Employment and Unemployment
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Unemployment - definition
The no. of people looking for work but who cannot find a job at a point in time - they are willing and able to work.
2 main measures of unemployment
The Claimant count
Labour Force Survey
Claimant Count - definition and evaluation
The number of people claiming job seekers allowance, they have to prove that they’re actively looking for work.
Generally an underestimate: not every unemployed person is eligible for, or bothers claiming JSA. Those with partners on high incomes are ineligible for the benefit, even though they’re unemployed.
Labour force survey - definition and explanation
Taken by the International Labour Organisation, a quarterly survey asking around 60k households if they've been out of work for 4 weeks and can start within 2 weeks.
\includes part time unemployed individuals, who are unlikely to claim JSA, so higher figures.
Is Labour Force Survey better than Claimant Count?
Yes: Internationally recognised, picks up trends in sectors, more accurate, data can be analysed.
No: Costly, subject to sampling errors.
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: Consumers
If consumers are unemployed, they have less disposable income and living standards may fall as a result.
There are also psychological consequences of losing a job, affecting mental health.
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: Firms
Higher unemployment = greater supply of labour = wages fall = reduced costs.
However, consumers have lower disposable income, so spending falls and firms may lose profits.
Reduced productivity and less incentive to invest.
Producers selling inferior goods may however see a rise in sales.
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: Workers
Unemployment is a waste of workers’ resources, they may also lose existing skills if they’re not fully utilised.
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: The government
Will have to spend more on JSA, which incurs an opportunity cost as that could have been invested elsewhere.
Will also receive less revenue from income tax, as less employed, and also less indirect taxes like VAT, as disposable incomes fall
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: Economy
Wastage of resources, so economy will be within the PPF, at point E.
AD will shift leftwards, due to lower consumption, due to lower incomes.
The significance of changes in the rates of unemployment on: Society
Opportunity cost, as workers could’ve produced goods and services if they were emplyed.
Could also be negative externalities like crime and vandalism.
What is economic inavticity? What groups are part of this?
Those who are not actively looking for jobs, e.g. retirees, children, disabled people, carers for the elderly.
Some workers are discouraged from the labour market since they have been out of work for so long that they have stopped looking for work.
6 Causes of unemployment
Structural
Frictional
Seasonal
Cyclical
Technological
Regional
Structural unemployment - explanation
Occurs with a long term decline in demand for the goods and services in an industry, which cost jobs.
Examples in UK: car manufacturing, decline of coal and ship building
Technological unemployment - explanation
Links to structural and the car building industry, where improved capital which may be more productive and efficient than labour, replaces labour as a factor of production
Regional unemployment - explanation
Links to structural, occurs when unemployment is specific to particular regions.
Often due to a local area specialising in a certain industry which is now uncompetitive internationally due to globalisation and cheap labour abroad.
Frictional unemployment - explanation
Occurs as workers move between jobs. Always going to be some frictional unemployment, it isn’t particularly damaging, as only temporary.
Occurs as people are always moving between jobs, and have imperfect info about job opportunities available to them.
Seasonal unemployment - definition
Occurs when workers are unemployed at different times of the year.
During summer more employed in tourist industry
During winter more employed in retail sectors.
Some figures are adjusted to smooth out these fluctuations.
Cyclical unemployment - explanation
Occurs when there’s a negative output gap in the economic cycle, where demand is very low, during periods of decline/recessions.
Firms are forced to either close or make workers redundant, as profits are falling due to decreased consumer spending, so need to cut costs, this leads to a fall in output.
This can be caused by an increase in productivity, meaning each worker can produce a higher output, and therefore fewer workers are required.
Voluntary/involuntary unemployment: Keynesian or classical?
Voluntary: Classical
Involuntary: Keynesian
Voluntary unemployment - definition
When workers choose not to work at the current equilibrium rate
Why may voluntary unemployment occur?
Excessively generous welfare benefits
High rates of income tax
Workers seeking better employment conditions
The equilibrium wage rate is insufficient in encouraging individuals to supply their labour
Involuntary unemployment- definition
When there’s insufficient demand in an economy, so jobs simply aren’t there.
Real wage unemployment - definition
A situation in which wages are set above the equilibrium level, resulting in an excess supply of labour or unemployment
Real wage unemployment: graph
There exists excess supply of labour as minimum wage is above the equilibrium wage rate.
Supply of labour > demand for labour
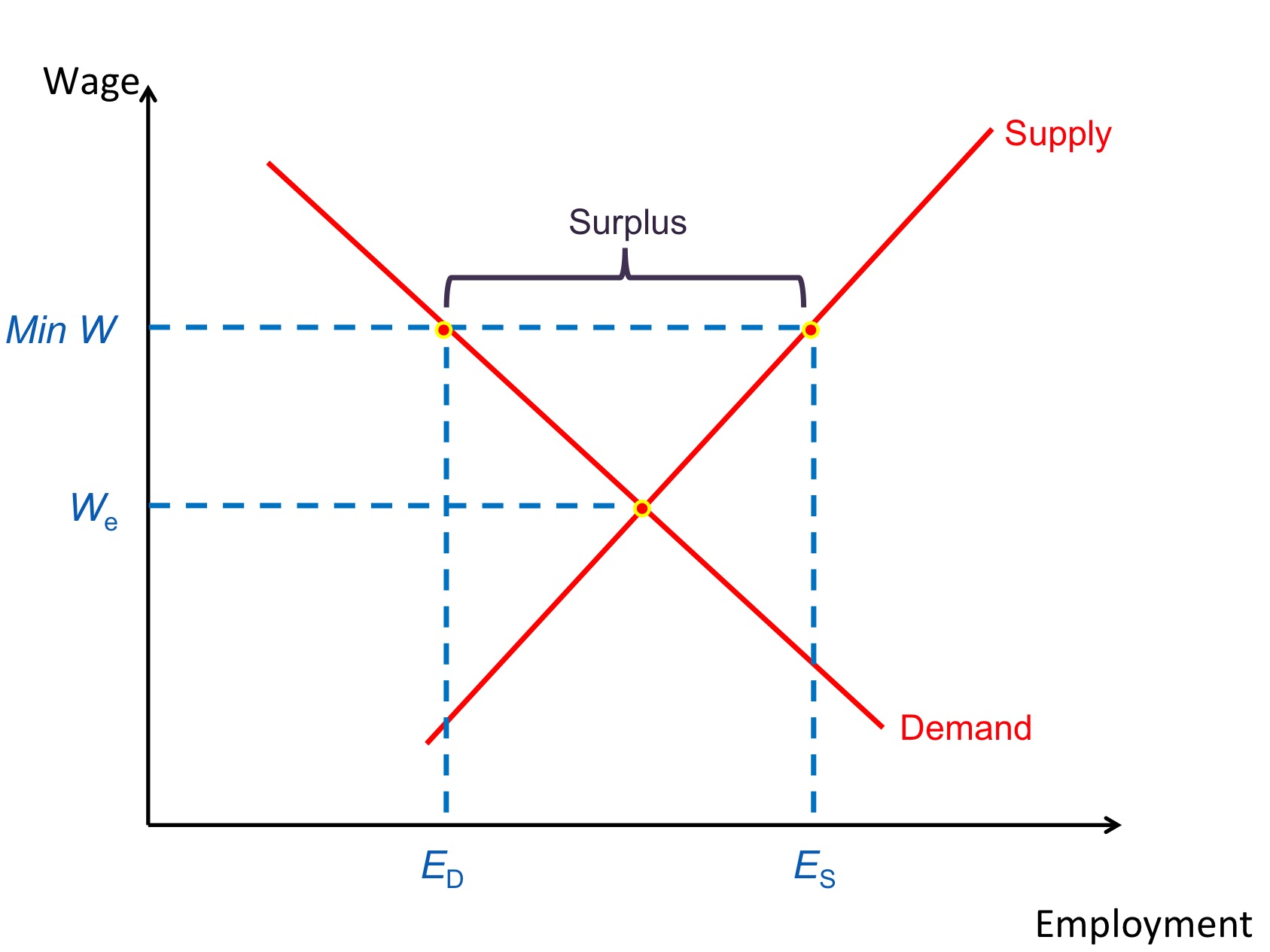
Types of intereference that may cause real wage unemployment
Trade unions - through collective bargaining, they negotiate higher wages for their members
Minimum wage - workers supply their labour more readily as a result
Opposing views on real wage unemployment
Classical economists advocate against labour market interventions, but others argue this erodes standards of living and job security
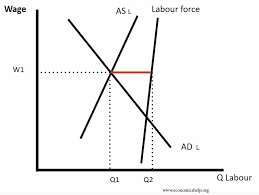
Natural rate of unemployment - definition
Frictional and structural unemployment will always exist, so always a degree of unemployment in an economy. So labour market can be in equilibrium even when a degree of natural unemployment remains.
Natural rate of unemployment: Graph
D1S1 is equilibrium point, even when quantity is less than labour force.`
Which type of factors determine the natural rate of unemployment?
Both frictional and structural
Frictional causes of natural unemployment
Availability of job information
Looser employment legislation/ weaker trade unions will increase flexibility and reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
Structural causes of natural unemployment
Skills and education: if improves, structural unemployment will decline
Occupational and geographical mobility
Hysteresis - workers become deskilled the longer they are unemployed, making it harder to find a new job when economy improves
Effect of natural rate of unemployment on individuals
Lower living standards
De-skilling
Health implications
Social issues
Unemployment trap
Longer term unemployability
Effect of natural rate of unemployment on Economy
Worsened government finances
Lost output
Reduced intl. competitiveness
Inequality
Lower consumer spending
Loss of resource invested in training
Demand deficient unemployment: other name?
Cyclical (caused by negative output gap)
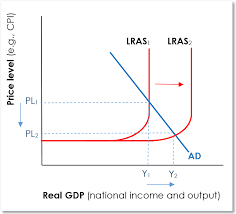
Cyclical unemployment - graph
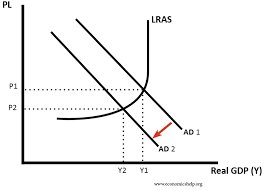
What types of unemployment are supply side?
Frictional, structural and seasonal
Supply side unemployment: Graph
If supply side of economy improves or worsens, this will shift LRAS left or right and thus decrease or increase unemployment