DSA01 OMM - Special Populations - Geriatric and Pediatric Patients
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Deformation of the head WITHOUT premature suture closure (can be repositioned with Helmets or OMT)
Define Nonsynostotic Plagiocephaly
Deformation of the head d/t PREMATURE CLOSURES OF SUTURES and often requires surgical correction
Define Synostotic Plagiocephaly
GI Irritation --> GI upset & Spitting up
How might the movement of the occipital condyles affecting CN X cause symptoms?
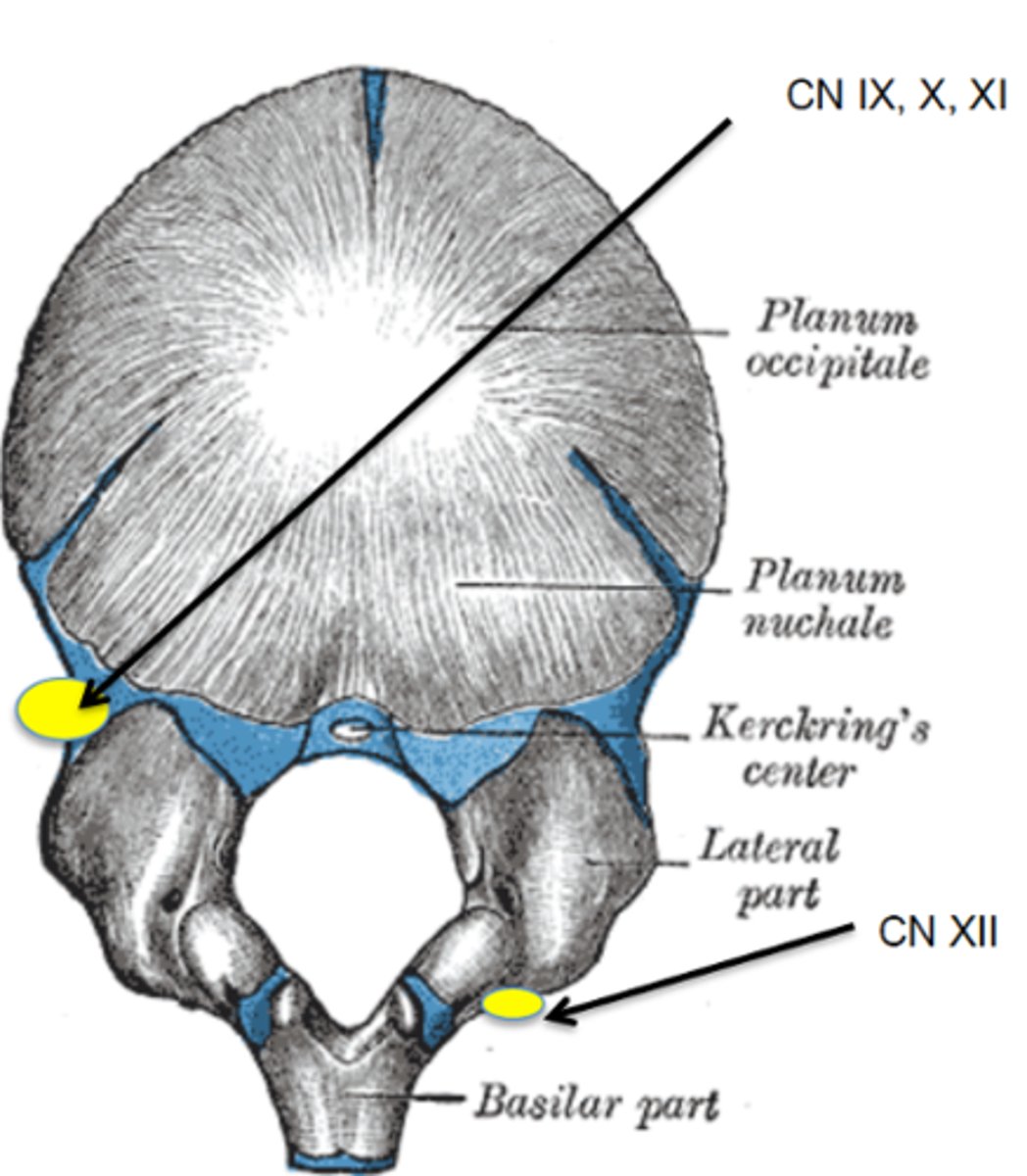
May cause torticollis
How might the movement of the occipital condyles affecting CN XI cause symptoms?
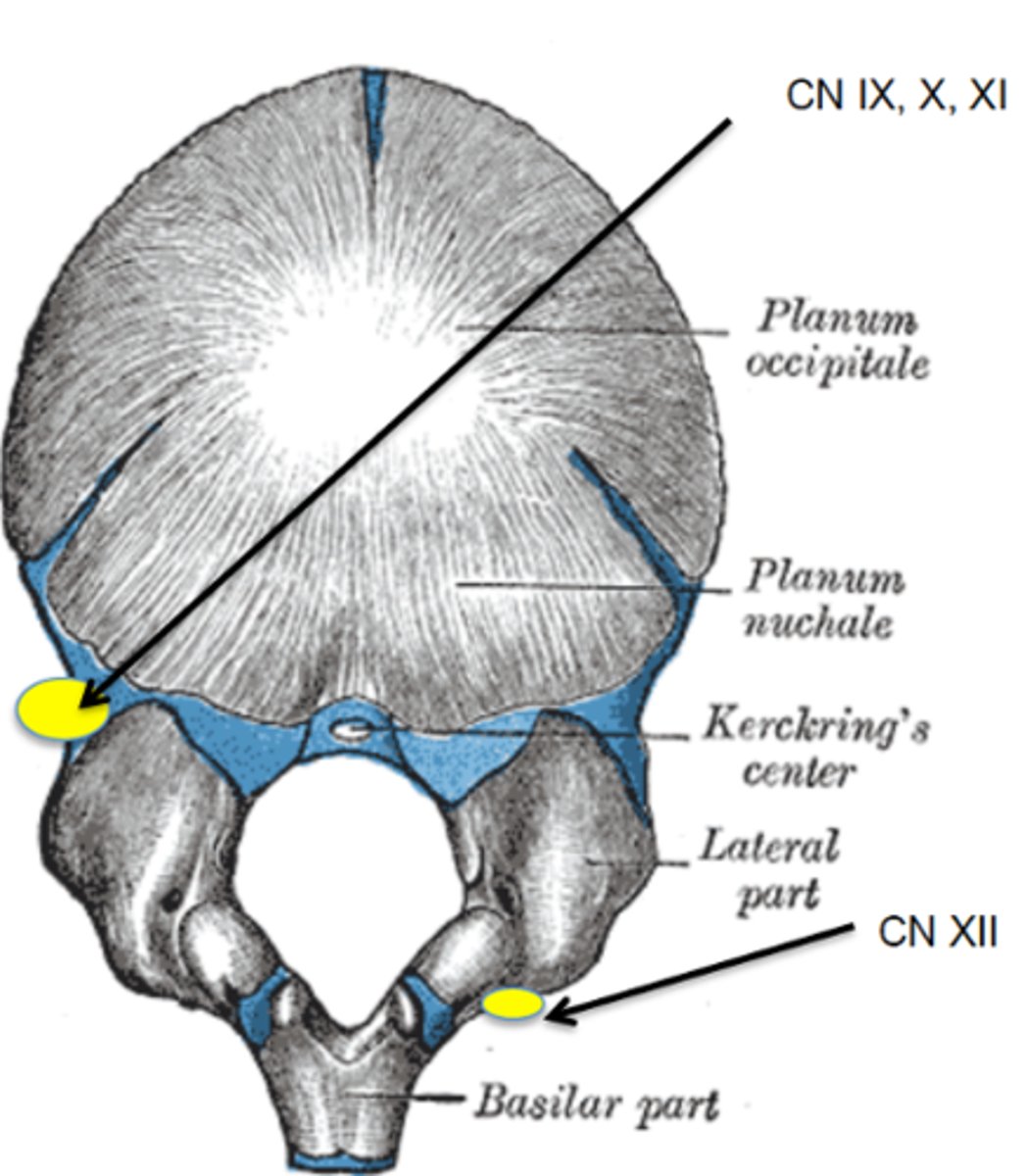
Poor sucking, latching or feeding
How might the movement of the occipital condyles affecting CN XII cause symptoms?
Colic
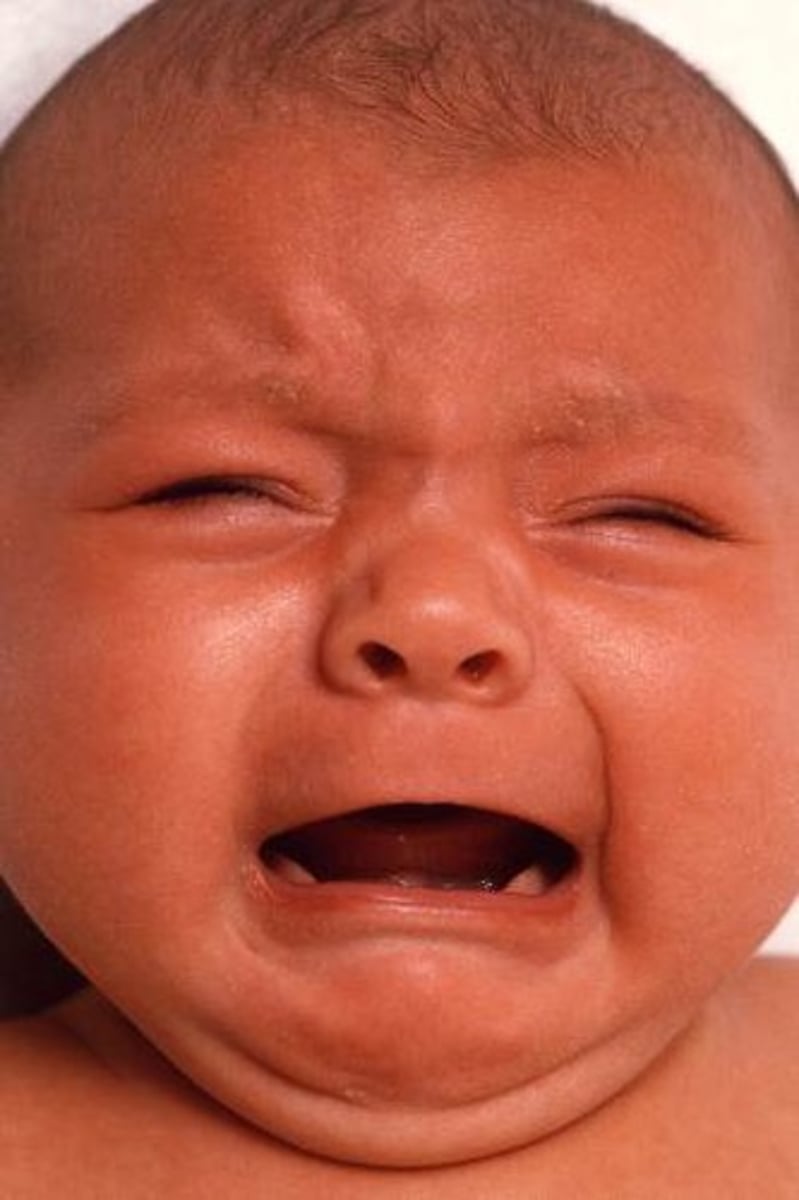
Define Condition:
Loud crying for several hours (often late in day) + drawing up legs & arching back
-Hx:
> Self-limiting in early childhoood
> 3 wks to 3 mo
> Multifactorial
-Tx:
> Release of Flatus
> OMT at Occipital Condyles (remove pressure of CN X or Vagus)

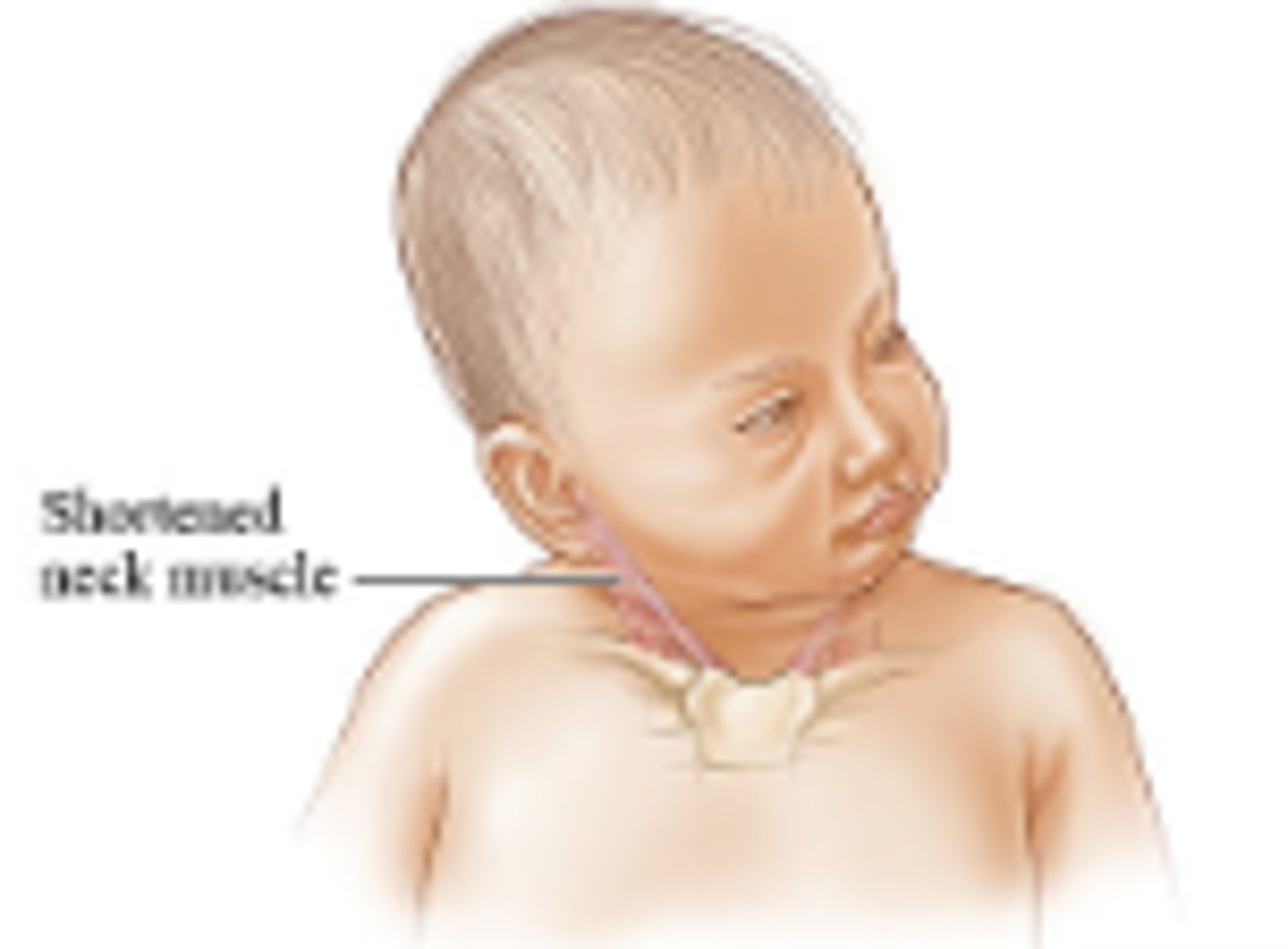
Congenital Muscular Torticollis
Define Condition:
Head being rotated to one side - caused by intrauterine & prenatal events --> Contracture + Fibrosis of SCM
-Hx:
> Infants subject to abnormal intrauterine crowding/positioning (First born, Oligohydramnios)
> Breech During Gestation
> Multiple births
> Difficult/prolonged delivery
-Tx: OMT (if no signs of infex, tumor or C/Is)
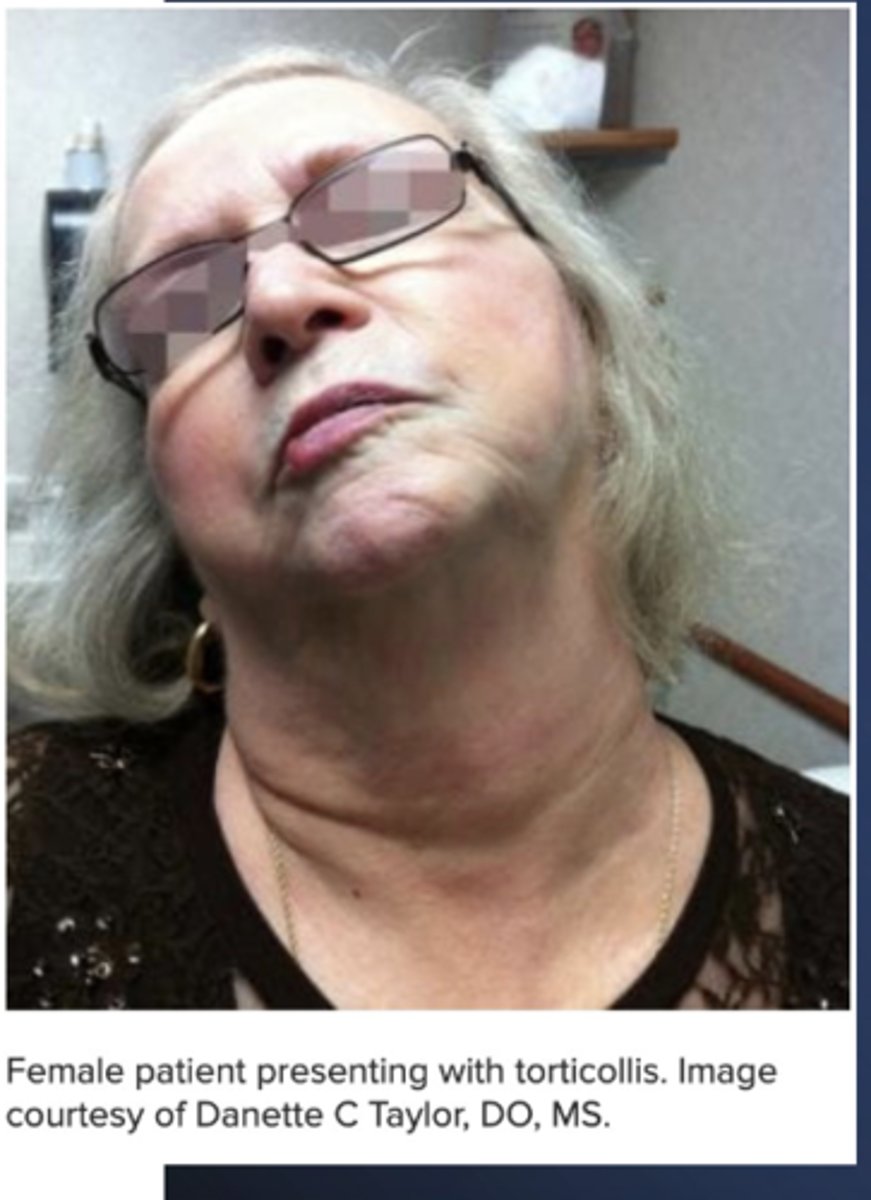
Acquired Torticollis
Define Condition:
Head being rotated to one side --> Abnormalities of motion of C1-2 Articulation
-Hx:
> Trauma
> Infex
> Tumor
-Tx: OMT (if no signs of infex, tumor or C/Is)
Otitis Media
Define Condition:
Inflammation and Irritation of middle ear
-Path:
> USUALLY Viral (but can be bacterial)
> Thought to be more prone due to the more horizontal orientation of the Eustachian tube along with increased pliability
-Hx:
> Self-limiting
> Most in 1st Year of Life
-Sx:
> Fever
> Fusiness
> Ear Pain
-Tx: Address lymphatic drainage along with temporal and cranial base SDs
> Galbreath Technique
> Auricular Drainage
•Birth history (duration of labor, use of Pitocin, Vacuum/Forceps)
•APGAR scores
•NICU time
•Feeding/sleeping history
•Favored positioning
•Full PE & OSE
What history should be collected to treat infants with OMT?
-Refusal by parents or lack of competence performing OMT
-Manipulation over wound, fracture, deformity (e.g. meningomyelocele)
-Internal bleeding
-Certain techniques based on age group (HVLA before joints are formed, MET/CS if patient cannot cooperate, etc.)
What are C/Is of OMT on infants?
1. Torticollis
2. Skull/Face deformity
3. Otitis Media
4. Feeding Problem
What are the top 4 diagnoses from Ages 0-11 mo?
1. Otitis Media
2. Skull/Face deformity
3. Torticollis
4. URI
What are the top 4 diagnoses from Ages 1-4 yrs?
1. HA
2. Scoliosis
3. Otitis Media
4. Neck pain
What are the top 4 diagnoses from Ages 5-12 yrs?
1. Lumbar back pain
2. Scoliosis
3. Neck Pain
4. HA
What are the top 4 diagnoses from Ages > 12 yrs?
-Decreased height
-Decreased lean body mass
-Decreased body water
-Increased body fat
-Aging skin
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of Body Composition & Confirmation?
•Changes in pharmacokinetics
•Decreased strength
•Arthritis
•Osteoporosis
•Injury, accidents, pressure sores, fractures
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of BIOMECHANICAL Clinical Predispositions?
•Increase in blood pressure
•Aorta and large arteries lose elasticity and systemic vascular resistance increases
•Decreased baroreceptor reflex activity
•Calcification and sclerosis of heart valves
•Calcification and sclerosis of conduction system
•Altered cardiac output
•Decreased heart rate
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Cardiovascular System?
•Hypertension
•LV Hypertrophy
•Orthostatic Hypotension
•Decreased response to stress
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of CV Clinical Predispositions?
•Calcification of costal cartilages
•Decline in alveolar surface area
•Alteration in pulmonary function tests
•Decreased vital capacity
•Decreased maximum breathing capacity
•Increased residual volume
•Decreased Pao2
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Respiratory System?
•Decreased lung capacity
•Decreased clearance
•Increased risk of pulmonary complications
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of Respiratory Clinical Predispositions?
-Decrease in cerumen glands
-Atrophy of cochlear hair cells
-Loss of auditory neurons
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Ears?
•Loss of elasticity of lens
•Increased density of lens
•Change in aqueous kinetics
•Decreased pupillary size
•Sluggish light reflex
•Decreased color vision
•Increased glare sensitivity
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Eyes?
•Decrease in brain weight
•Alteration in CNS neurotransmitters
•Decrease in memory
•Decreased reaction time
•Altered sleep with decreased deep sleep and increased wakefulness
•Decreased vibratory sense
•Decreased righting reflex
•Increased postural instability
•Altered gait
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Nervous System?
•Hearing loss
•Presbyopia
•Cataracts
•Glaucoma
•Forgetfulness
•Delirium, drug toxicities
•Sleep disturbances
•Altered gait
Falls, accidents
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of Neurologic Clinical Predispositions?
•impaired glucose tolerance
•increased insulin resistance
•Decreased estrogen
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Endocrine System?
•Decreased T-cell function
•Decreased antibody production to new or old antigen(s)
•Increased autoantibodies
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the Immune System?
•Decreased gastric HCl production
•Colonic motility diminished
•Decreased calcium absorption
•Decreased hepatic biotransformation
•Decreased hepatic albumin synthesis
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the GI System?
•Diabetes
•Osteoporosis
•Decreased antibody production- higher risk of infections
•Constipation
•Altered drug and nutrient metabolism
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of Metabolic-Energetic Clinical Predispositions?
•Retirement
•Moving (nursing homes)
•Death of friends and loved ones
Loss of independence
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of the "Change of Life Stages" (Behavioral)?
•Depression
•Anxiety
•Elder abuse
What are age-related changes that occur in terms of Behavioral Clinical Predispositions?
•Somatic Dysfunction
•Patient consent
•Absence of contraindication to OMT or specific technique based on comorbidities
What are indications for OMT in Geriatric Patients?
•Patient refusal
•Unable to give consent
•HVLA may be contraindicated in:
-osteoporosis
-concern for fracture or metastasis
What are C/Is for OMT in Geriatric Patients?