg method
A patient comes to radiology for an upper GI series. The patient has a clinical history of hiatal hernia. Which of the following positions may be helpful in demonstrating this condition
AP trendelenburg position
hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) is the most common form of intestinal obstruction found in infants
true
toward which aspect(s) of the stomach will barium gravitate with the patient in a prone position
body and pylorus
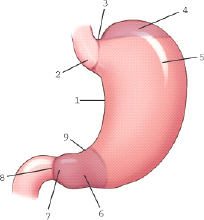
which part of the stomach is labeled 2
cardiac antrum
gastric emptying studies are performed using
radionuclides
other than the esophagogram, what imaging modality is performed to diagnose barrett’s esophagus
nuclear medicine
which structure is labeled 6
left hepatic duct
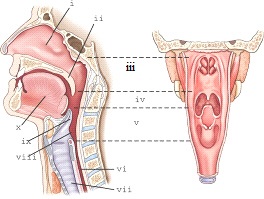
part i refers
nasal cavity
which aspect of the gallbladder is located most posterior within the abdomen
neck
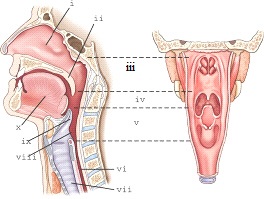
part ix refers to the
epiglottis
which two forces or processes propel food down the esophagus
peristalsis and gravity
duodenal ulcers are rarely malignant
true
which of the following definitions would describe a bezoar
mass of undigested material
in 80% of all individuals, the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct unite before entering the duodenum
false
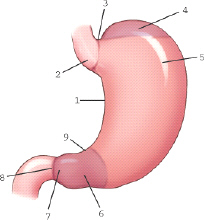
which part of the stomach is labeled 6
pyloric antrum
patient preparation for an esophagogram includes NPO _____ before the procedure
none of the above; patient preparation is not needed as long as an upper GI series is not scheduled to follow
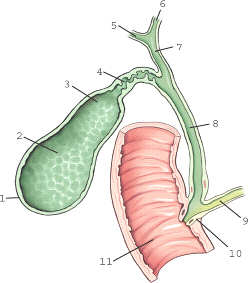
which aspect of the gallbladder is labeled 1
fundus
what is a primary function of cholecystokinin
stimulates the gallbladder to contract
the aortic arch and the ____ create a normal indentation seen along the lateral border of the esophagus
left primary bronchus
which division of the duodenum contains the duodenal bulb or cap
first (superior)
which of the following technical factors will best enhance a digital image taken during an upper GI series
use of wedge filter
what is an older term for the pancreatic duct
duct of wirsung
what is a potential risk associated with the use of water-soluble contrast agents, especially for geriatric patients
dehydration and renal impairment due to osmotic effects.
during an upper GI series, the “halo” sign appears in the duodenum. which of the following conditions will produce this radiographic sign
ulcer
which of the following is not a main subdivision of the stomach
cardium
a high and transverse stomach would be found in a _____ patient
hypersthenic
digital fluoroscopy does not require the use of an image intensifier
true
once food enters the stomach and is mixed with gastric secretions, it is termed
chyme
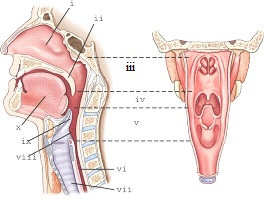
part iv refers to the
oropharynx
the main function of bile is to
emulsify fats
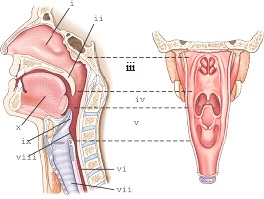
part vii refers to the
trachea
how much obliquity is required for the RAO position for the esophagus
35 to 40 degrees
a patient comes to radiology with a clinical history of HPS. which of the following imaging modalities will best demonstrate this condition
ultrasound