Muscular System
4 Properties of Muscles
- Excitability
- Contractibility
- Extensibility
- Elasticity
Functions of the Muscular System
Maintaining posture
- Spine(?)
Supporting soft tissue
Movement
- Voluntary
- involuntary
- heart muscles
- runnings
Guarding entrances and exits of the body
- Opening mouth
- ‘Making a deposit
Generate heat and maintain body temp
- shivering
Types of Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle
- Characteristics
- Striated
- Involuntary movement
- Structure
- Proteins for striations (sarcerations)
- Thick = Actin
- Thin = Myiacyn
- Short, cylindrical-shaped, branched cells
- They break off from each other.
- Un-nucleated
- Fibers are formed to create a network
- Cells connect to each other at intercalated discs
- Connects the cells together.
- Location
- Makes up walls of the wall
- How do they work?
- Contract quickly and rhythmically.
Visceral (smooth) Muscle
- Characteristics
- Involuntarily contracted
- Non-striated
- Structure
- Flat, short, spindle-shaped cells
- Uni-nucleated
- Fibers are arranged to form sheets
- Location
- Lines internal organs, and vessels
- How do they work?
- Pull action = Peristalsis.
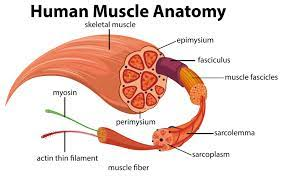
Skeletal Muscle
- Characteristics
- Striated
- Voluntarily controlled
- Attached to bones movement of fibrous tissue
- Structure
- Lond, cylindrical shaped cells
- Multinucleated
- Fibers are arranged to form bundles. Many bundles are in a Fascicle.
- Location
- Entire body
- How do they work?
- Contract quickly, but can’t stay contracted for long.
Muscle Movement
Origin
- Start of muscle
- ^^Fixed^^
Insertion
- End of the muscle
- The part that ^^actually moves^^
Prime Mover
- Muscle that ^^creates^^ the action
Synergists
- Help the movement happen
Antagonist
- Muscle that ^^opposes^^ the action
Range of Motion
- Abduction
- Adduction
- Flexion
- Extension
- Elevation
- Depression
- Rotation
- Circumduction
- Supination
- Pronation
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantar Flexion