Chemistry- gas laws
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gas law formulas, and their scientists
Last updated 2:23 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
pressure
force per area, p=f/a
2
New cards
Things that do affect pressure…
Mass/ size of particles
3
New cards
things that do __***not***__ affect pressure…
\# of particles
4
New cards
Units of pressure
kPA, Atm, torr, mmHg
5
New cards
conversion factors for pressure
760 torr= 760 mmHG= 1 atm= 101.325 kPa
6
New cards
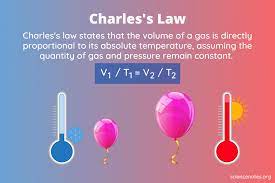
Charles law
when pressure is constant, volume and temp are directly related
when one goes up/down so does the other
when one goes up/down so does the other
7
New cards
Charles law formula
V1/T1= V2/T2
8
New cards
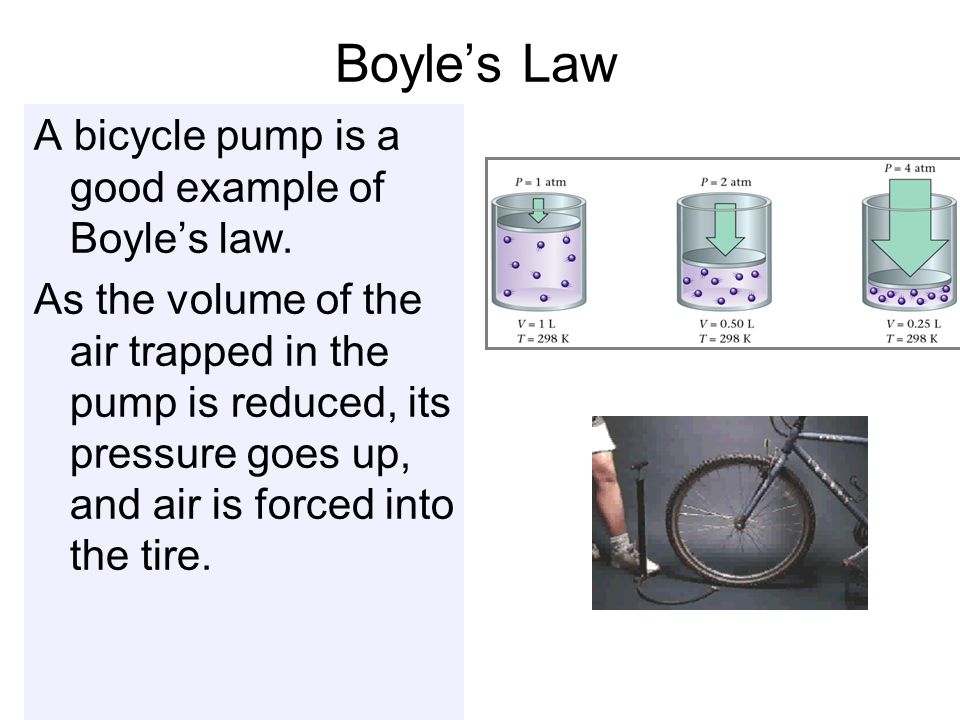
Boyle’s law
when temp is constant pressure and volume are inversely related ( when one goes up the other goes down)
9
New cards
Boyles formula
P1•V1=P2•V2
10
New cards
Gay-Lussacs law
\
\
when V is constant pressure and Temp are directly related
11
New cards
Gay-Lussacs law formula
P1/t1=p2/t2
12
New cards
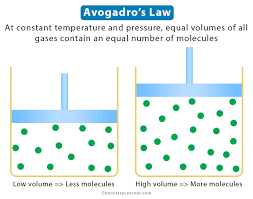
avagadros law
volumes of gas at same temp/pressure have = # of particles
13
New cards
Avagadros formula
V1/n1=V2/n2 ( directly realated)
14
New cards
what does the temperature always have to be in?
KELVIN!
15
New cards
How to convert Celcius to kelvin
C°+ 273= K
16
New cards
celsius to fahrenheit
F°= 1.8 C° +32
17
New cards
Fahrenheit to celsius
C°= F°-32/1.8
18
New cards
Daltons law
Partial=pressure if each gas in a mixture
ptotal= p1+p2+p3…
ptotal= p1+p2+p3…
19
New cards
combined law
p1 v1/T1= p2 v2/T1
20
New cards
ideal gas
an imaginary gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of kinetic molecular theory
PV=nRT
PV=nRT
21
New cards
kinetic molecular theory
* Gas particles in constant rapid motion
* The temperature depends on kinetic energy
* The temperature depends on kinetic energy
22
New cards
STP
temp- 0 C° or 293.15 K
Pressure- 1 Atm
\
\
Pressure- 1 Atm
\
\
23
New cards
Real gas
take up space have attraction
does not fit with kinetic theory
change more at high pressure and low temp
closest gas
does not fit with kinetic theory
change more at high pressure and low temp
closest gas
24
New cards
when do gases act most ideal
at high temps and low pressures
25
New cards
what is attraction like in ideal gases
there is no attractive or repulsive forces
26
New cards
how does energy behave in ideal gases
no energy is lost in collisions
27
New cards
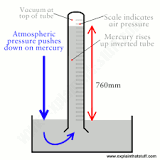
how does a barometer work
The mercury sits in a circular, shallow dish surrounding the tube. The mercury in the tube will adjust itself to match the atmospheric pressure above the dish. As the pressure increases, it forces the mercury up the tube.