10- Nitric Acid
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Nitric acid is also known as
aqua fortis
Laboratory preparation
Laboratory preparation using Potassium nitrate & Sodium Nitrate
KNO3 + H2SO4 (<200 C) → KHSO4 + HNO3
NaNO3 + H2SO4 (<200 C) → NaHSO4 + HNO3
Why is the acid obtained slightly yellow
Due to dissolution of reddish brown coloured Nitrogen dioxide gas in tthe acid
How is the yellow colour removed:
Two ways:
if dry air or CO2 is bubbled through the yellow acid, the latter turns colourless because it drives out NO2
By addition of excess of water, Nitrogen di oxide gas dissolves in water and thus the yellow colour of the acid is removed
Give 3 precautions
All glass apparatus is used because nitric acid vapours attack rubber and cork
HCl is not used because its volatile and hence nitric acid vapours will carry HCl vapours
The temperature of the reaction should not exceed 200 C
What happens if temperature exceeds 200 C
glass may crack
decomposition of nitric acid can occur
fuel is wasted
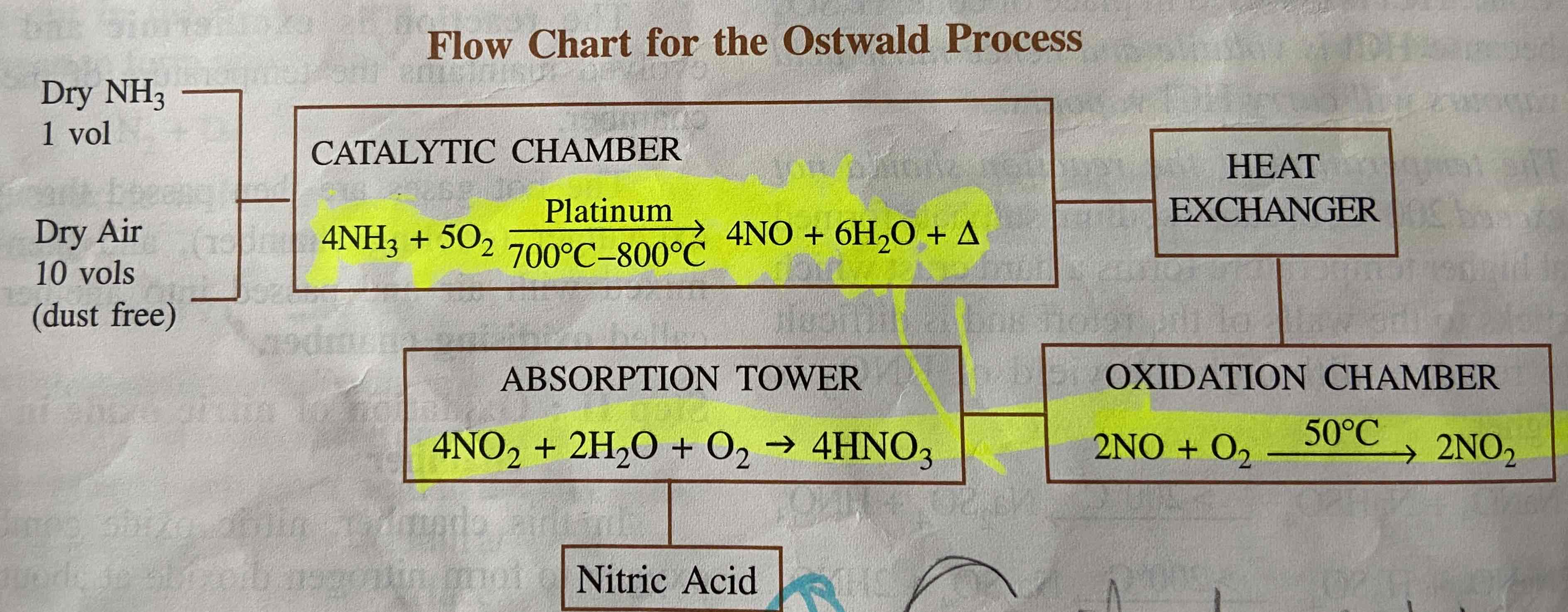
Catalyst used in Ostwald process
Platinum
Guve reaction for Ostwald process
What happens if pure nitric acid is left in sunlight
4HNO3 (Sunlight) → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
WHy is nitric acid stored in bottle turns yellow
The colour is due to dissolved NO2 in HNO3. To avoid the decomposition, nitric acid is generally stored in coloured bottles
How does nitric acid effects litmus paper
Blue → Red
Reaction: Action on Non metals
Two Reactions:
C + 4HNO3 → CO2 + 2H2O + 4NO2
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO3
Reaction: Action of metals
Cold dilute nitric acid: : 3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO
Concentrated Nitric Acid(Hot dilute): Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
What type of acid is dilute nitric acid and why?
Typical acid because it is a powerful oxidising agent
Reaction of nitric acid with aqua regia
HNO3 + 3HCl → NOCl + 2H2O + 2[Cl]