Limb Loss
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
How many people in the US currently live with limb loss or limb difference?
5.6 million
On average, how many Americans experience limb loss per year?
500,000
T or F: Lower limb amputations occur much more frequently than upper limb amputations
True
What lower limb amputation is the most common?
Toe amputation
What upper limb amputation is the most common?
partial hand amputation
What age population does limb loss occur the most in?
older adults, 45-65
What are the demographics associated with limb loss?
4x more likely to be black people
1.5x more likely to be Latinx people
More likely to be persons with lower incomes
What are the leading causes of limb loss? (rank ordered)
Diabetes (57%), infection (43%), vascular disease (40%)
True or false: A quarter of individuals who have an amputation due to vascular disease will die within 5 years
False: The statistic is half of individuals with an amputation
T or F: Of persons with diabetes who have a lower extremity amputation, up to 55% will require amputation of the second leg within 2 to 3 years.
True
Limb loss at the shoulder is called:
Shoulder disarticulation
Elbow disarticulation
limb loss through the elbow joint
Wrist disarticulation
Limb loss through the wrist joint
Transhumeral
Limb loss through the humerus
Transradial
limb loss through the forearm (both ulna and radius)
Hip disarticulation
limb loss through the hip joint
Through knee
Limb loss through the knee… lol
Transfemoral
Above the knee amputation
Transtibial
Below the knee amputation
Pediatric limb loss
acquired condition that results in the loss of a limb, usually from injury, disease, or surgery
How many pediatric limb loss cases are lower limb?
60%
How many pediatric limb loss cases are upper limb?
40%
What gender is more prominent with limb loss in pediatrics
Boys over girls 3:2 ratio
Congenital limb deficiency
when an infant is born without part of or full limb
Residual limb
remaining limb
Socket
interface connecting and containing the residual limb
Suspension
means of holding prosthesis to user
frame
rigid outer structure supporting the socket
harness
method of securing prosthesis to the body and incorporating physical control of the components
component
fingers, hand, wrist, elbow, and/or shoulder
terminal device
distal end of prosthesis, hook, hand, activity specific device, etc

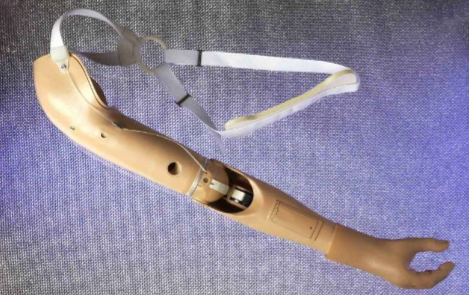
transradial prosthesis
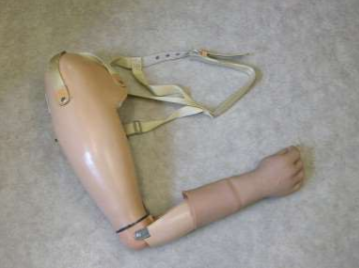
transhumeral prosthesis
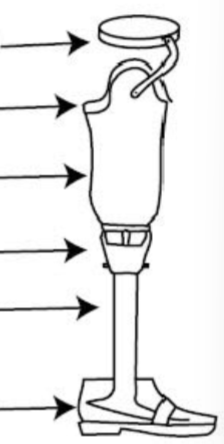
1) Suspension
2) Liner
3) Socket
4) Alignment device
5) shin
6) Foot/ankle

transtibial prosthesis

transfemoral prosthesis
What are the 6 prosthetic options?
no prosthesis
passive prosthesis
body-powered prosthesis
electrically power prosthesis
hybrid prosthesis
activity specific prosthesis
Passive prosthesis
Prosthetic does not move on its own
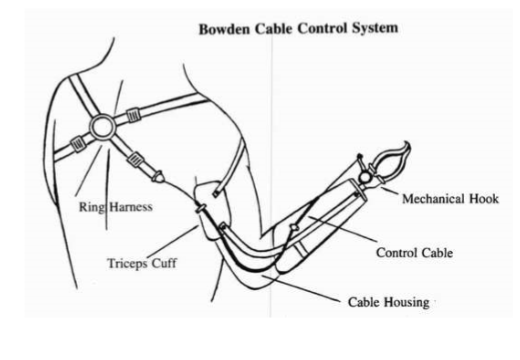
Body-powered prosthesis
controlled by body power and includes a system of cables, harness, and integrated mechanical parts
Electrically powered prosthesis
battery powered device operated by using muscle signals
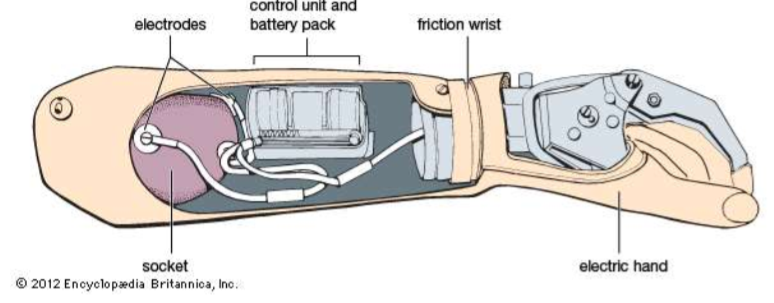
hybrid prosthesis
both electric and body-powered components, usually a body-powered elbow and myoelectric hand
activity specific prosthetic
a prosthetic designed for specific activities

initial prosthesis
first prosthesis that is intended to be temporary, designed to accommodate changes in size/shape and usually has a socket insert
Definitive prosthesis
final prosthesis for a mature residual limb. Does not have a socket insert
Important considerations involved with prosthesis
Level of limb loss, the condition of residual limb, condition of contralateral limb, condition of uninvolved limbs, stage of psychosocial adjustment
Complications after amputation
infection, delayed healing, hypersensitivity, limited range of motion, neuroma, scar adherence, poorly shaped residual limb, alienation of the residual limb
Colloborative rehabilitation
The amputation must be defined to the client with physical and psychological screens taking place. The client will need to go through grief management and be education on reconstruction and prosthetic options. It is important for all members of the healthcare team to define and communicate the plan with the client.
Assessment of needs of client
Muscle strength, range of motion, gross/fine motor skills, pain and phantom sensation, hypersensitivity of residual limb, self-concept, attitude or acceptance, coping skills, ADLs/IADLs, work history, leisure interests
Assessment tools for limb loss
manual muscle testing, dynameter and pinch gauge, goniometers, prosthetic checkout forms, formal and informal assessments of ADLs/IADLs, sensory tools, dexterity measures
Limb loss specific outcome measures
psychosocial screen, patient report, patient performance
Motor problems with limb loss
loss of motion, loss of strength, loss of coordination, loss of dexterity
sensory problems with limb loss
loss of touch and tactile sensation, loss of proprioception and kinesthesia, phantom pain, phantom limb sensation
Phantom limb sensation
perception of the presence of amputated limb, not clearly understood, most common in traumatic amputations, strongest in upper limb amputations, long-term
Phantom limb pain
Not clearly understood, the causation and management are controversial. Intense burning, cramping, or shooting pains are described and usually increase stress. Most common in traumatic amputations
Cognitive problems with limb loss
problem-solving may be difficult initially
Intrapersonal problems with limb loss
frustration, loss of self-worth, anger, and/or depression
Interpersonal problems with limb loss
avoidance of social situations, loss of self-confidence
self-care, work, and leisure problems with limb loss
loss of dominant extremity, loss of bimanual skills, need for modifications, need for assisted self-care, need to obtain other employment, unable to engage in chosen leisure routines
OT Treatment areas with limb loss
orientation to rehabilitation process, maximize ADLs, early mobilization, promote uncomplicated wound healing, proper shaping of the residual limb, desensitize sensitive tissues, introduce prosthetic options, coping with the psychological effect of loss
Four phases of rehabilitation
1) perioperative
2) pre-prosthetic
3) prosthetic training
4) advance training and lifelong care
Perioperative phase
patient education, physical interventions, pain management, functional assessment, psychological support
Patient education in perioperative phase
overuse syndromes, musculoskeletal imbalance, one-handed strategies, adaptive equipment, hand dominance retraining, prosthetic education, work simplification and energy conservation
physical interventions in perioperative phase
wound care, scar management, edema control, desensitization, ROM, strengthening, activity tolerance, increase independence, explore coping mechanisms, prosthetic options and devices
Motor interventions for limb loss
therapeutic exercises, positioning, wound care and dressing, limb shaping, don/doff prosthesis, prosthetic operation, bimanual training, posture
sensory interventions for limb loss
pain management, compensation, desensitization
wound care and scar management
protect wounds and areas of skin coverage, edema control, compression dressings or garments, massage (distal to proximal)
Range of motion in limb loss
To proximal uninvolved joints, then to residual joint around level of amputation. Monitor and correct poorly executed substitutions, orthotic devices may be used
Pain management with limb loss
medications, modalities, graded motor imagery, alternative treatments, compression wraps and silicon insert, TENS
Desensitization for pain management
gentle tapping, massage, skin/scar mobilization, lubrication
T or F: The OT should avoid emphasizing pain with a client who experiences phantom limb pain
True
What are medical interventions for phantom limb pain?
analgesics, nerve blocks, neurectomies
What are rehabilitation methods for phantom limn pain?
mirror therapy, thermal modalities, limb percussion, ultrasound, acupuncture, psychotherapy, hypnotherapy, and relaxation techniques
Functional assessment with limb loss
assess home tasks and environment, work duties, community mobility and integration, recreational interests
What psychological symptoms might a client experience from limb loss?
PTSD, anxiety, depression, grief, fear, substance abuse, and diminished quality of life
Intrapersonal interventions for limb loss
adjust to disability, learning new ways of task completion
Interpersonal interventions for limb loss
social engagement, support group attendence
Pre-prosthetic phase
wound closure, scar control, ongoing education, ongoing physical interventions, continued psychological support, myoelectric site testing and training, prosthetic options
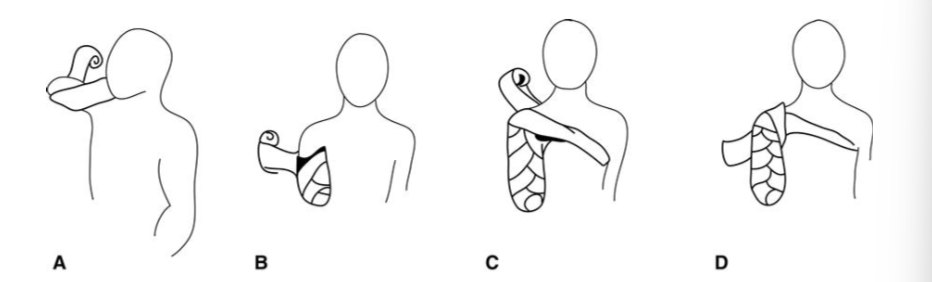
Shaping residual upper limb
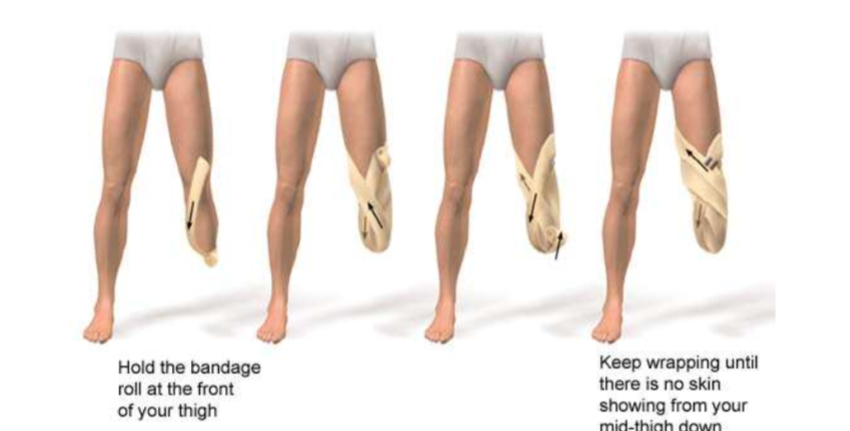
Shaping residual lower limb
Prosthetic training
comprehensive and accelerated fitting process, prosthetic education, basic skills, ADLs
Prescribing the prosthesis
look residual limb factors, and ask client for preference on cosmetics and function. Know the client’s occupational needs and their attitude. Their financial situation also needs to be considered
When should an upper limb prosthetic be fitted?
Within one month of limb loss
Ideal pediatric timeline for congenital limb absence
6 months → evaluation and passive device
18 months → electrically powered options
3 years → activity specific or body powered
Prosthetic education
proper terminology and operation of prosthetic. Client should know the control strategy, device limitations, and precautions. Appropriate care of device should be considered
Basic skills and ADLs with prosthetic
donning/doffing, wear schedule, control training, repetitive drills, functional training
Advanced training phase
IADL engagement, leisure skills, social engagement, return to work, routine follow up every 6 months, continuing education, lifelong care
Discharge readiness with limb loss
The client will have normal muscle strength and proficiency in care of residual limb. The client will have knowledge of prosthetic function and will independently don/doff device. The client can operate the prosthetic and use it safely. The client will have improved self-care skills and home management. Participation in work and leisure.