NSCI 2101 Exam 2 Lec 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
spinal nerves exit through ______
the intervertebral foramina
how do cranial nerves enter and exit the CNS?
through foramina in the skull
how many pairs of cranial nerves do humans have?
12
cranial nerves are organized by ____
function
which three pairs of cranial nerves ONLY carry special senses?
olfactory (CN1), optic (CN2), and vestibulocochlear (CN8)
olfactory nerve
senses smell
bunch of nerve cells derived from the olfactory placodes that extend their axons down into the nasal cavity
cells that form the olfactory nerves are sensitive to odorants
olfactory tracts carry information about smell into the cerebral cortex
how does information travel from the olfactory nerve to the cerebral cortex?
odorant binds to cell → cell fires → info is sent along axons that go through the cribriform plates → synapse on the olfactory bulb → olfactory tracts carry information about smell into the cerebral cortex
optic nerve
looks like an x and transmits information about sight
vestibulocochlear nerve
sticks out of the inferior pontine sulcus that forms the boundary between the medulla and pons
out on the lateral side of the brain
most lateral nerves, also the biggest
made of two parts: vestibular apparatus and cochlea
vestibular apparatus
part of the vestibulocochlear nerve that is in control of balance
senses head position and movement through cilia
cochlea
part of the vestibulocochlear nerve
physically connected to vestibular apparatus
senses sound through movement of cilia
which five cranial nerves ONLY innervate skeletal muscle?
oculomotor (CN3), trochlear (CN4), abducens (CN6), spinal accessory (CN11), hypoglossal (CN12)
which cranial nerves allow the eyes to move?
oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens
oculomotor nerve
controls 4/6 extraocular skeletal muscles (plus the eyelid)
includes the superior rectus on the top of the eye
inferior rectus on the bottom of the eye
inferior oblique which twists and upholds the eye medially, but causes it to rotate a bit
medial rectus on medial side of the eye
also deals with parasympathetic output of the oculomotor nerve: focuses lens and constricts pupil
trochlear nerve
only nerve not visible from the ventral view of the brain
only nerve that exits the dorsal side of the brain
between the pons and the midbrain
can see it on the dorsal side of the brainstem kind of
includes superior oblique
on the top and goes out the back of the eye and directs the gaze down and out
corresponds to interior oblique but in the opposite direction
abducens nerve
exits the inferior pontine sulcus, most medial nerve
innervates the lateral rectus muscle
pulls on your eye to the left or to the right
the muscles move in tandem to the opposite direction
Spinal accessory nerve
neck and shoulders
Weird because the cell bodies are not in the brain, they are in the upper spinal cord
From C5 up, the motor neurons in the spinal cord don’t send their axons out to the ventral roots, they send their axons straight up the side of the spinal cord and enter the skull through the foramen magnum
The nerve then exits the skull through the jugular foramen
Innervates trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
sternocleidomastoid
is on the side of your neck and allows you to turn your head
hypoglossal nerve
innervates the tongue
only motor to the tongue but not sensory to the tongue
what are the three mixed-function cranial nerves?
facial (CN7), glossopharyngeal (CN9), and vagus (CN10)
what nerve innervates muscle but also carries “general sensation” information (touch, vibration, pain)?
trigeminal nerve
trigeminal nerve
(jaw muscles, sensation for face, head, mouth)
next biggest nerve in the head after the optic nerve
exits the middle side of the pons
Muscles of mastication
allow for chewing
Cutaneous sensation to face and head
Three branches to the trigeminal nerve
facial nerve
Exits from the inferior pontine sulcus
Innervates muscles of facial expression
Innervates some autonomic ganglia
Special sensory (taste)
Innervates taste receptors in the anterior ⅔ of the tongue
glossopharyngeal nerve
Tongue and throat
Innervates the posterior ⅓ of the tongue
Does both taste and general sensation
Also senses blood pressure and oxygen level in carotid artery
Vagus nerve
Innervates skeletal muscles of throat and larynx
Allows us to talk
Muscles involved in swallowing
Autonomic input to heart and gut
Slows heart, speeds digestion
Special sensation (taste)
back of throat
General sensation
Behind ear (small region)
Larynx
Also senses blood oxygenation and CO2
Sensors in aortic arch
what do the mixed function nerves all have in common?
All innervate skeletal muscle
All innervate autonomic ganglia
All carry general sensory afferents
All carry special sensory afferents
Two (glossopharyngeal and vagus) carry afferents relaying information about O2, CO2, and/or blood pressure
what is the mnemonic for cranial nerves?
On (olfactory)
Old (optic)
Olympus’s (oculomotor)
Towering (trochlear)
Tops (trigeminal)
A (abducens)
Finn (facial)
And (“auditory”, i.e. vestibulocochlear)
German (glossopharyngeal)
Viewed (vagus)
Some (spinal accessory)
Hops (hypoglossal)
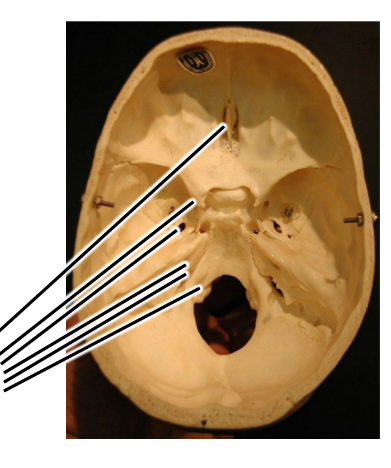
what are the lines pointing to?
cranial foramena
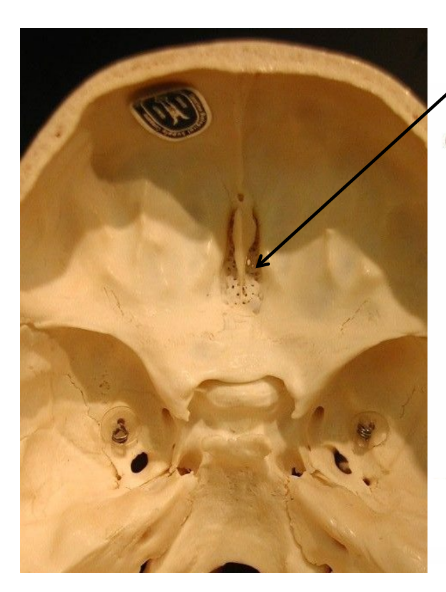
what is the arrow pointing at?
cribiform plate
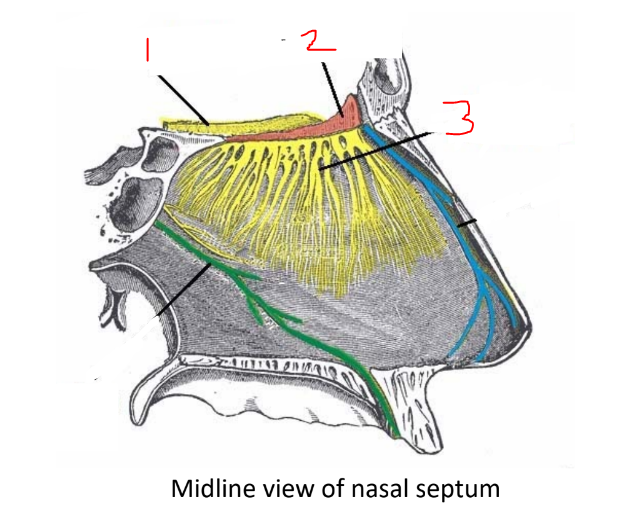
what is 1?
olfactory bulb
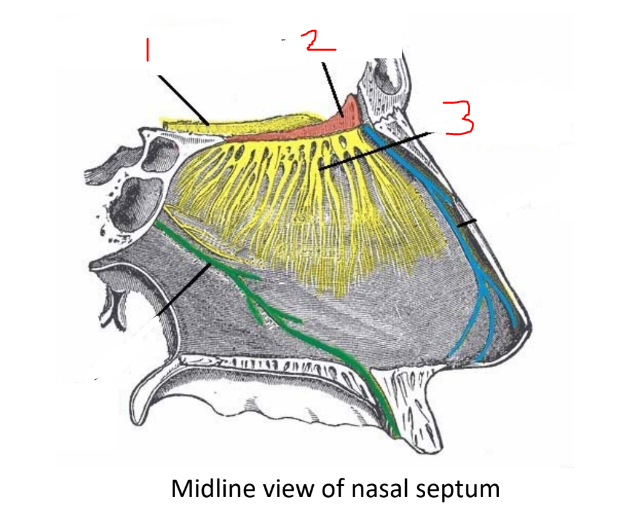
what is 2?
cribriform plate
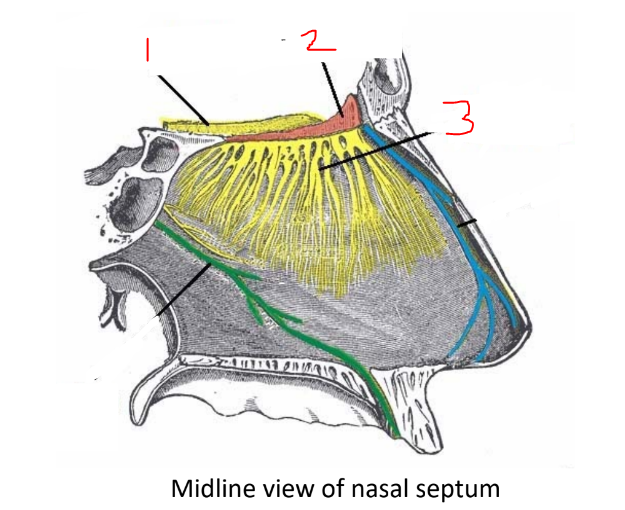
what is 3?
olfactory nerves
cribriform plate
transmits the olfactory nerves that carry the sense of smell
olfactory bulb
the region in the brain receiving input from the olfactory neurons in the nasal olfactory epithelium. olfactory nerves synapse on them
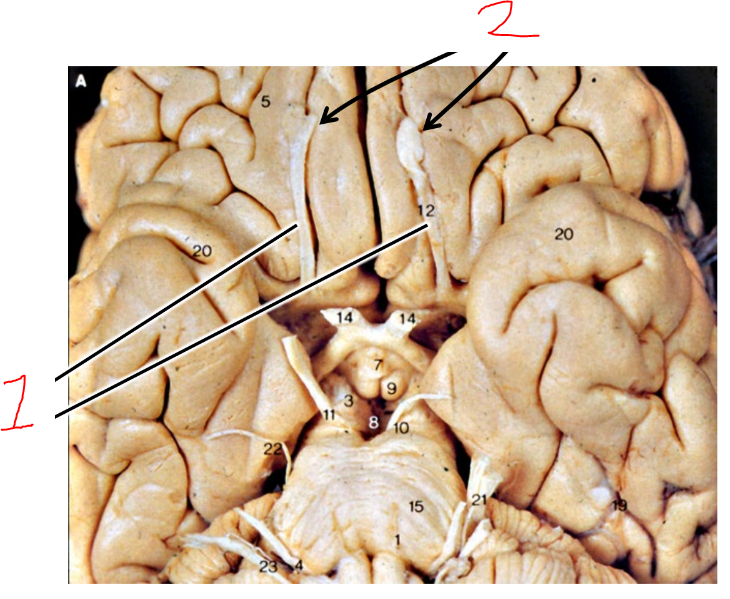
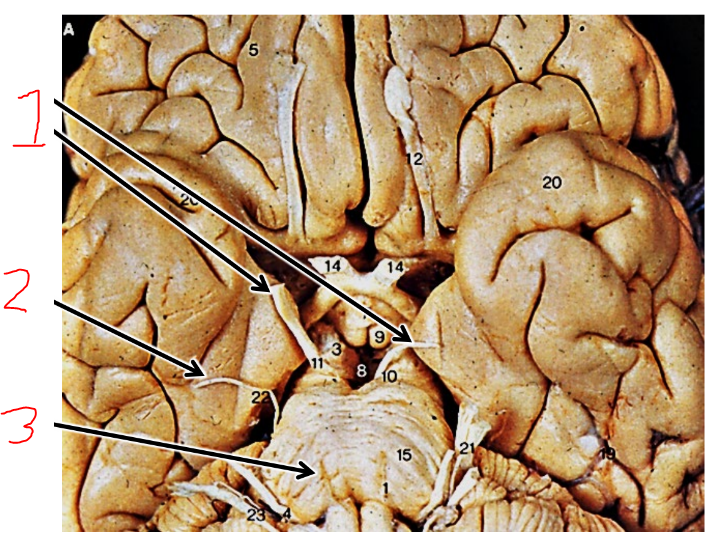
what are 1?
olfactory tracts
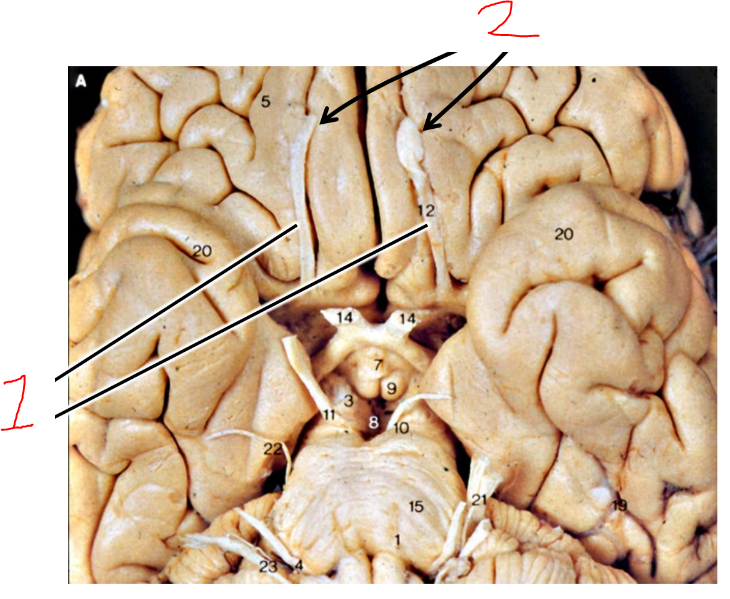
what are 2?
olfactory bulbs
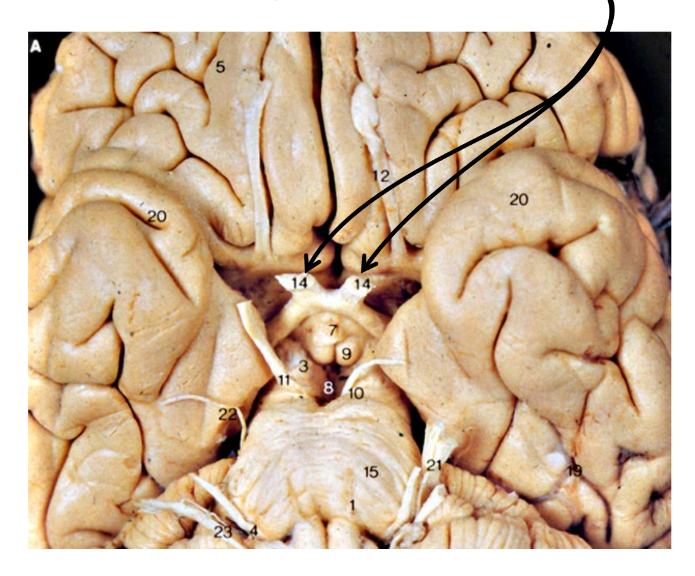
what are the arrows pointing at?
the optic nerve
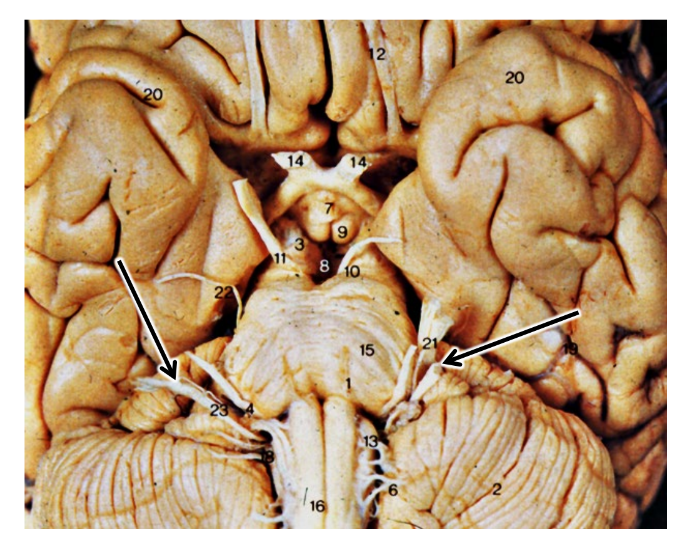
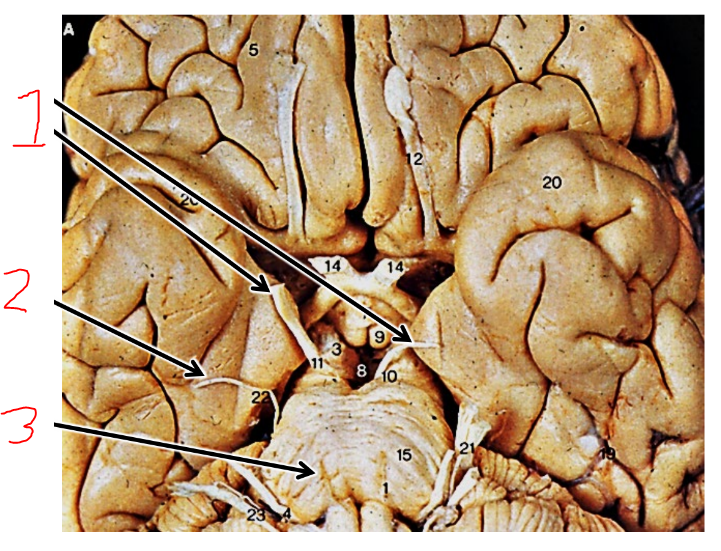
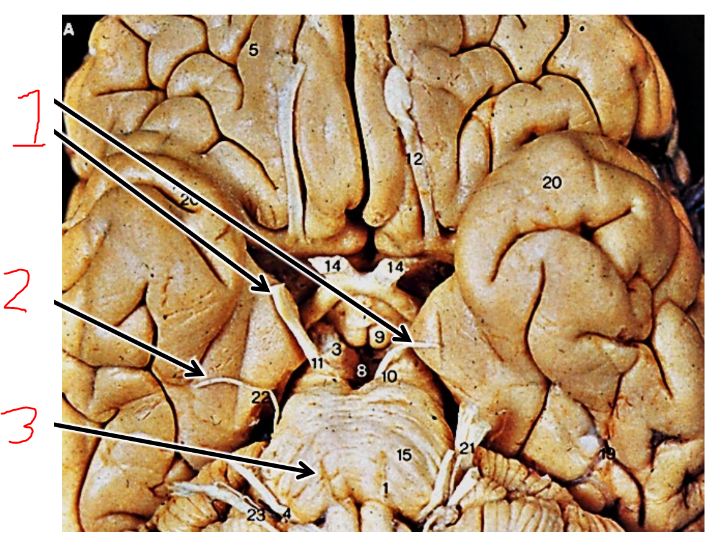
what are the arrows pointing at?
vestibulocochlear nerve
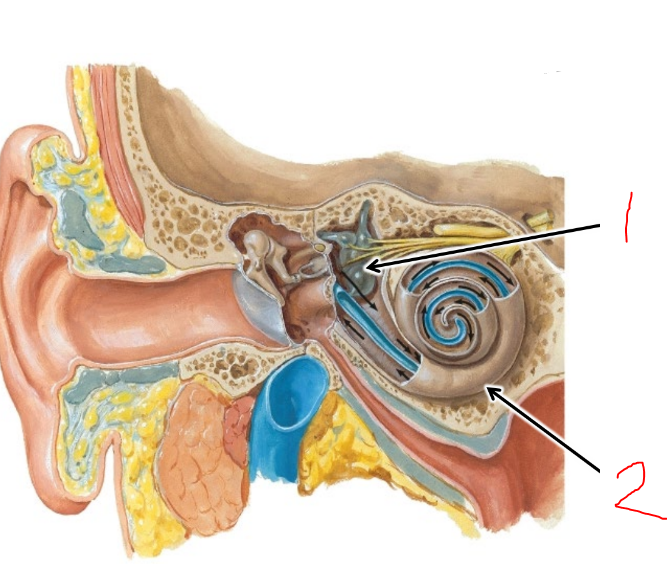
what is 1?
vestibular apparatus
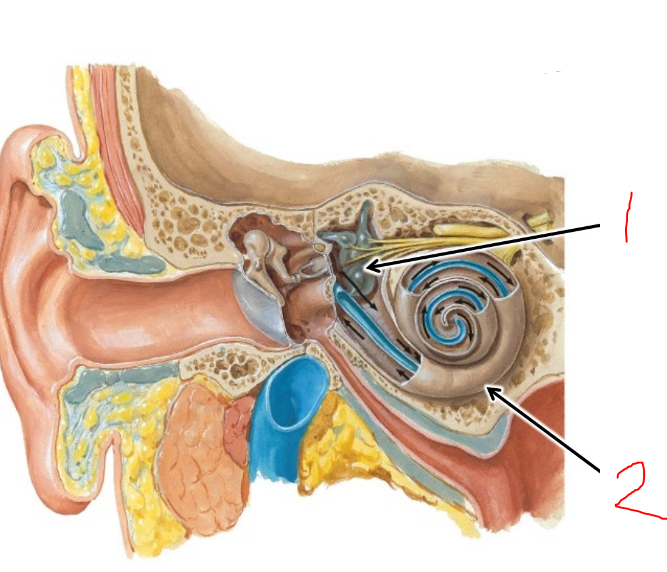
what is 2?
cochlea
what is 1?
oculomotor nerve
what is 2?
trochlear nerve
what is 3?
abducens nerve
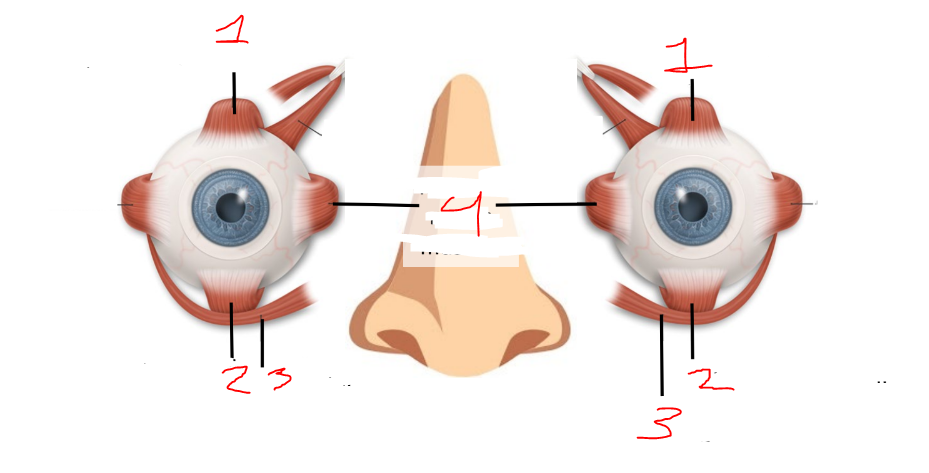
what is 1?
superior rectus muscles
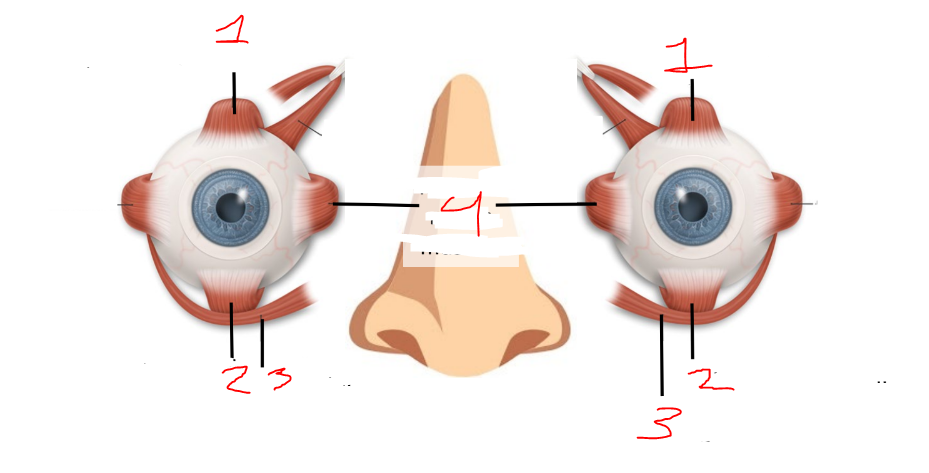
what is 2?
inferior rectus muscles
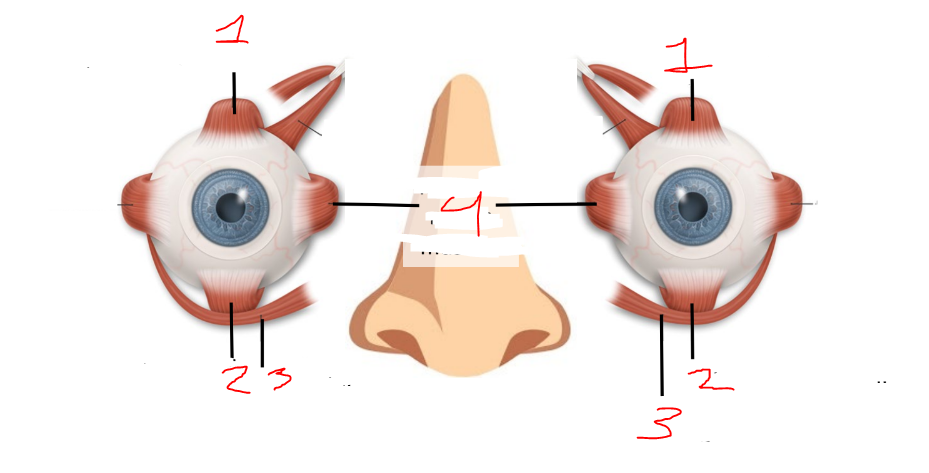
what is 3?
inferior oblique muscles
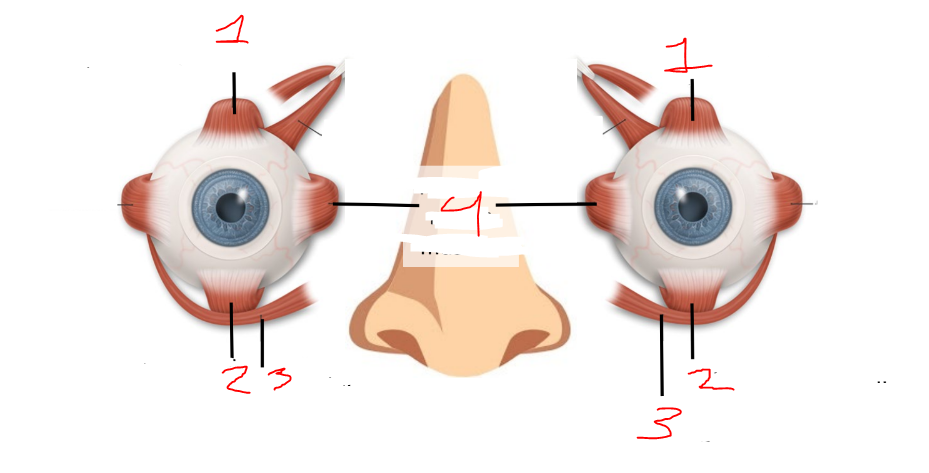
what is 4?
medial rectus muscles
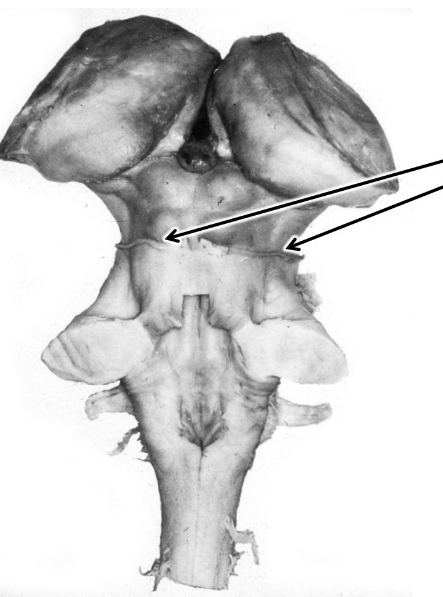
what are the arrows pointing at?
trochlear nerve
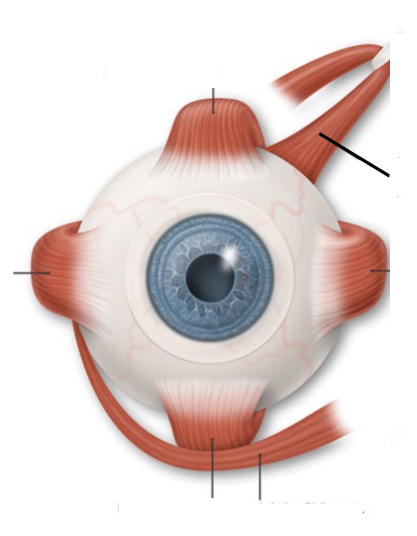
what dat
superior oblique muscle
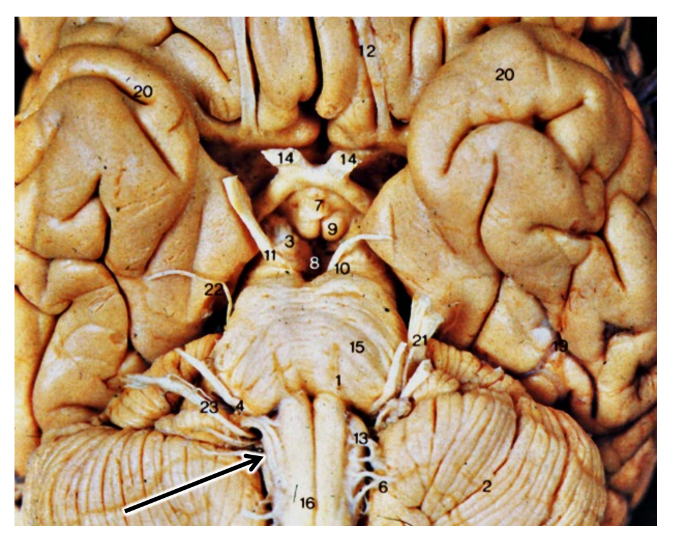
what are the arrows pointing at?
abducens nerve
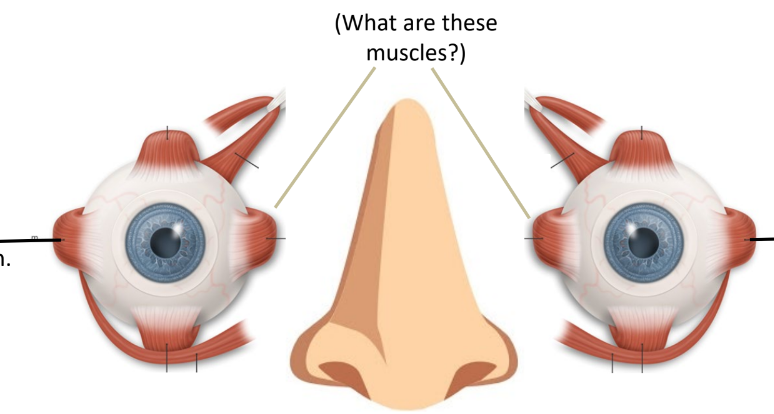
what are the lines pointing at
lateral rectus muscles
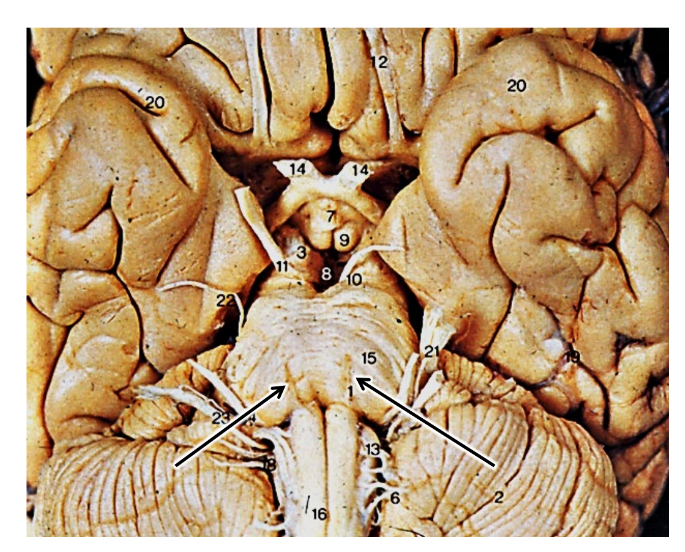
what are the arrows pointing at?
spinal accessory nerve
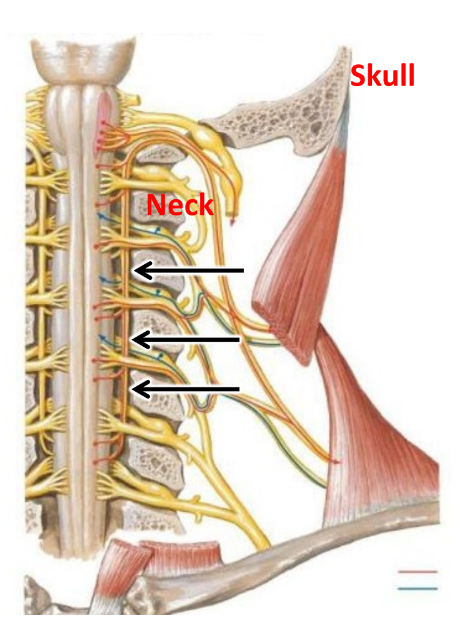
what dat
hypoglossal nerve
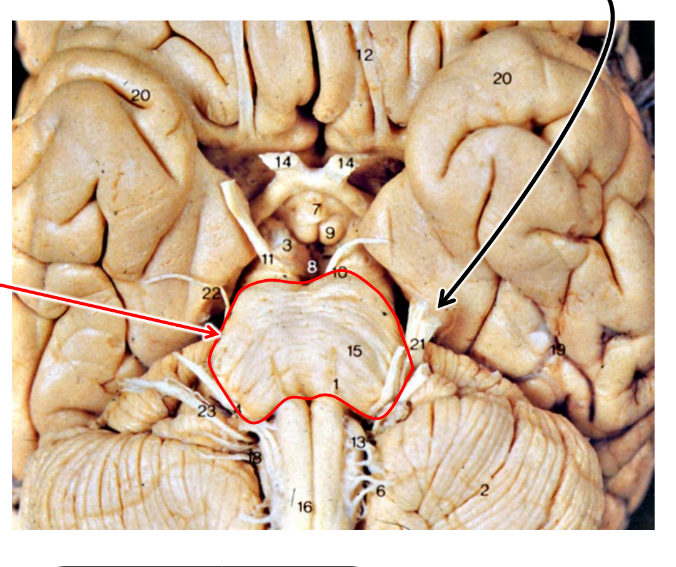
IGNORE THE RED ARROW but what is the black arrow pointing at
trigeminal nerve
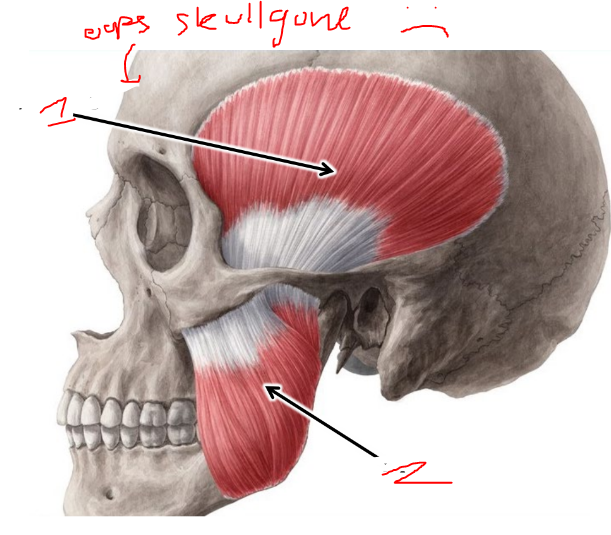
name these muscles
1 is temporalis and 2 is masseter
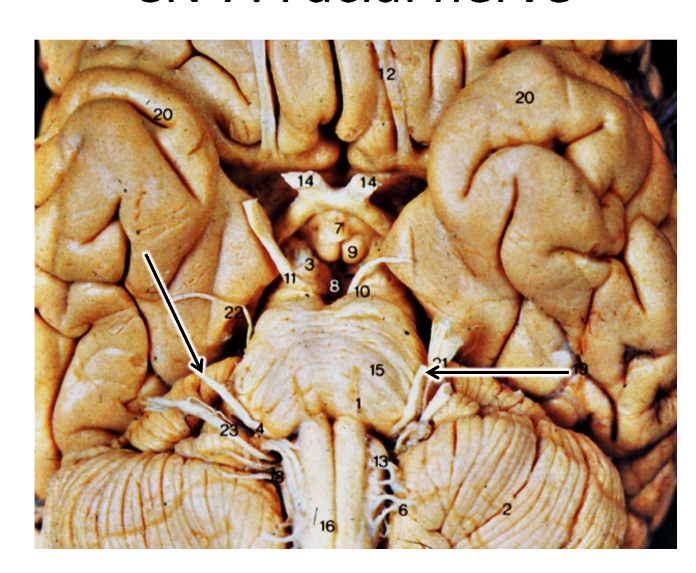
what are the arrows pointing at
facial nerves
autonomic ganglia in the facial nerves result in what?
tearing, nose-running, and salivating
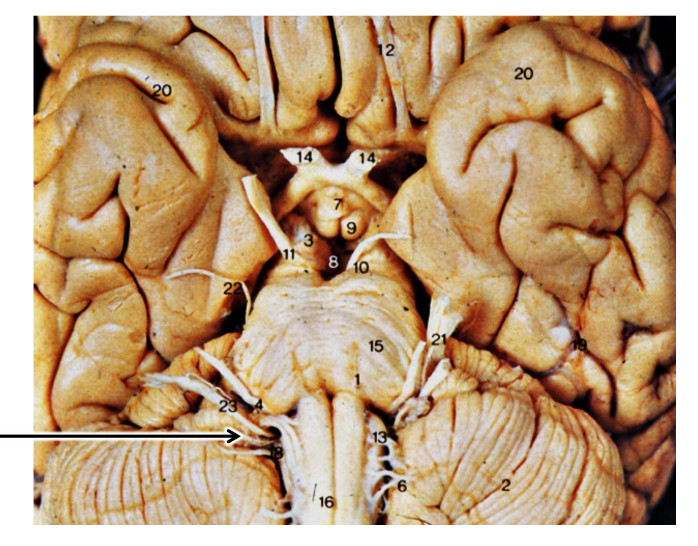
WHAT DIS
glossopharyngeal nerve
autonomic ganglia in the glossopharyngeal nerve result in…
salivation
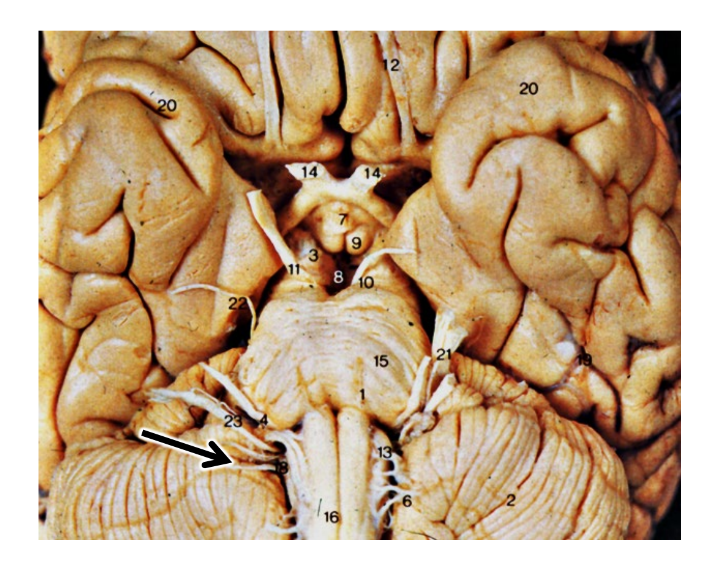
what dis
vagus nerve